
microchain
function calling-based LLM agents
Stars: 268
Microchain is a function calling-based LLM agents tool with no bloat. It allows users to define LLM and templates, use various functions like Sum and Product, and create LLM agents for specific tasks. The tool provides a simple and efficient way to interact with OpenAI models and create conversational agents for various applications.
README:
function calling-based LLM agents. Just that, no bloat.
pip install microchain-python
from microchain import OpenAITextGenerator, HFChatTemplate, LLM
generator = OpenAITextGenerator(
model=MODEL_NAME,
api_key=API_KEY,
api_base=API_BASE,
temperature=0.7
)
template = HFChatTemplate(CHAT_TEMPLATE)
llm = LLM(generator=generator, templates=[template])Use HFChatTemplate(template) to use tokenizer.apply_chat_template from huggingface.
You can also use VicunaTemplate() for a classic vicuna-style prompt.
To use ChatGPT APIs you don't need to apply a template:
from microchain import OpenAIChatGenerator, LLM
generator = OpenAIChatGenerator(
model="gpt-3.5-turbo",
api_key=API_KEY,
api_base="https://api.openai.com/v1",
temperature=0.7
)
llm = LLM(generator=generator)Define LLM callable functions as plain Python objects. Use type annotations to instruct the LLM to use the correct types.
from microchain import Function
class Sum(Function):
@property
def description(self):
return "Use this function to compute the sum of two numbers"
@property
def example_args(self):
return [2, 2]
def __call__(self, a: float, b: float):
return a + b
class Product(Function):
@property
def description(self):
return "Use this function to compute the product of two numbers"
@property
def example_args(self):
return [2, 2]
def __call__(self, a: float, b: float):
return a * b
print(Sum().help)
'''
Sum(a: float, b: float)
This function sums two numbers.
Example: Sum(a=2, b=2)
'''
print(Product().help)
'''
Product(a: float, b: float)
Use this function to compute the product of two numbers.
Example: Product(a=2, b=2)
'''Register your functions with an Engine() using the register() function.
Create an Agent() using the llm and the execution engine.
Define a prompt for the LLM and include the functions documentation using engine.help().
It's always a good idea to bootstrap the LLM with examples of function calls. Do this by setting engine.bootstrap = [...] with a list of function calls to run and prepend their results to the chat history.
from microchain import Agent, Engine
from microchain.functions import Reasoning, Stop
engine = Engine()
engine.register(Reasoning())
engine.register(Stop())
engine.register(Sum())
engine.register(Product())
agent = Agent(llm=llm, engine=engine)
agent.prompt = f"""Act as a calculator. You can use the following functions:
{engine.help}
Only output valid Python function calls.
How much is (2*4 + 3)*5?
"""
agent.bootstrap = [
'Reasoning("I need to reason step-by-step")',
]
agent.run()Running it will output something like:
prompt:
Act as a calculator. You can use the following functions:
Reasoning(reasoning: str)
Use this function for your internal reasoning.
Example: Reasoning(reasoning=The next step to take is...)
Stop()
Use this function to stop the program.
Example: Stop()
Sum(a: float, b: float)
Use this function to compute the sum of two numbers.
Example: Sum(a=2, b=2)
Product(a: float, b: float)
Use this function to compute the product of two numbers.
Example: Product(a=2, b=2)
Only output valid Python function calls.
How much is (2*4 + 3)*5?
Running 10 iterations
>> Reasoning("I need to reason step-by-step")
The reasoning has been recorded
>> Reasoning("First, calculate the product of 2 and 4")
The reasoning has been recorded
>> Product(a=2, b=4)
8
>> Reasoning("Then, add 3 to the product of 2 and 4")
The reasoning has been recorded
>> Sum(a=8, b=3)
11
>> Reasoning("Lastly, multiply the sum by 5")
The reasoning has been recorded
>> Product(a=11, b=5)
55
>> Reasoning("So, the result of (2*4 + 3)*5 is 55")
The reasoning has been recorded
>> Stop()
The program has been stopped
You can find more examples here
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for microchain
Similar Open Source Tools

microchain
Microchain is a function calling-based LLM agents tool with no bloat. It allows users to define LLM and templates, use various functions like Sum and Product, and create LLM agents for specific tasks. The tool provides a simple and efficient way to interact with OpenAI models and create conversational agents for various applications.

LightRAG
LightRAG is a PyTorch library designed for building and optimizing Retriever-Agent-Generator (RAG) pipelines. It follows principles of simplicity, quality, and optimization, offering developers maximum customizability with minimal abstraction. The library includes components for model interaction, output parsing, and structured data generation. LightRAG facilitates tasks like providing explanations and examples for concepts through a question-answering pipeline.
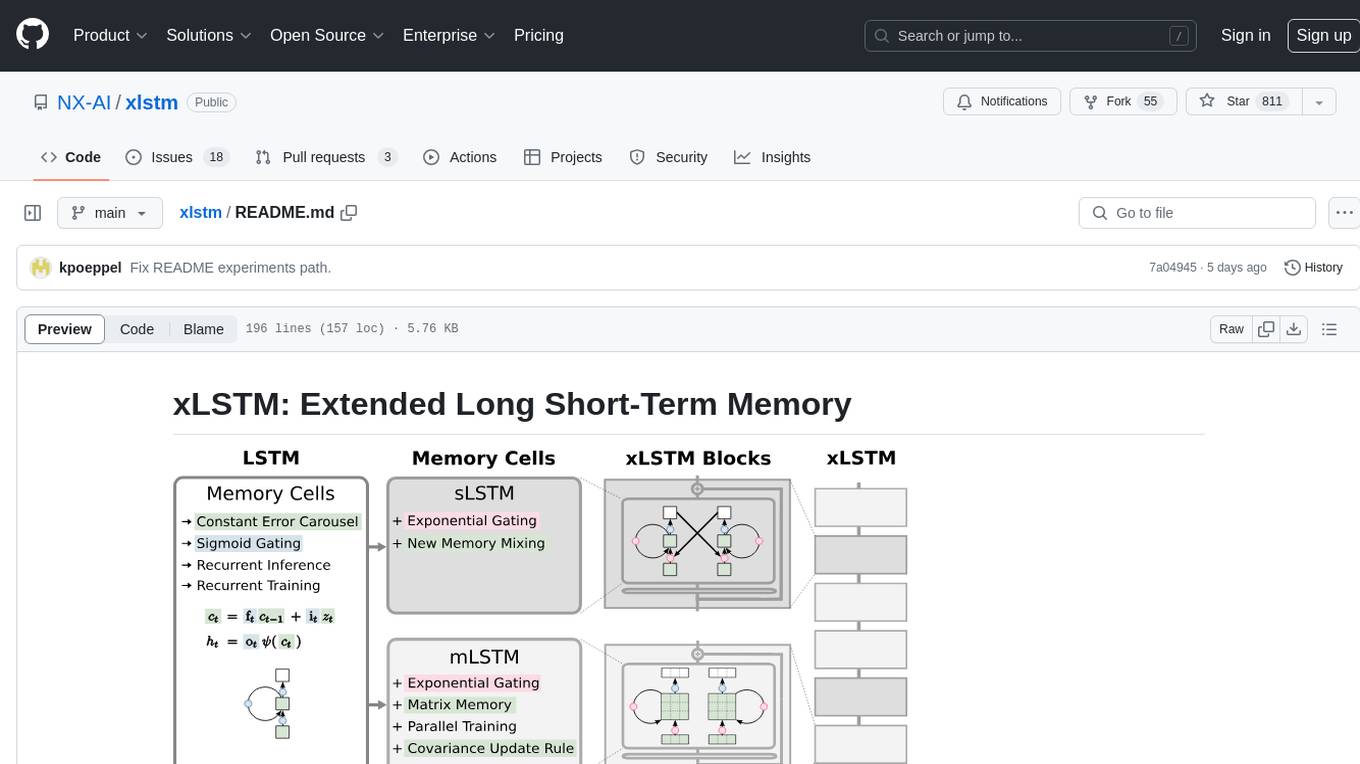
xlstm
xLSTM is a new Recurrent Neural Network architecture based on ideas of the original LSTM. Through Exponential Gating with appropriate normalization and stabilization techniques and a new Matrix Memory it overcomes the limitations of the original LSTM and shows promising performance on Language Modeling when compared to Transformers or State Space Models. The package is based on PyTorch and was tested for versions >=1.8. For the CUDA version of xLSTM, you need Compute Capability >= 8.0. The xLSTM tool provides two main components: xLSTMBlockStack for non-language applications or integrating in other architectures, and xLSTMLMModel for language modeling or other token-based applications.

fastfit
FastFit is a Python package designed for fast and accurate few-shot classification, especially for scenarios with many semantically similar classes. It utilizes a novel approach integrating batch contrastive learning and token-level similarity score, significantly improving multi-class classification performance in speed and accuracy across various datasets. FastFit provides a convenient command-line tool for training text classification models with customizable parameters. It offers a 3-20x improvement in training speed, completing training in just a few seconds. Users can also train models with Python scripts and perform inference using pretrained models for text classification tasks.
clarifai-python-grpc
This is the official Clarifai gRPC Python client for interacting with their recognition API. Clarifai offers a platform for data scientists, developers, researchers, and enterprises to utilize artificial intelligence for image, video, and text analysis through computer vision and natural language processing. The client allows users to authenticate, predict concepts in images, and access various functionalities provided by the Clarifai API. It follows a versioning scheme that aligns with the backend API updates and includes specific instructions for installation and troubleshooting. Users can explore the Clarifai demo, sign up for an account, and refer to the documentation for detailed information.
aigverse
aigverse is a Python infrastructure framework that bridges the gap between logic synthesis and AI/ML applications. It allows efficient representation and manipulation of logic circuits, making it easier to integrate logic synthesis and optimization tasks into machine learning pipelines. Built upon EPFL Logic Synthesis Libraries, particularly mockturtle, aigverse provides a high-level Python interface to state-of-the-art algorithms for And-Inverter Graph (AIG) manipulation and logic synthesis, widely used in formal verification, hardware design, and optimization tasks.

simple-openai
Simple-OpenAI is a Java library that provides a simple way to interact with the OpenAI API. It offers consistent interfaces for various OpenAI services like Audio, Chat Completion, Image Generation, and more. The library uses CleverClient for HTTP communication, Jackson for JSON parsing, and Lombok to reduce boilerplate code. It supports asynchronous requests and provides methods for synchronous calls as well. Users can easily create objects to communicate with the OpenAI API and perform tasks like text-to-speech, transcription, image generation, and chat completions.
litserve
LitServe is a high-throughput serving engine for deploying AI models at scale. It generates an API endpoint for a model, handles batching, streaming, autoscaling across CPU/GPUs, and more. Built for enterprise scale, it supports every framework like PyTorch, JAX, Tensorflow, and more. LitServe is designed to let users focus on model performance, not the serving boilerplate. It is like PyTorch Lightning for model serving but with broader framework support and scalability.

a2a-java
A2A Java SDK is a Java library that helps run agentic applications as A2AServers following the Agent2Agent (A2A) Protocol. It provides a Java server implementation of the A2A Protocol, allowing users to create A2A server agents and execute tasks. The SDK also includes a Java client implementation for communication with A2A servers using various transports like JSON-RPC 2.0, gRPC, and HTTP+JSON/REST. Users can configure different transport protocols, handle messages, tasks, push notifications, and interact with server agents. The SDK supports streaming and non-streaming responses, error handling, and task management functionalities.
architext
Architext is a Python library designed for Large Language Model (LLM) applications, focusing on Context Engineering. It provides tools to construct and reorganize input context for LLMs dynamically. The library aims to elevate context construction from ad-hoc to systematic engineering, enabling precise manipulation of context content for AI Agents.
ChatRex
ChatRex is a Multimodal Large Language Model (MLLM) designed to seamlessly integrate fine-grained object perception and robust language understanding. By adopting a decoupled architecture with a retrieval-based approach for object detection and leveraging high-resolution visual inputs, ChatRex addresses key challenges in perception tasks. It is powered by the Rexverse-2M dataset with diverse image-region-text annotations. ChatRex can be applied to various scenarios requiring fine-grained perception, such as object detection, grounded conversation, grounded image captioning, and region understanding.
continuous-eval
Open-Source Evaluation for LLM Applications. `continuous-eval` is an open-source package created for granular and holistic evaluation of GenAI application pipelines. It offers modularized evaluation, a comprehensive metric library covering various LLM use cases, the ability to leverage user feedback in evaluation, and synthetic dataset generation for testing pipelines. Users can define their own metrics by extending the Metric class. The tool allows running evaluation on a pipeline defined with modules and corresponding metrics. Additionally, it provides synthetic data generation capabilities to create user interaction data for evaluation or training purposes.

ivy
Ivy is an open-source machine learning framework that enables users to convert code between different ML frameworks and write framework-agnostic code. It allows users to transpile code from one framework to another, making it easy to use building blocks from different frameworks in a single project. Ivy also serves as a flexible framework that breaks free from framework limitations, allowing users to publish code that is interoperable with various frameworks and future frameworks. Users can define trainable modules and layers using Ivy's stateful API, making it easy to build and train models across different backends.
java-genai
Java idiomatic SDK for the Gemini Developer APIs and Vertex AI APIs. The SDK provides a Client class for interacting with both APIs, allowing seamless switching between the 2 backends without code rewriting. It supports features like generating content, embedding content, generating images, upscaling images, editing images, and generating videos. The SDK also includes options for setting API versions, HTTP request parameters, client behavior, and response schemas.
bellman
Bellman is a unified interface to interact with language and embedding models, supporting various vendors like VertexAI/Gemini, OpenAI, Anthropic, VoyageAI, and Ollama. It consists of a library for direct interaction with models and a service 'bellmand' for proxying requests with one API key. Bellman simplifies switching between models, vendors, and common tasks like chat, structured data, tools, and binary input. It addresses the lack of official SDKs for major players and differences in APIs, providing a single proxy for handling different models. The library offers clients for different vendors implementing common interfaces for generating and embedding text, enabling easy interchangeability between models.
UniChat
UniChat is a pipeline tool for creating online and offline chat-bots in Unity. It leverages Unity.Sentis and text vector embedding technology to enable offline mode text content search based on vector databases. The tool includes a chain toolkit for embedding LLM and Agent in games, along with middleware components for Text to Speech, Speech to Text, and Sub-classifier functionalities. UniChat also offers a tool for invoking tools based on ReActAgent workflow, allowing users to create personalized chat scenarios and character cards. The tool provides a comprehensive solution for designing flexible conversations in games while maintaining developer's ideas.
For similar tasks

microchain
Microchain is a function calling-based LLM agents tool with no bloat. It allows users to define LLM and templates, use various functions like Sum and Product, and create LLM agents for specific tasks. The tool provides a simple and efficient way to interact with OpenAI models and create conversational agents for various applications.

promptflow
**Prompt flow** is a suite of development tools designed to streamline the end-to-end development cycle of LLM-based AI applications, from ideation, prototyping, testing, evaluation to production deployment and monitoring. It makes prompt engineering much easier and enables you to build LLM apps with production quality.
unsloth
Unsloth is a tool that allows users to fine-tune large language models (LLMs) 2-5x faster with 80% less memory. It is a free and open-source tool that can be used to fine-tune LLMs such as Gemma, Mistral, Llama 2-5, TinyLlama, and CodeLlama 34b. Unsloth supports 4-bit and 16-bit QLoRA / LoRA fine-tuning via bitsandbytes. It also supports DPO (Direct Preference Optimization), PPO, and Reward Modelling. Unsloth is compatible with Hugging Face's TRL, Trainer, Seq2SeqTrainer, and Pytorch code. It is also compatible with NVIDIA GPUs since 2018+ (minimum CUDA Capability 7.0).
beyondllm
Beyond LLM offers an all-in-one toolkit for experimentation, evaluation, and deployment of Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems. It simplifies the process with automated integration, customizable evaluation metrics, and support for various Large Language Models (LLMs) tailored to specific needs. The aim is to reduce LLM hallucination risks and enhance reliability.
aiwechat-vercel
aiwechat-vercel is a tool that integrates AI capabilities into WeChat public accounts using Vercel functions. It requires minimal server setup, low entry barriers, and only needs a domain name that can be bound to Vercel, with almost zero cost. The tool supports various AI models, continuous Q&A sessions, chat functionality, system prompts, and custom commands. It aims to provide a platform for learning and experimentation with AI integration in WeChat public accounts.
hugging-chat-api
Unofficial HuggingChat Python API for creating chatbots, supporting features like image generation, web search, memorizing context, and changing LLMs. Users can log in, chat with the ChatBot, perform web searches, create new conversations, manage conversations, switch models, get conversation info, use assistants, and delete conversations. The API also includes a CLI mode with various commands for interacting with the tool. Users are advised not to use the application for high-stakes decisions or advice and to avoid high-frequency requests to preserve server resources.
embedchain
Embedchain is an Open Source Framework for personalizing LLM responses. It simplifies the creation and deployment of personalized AI applications by efficiently managing unstructured data, generating relevant embeddings, and storing them in a vector database. With diverse APIs, users can extract contextual information, find precise answers, and engage in interactive chat conversations tailored to their data. The framework follows the design principle of being 'Conventional but Configurable' to cater to both software engineers and machine learning engineers.
OpenAssistantGPT
OpenAssistantGPT is an open source platform for building chatbot assistants using OpenAI's Assistant. It offers features like easy website integration, low cost, and an open source codebase available on GitHub. Users can build their chatbot with minimal coding required, and OpenAssistantGPT supports direct billing through OpenAI without extra charges. The platform is user-friendly and cost-effective, appealing to those seeking to integrate AI chatbot functionalities into their websites.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.