
dynamiq
Dynamiq is an orchestration framework for agentic AI and LLM applications
Stars: 935

Dynamiq is an orchestration framework designed to streamline the development of AI-powered applications, specializing in orchestrating retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) and large language model (LLM) agents. It provides an all-in-one Gen AI framework for agentic AI and LLM applications, offering tools for multi-agent orchestration, document indexing, and retrieval flows. With Dynamiq, users can easily build and deploy AI solutions for various tasks.
README:
Dynamiq is an orchestration framework for agentic AI and LLM applications
Welcome to Dynamiq! 🤖
Dynamiq is your all-in-one Gen AI framework, designed to streamline the development of AI-powered applications. Dynamiq specializes in orchestrating retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) and large language model (LLM) agents.
Ready to dive in? Here's how you can get started with Dynamiq:
First, let's get Dynamiq installed. You'll need Python, so make sure that's set up on your machine. Then run:
pip install dynamiqOr build the Python package from the source code:
git clone https://github.com/dynamiq-ai/dynamiq.git
cd dynamiq
poetry installFor more examples and detailed guides, please refer to our documentation.
Here's a simple example to get you started with Dynamiq:
from dynamiq.nodes.llms.openai import OpenAI
from dynamiq.connections import OpenAI as OpenAIConnection
from dynamiq.prompts import Prompt, Message
# Define the prompt template for translation
prompt_template = """
Translate the following text into English: {{ text }}
"""
# Create a Prompt object with the defined template
prompt = Prompt(messages=[Message(content=prompt_template, role="user")])
# Setup your LLM (Large Language Model) Node
llm = OpenAI(
id="openai", # Unique identifier for the node
connection=OpenAIConnection(api_key="OPENAI_API_KEY"), # Connection using API key
model="gpt-4o", # Model to be used
temperature=0.3, # Sampling temperature for the model
max_tokens=1000, # Maximum number of tokens in the output
prompt=prompt # Prompt to be used for the model
)
# Run the LLM node with the input data
result = llm.run(
input_data={
"text": "Hola Mundo!" # Text to be translated
}
)
# Print the result of the translation
print(result.output)An agent that has the access to E2B Code Interpreter and is capable of solving complex coding tasks.
from dynamiq.nodes.llms.openai import OpenAI
from dynamiq.connections import OpenAI as OpenAIConnection, E2B as E2BConnection
from dynamiq.nodes.agents.react import ReActAgent
from dynamiq.nodes.tools.e2b_sandbox import E2BInterpreterTool
# Initialize the E2B tool
e2b_tool = E2BInterpreterTool(
connection=E2BConnection(api_key="E2B_API_KEY")
)
# Setup your LLM
llm = OpenAI(
id="openai",
connection=OpenAIConnection(api_key="OPENAI_API_KEY"),
model="gpt-4o",
temperature=0.3,
max_tokens=1000,
)
# Create the ReAct agent
agent = ReActAgent(
name="react-agent",
llm=llm, # Language model instance
tools=[e2b_tool], # List of tools that the agent can use
role="Senior Data Scientist", # Role of the agent
max_loops=10, # Limit on the number of processing loops
)
async def run_async_agent():
# Run the agent asynchronously with an input
result = await agent.run(
input_data={
"input": "Add the first 10 numbers and tell if the result is prime.",
}
)
print(result.output.get("content"))
# Execute the async function
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(run_async_agent())from dynamiq import Workflow
from dynamiq.nodes.llms import OpenAI
from dynamiq.connections import OpenAI as OpenAIConnection
from dynamiq.nodes.agents.reflection import ReflectionAgent
# Setup your LLM
llm = OpenAI(
connection=OpenAIConnection(api_key="OPENAI_API_KEY"),
model="gpt-4o",
temperature=0.1,
)
# Define the first agent: a question answering agent
first_agent = ReflectionAgent(
name="Expert Agent",
llm=llm,
role="Professional writer with the goal of producing well-written and informative responses.",
id="agent_1",
max_loops=5
)
# Define the second agent: a poetic writer
second_agent = ReflectionAgent(
name="Poetic Rewriter Agent",
llm=llm,
role="Professional writer with the goal of rewriting user input as a poem without changing its meaning.",
id="agent_2",
max_loops=5
)
# Create a workflow to run both agents with the same input
# The `Workflow` class simplifies setting up and executing a series of nodes in a pipeline.
# It automatically handles running the agents in parallel where possible.
wf = Workflow()
wf.flow.add_nodes(first_agent)
wf.flow.add_nodes(second_agent)
# Equivalent alternative way to define the workflow:
# from dynamiq.flows import Flow
# wf = Workflow(flow=Flow(nodes=[agent_first, agent_second]))
# Run the workflow with an input
result = wf.run(
input_data={"input": "How are sin(x) and cos(x) connected in electrodynamics?"},
)
# Print the input and output for both agents
print('--- Agent 1: Input ---\n', result.output[first_agent.id].get("input").get('input'))
print('--- Agent 1: Output ---\n', result.output[first_agent.id].get("output").get('content'))
print('--- Agent 2: Input ---\n', result.output[second_agent.id].get("input").get('input'))
print('--- Agent 2: Output ---\n', result.output[second_agent.id].get("output").get('content'))from dynamiq import Workflow
from dynamiq.nodes.llms import OpenAI
from dynamiq.connections import OpenAI as OpenAIConnection
from dynamiq.nodes.agents.reflection import ReflectionAgent
from dynamiq.nodes.node import InputTransformer, NodeDependency
# Setup your LLM
llm = OpenAI(
connection=OpenAIConnection(api_key="OPENAI_API_KEY"),
model="gpt-4o",
temperature=0.1,
)
first_agent = ReflectionAgent(
name="Expert Agent",
llm=llm,
role="Professional writer with the goal of producing well-written and informative responses.", # Role of the agent
id="agent_1",
max_loops=5
)
second_agent = ReflectionAgent(
name="Poetic Rewriter Agent",
llm=llm,
role="Professional writer with the goal of rewriting user input as a poem without changing its meaning.", # Role of the agent
id="agent_2",
depends=[NodeDependency(first_agent)], # Set dependency on the first agent
input_transformer=InputTransformer(
selector={"input": f"${[first_agent.id]}.output.content"} # Extract the output of the first agent as input
),
max_loops=5
)
# Create a workflow to run the agents sequentially based on dependencies.
# Without a workflow, you would need to run `first_agent`, collect its output,
# and then manually pass that output as input to `second_agent`. The workflow automates this process.
wf = Workflow()
wf.flow.add_nodes(first_agent)
wf.flow.add_nodes(second_agent)
# Equivalent alternative way to define the workflow:
# from dynamiq.flows import Flow
# wf = Workflow(flow=Flow(nodes=[agent_first, agent_second]))
# Run the workflow with an input
result = wf.run(
input_data={"input": "How are sin(x) and cos(x) connected in electrodynamics?"},
)
# Print the input and output for both agents
print('--- Agent 1: Input ---\n', result.output[first_agent.id].get("input").get('input'))
print('--- Agent 1: Output ---\n', result.output[first_agent.id].get("output").get('content'))
print('--- Agent 2: Input ---\n', result.output[second_agent.id].get("input").get('input'))
print('--- Agent 2: Output ---\n', result.output[second_agent.id].get("output").get('content'))from dynamiq.connections import (OpenAI as OpenAIConnection,
ScaleSerp as ScaleSerpConnection,
E2B as E2BConnection)
from dynamiq.nodes.llms import OpenAI
from dynamiq.nodes.agents.orchestrators.adaptive import AdaptiveOrchestrator
from dynamiq.nodes.agents.orchestrators.adaptive_manager import AdaptiveAgentManager
from dynamiq.nodes.agents.react import ReActAgent
from dynamiq.nodes.agents.reflection import ReflectionAgent
from dynamiq.nodes.tools.e2b_sandbox import E2BInterpreterTool
from dynamiq.nodes.tools.scale_serp import ScaleSerpTool
# Initialize tools
python_tool = E2BInterpreterTool(
connection=E2BConnection(api_key="E2B_API_KEY")
)
search_tool = ScaleSerpTool(
connection=ScaleSerpConnection(api_key="SCALESERP_API_KEY")
)
# Initialize LLM
llm = OpenAI(
connection=OpenAIConnection(api_key="OPENAI_API_KEY"),
model="gpt-4o",
temperature=0.1,
)
# Define agents
coding_agent = ReActAgent(
name="coding-agent",
llm=llm,
tools=[python_tool],
role=("Expert agent with coding skills."
"Goal is to provide the solution to the input task"
"using Python software engineering skills."),
max_loops=15,
)
planner_agent = ReflectionAgent(
name="planner-agent",
llm=llm,
role=("Expert agent with planning skills."
"Goal is to analyze complex requests"
"and provide a detailed action plan."),
)
search_agent = ReActAgent(
name="search-agent",
llm=llm,
tools=[search_tool],
role=("Expert agent with web search skills."
"Goal is to provide the solution to the input task"
"using web search and summarization skills."),
max_loops=10,
)
# Initialize the adaptive agent manager
agent_manager = AdaptiveAgentManager(llm=llm)
# Create the orchestrator
orchestrator = AdaptiveOrchestrator(
name="adaptive-orchestrator",
agents=[coding_agent, planner_agent, search_agent],
manager=agent_manager,
)
# Define the input task
input_task = (
"Use coding skills to gather data about Nvidia and Intel stock prices for the last 10 years, "
"calculate the average per year for each company, and create a table. Then craft a report "
"and add a conclusion: what would have been better if I had invested $100 ten years ago?"
)
# Run the orchestrator
result = orchestrator.run(
input_data={"input": input_task},
)
# Print the result
print(result.output.get("content"))This workflow takes input PDF files, pre-processes them, converts them to vector embeddings, and stores them in the Pinecone vector database.
The example provided is for an existing index in Pinecone. You can find examples for index creation on the docs/tutorials/rag page.
from io import BytesIO
from dynamiq import Workflow
from dynamiq.connections import OpenAI as OpenAIConnection, Pinecone as PineconeConnection
from dynamiq.nodes.converters import PyPDFConverter
from dynamiq.nodes.splitters.document import DocumentSplitter
from dynamiq.nodes.embedders import OpenAIDocumentEmbedder
from dynamiq.nodes.writers import PineconeDocumentWriter
rag_wf = Workflow()
# PyPDF document converter
converter = PyPDFConverter(document_creation_mode="one-doc-per-page")
rag_wf.flow.add_nodes(converter) # add node to the DAG
# Document splitter
document_splitter = (
DocumentSplitter(
split_by="sentence",
split_length=10,
split_overlap=1,
)
.inputs(documents=converter.outputs.documents) # map converter node output to the expected input of the current node
.depends_on(converter)
)
rag_wf.flow.add_nodes(document_splitter)
# OpenAI vector embeddings
embedder = (
OpenAIDocumentEmbedder(
connection=OpenAIConnection(api_key="OPENAI_API_KEY"),
model="text-embedding-3-small",
)
.inputs(documents=document_splitter.outputs.documents)
.depends_on(document_splitter)
)
rag_wf.flow.add_nodes(embedder)
# Pinecone vector storage
vector_store = (
PineconeDocumentWriter(
connection=PineconeConnection(api_key="PINECONE_API_KEY"),
index_name="default",
dimension=1536,
)
.inputs(documents=embedder.outputs.documents)
.depends_on(embedder)
)
rag_wf.flow.add_nodes(vector_store)
# Prepare input PDF files
file_paths = ["example.pdf"]
input_data = {
"files": [
BytesIO(open(path, "rb").read()) for path in file_paths
],
"metadata": [
{"filename": path} for path in file_paths
],
}
# Run RAG indexing flow
rag_wf.run(input_data=input_data)Simple retrieval RAG flow that searches for relevant documents and answers the original user question using retrieved documents.
from dynamiq import Workflow
from dynamiq.connections import OpenAI as OpenAIConnection, Pinecone as PineconeConnection
from dynamiq.nodes.embedders import OpenAITextEmbedder
from dynamiq.nodes.retrievers import PineconeDocumentRetriever
from dynamiq.nodes.llms import OpenAI
from dynamiq.prompts import Message, Prompt
# Initialize the RAG retrieval workflow
retrieval_wf = Workflow()
# Shared OpenAI connection
openai_connection = OpenAIConnection(api_key="OPENAI_API_KEY")
# OpenAI text embedder for query embedding
embedder = OpenAITextEmbedder(
connection=openai_connection,
model="text-embedding-3-small",
)
retrieval_wf.flow.add_nodes(embedder)
# Pinecone document retriever
document_retriever = (
PineconeDocumentRetriever(
connection=PineconeConnection(api_key="PINECONE_API_KEY"),
index_name="default",
dimension=1536,
top_k=5,
)
.inputs(embedding=embedder.outputs.embedding)
.depends_on(embedder)
)
retrieval_wf.flow.add_nodes(document_retriever)
# Define the prompt template
prompt_template = """
Please answer the question based on the provided context.
Question: {{ query }}
Context:
{% for document in documents %}
- {{ document.content }}
{% endfor %}
"""
# OpenAI LLM for answer generation
prompt = Prompt(messages=[Message(content=prompt_template, role="user")])
answer_generator = (
OpenAI(
connection=openai_connection,
model="gpt-4o",
prompt=prompt,
)
.inputs(
documents=document_retriever.outputs.documents,
query=embedder.outputs.query,
) # take documents from the vector store node and query from the embedder
.depends_on([document_retriever, embedder])
)
retrieval_wf.flow.add_nodes(answer_generator)
# Run the RAG retrieval flow
question = "What are the line intems provided in the invoice?"
result = retrieval_wf.run(input_data={"query": question})
answer = result.output.get(answer_generator.id).get("output", {}).get("content")
print(answer)A simple chatbot that uses the Memory module to store and retrieve conversation history.
from dynamiq.connections import OpenAI as OpenAIConnection
from dynamiq.memory import Memory
from dynamiq.memory.backends.in_memory import InMemory
from dynamiq.nodes.agents.simple import SimpleAgent
from dynamiq.nodes.llms import OpenAI
AGENT_ROLE = "helpful assistant, goal is to provide useful information and answer questions"
llm = OpenAI(
connection=OpenAIConnection(api_key="OPENAI_API_KEY"),
model="gpt-4o",
temperature=0.1,
)
memory = Memory(backend=InMemory())
agent = SimpleAgent(
name="Agent",
llm=llm,
role=AGENT_ROLE,
id="agent",
memory=memory,
)
def main():
print("Welcome to the AI Chat! (Type 'exit' to end)")
while True:
user_input = input("You: ")
user_id = "user"
session_id = "session"
if user_input.lower() == "exit":
break
response = agent.run({"input": user_input, "user_id": user_id, "session_id": session_id})
response_content = response.output.get("content")
print(f"AI: {response_content}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()Graph Orchestrator allows to create any architecture tailored to specific use cases. Example of simple workflow that manages iterative process of feedback and refinement of email.
from typing import Any
from dynamiq.connections import OpenAI as OpenAIConnection
from dynamiq.nodes.agents.orchestrators.graph import END, START, GraphOrchestrator
from dynamiq.nodes.agents.orchestrators.graph_manager import GraphAgentManager
from dynamiq.nodes.agents.simple import SimpleAgent
from dynamiq.nodes.llms import OpenAI
llm = OpenAI(
connection=OpenAIConnection(api_key="OPENAI_API_KEY"),
model="gpt-4o",
temperature=0.1,
)
email_writer = SimpleAgent(
name="email-writer-agent",
llm=llm,
role="Write personalized emails taking into account feedback.",
)
def gather_feedback(context: dict[str, Any], **kwargs):
"""Gather feedback about email draft."""
feedback = input(
f"Email draft:\n"
f"{context.get('history', [{}])[-1].get('content', 'No draft')}\n"
f"Type in SEND to send email, CANCEL to exit, or provide feedback to refine email: \n"
)
reiterate = True
result = f"Gathered feedback: {feedback}"
feedback = feedback.strip().lower()
if feedback == "send":
print("####### Email was sent! #######")
result = "Email was sent!"
reiterate = False
elif feedback == "cancel":
print("####### Email was canceled! #######")
result = "Email was canceled!"
reiterate = False
return {"result": result, "reiterate": reiterate}
def router(context: dict[str, Any], **kwargs):
"""Determines next state based on provided feedback."""
if context.get("reiterate", False):
return "generate_sketch"
return END
orchestrator = GraphOrchestrator(
name="Graph orchestrator",
manager=GraphAgentManager(llm=llm),
)
# Attach tasks to the states. These tasks will be executed when the respective state is triggered.
orchestrator.add_state_by_tasks("generate_sketch", [email_writer])
orchestrator.add_state_by_tasks("gather_feedback", [gather_feedback])
# Define the flow between states by adding edges.
# This configuration creates the sequence of states from START -> "generate_sketch" -> "gather_feedback".
orchestrator.add_edge(START, "generate_sketch")
orchestrator.add_edge("generate_sketch", "gather_feedback")
# Add a conditional edge to the "gather_feedback" state, allowing the flow to branch based on a condition.
# The router function will determine whether the flow should go to "generate_sketch" (reiterate) or END (finish the process).
orchestrator.add_conditional_edge("gather_feedback", ["generate_sketch", END], router)
if __name__ == "__main__":
print("Welcome to email writer.")
email_details = input("Provide email details: ")
orchestrator.run(input_data={"input": f"Write and post email, provide feedback about status of email: {email_details}"})We love contributions! Whether it's bug reports, feature requests, or pull requests, head over to our CONTRIBUTING.md to see how you can help.
Dynamiq is open-source and available under the Apache 2 License.
Happy coding! 🚀
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for dynamiq
Similar Open Source Tools

dynamiq
Dynamiq is an orchestration framework designed to streamline the development of AI-powered applications, specializing in orchestrating retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) and large language model (LLM) agents. It provides an all-in-one Gen AI framework for agentic AI and LLM applications, offering tools for multi-agent orchestration, document indexing, and retrieval flows. With Dynamiq, users can easily build and deploy AI solutions for various tasks.
continuous-eval
Open-Source Evaluation for LLM Applications. `continuous-eval` is an open-source package created for granular and holistic evaluation of GenAI application pipelines. It offers modularized evaluation, a comprehensive metric library covering various LLM use cases, the ability to leverage user feedback in evaluation, and synthetic dataset generation for testing pipelines. Users can define their own metrics by extending the Metric class. The tool allows running evaluation on a pipeline defined with modules and corresponding metrics. Additionally, it provides synthetic data generation capabilities to create user interaction data for evaluation or training purposes.
amadeus-java
Amadeus Java SDK provides a rich set of APIs for the travel industry, allowing developers to access various functionalities such as flight search, booking, airport information, and more. The SDK simplifies interaction with the Amadeus API by providing self-contained code examples and detailed documentation. Developers can easily make API calls, handle responses, and utilize features like pagination and logging. The SDK supports various endpoints for tasks like flight search, booking management, airport information retrieval, and travel analytics. It also offers functionalities for hotel search, booking, and sentiment analysis. Overall, the Amadeus Java SDK is a comprehensive tool for integrating Amadeus APIs into Java applications.
funcchain
Funcchain is a Python library that allows you to easily write cognitive systems by leveraging Pydantic models as output schemas and LangChain in the backend. It provides a seamless integration of LLMs into your apps, utilizing OpenAI Functions or LlamaCpp grammars (json-schema-mode) for efficient structured output. Funcchain compiles the Funcchain syntax into LangChain runnables, enabling you to invoke, stream, or batch process your pipelines effortlessly.
wandb
Weights & Biases (W&B) is a platform that helps users build better machine learning models faster by tracking and visualizing all components of the machine learning pipeline, from datasets to production models. It offers tools for tracking, debugging, evaluating, and monitoring machine learning applications. W&B provides integrations with popular frameworks like PyTorch, TensorFlow/Keras, Hugging Face Transformers, PyTorch Lightning, XGBoost, and Sci-Kit Learn. Users can easily log metrics, visualize performance, and compare experiments using W&B. The platform also supports hosting options in the cloud or on private infrastructure, making it versatile for various deployment needs.
mcp-go
MCP Go is a Go implementation of the Model Context Protocol (MCP), facilitating seamless integration between LLM applications and external data sources and tools. It handles complex protocol details and server management, allowing developers to focus on building tools. The tool is designed to be fast, simple, and complete, aiming to provide a high-level and easy-to-use interface for developing MCP servers. MCP Go is currently under active development, with core features working and advanced capabilities in progress.
ChatRex
ChatRex is a Multimodal Large Language Model (MLLM) designed to seamlessly integrate fine-grained object perception and robust language understanding. By adopting a decoupled architecture with a retrieval-based approach for object detection and leveraging high-resolution visual inputs, ChatRex addresses key challenges in perception tasks. It is powered by the Rexverse-2M dataset with diverse image-region-text annotations. ChatRex can be applied to various scenarios requiring fine-grained perception, such as object detection, grounded conversation, grounded image captioning, and region understanding.
aioshelly
Aioshelly is an asynchronous library designed to control Shelly devices. It is currently under development and requires Python version 3.11 or higher, along with dependencies like bluetooth-data-tools, aiohttp, and orjson. The library provides examples for interacting with Gen1 devices using CoAP protocol and Gen2/Gen3 devices using RPC and WebSocket protocols. Users can easily connect to Shelly devices, retrieve status information, and perform various actions through the provided APIs. The repository also includes example scripts for quick testing and usage guidelines for contributors to maintain consistency with the Shelly API.
unitxt
Unitxt is a customizable library for textual data preparation and evaluation tailored to generative language models. It natively integrates with common libraries like HuggingFace and LM-eval-harness and deconstructs processing flows into modular components, enabling easy customization and sharing between practitioners. These components encompass model-specific formats, task prompts, and many other comprehensive dataset processing definitions. The Unitxt-Catalog centralizes these components, fostering collaboration and exploration in modern textual data workflows. Beyond being a tool, Unitxt is a community-driven platform, empowering users to build, share, and advance their pipelines collaboratively.
agent-kit
AgentKit is a framework for creating and orchestrating AI Agents, enabling developers to build, test, and deploy reliable AI applications at scale. It allows for creating networked agents with separate tasks and instructions to solve specific tasks, as well as simple agents for tasks like writing content. The framework requires the Inngest TypeScript SDK as a dependency and provides documentation on agents, tools, network, state, and routing. Example projects showcase AgentKit in action, such as the Test Writing Network demo using Workflow Kit, Supabase, and OpenAI.

Janus
Janus is a series of unified multimodal understanding and generation models, including Janus-Pro, Janus, and JanusFlow. Janus-Pro is an advanced version that improves both multimodal understanding and visual generation significantly. Janus decouples visual encoding for unified multimodal understanding and generation, surpassing previous models. JanusFlow harmonizes autoregression and rectified flow for unified multimodal understanding and generation, achieving comparable or superior performance to specialized models. The models are available for download and usage, supporting a broad range of research in academic and commercial communities.
orch
orch is a library for building language model powered applications and agents for the Rust programming language. It can be used for tasks such as text generation, streaming text generation, structured data generation, and embedding generation. The library provides functionalities for executing various language model tasks and can be integrated into different applications and contexts. It offers flexibility for developers to create language model-powered features and applications in Rust.
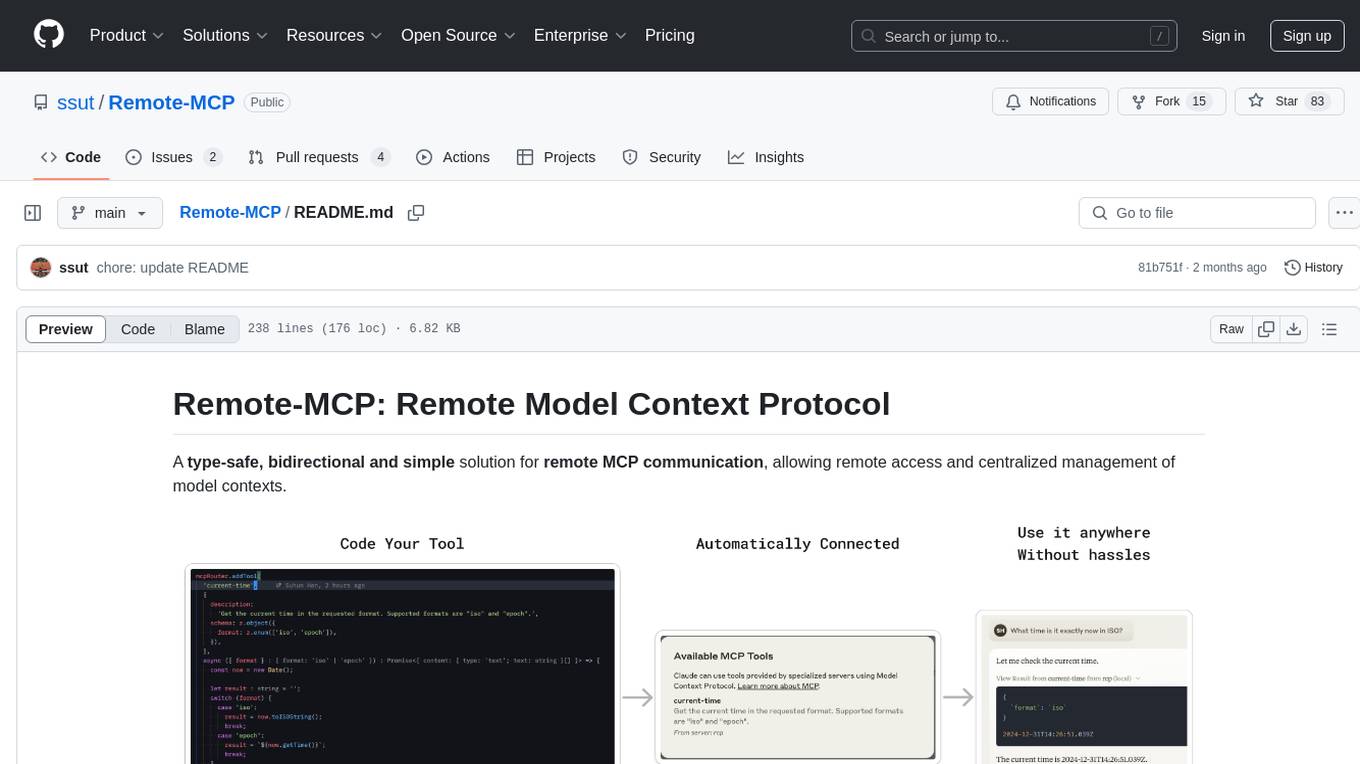
Remote-MCP
Remote-MCP is a type-safe, bidirectional, and simple solution for remote MCP communication, enabling remote access and centralized management of model contexts. It provides a bridge for immediate remote access to a remote MCP server from a local MCP client, without waiting for future official implementations. The repository contains client and server libraries for creating and connecting to remotely accessible MCP services. The core features include basic type-safe client/server communication, MCP command/tool/prompt support, custom headers, and ongoing work on crash-safe handling and event subscription system.
bosquet
Bosquet is a tool designed for LLMOps in large language model-based applications. It simplifies building AI applications by managing LLM and tool services, integrating with Selmer templating library for prompt templating, enabling prompt chaining and composition with Pathom graph processing, defining agents and tools for external API interactions, handling LLM memory, and providing features like call response caching. The tool aims to streamline the development process for AI applications that require complex prompt templates, memory management, and interaction with external systems.
bellman
Bellman is a unified interface to interact with language and embedding models, supporting various vendors like VertexAI/Gemini, OpenAI, Anthropic, VoyageAI, and Ollama. It consists of a library for direct interaction with models and a service 'bellmand' for proxying requests with one API key. Bellman simplifies switching between models, vendors, and common tasks like chat, structured data, tools, and binary input. It addresses the lack of official SDKs for major players and differences in APIs, providing a single proxy for handling different models. The library offers clients for different vendors implementing common interfaces for generating and embedding text, enabling easy interchangeability between models.
notte
Notte is a web browser designed specifically for LLM agents, providing a language-first web navigation experience without the need for DOM/HTML parsing. It transforms websites into structured, navigable maps described in natural language, enabling users to interact with the web using natural language commands. By simplifying browser complexity, Notte allows LLM policies to focus on conversational reasoning and planning, reducing token usage, costs, and latency. The tool supports various language model providers and offers a reinforcement learning style action space and controls for full navigation control.
For similar tasks

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.
AI-in-a-Box
AI-in-a-Box is a curated collection of solution accelerators that can help engineers establish their AI/ML environments and solutions rapidly and with minimal friction, while maintaining the highest standards of quality and efficiency. It provides essential guidance on the responsible use of AI and LLM technologies, specific security guidance for Generative AI (GenAI) applications, and best practices for scaling OpenAI applications within Azure. The available accelerators include: Azure ML Operationalization in-a-box, Edge AI in-a-box, Doc Intelligence in-a-box, Image and Video Analysis in-a-box, Cognitive Services Landing Zone in-a-box, Semantic Kernel Bot in-a-box, NLP to SQL in-a-box, Assistants API in-a-box, and Assistants API Bot in-a-box.
spring-ai
The Spring AI project provides a Spring-friendly API and abstractions for developing AI applications. It offers a portable client API for interacting with generative AI models, enabling developers to easily swap out implementations and access various models like OpenAI, Azure OpenAI, and HuggingFace. Spring AI also supports prompt engineering, providing classes and interfaces for creating and parsing prompts, as well as incorporating proprietary data into generative AI without retraining the model. This is achieved through Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG), which involves extracting, transforming, and loading data into a vector database for use by AI models. Spring AI's VectorStore abstraction allows for seamless transitions between different vector database implementations.
ragstack-ai
RAGStack is an out-of-the-box solution simplifying Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) in GenAI apps. RAGStack includes the best open-source for implementing RAG, giving developers a comprehensive Gen AI Stack leveraging LangChain, CassIO, and more. RAGStack leverages the LangChain ecosystem and is fully compatible with LangSmith for monitoring your AI deployments.
breadboard
Breadboard is a library for prototyping generative AI applications. It is inspired by the hardware maker community and their boundless creativity. Breadboard makes it easy to wire prototypes and share, remix, reuse, and compose them. The library emphasizes ease and flexibility of wiring, as well as modularity and composability.
cloudflare-ai-web
Cloudflare-ai-web is a lightweight and easy-to-use tool that allows you to quickly deploy a multi-modal AI platform using Cloudflare Workers AI. It supports serverless deployment, password protection, and local storage of chat logs. With a size of only ~638 kB gzip, it is a great option for building AI-powered applications without the need for a dedicated server.
app-builder
AppBuilder SDK is a one-stop development tool for AI native applications, providing basic cloud resources, AI capability engine, Qianfan large model, and related capability components to improve the development efficiency of AI native applications.
cookbook
This repository contains community-driven practical examples of building AI applications and solving various tasks with AI using open-source tools and models. Everyone is welcome to contribute, and we value everybody's contribution! There are several ways you can contribute to the Open-Source AI Cookbook: Submit an idea for a desired example/guide via GitHub Issues. Contribute a new notebook with a practical example. Improve existing examples by fixing issues/typos. Before contributing, check currently open issues and pull requests to avoid working on something that someone else is already working on.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.





