
LLM-Microscope
None
Stars: 60
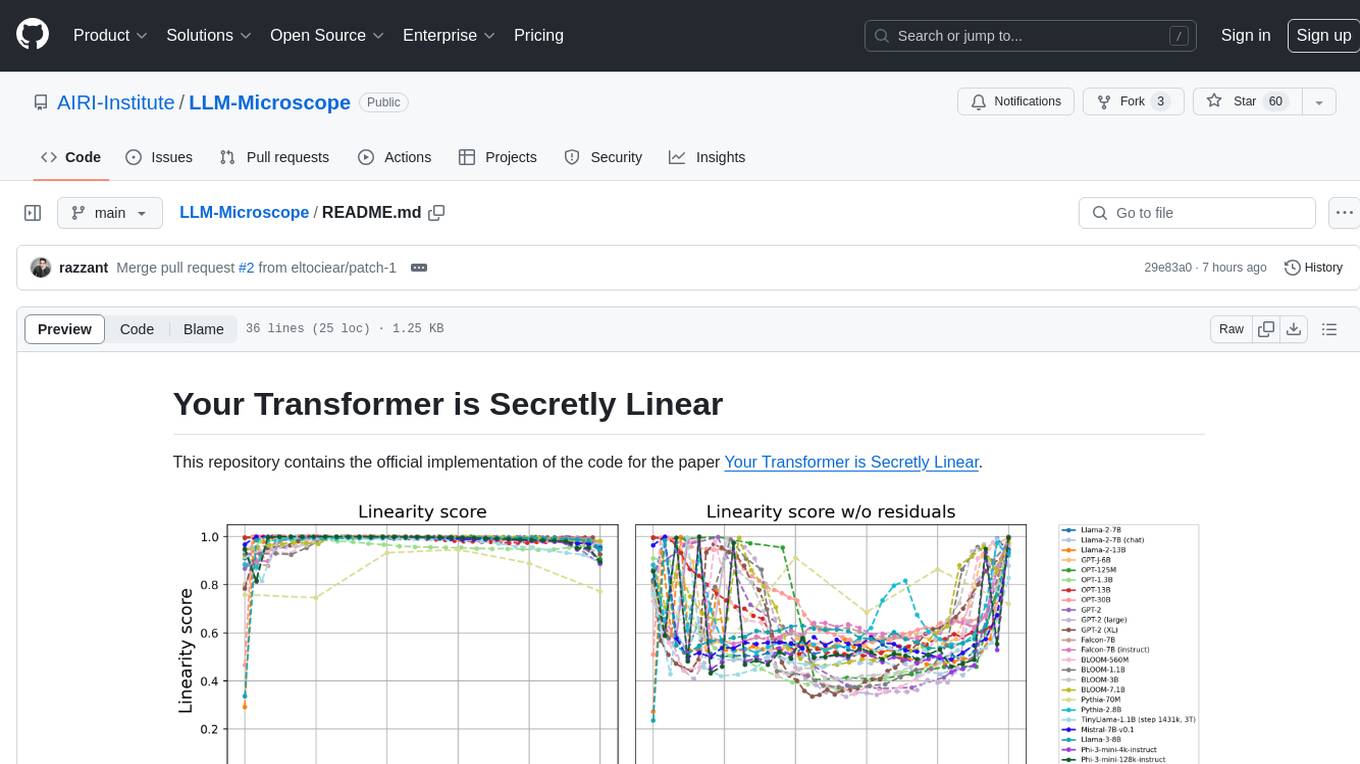
This repository contains the official implementation of the code for the paper 'Your Transformer is Secretly Linear'. It provides functions for calculating anisotropy score, intrinsic dimension, linearity score, and centered linearity score based on pseudo-random features. Additionally, a pip package is available for easy installation. Users can also download the dataset used in the paper for further analysis.
README:
This repository contains the official implementation of the code for the paper Your Transformer is Secretly Linear.
We've also created a pip package containing the functions from notebook.
Use pip install llm-microscope to install it.
import torch
from llm_microscope import (
calculate_anisotropy_torch,
intrinsic_dimension,
procrustes_similarity,
procrustes_similarity_centered,
load_enwiki_text
)
device = 'cpu'
X = torch.randn((1000, 10)) # pseudo-random "features", 1000 vectors with dim=10.
Y = torch.randn((1000, 10)) # pseudo-random "features", 1000 vectors with dim=10.
anisotropy = calculate_anisotropy_torch(X) # anisotropy score
int_dim = intrinsic_dimension(X, device) # intrinsic dimension
linearity_score = procrustes_similarity(X, Y) # linearity score from the paper
centered_linearity_score = procrustes_similarity_centered(X, Y) # the same as linearity between X and Y - X
# You can also download the dataset that we used in the paper using load_enwiki_text function:
text = llm_microscope.load_enwiki_text()For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for LLM-Microscope
Similar Open Source Tools

LLM-Microscope
This repository contains the official implementation of the code for the paper 'Your Transformer is Secretly Linear'. It provides functions for calculating anisotropy score, intrinsic dimension, linearity score, and centered linearity score based on pseudo-random features. Additionally, a pip package is available for easy installation. Users can also download the dataset used in the paper for further analysis.
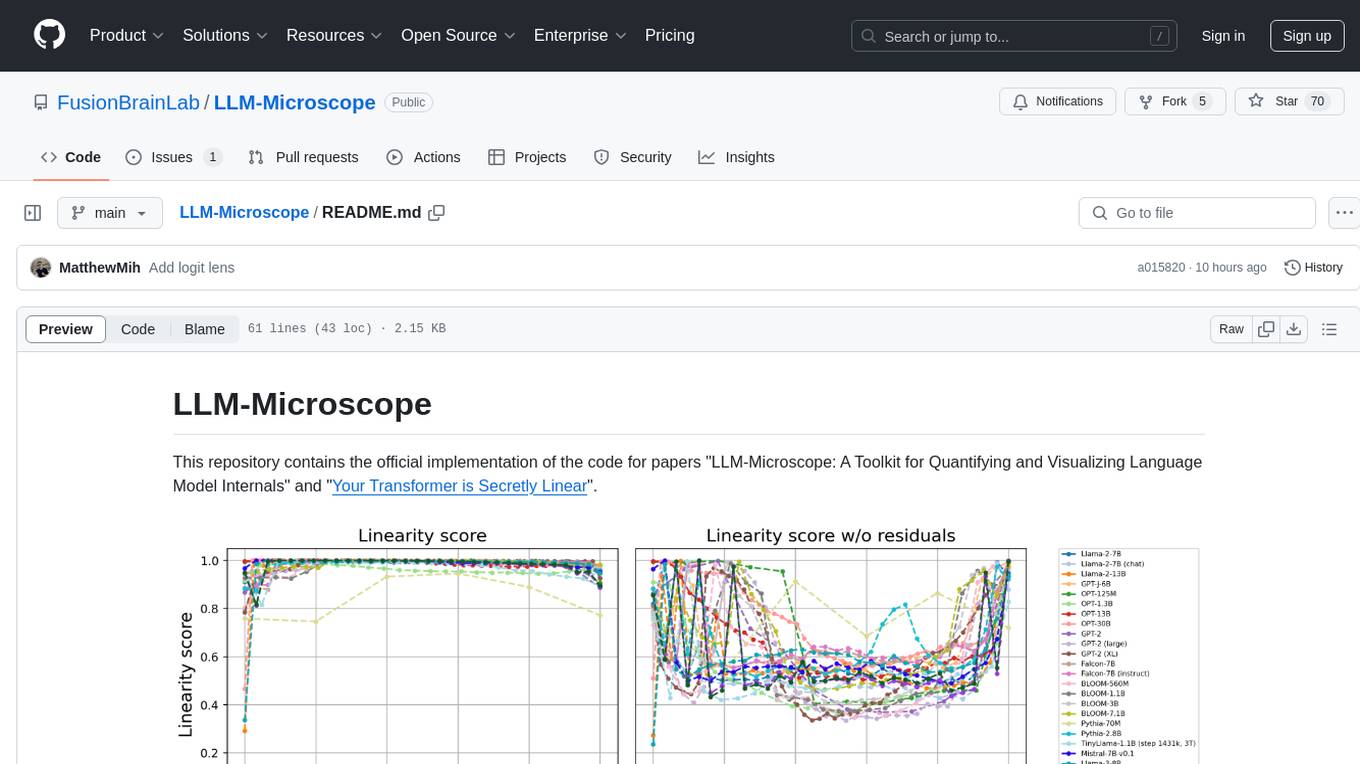
LLM-Microscope
LLM-Microscope is a toolkit designed for quantifying and visualizing language model internals. It provides functions for calculating anisotropy, intrinsic dimension, and linearity score. The toolkit also includes a Logit Lens feature for analyzing model predictions and losses. Users can easily install the toolkit using pip and explore the functionalities through provided examples.
Gemini
Gemini is an open-source model designed to handle multiple modalities such as text, audio, images, and videos. It utilizes a transformer architecture with special decoders for text and image generation. The model processes input sequences by transforming them into tokens and then decoding them to generate image outputs. Gemini differs from other models by directly feeding image embeddings into the transformer instead of using a visual transformer encoder. The model also includes a component called Codi for conditional generation. Gemini aims to effectively integrate image, audio, and video embeddings to enhance its performance.
create-million-parameter-llm-from-scratch
The 'create-million-parameter-llm-from-scratch' repository provides a detailed guide on creating a Large Language Model (LLM) with 2.3 million parameters from scratch. The blog replicates the LLaMA approach, incorporating concepts like RMSNorm for pre-normalization, SwiGLU activation function, and Rotary Embeddings. The model is trained on a basic dataset to demonstrate the ease of creating a million-parameter LLM without the need for a high-end GPU.
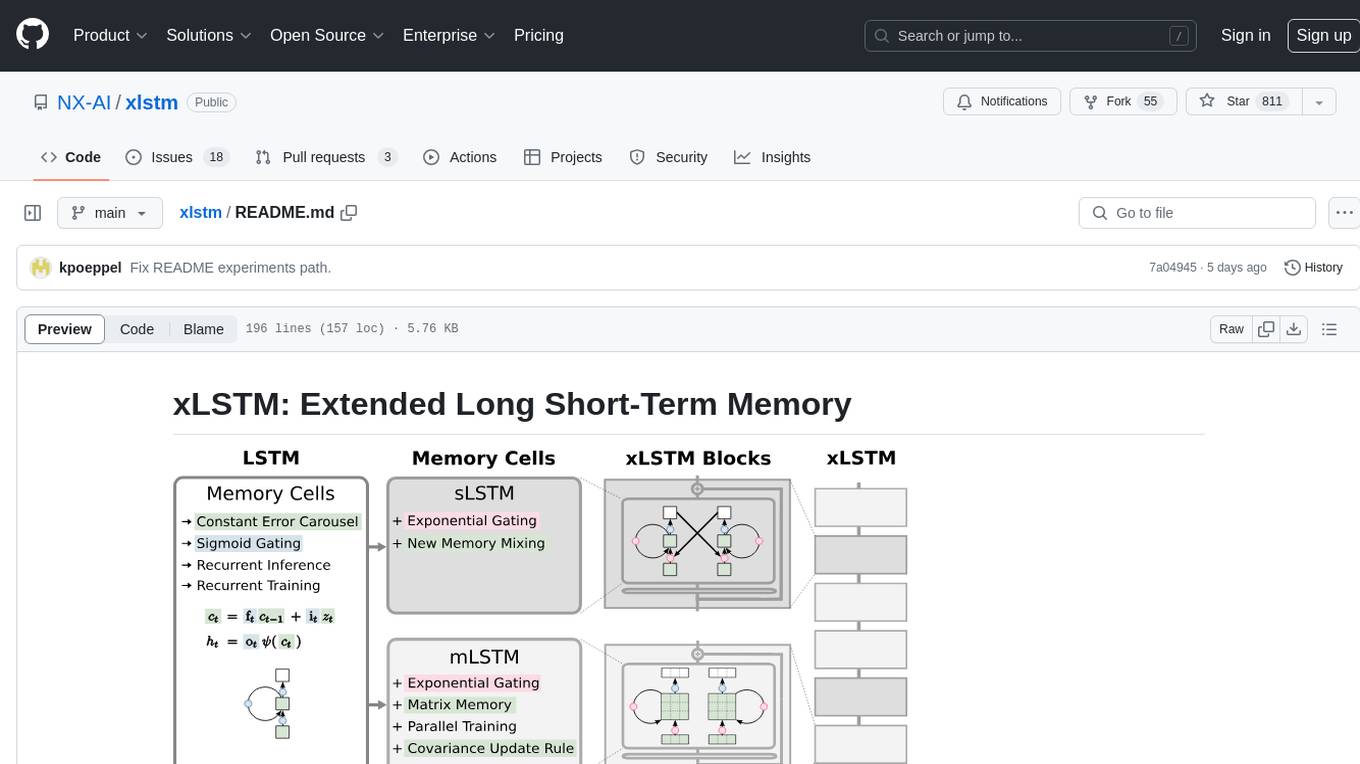
xlstm
xLSTM is a new Recurrent Neural Network architecture based on ideas of the original LSTM. Through Exponential Gating with appropriate normalization and stabilization techniques and a new Matrix Memory it overcomes the limitations of the original LSTM and shows promising performance on Language Modeling when compared to Transformers or State Space Models. The package is based on PyTorch and was tested for versions >=1.8. For the CUDA version of xLSTM, you need Compute Capability >= 8.0. The xLSTM tool provides two main components: xLSTMBlockStack for non-language applications or integrating in other architectures, and xLSTMLMModel for language modeling or other token-based applications.
Trinity
Trinity is an Explainable AI (XAI) Analysis and Visualization tool designed for Deep Learning systems or other models performing complex classification or decoding. It provides performance analysis through interactive 3D projections that are hyper-dimensional aware, allowing users to explore hyperspace, hypersurface, projections, and manifolds. Trinity primarily works with JSON data formats and supports the visualization of FeatureVector objects. Users can analyze and visualize data points, correlate inputs with classification results, and create custom color maps for better data interpretation. Trinity has been successfully applied to various use cases including Deep Learning Object detection models, COVID gene/tissue classification, Brain Computer Interface decoders, and Large Language Model (ChatGPT) Embeddings Analysis.
llm-analysis
llm-analysis is a tool designed for Latency and Memory Analysis of Transformer Models for Training and Inference. It automates the calculation of training or inference latency and memory usage for Large Language Models (LLMs) or Transformers based on specified model, GPU, data type, and parallelism configurations. The tool helps users to experiment with different setups theoretically, understand system performance, and optimize training/inference scenarios. It supports various parallelism schemes, communication methods, activation recomputation options, data types, and fine-tuning strategies. Users can integrate llm-analysis in their code using the `LLMAnalysis` class or use the provided entry point functions for command line interface. The tool provides lower-bound estimations of memory usage and latency, and aims to assist in achieving feasible and optimal setups for training or inference.
forust
Forust is a lightweight package for building gradient boosted decision tree ensembles. The algorithm code is written in Rust with a Python wrapper. It implements the same algorithm as XGBoost and provides nearly identical results. The package was developed to better understand XGBoost, as a fun project in Rust, and to experiment with adding new features to the algorithm in a simpler codebase. Forust allows training gradient boosted decision tree ensembles with multiple objective functions, predicting on datasets, inspecting model structures, calculating feature importance, and saving/loading trained boosters.
Quantus
Quantus is a toolkit designed for the evaluation of neural network explanations. It offers more than 30 metrics in 6 categories for eXplainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) evaluation. The toolkit supports different data types (image, time-series, tabular, NLP) and models (PyTorch, TensorFlow). It provides built-in support for explanation methods like captum, tf-explain, and zennit. Quantus is under active development and aims to provide a comprehensive set of quantitative evaluation metrics for XAI methods.
AIMNet2
AIMNet2 Calculator is a package that integrates the AIMNet2 neural network potential into simulation workflows, providing fast and reliable energy, force, and property calculations for molecules with diverse elements. It excels at modeling various systems, offers flexible interfaces for popular simulation packages, and supports long-range interactions using DSF or Ewald summation Coulomb models. The tool is designed for accurate and versatile molecular simulations, suitable for large molecules and periodic calculations.
probsem
ProbSem is a repository that provides a framework to leverage large language models (LLMs) for assigning context-conditional probability distributions over queried strings. It supports OpenAI engines and HuggingFace CausalLM models, and is flexible for research applications in linguistics, cognitive science, program synthesis, and NLP. Users can define prompts, contexts, and queries to derive probability distributions over possible completions, enabling tasks like cloze completion, multiple-choice QA, semantic parsing, and code completion. The repository offers CLI and API interfaces for evaluation, with options to customize models, normalize scores, and adjust temperature for probability distributions.
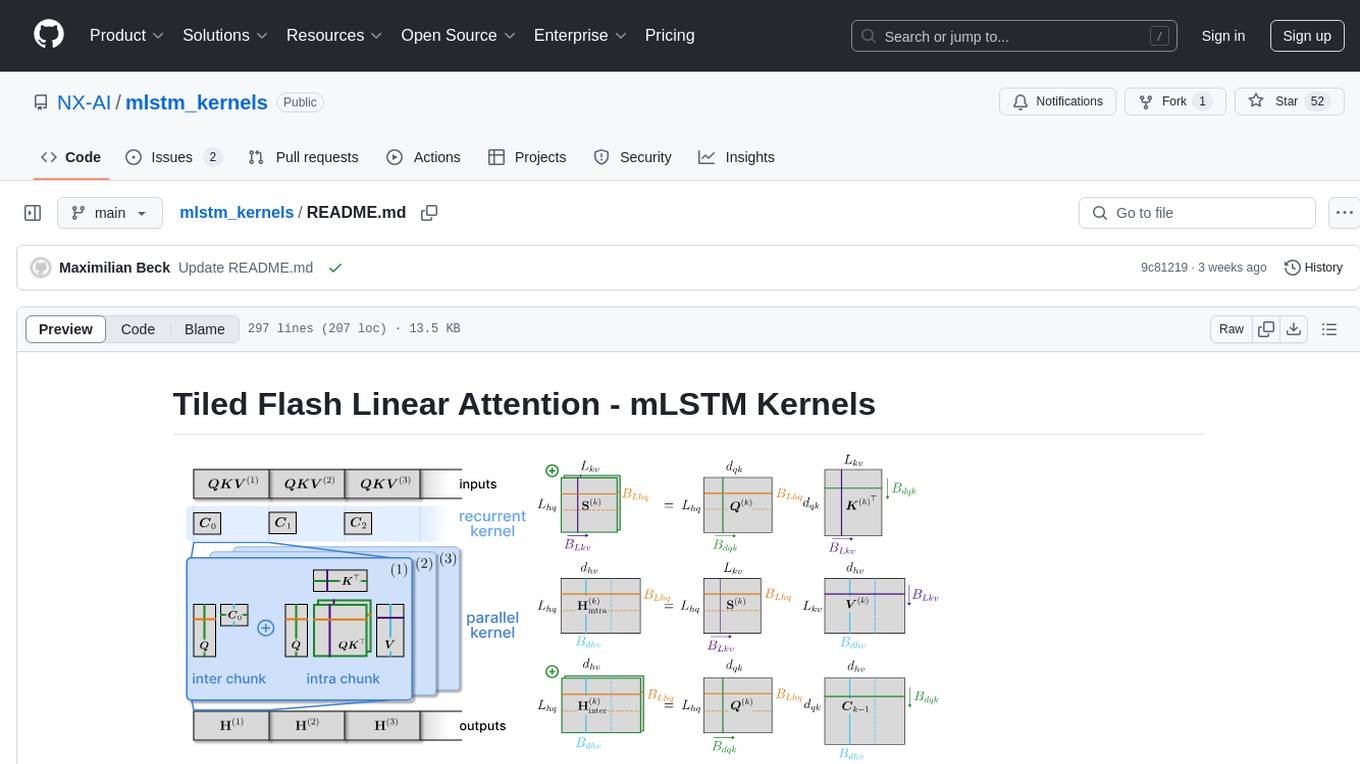
mlstm_kernels
This repository provides fast and efficient mLSTM training and inference Triton kernels built on Tiled Flash Linear Attention (TFLA). It includes implementations in JAX, PyTorch, and Triton, with chunkwise, parallel, and recurrent kernels for mLSTM. The repository also contains a benchmark library for runtime benchmarks and full mLSTM Huggingface models.
RTL-Coder
RTL-Coder is a tool designed to outperform GPT-3.5 in RTL code generation by providing a fully open-source dataset and a lightweight solution. It targets Verilog code generation and offers an automated flow to generate a large labeled dataset with over 27,000 diverse Verilog design problems and answers. The tool addresses the data availability challenge in IC design-related tasks and can be used for various applications beyond LLMs. The tool includes four RTL code generation models available on the HuggingFace platform, each with specific features and performance characteristics. Additionally, RTL-Coder introduces a new LLM training scheme based on code quality feedback to further enhance model performance and reduce GPU memory consumption.
kvpress
This repository implements multiple key-value cache pruning methods and benchmarks using transformers, aiming to simplify the development of new methods for researchers and developers in the field of long-context language models. It provides a set of 'presses' that compress the cache during the pre-filling phase, with each press having a compression ratio attribute. The repository includes various training-free presses, special presses, and supports KV cache quantization. Users can contribute new presses and evaluate the performance of different presses on long-context datasets.
topicGPT
TopicGPT is a repository containing scripts and prompts for the paper 'TopicGPT: Topic Modeling by Prompting Large Language Models' (NAACL'24). The 'topicgpt_python' package offers functions to generate high-level and specific topics, refine topics, assign topics to input text, and correct generated topics. It supports various APIs like OpenAI, VertexAI, Azure, Gemini, and vLLM for inference. Users can prepare data in JSONL format, run the pipeline using provided scripts, and evaluate topic alignment with ground-truth labels.
gepa
GEPA (Genetic-Pareto) is a framework for optimizing arbitrary systems composed of text components like AI prompts, code snippets, or textual specs against any evaluation metric. It employs LLMs to reflect on system behavior, using feedback from execution and evaluation traces to drive targeted improvements. Through iterative mutation, reflection, and Pareto-aware candidate selection, GEPA evolves robust, high-performing variants with minimal evaluations, co-evolving multiple components in modular systems for domain-specific gains. The repository provides the official implementation of the GEPA algorithm as proposed in the paper titled 'GEPA: Reflective Prompt Evolution Can Outperform Reinforcement Learning'.
For similar tasks

LLM-Microscope
This repository contains the official implementation of the code for the paper 'Your Transformer is Secretly Linear'. It provides functions for calculating anisotropy score, intrinsic dimension, linearity score, and centered linearity score based on pseudo-random features. Additionally, a pip package is available for easy installation. Users can also download the dataset used in the paper for further analysis.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.
