
GOLEM
Graph Optimiser for Learning and Evolution of Models
Stars: 53
GOLEM is an open-source AI framework focused on optimization and learning of structured graph-based models using meta-heuristic methods. It emphasizes the potential of meta-heuristics in complex problem spaces where gradient-based methods are not suitable, and the importance of structured models in various problem domains. The framework offers features like structured model optimization, metaheuristic methods, multi-objective optimization, constrained optimization, extensibility, interpretability, and reproducibility. It can be applied to optimization problems represented as directed graphs with defined fitness functions. GOLEM has applications in areas like AutoML, Bayesian network structure search, differential equation discovery, geometric design, and neural architecture search. The project structure includes packages for core functionalities, adapters, graph representation, optimizers, genetic algorithms, utilities, serialization, visualization, examples, and testing. Contributions are welcome, and the project is supported by ITMO University's Research Center Strong Artificial Intelligence in Industry.
README:
.. image:: /docs/source/img/golem_logo-02.png :alt: Logo of GOLEM framework :align: center :width: 500
.. class:: center
|sai| |itmo|
|python| |pypi| |build| |integration| |coverage| |docs| |license| |tg| |rus| |mirror|
GOLEM is an open-source AI framework for optimization and learning of structured graph-based models with meta-heuristic methods. It is centered around 2 ideas:
- The potential of meta-heuristic methods in complex problem spaces.
The focus on meta-heuristics allows approaching the kinds of problems where gradient-based learning methods (notably, neural networks) can't be easily applied, like optimization problems with multiple conflicting objectives or having a combinatorial nature.
- The importance of structured models in multiple problem domains.
Graph-based learning enables solutions in the form of structured and hybrid probabilistic models, not to mention that a wide range of domain-specific problems have a natural formulation in the form of graphs.
Together this constitutes an approach to AI that potentially leads to structured, intuitive, interpretable methods and solutions for a wide range of tasks.
- Structured models with joint optimization of graph structure and properties (node attributes).
- Metaheuristic methods (mainly evolutionary) applicable to any task with a well-defined objective.
- Multi-objective optimization that can take into account both quality and complexity.
- Constrained optimization with support for arbitrary domain-specific constraints.
- Extensible to new domains.
- Interpretable thanks to meta-heuristics, structured models, and visualisation tools.
- Reproducible thanks to rich optimization history and model serialization.
GOLEM is potentially applicable to any optimization problem structures:
- that can be represented as directed graphs;
- that have some clearly defined fitness function on them.
Graph models can represent fixed structures (e.g. physical models such as truss structures) or functional models that define a data-flow or inference process (e.g. bayesian networks that can be fitted and queried).
Examples of GOLEM applications:
- Automatic Machine Learning (AutoML) with optimal ML pipelines search in
FEDOT framework <https://github.com/aimclub/FEDOT>_ - Bayesian network structure search in
BAMT framework <https://github.com/aimclub/BAMT>_ - Differential equation discovery for physical models in
EPDE framework <https://github.com/ITMO-NSS-team/EPDE>_ - Geometric design of physical objects in
GEFEST framework <https://github.com/aimclub/GEFEST>_ -
Neural architecture search <https://github.com/ITMO-NSS-team/nas-fedot>_
As GOLEM is a general-purpose framework, it's easy to imagine potential applications, for example, finite state automata search for robotics control or molecular graph learning for drug discovery, and more.
GOLEM can be installed with pip:
.. code-block::
$ pip install thegolem
Following example demonstrates graph search using reference graph & edit distance metric. Optimizer is set up with a minimal set of parameters and simple single-point mutations. For more details see examples simple_run.py <https://github.com/aimclub/GOLEM/blob/main/examples/synthetic_graph_evolution/simple_run.py>, graph_search.py <https://github.com/aimclub/GOLEM/blob/main/examples/synthetic_graph_evolution/graph_search.py> and tree_search.py <https://github.com/aimclub/GOLEM/blob/main/examples/synthetic_graph_evolution/tree_search.py>_ in directory examples/synthetic_graph_evolution <https://github.com/aimclub/GOLEM/tree/main/examples/synthetic_graph_evolution>_.
.. code-block:: python
def run_graph_search(size=16, timeout=8):
# Generate target graph sought by optimizer using edit distance objective
node_types = ('a', 'b') # Available node types that can appear in graphs
target_graph = generate_labeled_graph('tree', size, node_types)
objective = Objective(partial(tree_edit_dist, target_graph))
initial_population = [generate_labeled_graph('tree', 5, node_types) for _ in range(10)]
# Setup optimization parameters
requirements = GraphRequirements(timeout=timedelta(minutes=timeout))
gen_params = GraphGenerationParams(adapter=BaseNetworkxAdapter(), available_node_types=node_types)
algo_params = GPAlgorithmParameters(pop_size=30)
# Build and run the optimizer
optimiser = EvoGraphOptimizer(objective, initial_population, requirements, gen_params, algo_params)
found_graphs = optimiser.optimise(objective)
# Visualize results
found_graph = gen_params.adapter.restore(found_graphs[0]) # Transform back to NetworkX graph
draw_graphs_subplots(target_graph, found_graph, titles=['Target Graph', 'Found Graph'])
optimiser.history.show.fitness_line()
return found_graph
Tracing the lineage of the found_graph reveals how genetic operators (mutations, crossovers, etc.) are applied to a random graph one after another, eventually leading to the target graph:
.. image:: /docs/source/img/evolution_process.gif :alt: Evolution process :align: center
One can also notice that despite the fact that the edit distance generally decreases along the genealogical path, the optimizer sometimes sacrifices local fitness gain of some graphs in order to achieve diversity and thus obtain the best possible solution at the end.
The repository includes the following packages and directories:
- Package
corecontains the main classes and scripts. - Package
core.adapteris responsible for transformation between domain graphs and internal graph representation used by optimisers. - Package
core.dagcontains classes and algorithms for representation and processing of graphs. - Package
core.optimiserscontains graph optimisers and all related classes (like those representing fitness, individuals, populations, etc.), including optimization history. - Package
core.optimisers.geneticcontains genetic (also called evolutionary) graph optimiser and operators (mutation, selection, and so on). - Package
core.utilitiescontains utilities and data structures used by other modules. - Package
serializerscontains classSerializerwith required facilities, and is responsible for serialization of project classes (graphs, optimization history, and everything related). - Package
visualisationcontains classes that allow to visualise optimization history, graphs, and certain plots useful for analysis. - Package
examplesincludes several use-cases where you can start to discover how the framework works. - All unit and integration tests are contained in the
testdirectory. - The sources of the documentation are in the
docsdirectory.
Any contribution is welcome. Our R&D team is open for cooperation with other scientific teams as well as with industrial partners.
- The contribution guide is available in the
repository </docs/source/contribution.rst>__.
We acknowledge the contributors for their important impact and the participants of the numerous scientific conferences and workshops for their valuable advice and suggestions.
The study is supported by the Research Center Strong Artificial Intelligence in Industry <https://sai.itmo.ru/>_
of ITMO University <https://itmo.ru/>_ as part of the plan of the center's program:
Development and testing of an experimental prototype of the library of strong AI algorithms
in terms of basic algorithms of automatic ML for structural training of composite AI models,
including automation of feature selection
-
Telegram channel <https://t.me/FEDOT_helpdesk>_ for solving problems and answering questions about FEDOT -
Natural System Simulation Team <https://itmo-nss-team.github.io/>_ -
Nikolay Nikitin <https://scholar.google.com/citations?user=eQBTGccAAAAJ&hl=ru>_, AutoML Lead ([email protected]) -
Newsfeed <https://t.me/NSS_group>_ -
Youtube channel <https://www.youtube.com/channel/UC4K9QWaEUpT_p3R4FeDp5jA>_
If you use our project in your work or research, we would appreciate citations.
@article{nikitin2021automated, title = {Automated evolutionary approach for the design of composite machine learning pipelines}, author = {Nikolay O. Nikitin and Pavel Vychuzhanin and Mikhail Sarafanov and Iana S. Polonskaia and Ilia Revin and Irina V. Barabanova and Gleb Maximov and Anna V. Kalyuzhnaya and Alexander Boukhanovsky}, journal = {Future Generation Computer Systems}, year = {2021}, issn = {0167-739X}, doi = {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2021.08.022}}
There are various cases solved with GOLEM's algorithms:
-
Algorithms for time series forecasting pipeline design: Sarafanov M., Pokrovskii V., Nikitin N. O. Evolutionary Automated Machine Learning for Multi-Scale Decomposition and Forecasting of Sensor Time Series //2022 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC). – IEEE, 2022. – С. 01-08.
-
Algorithms for acoustic equation discovery: Hvatov A. Data-Driven Approach for the Floquet Propagator Inverse Problem Solution //ICASSP 2022-2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP). – IEEE, 2022. – С. 3813-3817.
-
Algorithms for PDE discovery: Maslyaev M., Hvatov A. Solver-Based Fitness Function for the Data-Driven Evolutionary Discovery of Partial Differential Equations //2022 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC). – IEEE, 2022. – С. 1-8.
-
Algorithms for structural learning of Bayesian Networks: Deeva I., Kalyuzhnaya A. V., Alexander V. Boukhanovsky Adaptive Learning Algorithm for Bayesian Networks Based on Kernel Mixtures Distributions//International Journal of Artificial Intelligence. – 2023. - Т.21. - №. 1. - С. 90.
.. |docs| image:: https://readthedocs.org/projects/thegolem/badge/?version=latest :target: https://thegolem.readthedocs.io/en/latest/?badge=latest :alt: Documentation Status
.. |build| image:: https://github.com/aimclub/GOLEM/actions/workflows/unit-build.yml/badge.svg?branch=main :alt: Build Status :target: https://github.com/aimclub/GOLEM/actions/workflows/unit-build.yml
.. |integration| image:: https://github.com/aimclub/GOLEM/actions/workflows/integration-build.yml/badge.svg?branch=main :alt: Integration Build Status :target: https://github.com/aimclub/GOLEM/actions/workflows/integration-build.yml
.. |coverage| image:: https://codecov.io/gh/aimclub/GOLEM/branch/main/graph/badge.svg :alt: Coverage Status :target: https://codecov.io/gh/aimclub/GOLEM
.. |pypi| image:: https://img.shields.io/pypi/v/thegolem.svg :alt: PyPI Package Version :target: https://img.shields.io/pypi/v/thegolem
.. |python| image:: https://img.shields.io/pypi/pyversions/thegolem.svg :alt: Supported Python Versions :target: https://img.shields.io/pypi/pyversions/thegolem
.. |license| image:: https://img.shields.io/github/license/aimclub/GOLEM :alt: Supported Python Versions :target: https://github.com/aimclub/GOLEM/blob/main/LICENSE.md
.. |downloads_stats| image:: https://static.pepy.tech/personalized-badge/thegolem?period=total&units=international_system&left_color=grey&right_color=brightgreen&left_text=Downloads :target: https://pepy.tech/project/thegolem
.. |tg| image:: https://img.shields.io/badge/Telegram-Group-blue.svg :alt: Telegram Chat :target: https://t.me/FEDOT_helpdesk
.. |by-golem| image:: http://img.shields.io/badge/powered%20by-GOLEM-orange.svg?style=flat :target: http://github.com/aimclub/GOLEM :alt: Powered by GOLEM
.. |rus| image:: https://img.shields.io/badge/lang-ru-yellow.svg :target: /README.rst
.. |ITMO| image:: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/aimclub/open-source-ops/43bb283758b43d75ec1df0a6bb4ae3eb20066323/badges/ITMO_badge.svg :alt: Acknowledgement to ITMO :target: https://en.itmo.ru/en/
.. |SAI| image:: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/aimclub/open-source-ops/43bb283758b43d75ec1df0a6bb4ae3eb20066323/badges/SAI_badge.svg :alt: Acknowledgement to SAI :target: https://sai.itmo.ru/
.. |mirror| image:: https://img.shields.io/badge/mirror-GitLab-orange :alt: GitLab mirror for this repository :target: https://gitlab.actcognitive.org/itmo-nss-team/GOLEM
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for GOLEM
Similar Open Source Tools

GOLEM
GOLEM is an open-source AI framework focused on optimization and learning of structured graph-based models using meta-heuristic methods. It emphasizes the potential of meta-heuristics in complex problem spaces where gradient-based methods are not suitable, and the importance of structured models in various problem domains. The framework offers features like structured model optimization, metaheuristic methods, multi-objective optimization, constrained optimization, extensibility, interpretability, and reproducibility. It can be applied to optimization problems represented as directed graphs with defined fitness functions. GOLEM has applications in areas like AutoML, Bayesian network structure search, differential equation discovery, geometric design, and neural architecture search. The project structure includes packages for core functionalities, adapters, graph representation, optimizers, genetic algorithms, utilities, serialization, visualization, examples, and testing. Contributions are welcome, and the project is supported by ITMO University's Research Center Strong Artificial Intelligence in Industry.
HuixiangDou2
HuixiangDou2 is a robustly optimized GraphRAG approach that integrates multiple open-source projects to improve performance in graph-based augmented generation. It conducts comparative experiments and achieves a significant score increase, leading to a GraphRAG implementation with recognized performance. The repository provides code improvements, dense retrieval for querying entities and relationships, real domain knowledge testing, and impact analysis on accuracy.

fuse-med-ml
FuseMedML is a Python framework designed to accelerate machine learning-based discovery in the medical field by promoting code reuse. It provides a flexible design concept where data is stored in a nested dictionary, allowing easy handling of multi-modality information. The framework includes components for creating custom models, loss functions, metrics, and data processing operators. Additionally, FuseMedML offers 'batteries included' key components such as fuse.data for data processing, fuse.eval for model evaluation, and fuse.dl for reusable deep learning components. It supports PyTorch and PyTorch Lightning libraries and encourages the creation of domain extensions for specific medical domains.

RAG-FiT
RAG-FiT is a library designed to improve Language Models' ability to use external information by fine-tuning models on specially created RAG-augmented datasets. The library assists in creating training data, training models using parameter-efficient finetuning (PEFT), and evaluating performance using RAG-specific metrics. It is modular, customizable via configuration files, and facilitates fast prototyping and experimentation with various RAG settings and configurations.

RAGFoundry
RAG Foundry is a library designed to enhance Large Language Models (LLMs) by fine-tuning models on RAG-augmented datasets. It helps create training data, train models using parameter-efficient finetuning (PEFT), and measure performance using RAG-specific metrics. The library is modular, customizable using configuration files, and facilitates prototyping with various RAG settings and configurations for tasks like data processing, retrieval, training, inference, and evaluation.
Docs2KG
Docs2KG is a tool designed for constructing a unified knowledge graph from heterogeneous documents. It addresses the challenges of digitizing diverse unstructured documents and constructing a high-quality knowledge graph with less effort. The tool combines bottom-up and top-down approaches, utilizing a human-LLM collaborative interface to enhance the generated knowledge graph. It organizes the knowledge graph into MetaKG, LayoutKG, and SemanticKG, providing a comprehensive view of document content. Docs2KG aims to streamline the process of knowledge graph construction and offers metrics for evaluating the quality of automatic construction.

semlib
Semlib is a Python library for building data processing and data analysis pipelines that leverage the power of large language models (LLMs). It provides functional programming primitives like map, reduce, sort, and filter, programmed with natural language descriptions. Semlib handles complexities such as prompting, parsing, concurrency control, caching, and cost tracking. The library breaks down sophisticated data processing tasks into simpler steps to improve quality, feasibility, latency, cost, security, and flexibility of data processing tasks.
InstructGraph
InstructGraph is a framework designed to enhance large language models (LLMs) for graph-centric tasks by utilizing graph instruction tuning and preference alignment. The tool collects and decomposes 29 standard graph datasets into four groups, enabling LLMs to better understand and generate graph data. It introduces a structured format verbalizer to transform graph data into a code-like format, facilitating code understanding and generation. Additionally, it addresses hallucination problems in graph reasoning and generation through direct preference optimization (DPO). The tool aims to bridge the gap between textual LLMs and graph data, offering a comprehensive solution for graph-related tasks.
pytorch-forecasting
PyTorch Forecasting is a PyTorch-based package for time series forecasting with state-of-the-art network architectures. It offers a high-level API for training networks on pandas data frames and utilizes PyTorch Lightning for scalable training on GPUs and CPUs. The package aims to simplify time series forecasting with neural networks by providing a flexible API for professionals and default settings for beginners. It includes a timeseries dataset class, base model class, multiple neural network architectures, multi-horizon timeseries metrics, and hyperparameter tuning with optuna. PyTorch Forecasting is built on pytorch-lightning for easy training on various hardware configurations.
llm-analysis
llm-analysis is a tool designed for Latency and Memory Analysis of Transformer Models for Training and Inference. It automates the calculation of training or inference latency and memory usage for Large Language Models (LLMs) or Transformers based on specified model, GPU, data type, and parallelism configurations. The tool helps users to experiment with different setups theoretically, understand system performance, and optimize training/inference scenarios. It supports various parallelism schemes, communication methods, activation recomputation options, data types, and fine-tuning strategies. Users can integrate llm-analysis in their code using the `LLMAnalysis` class or use the provided entry point functions for command line interface. The tool provides lower-bound estimations of memory usage and latency, and aims to assist in achieving feasible and optimal setups for training or inference.
gepa
GEPA (Genetic-Pareto) is a framework for optimizing arbitrary systems composed of text components like AI prompts, code snippets, or textual specs against any evaluation metric. It employs LLMs to reflect on system behavior, using feedback from execution and evaluation traces to drive targeted improvements. Through iterative mutation, reflection, and Pareto-aware candidate selection, GEPA evolves robust, high-performing variants with minimal evaluations, co-evolving multiple components in modular systems for domain-specific gains. The repository provides the official implementation of the GEPA algorithm as proposed in the paper titled 'GEPA: Reflective Prompt Evolution Can Outperform Reinforcement Learning'.
RAGEN
RAGEN is a reinforcement learning framework designed to train reasoning-capable large language model (LLM) agents in interactive, stochastic environments. It addresses challenges such as multi-turn interactions and stochastic environments through a Markov Decision Process (MDP) formulation, Reason-Interaction Chain Optimization (RICO) algorithm, and progressive reward normalization strategies. The framework enables LLMs to reason and interact with the environment, optimizing entire trajectories for long-horizon reasoning while maintaining computational efficiency.
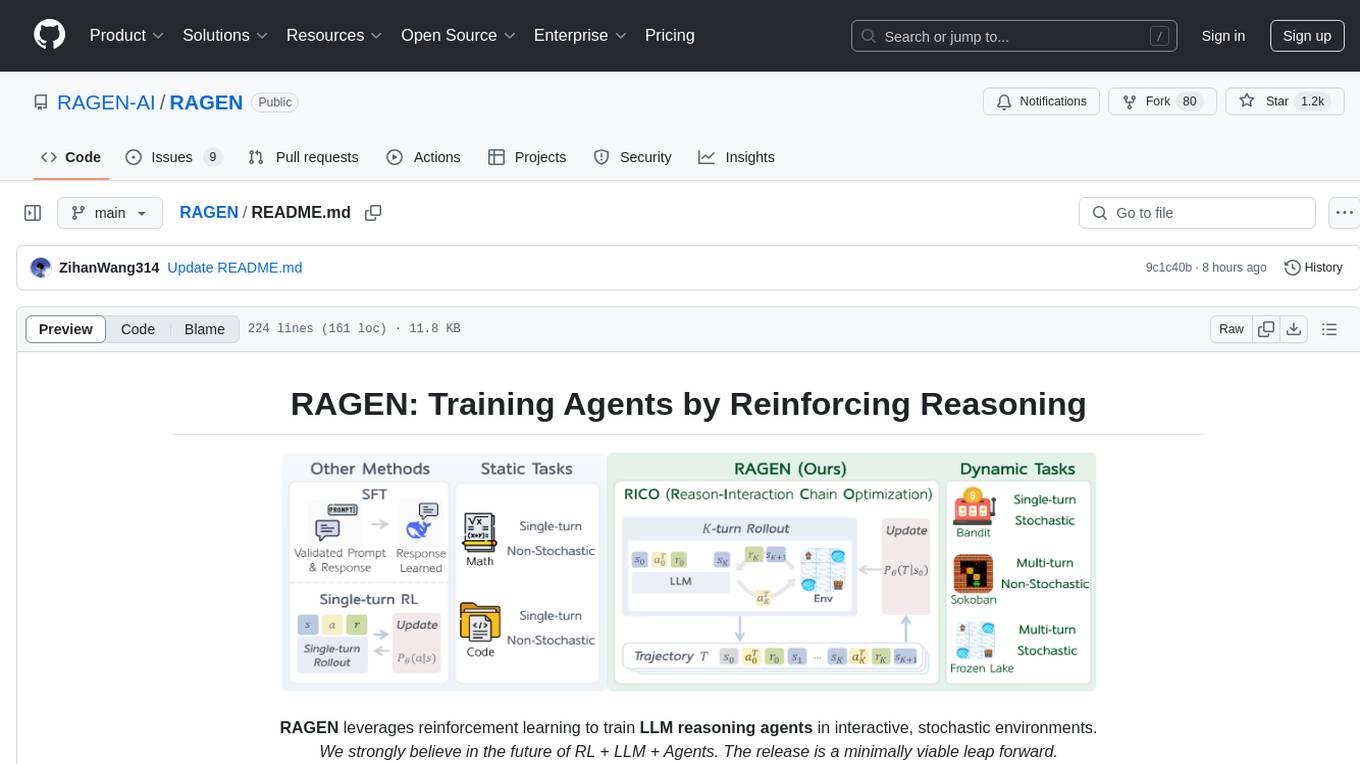
RAGEN
RAGEN is a reinforcement learning framework designed to train reasoning-capable large language model (LLM) agents in interactive, stochastic environments. It addresses challenges such as multi-turn interactions and stochastic environments through a Markov Decision Process (MDP) formulation, Reason-Interaction Chain Optimization (RICO) algorithm, and progressive reward normalization strategies. The framework consists of MDP formulation, RICO algorithm with rollout and update stages, and reward normalization strategies to stabilize training. RAGEN aims to optimize reasoning and action strategies for LLM agents operating in complex environments.

AutoMathText
AutoMathText is an extensive dataset of around 200 GB of mathematical texts autonomously selected by the language model Qwen-72B. It aims to facilitate research in mathematics and artificial intelligence, serve as an educational tool for learning complex mathematical concepts, and provide a foundation for developing AI models specialized in processing mathematical content.
AGI-Papers
This repository contains a collection of papers and resources related to Large Language Models (LLMs), including their applications in various domains such as text generation, translation, question answering, and dialogue systems. The repository also includes discussions on the ethical and societal implications of LLMs. **Description** This repository is a collection of papers and resources related to Large Language Models (LLMs). LLMs are a type of artificial intelligence (AI) that can understand and generate human-like text. They have a wide range of applications, including text generation, translation, question answering, and dialogue systems. **For Jobs** - **Content Writer** - **Copywriter** - **Editor** - **Journalist** - **Marketer** **AI Keywords** - **Large Language Models** - **Natural Language Processing** - **Machine Learning** - **Artificial Intelligence** - **Deep Learning** **For Tasks** - **Generate text** - **Translate text** - **Answer questions** - **Engage in dialogue** - **Summarize text**

interpreto
Interpreto is an interpretability toolkit for large language models (LLMs) that provides a modular framework encompassing attribution methods, concept-based methods, and evaluation metrics. It includes various inference-based and gradient-based attribution methods for both classification and generation tasks. The toolkit also offers concept-based explanations to provide high-level interpretations of latent model representations through steps like concept discovery, interpretation, and concept-to-output attribution. Interpreto aims to enhance model interpretability and facilitate understanding of model decisions and outputs.
For similar tasks

GOLEM
GOLEM is an open-source AI framework focused on optimization and learning of structured graph-based models using meta-heuristic methods. It emphasizes the potential of meta-heuristics in complex problem spaces where gradient-based methods are not suitable, and the importance of structured models in various problem domains. The framework offers features like structured model optimization, metaheuristic methods, multi-objective optimization, constrained optimization, extensibility, interpretability, and reproducibility. It can be applied to optimization problems represented as directed graphs with defined fitness functions. GOLEM has applications in areas like AutoML, Bayesian network structure search, differential equation discovery, geometric design, and neural architecture search. The project structure includes packages for core functionalities, adapters, graph representation, optimizers, genetic algorithms, utilities, serialization, visualization, examples, and testing. Contributions are welcome, and the project is supported by ITMO University's Research Center Strong Artificial Intelligence in Industry.
intel-extension-for-tensorflow
Intel® Extension for TensorFlow* is a high performance deep learning extension plugin based on TensorFlow PluggableDevice interface. It aims to accelerate AI workloads by allowing users to plug Intel CPU or GPU devices into TensorFlow on-demand, exposing the computing power inside Intel's hardware. The extension provides XPU specific implementation, kernels & operators, graph optimizer, device runtime, XPU configuration management, XPU backend selection, and options for turning on/off advanced features.
lightning-bolts
Bolts package provides a variety of components to extend PyTorch Lightning, such as callbacks & datasets, for applied research and production. Users can accelerate Lightning training with the Torch ORT Callback to optimize ONNX graph for faster training & inference. Additionally, users can introduce sparsity with the SparseMLCallback to accelerate inference by leveraging the DeepSparse engine. Specific research implementations are encouraged, with contributions that help train SSL models and integrate with Lightning Flash for state-of-the-art models in applied research.

tt-xla
TT-XLA is a repository that enables running PyTorch and JAX models on Tenstorrent's AI hardware. It serves as a backend integration between the JAX ecosystem and Tenstorrent's ML accelerators using the PJRT (Portable JAX Runtime) interface. It supports ingestion of PyTorch models through PyTorch/XLA and JAX models via jit compile, providing a StableHLO (SHLO) graph to TT-MLIR compiler.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.