LLM-Microscope
None
Stars: 70
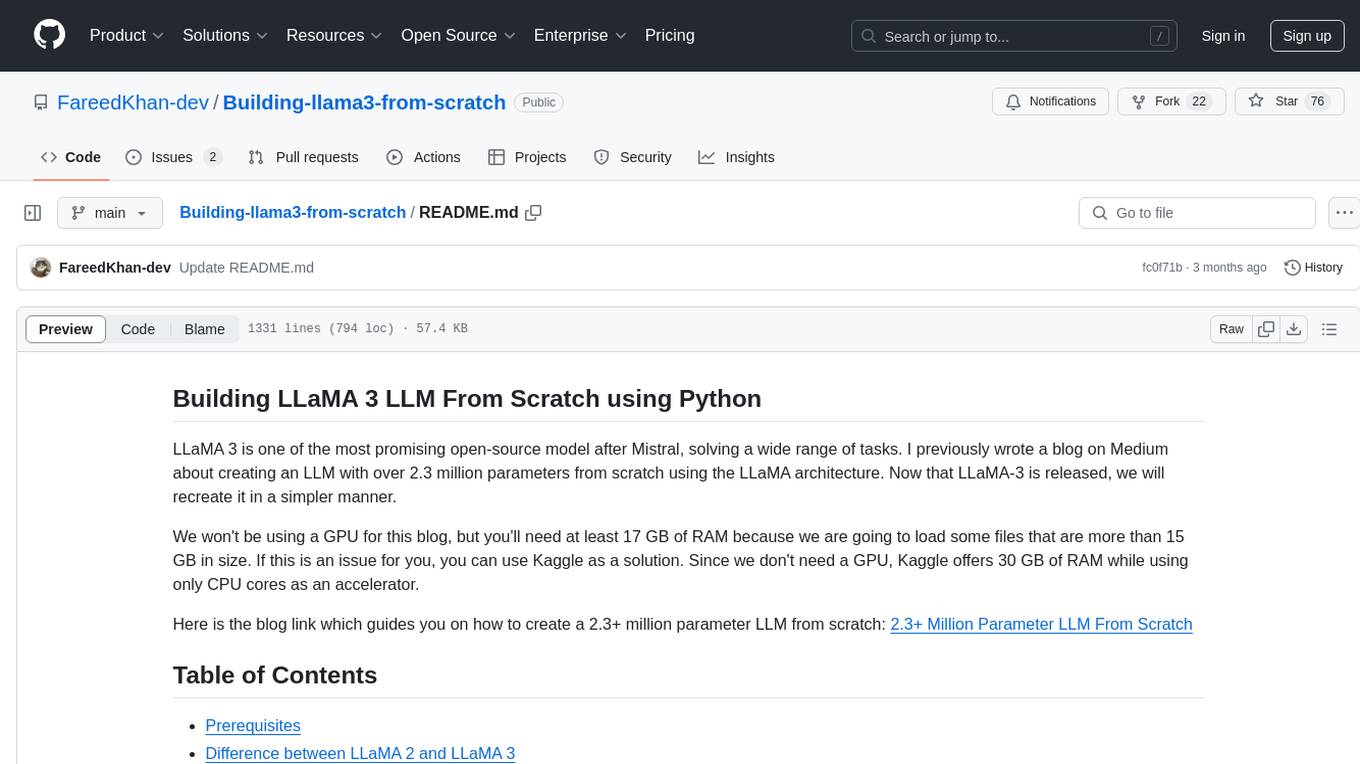
LLM-Microscope is a toolkit designed for quantifying and visualizing language model internals. It provides functions for calculating anisotropy, intrinsic dimension, and linearity score. The toolkit also includes a Logit Lens feature for analyzing model predictions and losses. Users can easily install the toolkit using pip and explore the functionalities through provided examples.
README:
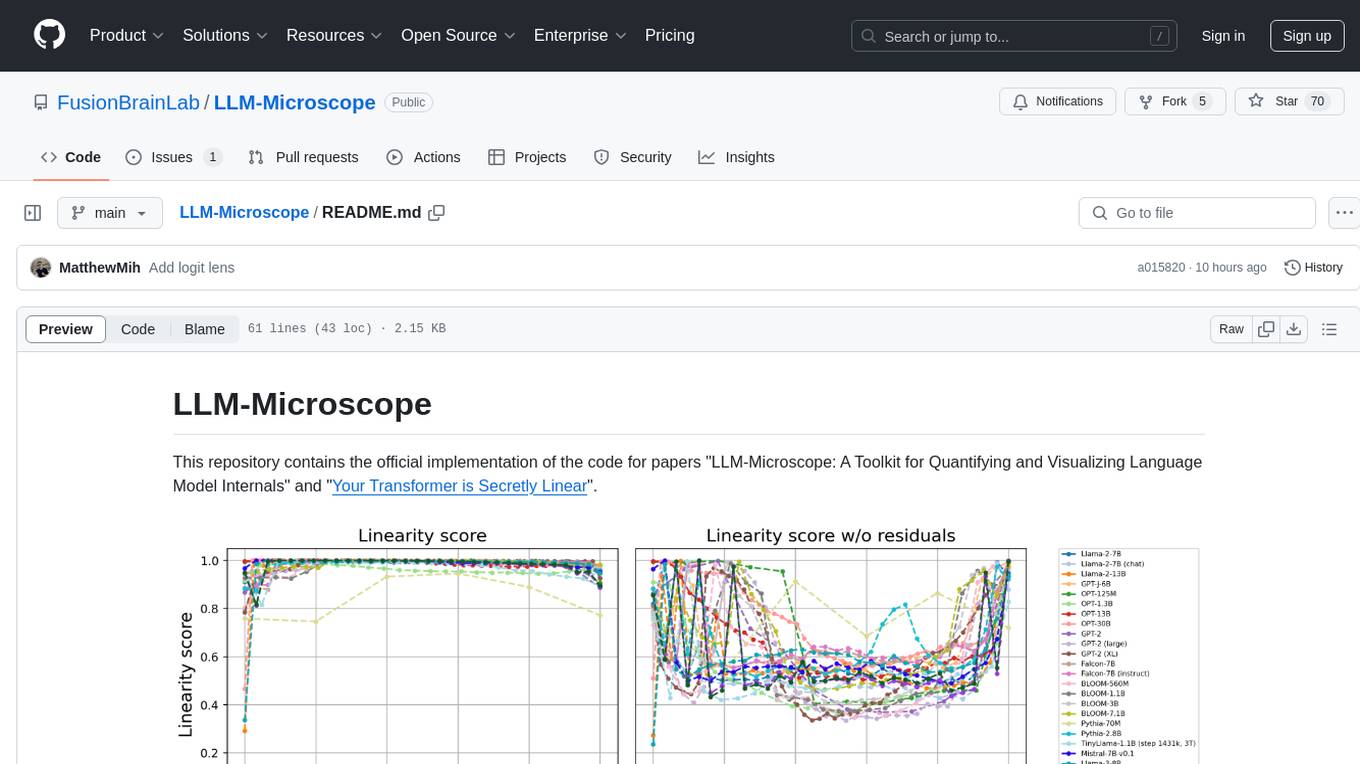
This repository contains the official implementation of the code for papers "LLM-Microscope: A Toolkit for Quantifying and Visualizing Language Model Internals" and "Your Transformer is Secretly Linear".
We've also created a pip package containing the functions from demo notebook.
Use pip install llm-microscope to install it.
import torch
from llm_microscope import (
calculate_anisotropy_torch,
intrinsic_dimension,
procrustes_similarity,
procrustes_similarity_centered,
load_enwiki_text
)
device = 'cpu'
X = torch.randn((1000, 10)) # pseudo-random "features", 1000 vectors with dim=10.
Y = torch.randn((1000, 10)) # pseudo-random "features", 1000 vectors with dim=10.
anisotropy = calculate_anisotropy_torch(X) # anisotropy score
int_dim = intrinsic_dimension(X, device) # intrinsic dimension
linearity_score = procrustes_similarity(X, Y) # linearity score from the paper
centered_linearity_score = procrustes_similarity_centered(X, Y) # the same as linearity between X and Y - X
# You can also download the dataset that we used in the paper using load_enwiki_text function:
text = llm_microscope.load_enwiki_text()import torch
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM
from llm_microscope import logit_lens, normalize_weights, plot_word_table, replace_bad_chars
device = 'cuda'
model_name = "facebook/opt-1.3b"
text = "Lorem Ipsum is simply dummy text of the printing"
tokenizer= AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_name, trust_remote_code=True).bfloat16().to(device)
tokens = tokenizer.encode(text)
words = [tokenizer.decode([tok]) for tok in tokens]
words = [replace_bad_chars(word) for word in words]
predictions, losses, decoded_words = logit_lens(model, tokenizer, text)
losses = normalize_weights(-losses, normalization_type="global")
plot_word_table(decoded_words, losses, words)For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for LLM-Microscope
Similar Open Source Tools

LLM-Microscope
LLM-Microscope is a toolkit designed for quantifying and visualizing language model internals. It provides functions for calculating anisotropy, intrinsic dimension, and linearity score. The toolkit also includes a Logit Lens feature for analyzing model predictions and losses. Users can easily install the toolkit using pip and explore the functionalities through provided examples.
LLM-Microscope
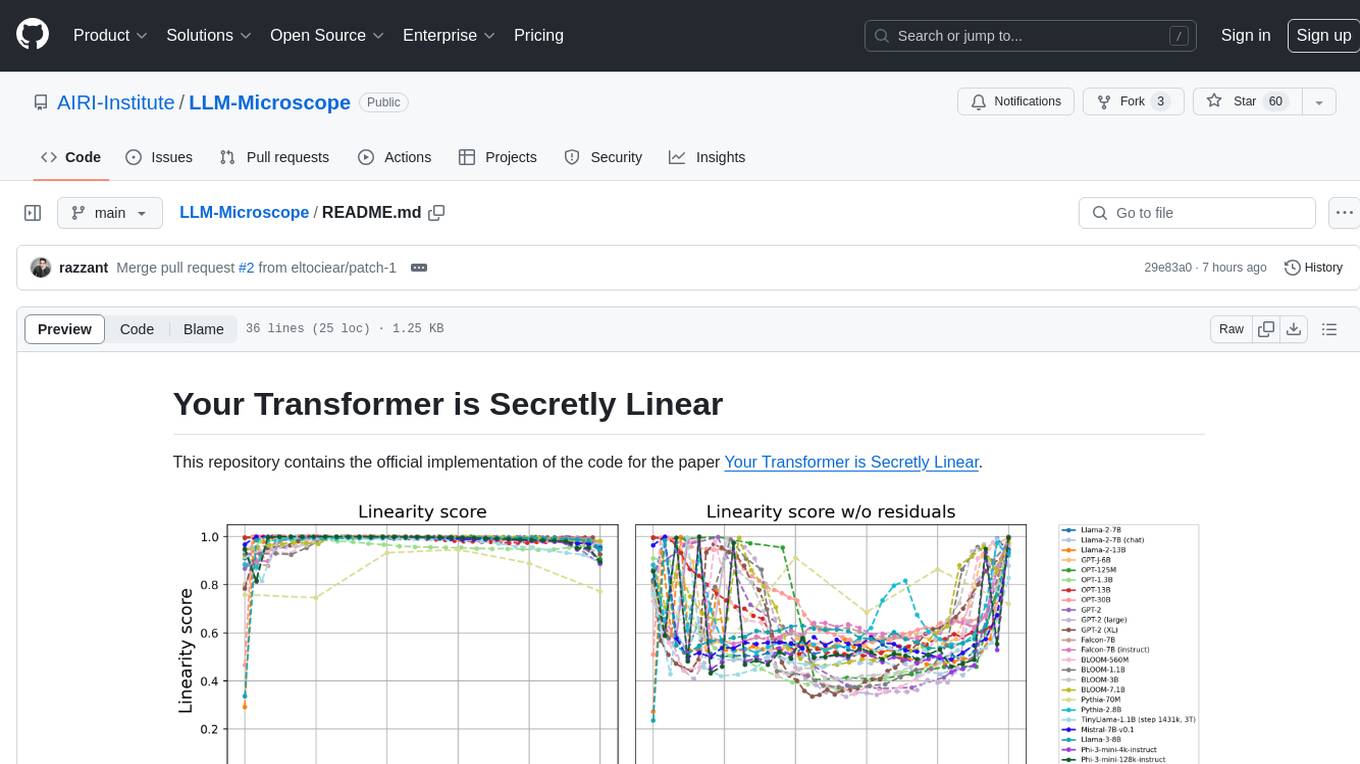
This repository contains the official implementation of the code for the paper 'Your Transformer is Secretly Linear'. It provides functions for calculating anisotropy score, intrinsic dimension, linearity score, and centered linearity score based on pseudo-random features. Additionally, a pip package is available for easy installation. Users can also download the dataset used in the paper for further analysis.
ragoon
RAGoon is a high-level library designed for batched embeddings generation, fast web-based RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) processing, and quantized indexes processing. It provides NLP utilities for multi-model embedding production, high-dimensional vector visualization, and enhancing language model performance through search-based querying, web scraping, and data augmentation techniques.
create-million-parameter-llm-from-scratch
The 'create-million-parameter-llm-from-scratch' repository provides a detailed guide on creating a Large Language Model (LLM) with 2.3 million parameters from scratch. The blog replicates the LLaMA approach, incorporating concepts like RMSNorm for pre-normalization, SwiGLU activation function, and Rotary Embeddings. The model is trained on a basic dataset to demonstrate the ease of creating a million-parameter LLM without the need for a high-end GPU.

zeta
Zeta is a tool designed to build state-of-the-art AI models faster by providing modular, high-performance, and scalable building blocks. It addresses the common issues faced while working with neural nets, such as chaotic codebases, lack of modularity, and low performance modules. Zeta emphasizes usability, modularity, and performance, and is currently used in hundreds of models across various GitHub repositories. It enables users to prototype, train, optimize, and deploy the latest SOTA neural nets into production. The tool offers various modules like FlashAttention, SwiGLUStacked, RelativePositionBias, FeedForward, BitLinear, PalmE, Unet, VisionEmbeddings, niva, FusedDenseGELUDense, FusedDropoutLayerNorm, MambaBlock, Film, hyper_optimize, DPO, and ZetaCloud for different tasks in AI model development.
ChatRex
ChatRex is a Multimodal Large Language Model (MLLM) designed to seamlessly integrate fine-grained object perception and robust language understanding. By adopting a decoupled architecture with a retrieval-based approach for object detection and leveraging high-resolution visual inputs, ChatRex addresses key challenges in perception tasks. It is powered by the Rexverse-2M dataset with diverse image-region-text annotations. ChatRex can be applied to various scenarios requiring fine-grained perception, such as object detection, grounded conversation, grounded image captioning, and region understanding.
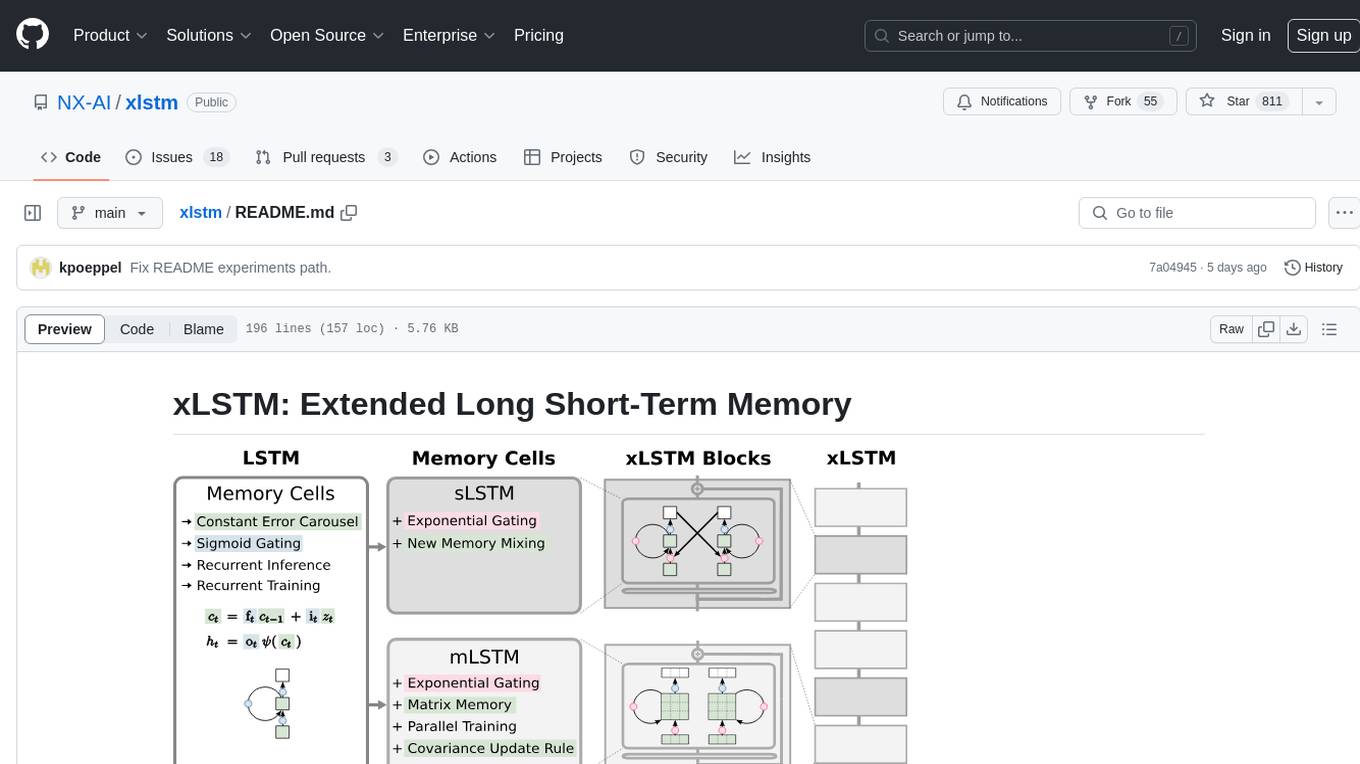
xlstm
xLSTM is a new Recurrent Neural Network architecture based on ideas of the original LSTM. Through Exponential Gating with appropriate normalization and stabilization techniques and a new Matrix Memory it overcomes the limitations of the original LSTM and shows promising performance on Language Modeling when compared to Transformers or State Space Models. The package is based on PyTorch and was tested for versions >=1.8. For the CUDA version of xLSTM, you need Compute Capability >= 8.0. The xLSTM tool provides two main components: xLSTMBlockStack for non-language applications or integrating in other architectures, and xLSTMLMModel for language modeling or other token-based applications.
continuous-eval
Open-Source Evaluation for LLM Applications. `continuous-eval` is an open-source package created for granular and holistic evaluation of GenAI application pipelines. It offers modularized evaluation, a comprehensive metric library covering various LLM use cases, the ability to leverage user feedback in evaluation, and synthetic dataset generation for testing pipelines. Users can define their own metrics by extending the Metric class. The tool allows running evaluation on a pipeline defined with modules and corresponding metrics. Additionally, it provides synthetic data generation capabilities to create user interaction data for evaluation or training purposes.
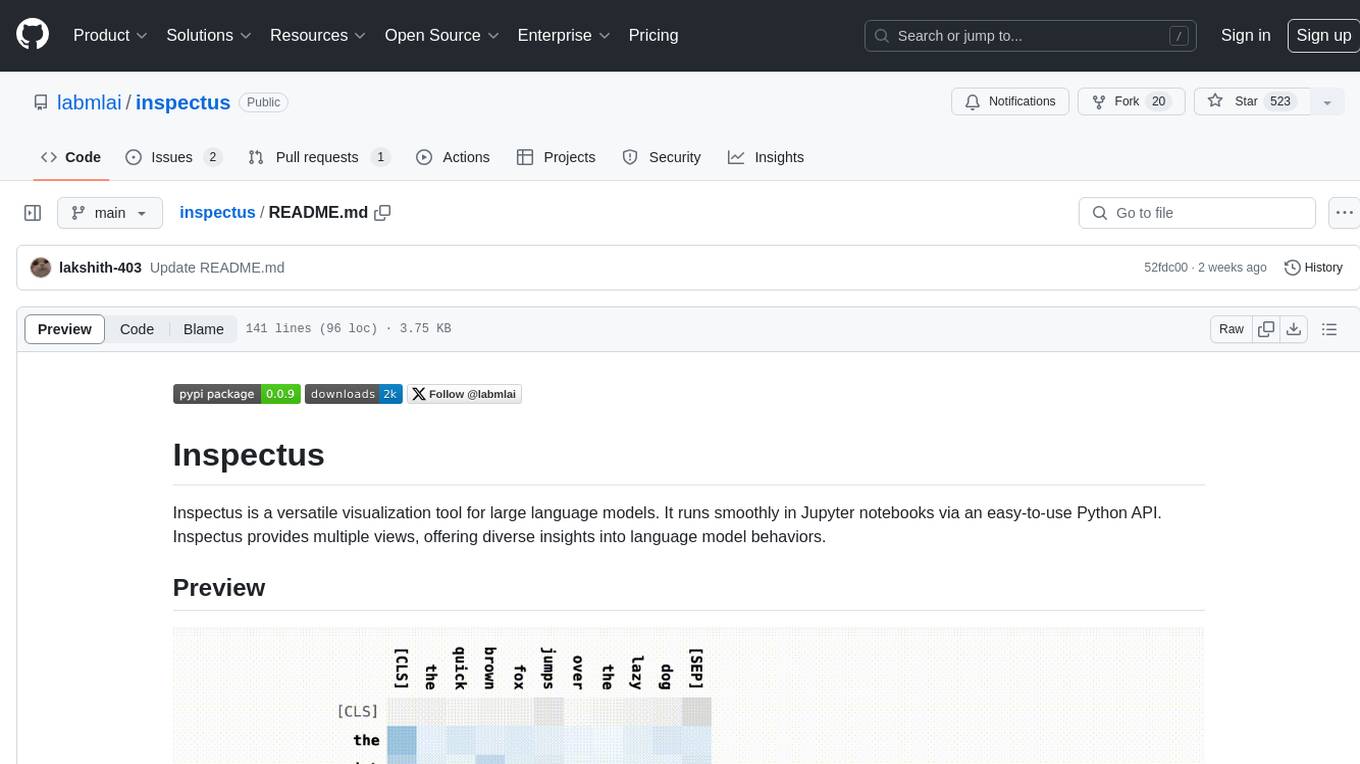
inspectus
Inspectus is a versatile visualization tool for large language models. It provides multiple views, including Attention Matrix, Query Token Heatmap, Key Token Heatmap, and Dimension Heatmap, to offer insights into language model behaviors. Users can interact with the tool in Jupyter notebooks through an easy-to-use Python API. Inspectus allows users to visualize attention scores between tokens, analyze how tokens focus on each other during processing, and explore the relationships between query and key tokens. The tool supports the visualization of attention maps from Huggingface transformers and custom attention maps, making it a valuable resource for researchers and developers working with language models.

LightRAG
LightRAG is a PyTorch library designed for building and optimizing Retriever-Agent-Generator (RAG) pipelines. It follows principles of simplicity, quality, and optimization, offering developers maximum customizability with minimal abstraction. The library includes components for model interaction, output parsing, and structured data generation. LightRAG facilitates tasks like providing explanations and examples for concepts through a question-answering pipeline.
Phi-3-Vision-MLX
Phi-3-MLX is a versatile AI framework that leverages both the Phi-3-Vision multimodal model and the Phi-3-Mini-128K language model optimized for Apple Silicon using the MLX framework. It provides an easy-to-use interface for a wide range of AI tasks, from advanced text generation to visual question answering and code execution. The project features support for batched generation, flexible agent system, custom toolchains, model quantization, LoRA fine-tuning capabilities, and API integration for extended functionality.

EasySteer
EasySteer is a unified framework built on vLLM for high-performance LLM steering. It offers fast, flexible, and easy-to-use steering capabilities with features like high performance, modular design, fine-grained control, pre-computed steering vectors, and an interactive demo. Users can interactively configure models, adjust steering parameters, and test interventions without writing code. The tool supports OpenAI-compatible APIs and provides modules for hidden states extraction, analysis-based steering, learning-based steering, and a frontend web interface for interactive steering and ReFT interventions.
WordLlama
WordLlama is a fast, lightweight NLP toolkit optimized for CPU hardware. It recycles components from large language models to create efficient word representations. It offers features like Matryoshka Representations, low resource requirements, binarization, and numpy-only inference. The tool is suitable for tasks like semantic matching, fuzzy deduplication, ranking, and clustering, making it a good option for NLP-lite tasks and exploratory analysis.
Endia
Endia is a dynamic Array library for Scientific Computing, offering automatic differentiation of arbitrary order, complex number support, dual API with PyTorch-like imperative or JAX-like functional interface, and JIT Compilation for speeding up training and inference. It can handle complex valued functions, perform both forward and reverse-mode automatic differentiation, and has a builtin JIT compiler. Endia aims to advance AI & Scientific Computing by pushing boundaries with clear algorithms, providing high-performance open-source code that remains readable and pythonic, and prioritizing clarity and educational value over exhaustive features.
llm-baselines
LLM-baselines is a modular codebase to experiment with transformers, inspired from NanoGPT. It provides a quick and easy way to train and evaluate transformer models on a variety of datasets. The codebase is well-documented and easy to use, making it a great resource for researchers and practitioners alike.
For similar tasks
ExplainableAI.jl
ExplainableAI.jl is a Julia package that implements interpretability methods for black-box classifiers, focusing on local explanations and attribution maps in input space. The package requires models to be differentiable with Zygote.jl. It is similar to Captum and Zennit for PyTorch and iNNvestigate for Keras models. Users can analyze and visualize explanations for model predictions, with support for different XAI methods and customization. The package aims to provide transparency and insights into model decision-making processes, making it a valuable tool for understanding and validating machine learning models.

LLM-Microscope
LLM-Microscope is a toolkit designed for quantifying and visualizing language model internals. It provides functions for calculating anisotropy, intrinsic dimension, and linearity score. The toolkit also includes a Logit Lens feature for analyzing model predictions and losses. Users can easily install the toolkit using pip and explore the functionalities through provided examples.
dranet
Dranet is a Python library for analyzing and visualizing data from neural networks. It provides tools for interpreting model predictions, understanding feature importance, and evaluating model performance. With Dranet, users can gain insights into how neural networks make decisions and improve model transparency and interpretability.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.