
xlstm
Official repository of the xLSTM.
Stars: 1740
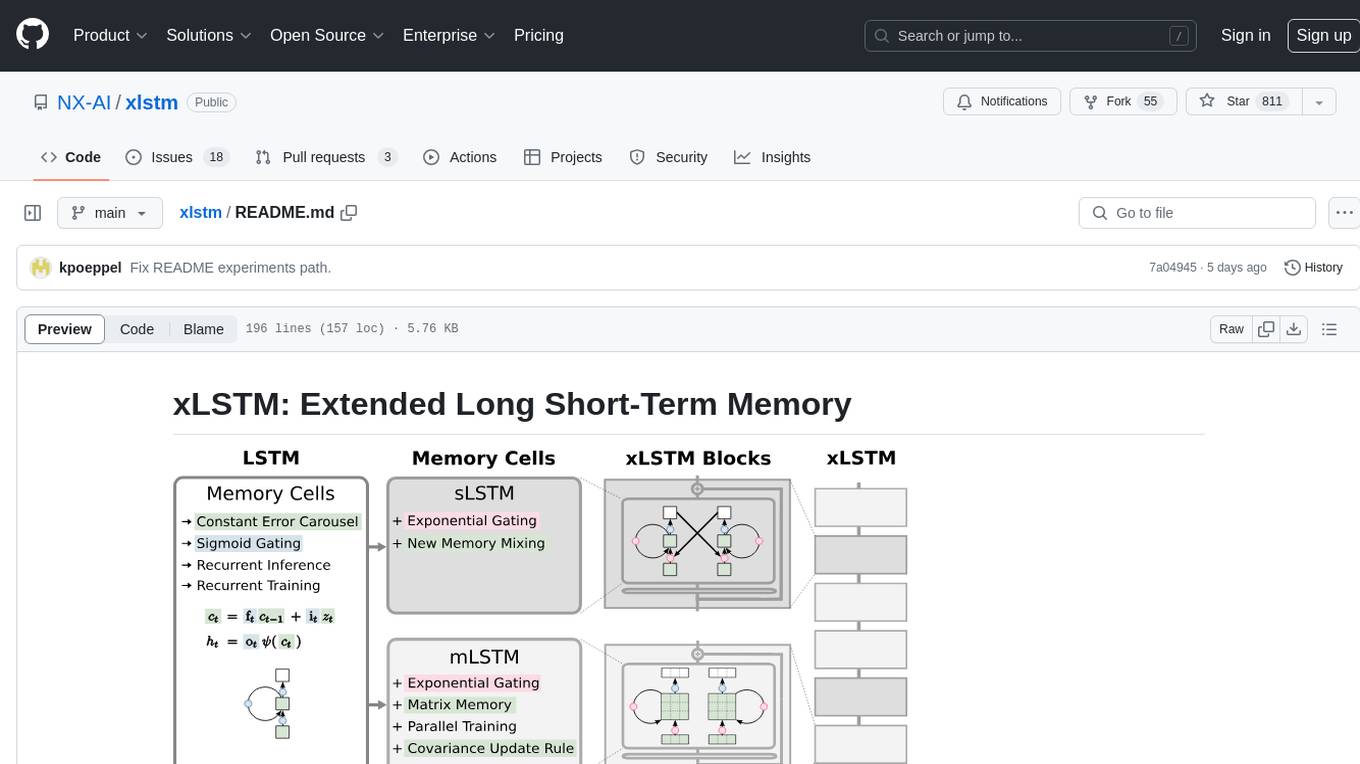
xLSTM is a new Recurrent Neural Network architecture based on ideas of the original LSTM. Through Exponential Gating with appropriate normalization and stabilization techniques and a new Matrix Memory it overcomes the limitations of the original LSTM and shows promising performance on Language Modeling when compared to Transformers or State Space Models. The package is based on PyTorch and was tested for versions >=1.8. For the CUDA version of xLSTM, you need Compute Capability >= 8.0. The xLSTM tool provides two main components: xLSTMBlockStack for non-language applications or integrating in other architectures, and xLSTMLMModel for language modeling or other token-based applications.
README:
xLSTM is a new Recurrent Neural Network architecture based on ideas of the original LSTM. Through Exponential Gating with appropriate normalization and stabilization techniques and a new Matrix Memory it overcomes the limitations of the original LSTM and shows promising performance on Language Modeling when compared to Transformers or State Space Models.
🚨 We trained a 7B parameter xLSTM Language Model 🚨
We have optimized the xLSTM architecture in terms of training throughput and stability.
The code for the updated architecture is located in xlstm/xlstm_large.
The model weights are available on Huggingface at https://huggingface.co/NX-AI/xLSTM-7b.
Create a conda environment from the file environment_pt220cu121.yaml.
Install the model code only (i.e. the module xlstm) as package:
Install via pip:
pip install xlstmClone from github:
git clone https://github.com/NX-AI/xlstm.git
cd xlstm
pip install -e .For using the 7B xLSTM model install mlstm_kernels via:
pip install mlstm_kernels
This package is based on PyTorch and was tested for versions >=1.8. For the CUDA version of sLSTM, you need Compute Capability >= 8.0, see https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda-gpus. For a well-tested environment, install the environment_pt220cu121.yaml as:
conda env create -n xlstm -f environment_pt220cu121.yaml
conda activate xlstmFor the xLSTM Large 7B model we require our mlstm_kernels (TODO add github link) package, which provides fast kernels for the xLSTM.
This section explains how to use the models from the xLSTM paper.
For non language applications or for integrating in other architectures you can use the xLSTMBlockStack and for language modeling or other token-based applications you can use the xLSTMLMModel.
The xLSTMBLockStack is meant for use as alternative backbone in existing projects. It is similar to a stack of Transformer blocks, but uses xLSTM blocks:
import torch
from xlstm import (
xLSTMBlockStack,
xLSTMBlockStackConfig,
mLSTMBlockConfig,
mLSTMLayerConfig,
sLSTMBlockConfig,
sLSTMLayerConfig,
FeedForwardConfig,
)
cfg = xLSTMBlockStackConfig(
mlstm_block=mLSTMBlockConfig(
mlstm=mLSTMLayerConfig(
conv1d_kernel_size=4, qkv_proj_blocksize=4, num_heads=4
)
),
slstm_block=sLSTMBlockConfig(
slstm=sLSTMLayerConfig(
backend="cuda",
num_heads=4,
conv1d_kernel_size=4,
bias_init="powerlaw_blockdependent",
),
feedforward=FeedForwardConfig(proj_factor=1.3, act_fn="gelu"),
),
context_length=256,
num_blocks=7,
embedding_dim=128,
slstm_at=[1],
)
xlstm_stack = xLSTMBlockStack(cfg)
x = torch.randn(4, 256, 128).to("cuda")
xlstm_stack = xlstm_stack.to("cuda")
y = xlstm_stack(x)
y.shape == x.shapeIf you are working with yaml strings / files for configuration you can also use dacite to create the config dataclasses. This is the same as the snippet above:
from omegaconf import OmegaConf
from dacite import from_dict
from dacite import Config as DaciteConfig
from xlstm import xLSTMBlockStack, xLSTMBlockStackConfig
xlstm_cfg = """
mlstm_block:
mlstm:
conv1d_kernel_size: 4
qkv_proj_blocksize: 4
num_heads: 4
slstm_block:
slstm:
backend: cuda
num_heads: 4
conv1d_kernel_size: 4
bias_init: powerlaw_blockdependent
feedforward:
proj_factor: 1.3
act_fn: gelu
context_length: 256
num_blocks: 7
embedding_dim: 128
slstm_at: [1]
"""
cfg = OmegaConf.create(xlstm_cfg)
cfg = from_dict(data_class=xLSTMBlockStackConfig, data=OmegaConf.to_container(cfg), config=DaciteConfig(strict=True))
xlstm_stack = xLSTMBlockStack(cfg)
x = torch.randn(4, 256, 128).to("cuda")
xlstm_stack = xlstm_stack.to("cuda")
y = xlstm_stack(x)
y.shape == x.shapeThe xLSTMLMModel is a wrapper around the xLSTMBlockStack that adds the token embedding and lm head.
from omegaconf import OmegaConf
from dacite import from_dict
from dacite import Config as DaciteConfig
from xlstm import xLSTMLMModel, xLSTMLMModelConfig
xlstm_cfg = """
vocab_size: 50304
mlstm_block:
mlstm:
conv1d_kernel_size: 4
qkv_proj_blocksize: 4
num_heads: 4
slstm_block:
slstm:
backend: cuda
num_heads: 4
conv1d_kernel_size: 4
bias_init: powerlaw_blockdependent
feedforward:
proj_factor: 1.3
act_fn: gelu
context_length: 256
num_blocks: 7
embedding_dim: 128
slstm_at: [1]
"""
cfg = OmegaConf.create(xlstm_cfg)
cfg = from_dict(data_class=xLSTMLMModelConfig, data=OmegaConf.to_container(cfg), config=DaciteConfig(strict=True))
xlstm_stack = xLSTMLMModel(cfg)
x = torch.randint(0, 50304, size=(4, 256)).to("cuda")
xlstm_stack = xlstm_stack.to("cuda")
y = xlstm_stack(x)
y.shape[1:] == (256, 50304)The synthetic experiments show-casing the benefits of sLSTM over mLSTM and vice versa best are the Parity task and the Multi-Query Associative Recall task. The Parity task can only be solved with state-tracking capabilities provided by the memory-mixing of sLSTM. The Multi-Query Associative Recall task measures memorization capabilities, where the matrix-memory and state expansion of mLSTM is very beneficial. In combination they do well on both tasks.
To run each, run the main.py in the experiments folder like:
PYTHONPATH=. python experiments/main.py --config experiments/parity_xlstm01.yaml # xLSTM[0:1], sLSTM only
PYTHONPATH=. python experiments/main.py --config experiments/parity_xlstm10.yaml # xLSTM[1:0], mLSTM only
PYTHONPATH=. python experiments/main.py --config experiments/parity_xlstm11.yaml # xLSTM[1:1], mLSTM and sLSTM
Note that the training loop does not contain early stopping or test evaluation.
If you use this codebase, or otherwise find our work valuable, please cite the xLSTM paper:
@inproceedings{beck:24xlstm,
title={xLSTM: Extended Long Short-Term Memory},
author={Maximilian Beck and Korbinian Pöppel and Markus Spanring and Andreas Auer and Oleksandra Prudnikova and Michael Kopp and Günter Klambauer and Johannes Brandstetter and Sepp Hochreiter},
booktitle = {Thirty-eighth Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems},
year={2024},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2405.04517},
}
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for xlstm
Similar Open Source Tools

xlstm
xLSTM is a new Recurrent Neural Network architecture based on ideas of the original LSTM. Through Exponential Gating with appropriate normalization and stabilization techniques and a new Matrix Memory it overcomes the limitations of the original LSTM and shows promising performance on Language Modeling when compared to Transformers or State Space Models. The package is based on PyTorch and was tested for versions >=1.8. For the CUDA version of xLSTM, you need Compute Capability >= 8.0. The xLSTM tool provides two main components: xLSTMBlockStack for non-language applications or integrating in other architectures, and xLSTMLMModel for language modeling or other token-based applications.
probsem
ProbSem is a repository that provides a framework to leverage large language models (LLMs) for assigning context-conditional probability distributions over queried strings. It supports OpenAI engines and HuggingFace CausalLM models, and is flexible for research applications in linguistics, cognitive science, program synthesis, and NLP. Users can define prompts, contexts, and queries to derive probability distributions over possible completions, enabling tasks like cloze completion, multiple-choice QA, semantic parsing, and code completion. The repository offers CLI and API interfaces for evaluation, with options to customize models, normalize scores, and adjust temperature for probability distributions.
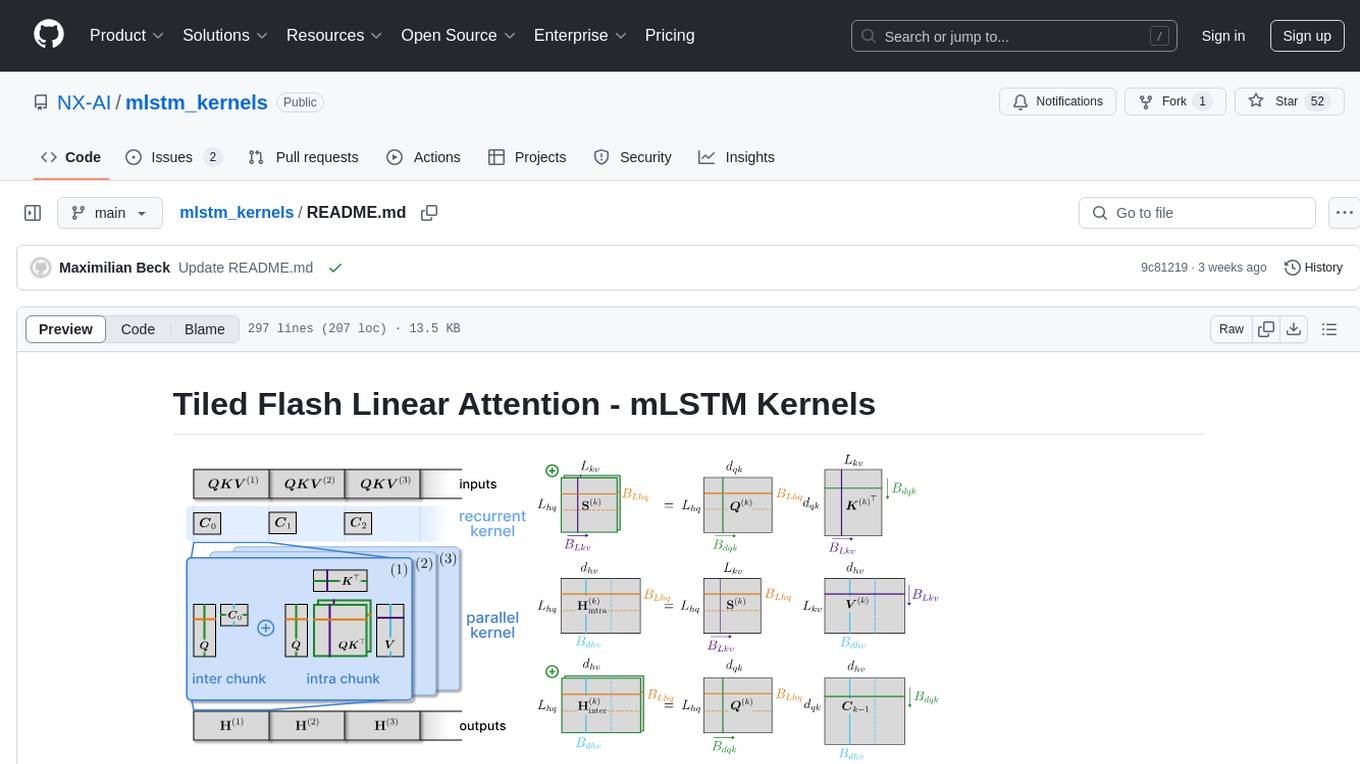
mlstm_kernels
This repository provides fast and efficient mLSTM training and inference Triton kernels built on Tiled Flash Linear Attention (TFLA). It includes implementations in JAX, PyTorch, and Triton, with chunkwise, parallel, and recurrent kernels for mLSTM. The repository also contains a benchmark library for runtime benchmarks and full mLSTM Huggingface models.

LightRAG
LightRAG is a PyTorch library designed for building and optimizing Retriever-Agent-Generator (RAG) pipelines. It follows principles of simplicity, quality, and optimization, offering developers maximum customizability with minimal abstraction. The library includes components for model interaction, output parsing, and structured data generation. LightRAG facilitates tasks like providing explanations and examples for concepts through a question-answering pipeline.
ChatRex
ChatRex is a Multimodal Large Language Model (MLLM) designed to seamlessly integrate fine-grained object perception and robust language understanding. By adopting a decoupled architecture with a retrieval-based approach for object detection and leveraging high-resolution visual inputs, ChatRex addresses key challenges in perception tasks. It is powered by the Rexverse-2M dataset with diverse image-region-text annotations. ChatRex can be applied to various scenarios requiring fine-grained perception, such as object detection, grounded conversation, grounded image captioning, and region understanding.
leva
Leva is a Ruby on Rails framework designed for evaluating Language Models (LLMs) using ActiveRecord datasets on production models. It offers a flexible structure for creating experiments, managing datasets, and implementing various evaluation logic on production data with security in mind. Users can set up datasets, implement runs and evals, run experiments with different configurations, use prompts, and analyze results. Leva's components include classes like Leva, Leva::BaseRun, and Leva::BaseEval, as well as models like Leva::Dataset, Leva::DatasetRecord, Leva::Experiment, Leva::RunnerResult, Leva::EvaluationResult, and Leva::Prompt. The tool aims to provide a comprehensive solution for evaluating language models efficiently and securely.
topicGPT
TopicGPT is a repository containing scripts and prompts for the paper 'TopicGPT: Topic Modeling by Prompting Large Language Models' (NAACL'24). The 'topicgpt_python' package offers functions to generate high-level and specific topics, refine topics, assign topics to input text, and correct generated topics. It supports various APIs like OpenAI, VertexAI, Azure, Gemini, and vLLM for inference. Users can prepare data in JSONL format, run the pipeline using provided scripts, and evaluate topic alignment with ground-truth labels.
PDEBench
PDEBench provides a diverse and comprehensive set of benchmarks for scientific machine learning, including challenging and realistic physical problems. The repository consists of code for generating datasets, uploading and downloading datasets, training and evaluating machine learning models as baselines. It features a wide range of PDEs, realistic and difficult problems, ready-to-use datasets with various conditions and parameters. PDEBench aims for extensibility and invites participation from the SciML community to improve and extend the benchmark.
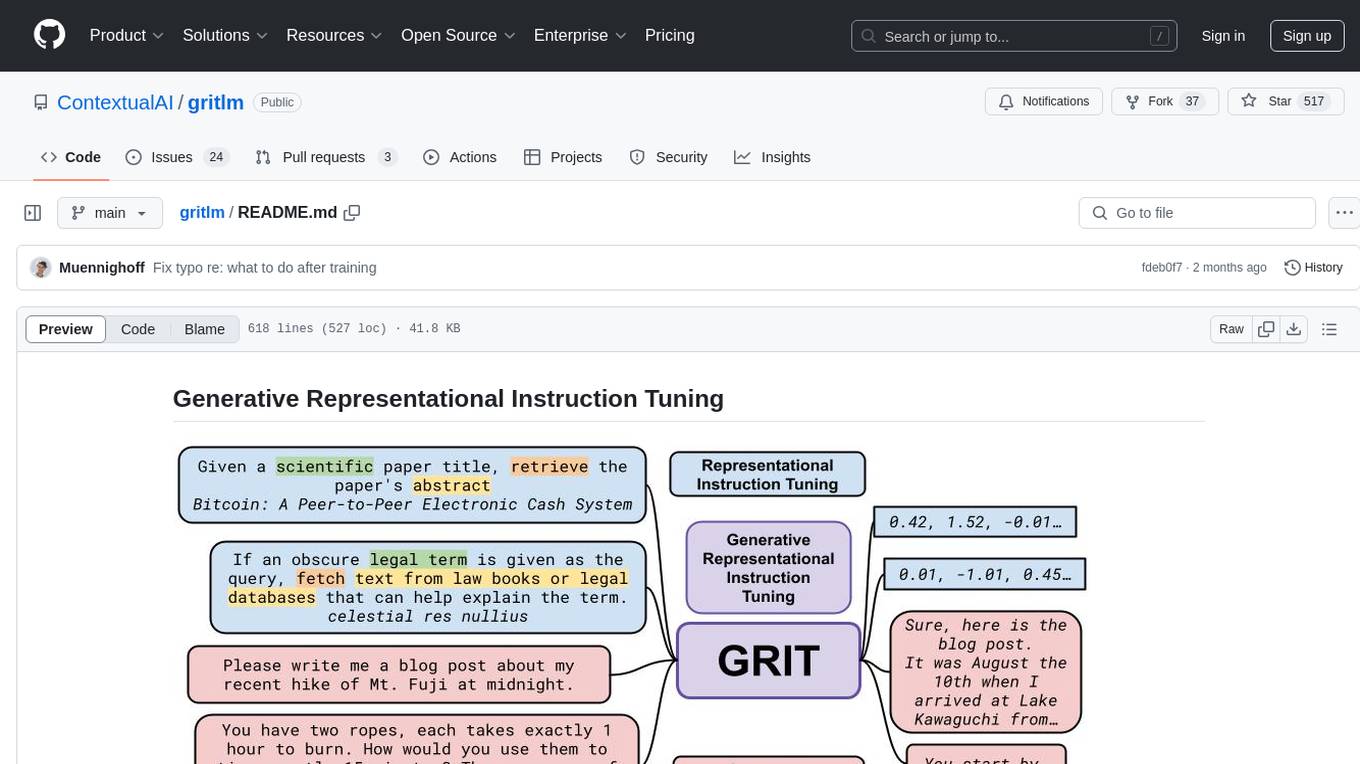
gritlm
The 'gritlm' repository provides all materials for the paper Generative Representational Instruction Tuning. It includes code for inference, training, evaluation, and known issues related to the GritLM model. The repository also offers models for embedding and generation tasks, along with instructions on how to train and evaluate the models. Additionally, it contains visualizations, acknowledgements, and a citation for referencing the work.
MemoryLLM
MemoryLLM is a large language model designed for self-updating capabilities. It offers pretrained models with different memory capacities and features, such as chat models. The repository provides training code, evaluation scripts, and datasets for custom experiments. MemoryLLM aims to enhance knowledge retention and performance on various natural language processing tasks.

zeta
Zeta is a tool designed to build state-of-the-art AI models faster by providing modular, high-performance, and scalable building blocks. It addresses the common issues faced while working with neural nets, such as chaotic codebases, lack of modularity, and low performance modules. Zeta emphasizes usability, modularity, and performance, and is currently used in hundreds of models across various GitHub repositories. It enables users to prototype, train, optimize, and deploy the latest SOTA neural nets into production. The tool offers various modules like FlashAttention, SwiGLUStacked, RelativePositionBias, FeedForward, BitLinear, PalmE, Unet, VisionEmbeddings, niva, FusedDenseGELUDense, FusedDropoutLayerNorm, MambaBlock, Film, hyper_optimize, DPO, and ZetaCloud for different tasks in AI model development.
neural-speed
Neural Speed is an innovative library designed to support the efficient inference of large language models (LLMs) on Intel platforms through the state-of-the-art (SOTA) low-bit quantization powered by Intel Neural Compressor. The work is inspired by llama.cpp and further optimized for Intel platforms with our innovations in NeurIPS' 2023
paxml
Pax is a framework to configure and run machine learning experiments on top of Jax.
aigverse
aigverse is a Python infrastructure framework that bridges the gap between logic synthesis and AI/ML applications. It allows efficient representation and manipulation of logic circuits, making it easier to integrate logic synthesis and optimization tasks into machine learning pipelines. Built upon EPFL Logic Synthesis Libraries, particularly mockturtle, aigverse provides a high-level Python interface to state-of-the-art algorithms for And-Inverter Graph (AIG) manipulation and logic synthesis, widely used in formal verification, hardware design, and optimization tasks.
python-aiplatform
The Vertex AI SDK for Python is a library that provides a convenient way to use the Vertex AI API. It offers a high-level interface for creating and managing Vertex AI resources, such as datasets, models, and endpoints. The SDK also provides support for training and deploying custom models, as well as using AutoML models. With the Vertex AI SDK for Python, you can quickly and easily build and deploy machine learning models on Vertex AI.
clarifai-python-grpc
This is the official Clarifai gRPC Python client for interacting with their recognition API. Clarifai offers a platform for data scientists, developers, researchers, and enterprises to utilize artificial intelligence for image, video, and text analysis through computer vision and natural language processing. The client allows users to authenticate, predict concepts in images, and access various functionalities provided by the Clarifai API. It follows a versioning scheme that aligns with the backend API updates and includes specific instructions for installation and troubleshooting. Users can explore the Clarifai demo, sign up for an account, and refer to the documentation for detailed information.
For similar tasks

xlstm
xLSTM is a new Recurrent Neural Network architecture based on ideas of the original LSTM. Through Exponential Gating with appropriate normalization and stabilization techniques and a new Matrix Memory it overcomes the limitations of the original LSTM and shows promising performance on Language Modeling when compared to Transformers or State Space Models. The package is based on PyTorch and was tested for versions >=1.8. For the CUDA version of xLSTM, you need Compute Capability >= 8.0. The xLSTM tool provides two main components: xLSTMBlockStack for non-language applications or integrating in other architectures, and xLSTMLMModel for language modeling or other token-based applications.
TokenFormer
TokenFormer is a fully attention-based neural network architecture that leverages tokenized model parameters to enhance architectural flexibility. It aims to maximize the flexibility of neural networks by unifying token-token and token-parameter interactions through the attention mechanism. The architecture allows for incremental model scaling and has shown promising results in language modeling and visual modeling tasks. The codebase is clean, concise, easily readable, state-of-the-art, and relies on minimal dependencies.

ai-on-gke
This repository contains assets related to AI/ML workloads on Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE). Run optimized AI/ML workloads with Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) platform orchestration capabilities. A robust AI/ML platform considers the following layers: Infrastructure orchestration that support GPUs and TPUs for training and serving workloads at scale Flexible integration with distributed computing and data processing frameworks Support for multiple teams on the same infrastructure to maximize utilization of resources

ray
Ray is a unified framework for scaling AI and Python applications. It consists of a core distributed runtime and a set of AI libraries for simplifying ML compute, including Data, Train, Tune, RLlib, and Serve. Ray runs on any machine, cluster, cloud provider, and Kubernetes, and features a growing ecosystem of community integrations. With Ray, you can seamlessly scale the same code from a laptop to a cluster, making it easy to meet the compute-intensive demands of modern ML workloads.

labelbox-python
Labelbox is a data-centric AI platform for enterprises to develop, optimize, and use AI to solve problems and power new products and services. Enterprises use Labelbox to curate data, generate high-quality human feedback data for computer vision and LLMs, evaluate model performance, and automate tasks by combining AI and human-centric workflows. The academic & research community uses Labelbox for cutting-edge AI research.

djl
Deep Java Library (DJL) is an open-source, high-level, engine-agnostic Java framework for deep learning. It is designed to be easy to get started with and simple to use for Java developers. DJL provides a native Java development experience and allows users to integrate machine learning and deep learning models with their Java applications. The framework is deep learning engine agnostic, enabling users to switch engines at any point for optimal performance. DJL's ergonomic API interface guides users with best practices to accomplish deep learning tasks, such as running inference and training neural networks.

mojo
Mojo is a new programming language that bridges the gap between research and production by combining Python syntax and ecosystem with systems programming and metaprogramming features. Mojo is still young, but it is designed to become a superset of Python over time.
tt-metal
TT-NN is a python & C++ Neural Network OP library. It provides a low-level programming model, TT-Metalium, enabling kernel development for Tenstorrent hardware.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.