
pywhy-llm
Experimental library integrating LLM capabilities to support causal analyses
Stars: 60
PyWhy-LLM is an innovative library that integrates Large Language Models (LLMs) into the causal analysis process, empowering users with knowledge previously only available through domain experts. It seamlessly augments existing causal inference processes by suggesting potential confounders, relationships between variables, backdoor sets, front door sets, IV sets, estimands, critiques of DAGs, latent confounders, and negative controls. By leveraging LLMs and formalizing human-LLM collaboration, PyWhy-LLM aims to enhance causal analysis accessibility and insight.
README:
PyWhy-LLM is an innovative library designed to augment human expertise by seamlessly integrating Large Language Models (LLMs) into the causal analysis process. It empowers users with access to knowledge previously only available through domain experts. As part of the DoWhy community, we aim to investigate and harness the capabilities of LLMs for enhancing causal analysis process.
For detailed usage instructions and tutorials, refer to Notebook.
To install PyWhy-LLM, you can use pip:
pip install pywhy-llmPyWhy-LLM seamlessly integrates into your existing causal inference process. Import the necessary classes and start exploring the power of LLM-augmented causal analysis.
from pywhy-llm import ModelSuggester, IdentificationSuggester, ValidationSuggester# Create instance of Modeler
modeler = Modeler()
# Suggest a set of potential confounders
suggested_confounders = modeler.suggest_confounders(variables=_variables, treatment=treatment, outcome=outcome, llm=gpt4)
# Suggest pair-wise relationship between variables
suggested_dag = modeler.suggest_relationships(variables=selected_variables, llm=gpt4)
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 5))
nx.draw(suggested_dag, with_labels=True, node_color='lightblue')
plt.show()# Create instance of Identifier
identifier = Identifier()
# Suggest a backdoor set, front door set, and iv set
suggested_backdoor = identifier.suggest_backdoor(llm=gpt4, treatment=treatment, outcome=outcome, confounders=suggested_confounders)
suggested_frontdoor = identifier.suggest_frontdoor(llm=gpt4, treatment=treatment, outcome=outcome, confounders=suggested_confounders)
suggested_iv = identifier.suggest_iv(llm=gpt4, treatment=treatment, outcome=outcome, confounders=suggested_confounders)
# Suggest an estimand based on the suggester backdoor set, front door set, and iv set
estimand = identifier.suggest_estimand(confounders=suggested_confounders, treatment=treatment, outcome=outcome, backdoor=suggested_backdoor, frontdoor=suggested_frontdoor, iv=suggested_iv, llm=gpt4) # Create instance of Validator
validator = Validator()
# Suggest a critique of the provided DAG
suggested_critiques_dag = validator.critique_graph(graph=suggested_dag, llm=gpt4)
# Suggest latent confounders
suggested_latent_confounders = validator.suggest_latent_confounders(treatment=treatment, outcome=outcome, llm=gpt4)
# Suggest negative controls
suggested_negative_controls = validator.suggest_negative_controls(variables=selected_variables, treatment=treatment, outcome=outcome, llm=gpt4)
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 5))
nx.draw(suggested_critiques_dag, with_labels=True, node_color='lightblue')
plt.show()PyWhy-LLM is licensed under the MIT License. See the LICENSE file for more information.
For any questions, feedback, or inquiries, please reach out to Emre Kiciman and Rose De Sicilia.
By leveraging LLMs and formalizing human-LLM collaboration, PyWhy-LLM takes causal inference to new heights. Explore its potential and join us in making causal analysis more accessible and insightful.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for pywhy-llm
Similar Open Source Tools

pywhy-llm
PyWhy-LLM is an innovative library that integrates Large Language Models (LLMs) into the causal analysis process, empowering users with knowledge previously only available through domain experts. It seamlessly augments existing causal inference processes by suggesting potential confounders, relationships between variables, backdoor sets, front door sets, IV sets, estimands, critiques of DAGs, latent confounders, and negative controls. By leveraging LLMs and formalizing human-LLM collaboration, PyWhy-LLM aims to enhance causal analysis accessibility and insight.
pywhyllm
PyWhy-LLM is an innovative library that integrates Large Language Models (LLMs) into the causal analysis process, empowering users with knowledge previously only available through domain experts. It seamlessly augments causal inference by suggesting potential confounders, relationships between variables, backdoor/frontdoor/iv sets, estimands, critiques of DAGs, latent confounders, and negative controls. The tool aims to enhance the causal analysis process by leveraging the capabilities of LLMs.

zeta
Zeta is a tool designed to build state-of-the-art AI models faster by providing modular, high-performance, and scalable building blocks. It addresses the common issues faced while working with neural nets, such as chaotic codebases, lack of modularity, and low performance modules. Zeta emphasizes usability, modularity, and performance, and is currently used in hundreds of models across various GitHub repositories. It enables users to prototype, train, optimize, and deploy the latest SOTA neural nets into production. The tool offers various modules like FlashAttention, SwiGLUStacked, RelativePositionBias, FeedForward, BitLinear, PalmE, Unet, VisionEmbeddings, niva, FusedDenseGELUDense, FusedDropoutLayerNorm, MambaBlock, Film, hyper_optimize, DPO, and ZetaCloud for different tasks in AI model development.
beyondllm
Beyond LLM offers an all-in-one toolkit for experimentation, evaluation, and deployment of Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems. It simplifies the process with automated integration, customizable evaluation metrics, and support for various Large Language Models (LLMs) tailored to specific needs. The aim is to reduce LLM hallucination risks and enhance reliability.
create-million-parameter-llm-from-scratch
The 'create-million-parameter-llm-from-scratch' repository provides a detailed guide on creating a Large Language Model (LLM) with 2.3 million parameters from scratch. The blog replicates the LLaMA approach, incorporating concepts like RMSNorm for pre-normalization, SwiGLU activation function, and Rotary Embeddings. The model is trained on a basic dataset to demonstrate the ease of creating a million-parameter LLM without the need for a high-end GPU.
Arcade-Learning-Environment
The Arcade Learning Environment (ALE) is a simple framework that allows researchers and hobbyists to develop AI agents for Atari 2600 games. It is built on top of the Atari 2600 emulator Stella and separates the details of emulation from agent design. The ALE currently supports three different interfaces: C++, Python, and OpenAI Gym.
wandb
Weights & Biases (W&B) is a platform that helps users build better machine learning models faster by tracking and visualizing all components of the machine learning pipeline, from datasets to production models. It offers tools for tracking, debugging, evaluating, and monitoring machine learning applications. W&B provides integrations with popular frameworks like PyTorch, TensorFlow/Keras, Hugging Face Transformers, PyTorch Lightning, XGBoost, and Sci-Kit Learn. Users can easily log metrics, visualize performance, and compare experiments using W&B. The platform also supports hosting options in the cloud or on private infrastructure, making it versatile for various deployment needs.
gem
GEM is an open-source General Experience Maker designed for training Large Language Models (LLMs) in dynamic environments. Similar to OpenAI Gym for traditional Reinforcement Learning, GEM provides a variety of environments with standardized interfaces for seamless integration with existing LLM training frameworks. It offers tool integration, flexible wrappers, async vectorized environment execution, multi-environment training, and more to simplify LLM agent training.
MotionLLM
MotionLLM is a framework for human behavior understanding that leverages Large Language Models (LLMs) to jointly model videos and motion sequences. It provides a unified training strategy, dataset MoVid, and MoVid-Bench for evaluating human behavior comprehension. The framework excels in captioning, spatial-temporal comprehension, and reasoning abilities.
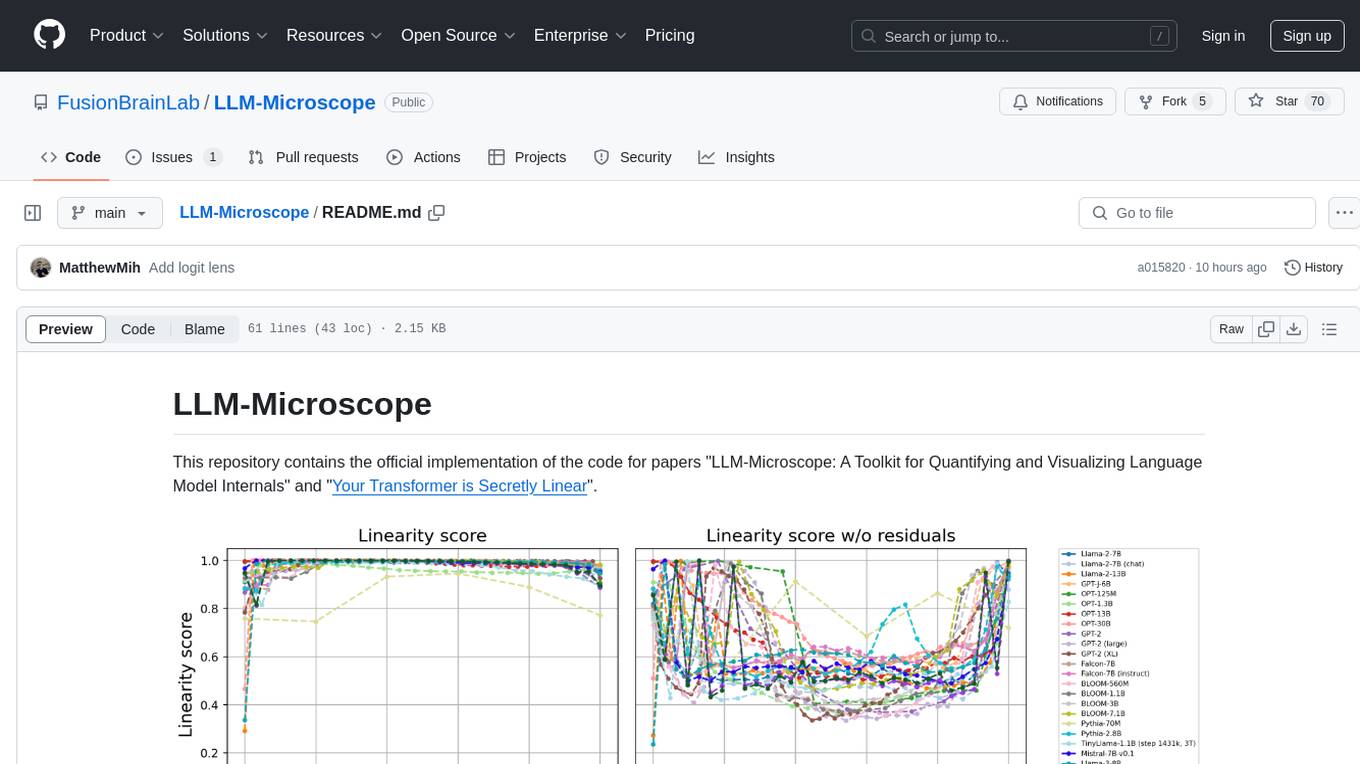
LLM-Microscope
LLM-Microscope is a toolkit designed for quantifying and visualizing language model internals. It provides functions for calculating anisotropy, intrinsic dimension, and linearity score. The toolkit also includes a Logit Lens feature for analyzing model predictions and losses. Users can easily install the toolkit using pip and explore the functionalities through provided examples.
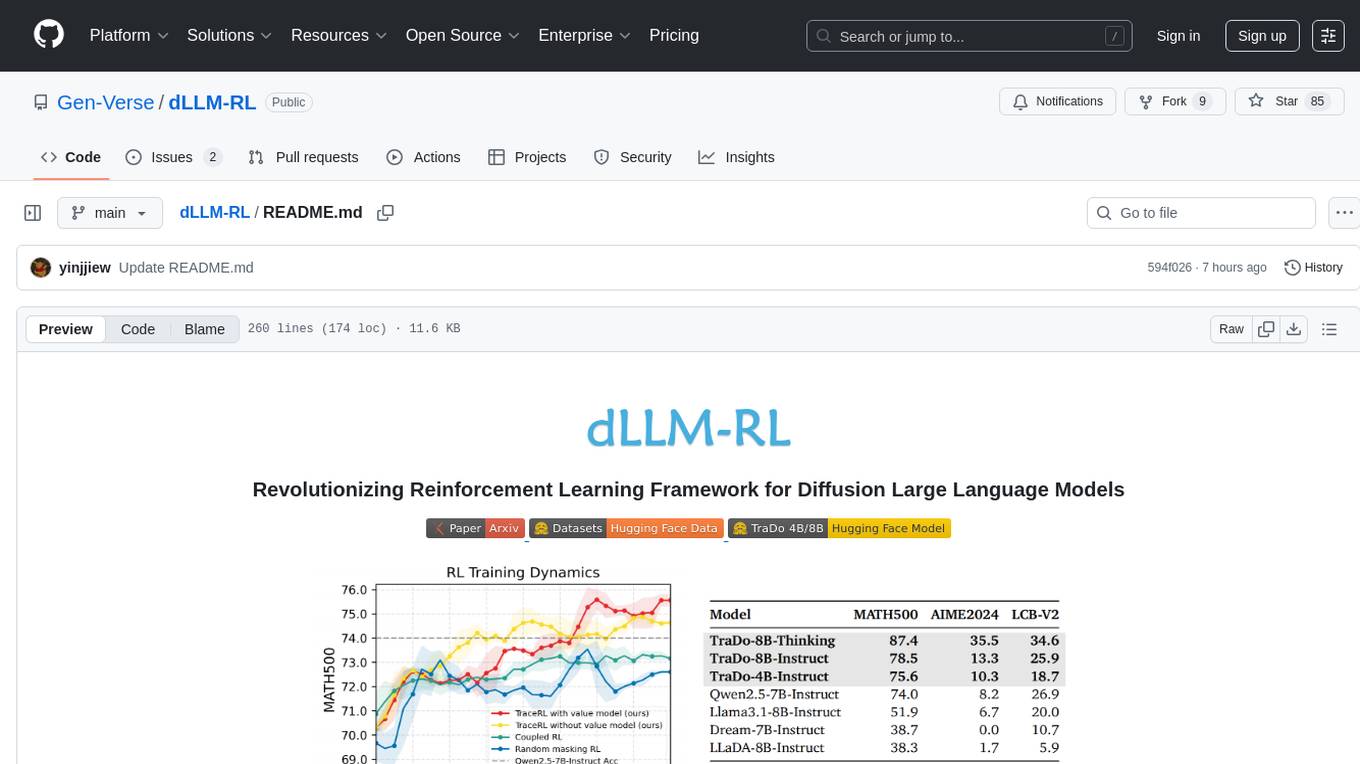
dLLM-RL
dLLM-RL is a revolutionary reinforcement learning framework designed for Diffusion Large Language Models. It supports various models with diverse structures, offers inference acceleration, RL training capabilities, and SFT functionalities. The tool introduces TraceRL for trajectory-aware RL and diffusion-based value models for optimization stability. Users can download and try models like TraDo-4B-Instruct and TraDo-8B-Instruct. The tool also provides support for multi-node setups and easy building of reinforcement learning methods. Additionally, it offers supervised fine-tuning strategies for different models and tasks.
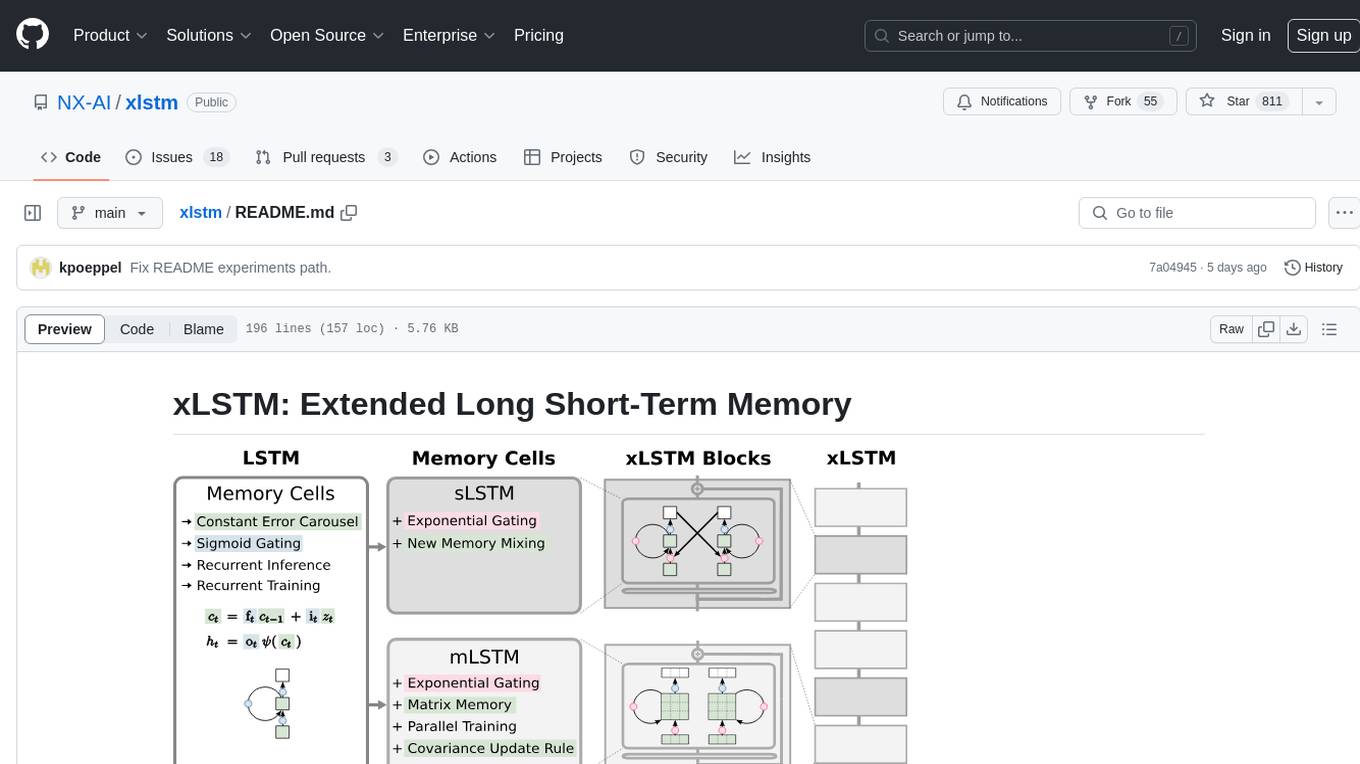
xlstm
xLSTM is a new Recurrent Neural Network architecture based on ideas of the original LSTM. Through Exponential Gating with appropriate normalization and stabilization techniques and a new Matrix Memory it overcomes the limitations of the original LSTM and shows promising performance on Language Modeling when compared to Transformers or State Space Models. The package is based on PyTorch and was tested for versions >=1.8. For the CUDA version of xLSTM, you need Compute Capability >= 8.0. The xLSTM tool provides two main components: xLSTMBlockStack for non-language applications or integrating in other architectures, and xLSTMLMModel for language modeling or other token-based applications.
ragoon
RAGoon is a high-level library designed for batched embeddings generation, fast web-based RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) processing, and quantized indexes processing. It provides NLP utilities for multi-model embedding production, high-dimensional vector visualization, and enhancing language model performance through search-based querying, web scraping, and data augmentation techniques.

langfair
LangFair is a Python library for bias and fairness assessments of large language models (LLMs). It offers a comprehensive framework for choosing bias and fairness metrics, demo notebooks, and a technical playbook. Users can tailor evaluations to their use cases with a Bring Your Own Prompts approach. The focus is on output-based metrics practical for governance audits and real-world testing.
openagi
OpenAGI is a framework designed to make the development of autonomous human-like agents accessible to all. It aims to pave the way towards open agents and eventually AGI for everyone. The initiative strongly believes in the transformative power of AI and offers developers a platform to create autonomous human-like agents. OpenAGI features a flexible agent architecture, streamlined integration and configuration processes, and automated/manual agent configuration generation. It can be used in education for personalized learning experiences, in finance and banking for fraud detection and personalized banking advice, and in healthcare for patient monitoring and disease diagnosis.
next-token-prediction
Next-Token Prediction is a language model tool that allows users to create high-quality predictions for the next word, phrase, or pixel based on a body of text. It can be used as an alternative to well-known decoder-only models like GPT and Mistral. The tool provides options for simple usage with built-in data bootstrap or advanced customization by providing training data or creating it from .txt files. It aims to simplify methodologies, provide autocomplete, autocorrect, spell checking, search/lookup functionalities, and create pixel and audio transformers for various prediction formats.
For similar tasks

pywhy-llm
PyWhy-LLM is an innovative library that integrates Large Language Models (LLMs) into the causal analysis process, empowering users with knowledge previously only available through domain experts. It seamlessly augments existing causal inference processes by suggesting potential confounders, relationships between variables, backdoor sets, front door sets, IV sets, estimands, critiques of DAGs, latent confounders, and negative controls. By leveraging LLMs and formalizing human-LLM collaboration, PyWhy-LLM aims to enhance causal analysis accessibility and insight.

OneKE
OneKE is a flexible dockerized system for schema-guided knowledge extraction, capable of extracting information from the web and raw PDF books across multiple domains like science and news. It employs a collaborative multi-agent approach and includes a user-customizable knowledge base to enable tailored extraction. OneKE offers various IE tasks support, data sources support, LLMs support, extraction method support, and knowledge base configuration. Users can start with examples using YAML, Python, or Web UI, and perform tasks like Named Entity Recognition, Relation Extraction, Event Extraction, Triple Extraction, and Open Domain IE. The tool supports different source formats like Plain Text, HTML, PDF, Word, TXT, and JSON files. Users can choose from various extraction models like OpenAI, DeepSeek, LLaMA, Qwen, ChatGLM, MiniCPM, and OneKE for information extraction tasks. Extraction methods include Schema Agent, Extraction Agent, and Reflection Agent. The tool also provides support for schema repository and case repository management, along with solutions for network issues. Contributors to the project include Ningyu Zhang, Haofen Wang, Yujie Luo, Xiangyuan Ru, Kangwei Liu, Lin Yuan, Mengshu Sun, Lei Liang, Zhiqiang Zhang, Jun Zhou, Lanning Wei, Da Zheng, and Huajun Chen.

pywhyllm
PyWhy-LLM is an innovative library that integrates Large Language Models (LLMs) into the causal analysis process, empowering users with knowledge previously only available through domain experts. It seamlessly augments causal inference by suggesting potential confounders, relationships between variables, backdoor/frontdoor/iv sets, estimands, critiques of DAGs, latent confounders, and negative controls. The tool aims to enhance the causal analysis process by leveraging the capabilities of LLMs.
For similar jobs

pywhy-llm
PyWhy-LLM is an innovative library that integrates Large Language Models (LLMs) into the causal analysis process, empowering users with knowledge previously only available through domain experts. It seamlessly augments existing causal inference processes by suggesting potential confounders, relationships between variables, backdoor sets, front door sets, IV sets, estimands, critiques of DAGs, latent confounders, and negative controls. By leveraging LLMs and formalizing human-LLM collaboration, PyWhy-LLM aims to enhance causal analysis accessibility and insight.

pywhyllm
PyWhy-LLM is an innovative library that integrates Large Language Models (LLMs) into the causal analysis process, empowering users with knowledge previously only available through domain experts. It seamlessly augments causal inference by suggesting potential confounders, relationships between variables, backdoor/frontdoor/iv sets, estimands, critiques of DAGs, latent confounders, and negative controls. The tool aims to enhance the causal analysis process by leveraging the capabilities of LLMs.

lollms-webui
LoLLMs WebUI (Lord of Large Language Multimodal Systems: One tool to rule them all) is a user-friendly interface to access and utilize various LLM (Large Language Models) and other AI models for a wide range of tasks. With over 500 AI expert conditionings across diverse domains and more than 2500 fine tuned models over multiple domains, LoLLMs WebUI provides an immediate resource for any problem, from car repair to coding assistance, legal matters, medical diagnosis, entertainment, and more. The easy-to-use UI with light and dark mode options, integration with GitHub repository, support for different personalities, and features like thumb up/down rating, copy, edit, and remove messages, local database storage, search, export, and delete multiple discussions, make LoLLMs WebUI a powerful and versatile tool.

Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement
The Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement repository provides packaged Industry Scenario DREAM Demos with ARM templates (Containing a demo web application, Power BI reports, Synapse resources, AML Notebooks etc.) that can be deployed in a customer’s subscription using the CAPE tool within a matter of few hours. Partners can also deploy DREAM Demos in their own subscriptions using DPoC.

minio
MinIO is a High Performance Object Storage released under GNU Affero General Public License v3.0. It is API compatible with Amazon S3 cloud storage service. Use MinIO to build high performance infrastructure for machine learning, analytics and application data workloads.

mage-ai
Mage is an open-source data pipeline tool for transforming and integrating data. It offers an easy developer experience, engineering best practices built-in, and data as a first-class citizen. Mage makes it easy to build, preview, and launch data pipelines, and provides observability and scaling capabilities. It supports data integrations, streaming pipelines, and dbt integration.

AiTreasureBox
AiTreasureBox is a versatile AI tool that provides a collection of pre-trained models and algorithms for various machine learning tasks. It simplifies the process of implementing AI solutions by offering ready-to-use components that can be easily integrated into projects. With AiTreasureBox, users can quickly prototype and deploy AI applications without the need for extensive knowledge in machine learning or deep learning. The tool covers a wide range of tasks such as image classification, text generation, sentiment analysis, object detection, and more. It is designed to be user-friendly and accessible to both beginners and experienced developers, making AI development more efficient and accessible to a wider audience.

tidb
TiDB is an open-source distributed SQL database that supports Hybrid Transactional and Analytical Processing (HTAP) workloads. It is MySQL compatible and features horizontal scalability, strong consistency, and high availability.
