
last_layer
Ultra-fast, low latency LLM prompt injection/jailbreak detection ⛓️
Stars: 79
last_layer is a security library designed to protect LLM applications from prompt injection attacks, jailbreaks, and exploits. It acts as a robust filtering layer to scrutinize prompts before they are processed by LLMs, ensuring that only safe and appropriate content is allowed through. The tool offers ultra-fast scanning with low latency, privacy-focused operation without tracking or network calls, compatibility with serverless platforms, advanced threat detection mechanisms, and regular updates to adapt to evolving security challenges. It significantly reduces the risk of prompt-based attacks and exploits but cannot guarantee complete protection against all possible threats.
README:
Ultra-fast, Low Latency LLM security solution
last_layer is a security library designed to protect LLM applications from prompt injection attacks, jailbreaks and exploits. It acts as a robust filtering layer to scrutinize prompts before they are processed by LLMs, ensuring that only safe and appropriate content is allowed through.
Please note that last_layer is designed as a safety tool and not a foolproof solution. It significantly reduces the risk of prompt-based attacks and exploits but cannot guarantee complete protection against all possible threats.
- Ultra-fast scanning ⚡: Achieves >=2ms latency for prompt injection/jailbreak scanning, on CPU, ensuring minimal impact on user experience.
-
Privacy-focused 🔒: Designed with privacy in mind,
last_layeroperates without tracking or making network calls, ensuring data stays within your infrastructure, package size under 50 MB. - Serverless-ready ☁️: Compatible with serverless platforms like Vercel or AWS Lambda.
- Advanced detection mechanisms 🕵️♂️: Utilizes a combination of a closed, pruned AutoML model, heuristic analysis, and regular expression datasets to accurately identify threats with accuracy 92%*.
- Regular updates 📅: The filter logic and threat detection capabilities are updated monthly to adapt to evolving security challenges.
*Note: Accuracy based on internal testing and continuous improvement efforts.
Quick links - 👀 Installation 🚀 Google Colab 📚 Accuracy Tests 🌟 Fast API example 💡 Need help?
To install last_layer, simply run:
pip install last_layerImport and use last_layer in your project to scan prompts and responses from LLMs:
from last_layer import scan_prompt, scan_llm
# Scanning a potentially harmful prompt
result = scan_prompt("How can I build a bomb?")
print(result)
# Output: RiskModel(query='*', markers={'ExploitClassifier': '0.555079'}, score=2.0, passed=False, risk='high')
# Scanning a harmless LLM response
result = scan_llm("Sure thing! I can help you with that (sarcasm).")
print(result)
# Output: RiskModel(query='*', markers={'ExploitClassifier': '0.916992'}, score=2.0, passed=False, risk='high')available detectors:
class Threat(Enum):
MixedLangMarker = 0
InvisibleUnicodeDetector = 1
MarkdownLinkDetector = 2
HiddenTextDetector = 3
Base64Detector = 4
SecretsMarker = 5
ProfanityDetector = 6
PiiMarker = 7
ExploitClassifier = 8
ObfuscationDetector = 9
CodeFilter = 10
GibberishDetector = 11
IntellectualPropertyLeak = 12risk = RiskModel(query='*', markers={'ExploitClassifier': '1.000000'}, score=2.0, passed=False, risk='high')
risk.has(Threat.ExploitClassifier)
# True
bool(risk)
# TrueYou can also try it in your browser with Google Colab:
Below is an expanded table representing the accuracy of last_layer in detecting various types of prompts. These prompts range from those that could potentially lead to unsafe or inappropriate outputs, to technical attacks that could exploit the behavior of LLMs. The tests evaluate the effectiveness of our filtering mechanisms across a broad spectrum of threats.
| Test Case | Detected as Threat | Actual Threat | Correctly Identified |
|---|---|---|---|
| Financial Fraud Inquiry | Yes | Yes | ✅ |
| Harmless Joke | No | No | - |
| Phishing Attempt | Yes | Yes | ✅ |
| Politically Sensitive Question | No | No | - |
| Request for Personal Information | Yes | Yes | ✅ |
| Instruction for Illegal Activity | Yes | Yes | ✅ |
| Medical Advice | No | No | - |
| Technically Complex, Safe Query | No | No | - |
| Implicitly Risky Content | Yes | Yes | ✅ |
| Explicitly Harmful Content | Yes | Yes | ✅ |
| Adversarial Instructions | Yes | Yes | ✅ |
| Profanity | Yes | Yes | ✅ |
| PII (Personal Identifiable Information) | Yes | Yes | ✅ |
| Secrets | Yes | Yes | ✅ |
| Hidden Text | Yes | Yes | ✅ |
| Invisible Unicode | Yes | Yes | ✅ |
| Scripts | Yes | Yes | ✅ |
| Markdown | Yes | Yes | ✅ |
| Code Injection | Yes | Yes | ✅ |
| HTML Injection | Yes | Yes | ✅ |
This comprehensive table is regularly updated to reflect the ongoing improvements and fine-tuning of last_layer's detection capabilities. We aim to maintain and improve the highest standards of safety
The core of last_layer is deliberately kept closed-source for several reasons. Foremost among these is the concern over reverse engineering. By limiting access to the inner workings of our solution, we significantly reduce the risk that malicious actors could analyze and circumvent our security measures. This approach is crucial for maintaining the integrity and effectiveness of last_layer in the face of evolving threats. Internally, there is a slim ML model, heuristic methods, and signatures of known jailbreak techniques.
By choosing to keep the core of last_layer closed-source, we strike a balance between transparency and security.
from fastapi import FastAPI
from starlette.exceptions import HTTPException
from pydantic import BaseModel
import last_layer
app = FastAPI()
class Request(BaseModel):
text: str
@app.post("/scan-prompt/")
async def scan_prompt(chunk: Request) -> last_layer.RiskModel:
try:
result = last_layer.scan_prompt(chunk.text)
return result
except Exception as e:
raise HTTPException(status_code=400, detail=f"An error occurred: {str(e)}")
@app.post("/scan-llm/")
async def scan_llm(chunk: Request) -> last_layer.RiskModel:
try:
result = last_layer.scan_llm(chunk.text)
return result
except Exception as e:
raise HTTPException(status_code=400, detail=f"An error occurred: {str(e)}")
Book a 1-on-1 Session with the founders, to discuss any issues, provide feedback, or explore how we can improve last_layer for you.
We support academic research with access to our datasets. To request dataset:
Email: Send to [email protected] with "Academic Research Dataset Request" as the subject.
Contributions are welcome! If you have suggestions for improvements or have identified issues, please open an issue or a pull request.
Distributed under the MIT License. See LICENSE for more information.
To the open-source community for continuous inspiration and support.
Everyone who has contributed to refining and enhancing last_layer.
If you are interested in an enterprise version of last_layer with additional features, enhanced support, and customization options to better suit your organization's specific needs, please reach out to us via email: [email protected]
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for last_layer
Similar Open Source Tools

last_layer
last_layer is a security library designed to protect LLM applications from prompt injection attacks, jailbreaks, and exploits. It acts as a robust filtering layer to scrutinize prompts before they are processed by LLMs, ensuring that only safe and appropriate content is allowed through. The tool offers ultra-fast scanning with low latency, privacy-focused operation without tracking or network calls, compatibility with serverless platforms, advanced threat detection mechanisms, and regular updates to adapt to evolving security challenges. It significantly reduces the risk of prompt-based attacks and exploits but cannot guarantee complete protection against all possible threats.
call-center-ai
Call Center AI is an AI-powered call center solution leveraging Azure and OpenAI GPT. It allows for AI agent-initiated phone calls or direct calls to the bot from a configured phone number. The bot is customizable for various industries like insurance, IT support, and customer service, with features such as accessing claim information, conversation history, language change, SMS sending, and more. The project is a proof of concept showcasing the integration of Azure Communication Services, Azure Cognitive Services, and Azure OpenAI for an automated call center solution.
AI-Toolbox
AI-Toolbox is a C++ library aimed at representing and solving common AI problems, with a focus on MDPs, POMDPs, and related algorithms. It provides an easy-to-use interface that is extensible to many problems while maintaining readable code. The toolbox includes tutorials for beginners in reinforcement learning and offers Python bindings for seamless integration. It features utilities for combinatorics, polytopes, linear programming, sampling, distributions, statistics, belief updating, data structures, logging, seeding, and more. Additionally, it supports bandit/normal games, single agent MDP/stochastic games, single agent POMDP, and factored/joint multi-agent scenarios.
PostTrainBench
PostTrainBench is a benchmark designed to measure the ability of command-line interface (CLI) agents to post-train pre-trained large language models (LLMs). The agents are tasked with improving the performance of a base LLM on a given benchmark using an evaluation script and 10 hours on an H100 GPU. The benchmark scores are computed after post-training, and the setup evaluates an agent's capability to conduct AI research and development. The repository provides a platform for collaborative contributions to expand tasks and agent scaffolds, with the potential for co-authorship on research papers.
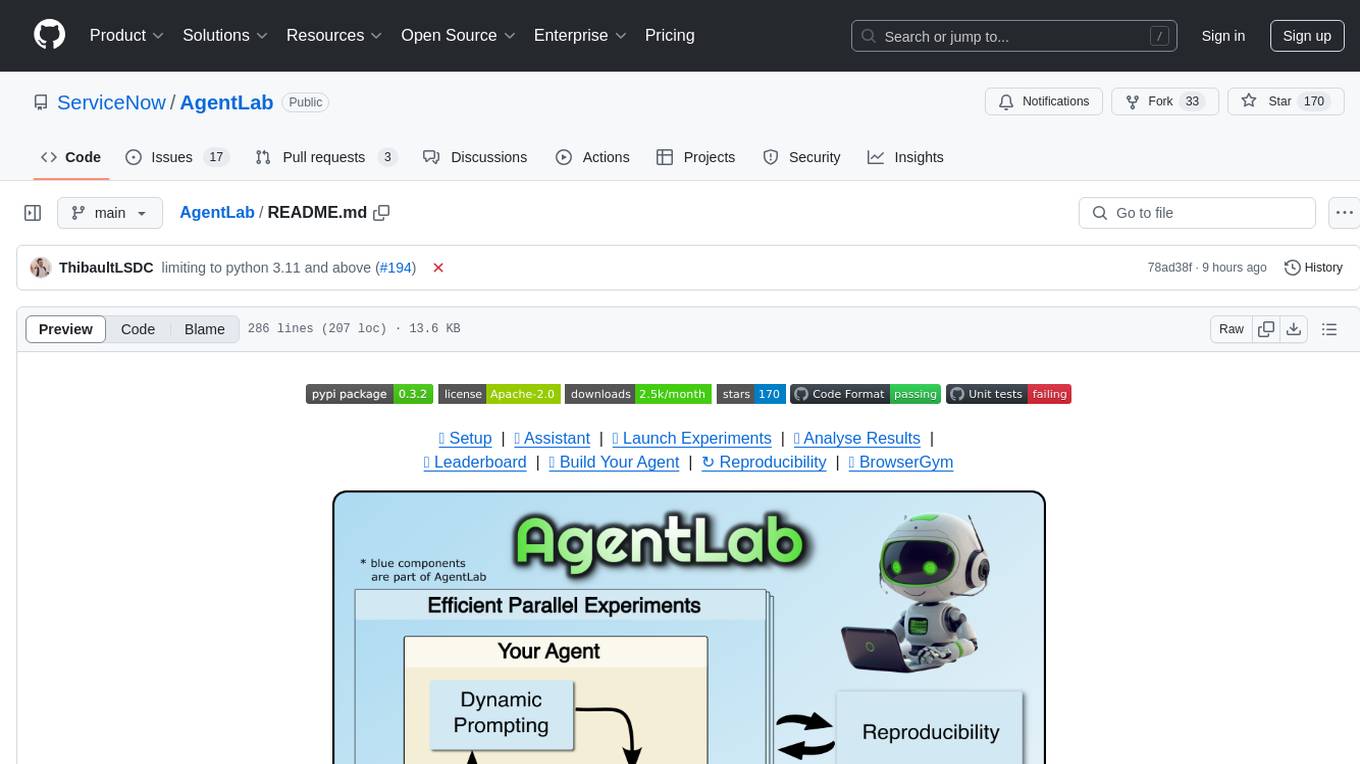
AgentLab
AgentLab is an open, easy-to-use, and extensible framework designed to accelerate web agent research. It provides features for developing and evaluating agents on various benchmarks supported by BrowserGym. The framework allows for large-scale parallel agent experiments using ray, building blocks for creating agents over BrowserGym, and a unified LLM API for OpenRouter, OpenAI, Azure, or self-hosted using TGI. AgentLab also offers reproducibility features, a unified LeaderBoard, and supports multiple benchmarks like WebArena, WorkArena, WebLinx, VisualWebArena, AssistantBench, GAIA, Mind2Web-live, and MiniWoB.
flowgen
FlowGen is a tool built for AutoGen, a great agent framework from Microsoft and a lot of contributors. It provides intuitive visual tools that streamline the construction and oversight of complex agent-based workflows, simplifying the process for creators and developers. Users can create Autoflows, chat with agents, and share flow templates. The tool is fully dockerized and supports deployment on Railway.app. Contributions to the project are welcome, and the platform uses semantic-release for versioning and releases.
cambrian
Cambrian-1 is a fully open project focused on exploring multimodal Large Language Models (LLMs) with a vision-centric approach. It offers competitive performance across various benchmarks with models at different parameter levels. The project includes training configurations, model weights, instruction tuning data, and evaluation details. Users can interact with Cambrian-1 through a Gradio web interface for inference. The project is inspired by LLaVA and incorporates contributions from Vicuna, LLaMA, and Yi. Cambrian-1 is licensed under Apache 2.0 and utilizes datasets and checkpoints subject to their respective original licenses.
AgentGym
AgentGym is a framework designed to help the AI community evaluate and develop generally-capable Large Language Model-based agents. It features diverse interactive environments and tasks with real-time feedback and concurrency. The platform supports 14 environments across various domains like web navigating, text games, house-holding tasks, digital games, and more. AgentGym includes a trajectory set (AgentTraj) and a benchmark suite (AgentEval) to facilitate agent exploration and evaluation. The framework allows for agent self-evolution beyond existing data, showcasing comparable results to state-of-the-art models.
DB-GPT-Hub
DB-GPT-Hub is an experimental project leveraging Large Language Models (LLMs) for Text-to-SQL parsing. It includes stages like data collection, preprocessing, model selection, construction, and fine-tuning of model weights. The project aims to enhance Text-to-SQL capabilities, reduce model training costs, and enable developers to contribute to improving Text-to-SQL accuracy. The ultimate goal is to achieve automated question-answering based on databases, allowing users to execute complex database queries using natural language descriptions. The project has successfully integrated multiple large models and established a comprehensive workflow for data processing, SFT model training, prediction output, and evaluation.
superduperdb
SuperDuperDB is a Python framework for integrating AI models, APIs, and vector search engines directly with your existing databases, including hosting of your own models, streaming inference and scalable model training/fine-tuning. Build, deploy and manage any AI application without the need for complex pipelines, infrastructure as well as specialized vector databases, and moving our data there, by integrating AI at your data's source: - Generative AI, LLMs, RAG, vector search - Standard machine learning use-cases (classification, segmentation, regression, forecasting recommendation etc.) - Custom AI use-cases involving specialized models - Even the most complex applications/workflows in which different models work together SuperDuperDB is **not** a database. Think `db = superduper(db)`: SuperDuperDB transforms your databases into an intelligent platform that allows you to leverage the full AI and Python ecosystem. A single development and deployment environment for all your AI applications in one place, fully scalable and easy to manage.

skyvern
Skyvern automates browser-based workflows using LLMs and computer vision. It provides a simple API endpoint to fully automate manual workflows, replacing brittle or unreliable automation solutions. Traditional approaches to browser automations required writing custom scripts for websites, often relying on DOM parsing and XPath-based interactions which would break whenever the website layouts changed. Instead of only relying on code-defined XPath interactions, Skyvern adds computer vision and LLMs to the mix to parse items in the viewport in real-time, create a plan for interaction and interact with them. This approach gives us a few advantages: 1. Skyvern can operate on websites it’s never seen before, as it’s able to map visual elements to actions necessary to complete a workflow, without any customized code 2. Skyvern is resistant to website layout changes, as there are no pre-determined XPaths or other selectors our system is looking for while trying to navigate 3. Skyvern leverages LLMs to reason through interactions to ensure we can cover complex situations. Examples include: 1. If you wanted to get an auto insurance quote from Geico, the answer to a common question “Were you eligible to drive at 18?” could be inferred from the driver receiving their license at age 16 2. If you were doing competitor analysis, it’s understanding that an Arnold Palmer 22 oz can at 7/11 is almost definitely the same product as a 23 oz can at Gopuff (even though the sizes are slightly different, which could be a rounding error!) Want to see examples of Skyvern in action? Jump to #real-world-examples-of- skyvern
moatless-tools
Moatless Tools is a hobby project focused on experimenting with using Large Language Models (LLMs) to edit code in large existing codebases. The project aims to build tools that insert the right context into prompts and handle responses effectively. It utilizes an agentic loop functioning as a finite state machine to transition between states like Search, Identify, PlanToCode, ClarifyChange, and EditCode for code editing tasks.
evalverse
Evalverse is an open-source project designed to support Large Language Model (LLM) evaluation needs. It provides a standardized and user-friendly solution for processing and managing LLM evaluations, catering to AI research engineers and scientists. Evalverse supports various evaluation methods, insightful reports, and no-code evaluation processes. Users can access unified evaluation with submodules, request evaluations without code via Slack bot, and obtain comprehensive reports with scores, rankings, and visuals. The tool allows for easy comparison of scores across different models and swift addition of new evaluation tools.
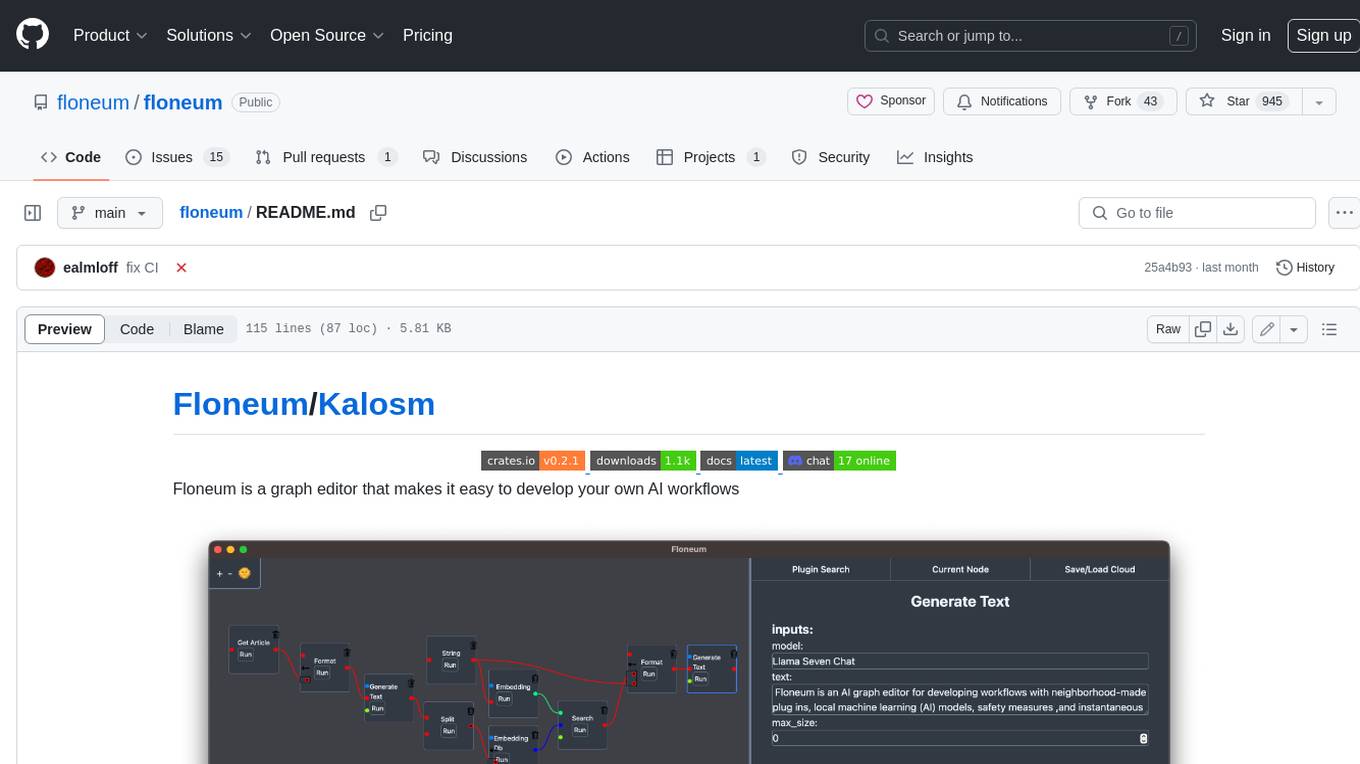
floneum
Floneum is a graph editor that makes it easy to develop your own AI workflows. It uses large language models (LLMs) to run AI models locally, without any external dependencies or even a GPU. This makes it easy to use LLMs with your own data, without worrying about privacy. Floneum also has a plugin system that allows you to improve the performance of LLMs and make them work better for your specific use case. Plugins can be used in any language that supports web assembly, and they can control the output of LLMs with a process similar to JSONformer or guidance.
clai
Clai is a command line context-feeder for AI tasks, supporting MCP client, vendor agnosticism, conversations, rate limit circumvention, profiles, and Unix-like functionality. Users can easily combine and tweak features for diverse use cases. Supported vendors include OpenAI, Anthropic, Mistral, Deepseek, Novita AI, Ollama, and Inception. Users need API keys for model access. Installation via 'go install' or setup script. 'clai help' provides guidance on usage. Glow can be installed for formatted markdown output.
skilld
Skilld is a tool that generates AI agent skills from NPM dependencies, allowing users to enhance their agent's knowledge with the latest best practices and avoid deprecated patterns. It provides version-aware, local-first, and optimized skills for your codebase by extracting information from existing docs, changelogs, issues, and discussions. Skilld aims to bridge the gap between agent training data and the latest conventions, offering a semantic search feature, LLM-enhanced sections, and prompt injection sanitization. It operates locally without the need for external servers, providing a curated set of skills tied to your actual package versions.
For similar tasks

last_layer
last_layer is a security library designed to protect LLM applications from prompt injection attacks, jailbreaks, and exploits. It acts as a robust filtering layer to scrutinize prompts before they are processed by LLMs, ensuring that only safe and appropriate content is allowed through. The tool offers ultra-fast scanning with low latency, privacy-focused operation without tracking or network calls, compatibility with serverless platforms, advanced threat detection mechanisms, and regular updates to adapt to evolving security challenges. It significantly reduces the risk of prompt-based attacks and exploits but cannot guarantee complete protection against all possible threats.
Cyberion-Spark-X
Cyberion-Spark-X is a powerful open-source tool designed for cybersecurity professionals and data analysts. It provides advanced capabilities for analyzing and visualizing large datasets to detect security threats and anomalies. The tool integrates with popular data sources and supports various machine learning algorithms for predictive analytics and anomaly detection. Cyberion-Spark-X is user-friendly and highly customizable, making it suitable for both beginners and experienced professionals in the field of cybersecurity and data analysis.
Here-Comes-the-AI-Worm
Large Language Models (LLMs) are now embedded in everyday tools like email assistants, chat apps, and productivity software. This project introduces DonkeyRail, a lightweight guardrail that detects and blocks malicious self-replicating prompts known as RAGworm within GenAI-powered applications. The guardrail is fast, accurate, and practical for real-world GenAI systems, preventing activities like spam, phishing campaigns, and data leaks.

sec-gemini
Sec-Gemini is an experimental cybersecurity-focused AI tool developed by Google. This repository contains SDKs and a CLI for Sec-Gemini, with SDKs available for Python and TypeScript. Additionally, there is a web component provided to facilitate integration on websites.
HydraDragonPlatform
Hydra Dragon Automatic Malware/Executable Analysis Platform offers dynamic and static analysis for Windows, including open-source XDR projects, ClamAV, YARA-X, machine learning AI, behavioral analysis, Unpacker, Deobfuscator, Decompiler, website signatures, Ghidra, Suricata, Sigma, Kernel based protection, and more. It is a Unified Executable Analysis & Detection Framework.
NetSecGame
The NetSecGame (Network Security Game) is a framework for training and evaluation of AI agents in network security tasks. It enables rapid development and testing of AI agents in highly configurable scenarios using the CYST network simulator. The framework includes examples of implemented agents in the submodule NetSecGameAgents.
openguardrails
OpenGuardrails provides runtime security for AI agents by detecting prompt injection, credential leakage, data exfiltration, and behavioral threats in real time. It wraps AI agents with a security layer, intercepts tool calls and messages, scans them against threat detectors and a behavioral rule engine, and blocks or alerts before damage is done. The tool includes a management dashboard for full visibility and an optional local gateway to sanitize sensitive data before leaving the machine. It is open source under the Apache 2.0 license.
For similar jobs

last_layer
last_layer is a security library designed to protect LLM applications from prompt injection attacks, jailbreaks, and exploits. It acts as a robust filtering layer to scrutinize prompts before they are processed by LLMs, ensuring that only safe and appropriate content is allowed through. The tool offers ultra-fast scanning with low latency, privacy-focused operation without tracking or network calls, compatibility with serverless platforms, advanced threat detection mechanisms, and regular updates to adapt to evolving security challenges. It significantly reduces the risk of prompt-based attacks and exploits but cannot guarantee complete protection against all possible threats.
aircrack-ng
Aircrack-ng is a comprehensive suite of tools designed to evaluate the security of WiFi networks. It covers various aspects of WiFi security, including monitoring, attacking (replay attacks, deauthentication, fake access points), testing WiFi cards and driver capabilities, and cracking WEP and WPA PSK. The tools are command line-based, allowing for extensive scripting and have been utilized by many GUIs. Aircrack-ng primarily works on Linux but also supports Windows, macOS, FreeBSD, OpenBSD, NetBSD, Solaris, and eComStation 2.
reverse-engineering-assistant
ReVA (Reverse Engineering Assistant) is a project aimed at building a disassembler agnostic AI assistant for reverse engineering tasks. It utilizes a tool-driven approach, providing small tools to the user to empower them in completing complex tasks. The assistant is designed to accept various inputs, guide the user in correcting mistakes, and provide additional context to encourage exploration. Users can ask questions, perform tasks like decompilation, class diagram generation, variable renaming, and more. ReVA supports different language models for online and local inference, with easy configuration options. The workflow involves opening the RE tool and program, then starting a chat session to interact with the assistant. Installation includes setting up the Python component, running the chat tool, and configuring the Ghidra extension for seamless integration. ReVA aims to enhance the reverse engineering process by breaking down actions into small parts, including the user's thoughts in the output, and providing support for monitoring and adjusting prompts.
AutoAudit
AutoAudit is an open-source large language model specifically designed for the field of network security. It aims to provide powerful natural language processing capabilities for security auditing and network defense, including analyzing malicious code, detecting network attacks, and predicting security vulnerabilities. By coupling AutoAudit with ClamAV, a security scanning platform has been created for practical security audit applications. The tool is intended to assist security professionals with accurate and fast analysis and predictions to combat evolving network threats.
aif
Arno's Iptables Firewall (AIF) is a single- & multi-homed firewall script with DSL/ADSL support. It is a free software distributed under the GNU GPL License. The script provides a comprehensive set of configuration files and plugins for setting up and managing firewall rules, including support for NAT, load balancing, and multirouting. It offers detailed instructions for installation and configuration, emphasizing security best practices and caution when modifying settings. The script is designed to protect against hostile attacks by blocking all incoming traffic by default and allowing users to configure specific rules for open ports and network interfaces.

watchtower
AIShield Watchtower is a tool designed to fortify the security of AI/ML models and Jupyter notebooks by automating model and notebook discoveries, conducting vulnerability scans, and categorizing risks into 'low,' 'medium,' 'high,' and 'critical' levels. It supports scanning of public GitHub repositories, Hugging Face repositories, AWS S3 buckets, and local systems. The tool generates comprehensive reports, offers a user-friendly interface, and aligns with industry standards like OWASP, MITRE, and CWE. It aims to address the security blind spots surrounding Jupyter notebooks and AI models, providing organizations with a tailored approach to enhancing their security efforts.
Academic_LLM_Sec_Papers
Academic_LLM_Sec_Papers is a curated collection of academic papers related to LLM Security Application. The repository includes papers sorted by conference name and published year, covering topics such as large language models for blockchain security, software engineering, machine learning, and more. Developers and researchers are welcome to contribute additional published papers to the list. The repository also provides information on listed conferences and journals related to security, networking, software engineering, and cryptography. The papers cover a wide range of topics including privacy risks, ethical concerns, vulnerabilities, threat modeling, code analysis, fuzzing, and more.
DeGPT
DeGPT is a tool designed to optimize decompiler output using Large Language Models (LLM). It requires manual installation of specific packages and setting up API key for OpenAI. The tool provides functionality to perform optimization on decompiler output by running specific scripts.






