
aircrack-ng
WiFi security auditing tools suite
Stars: 5187
Aircrack-ng is a comprehensive suite of tools designed to evaluate the security of WiFi networks. It covers various aspects of WiFi security, including monitoring, attacking (replay attacks, deauthentication, fake access points), testing WiFi cards and driver capabilities, and cracking WEP and WPA PSK. The tools are command line-based, allowing for extensive scripting and have been utilized by many GUIs. Aircrack-ng primarily works on Linux but also supports Windows, macOS, FreeBSD, OpenBSD, NetBSD, Solaris, and eComStation 2.
README:
Aircrack-ng is a complete suite of tools to assess WiFi network security.
It focuses on different areas of WiFi security:
- Monitoring: Packet capture and export of data to text files for further processing by third party tools.
- Attacking: Replay attacks, deauthentication, fake access points and others via packet injection.
- Testing: Checking WiFi cards and driver capabilities (capture and injection).
- Cracking: WEP and WPA PSK (WPA 1 and 2).
All tools are command line which allows for heavy scripting. A lot of GUIs have taken advantage of this feature. It works primarily on Linux but also Windows, macOS, FreeBSD, OpenBSD, NetBSD, as well as Solaris and even eComStation 2.
- Autoconf
- Automake
- Libtool
- shtool
- OpenSSL development package or libgcrypt development package.
- Airmon-ng (Linux) requires ethtool, usbutils, and often pciutils.
- On Windows, cygwin has to be used and it also requires w32api package.
- On Windows, if using clang, libiconv and libiconv-devel
- Linux: LibNetlink 1 or 3. It can be disabled by passing --disable-libnl to configure.
- pkg-config (pkgconf on FreeBSD, DragonFlyBSD, OpenBSD and NetBSD)
- FreeBSD, DragonFlyBSD, OpenBSD, NetBSD, Solaris and OS X with Macports: gmake
- Linux/Cygwin: make and Standard C++ Library development package (Debian: libstdc++-dev)
Note: Airmon-ng only requires pciutils if the system has a PCI/PCIe bus and it is populated. Such bus can be present even if not physically visible. For example, it is present, and populated on the Raspberry Pi 4, therefore pciutils is required on that device.
- If you want SSID filtering with regular expression in airodump-ng (--essid-regex) PCRE or PCRE2 development package is required.
- If you want to use airolib-ng and '-r' option in aircrack-ng, SQLite development package >= 3.3.17 (3.6.X version or better is recommended)
- If you want to use Airpcap, the 'developer' directory from the CD/ISO/SDK is required.
- In order to build
besside-ng,besside-ng-crawler,easside-ng,tkiptun-ngandwesside-ng, libpcap development package is required (on Cygwin, use the Airpcap SDK instead; see above) - rfkill
- If you want Airodump-ng to log GPS coordinates, gpsd is needed
- For best performance on SMP machines, ensure the hwloc library and headers are installed. It is strongly recommended on high core count systems, it may give a serious speed boost
- CMocka and expect for testing
- For integration testing on Linux only: tcpdump, HostAPd, WPA Supplicant and screen
Below are instructions for installing the basic requirements to build
aircrack-ng for a number of operating systems.
Note: CMocka, tcpdump, screen, HostAPd and WPA Supplicant should not be dependencies when packaging Aircrack-ng.
sudo pacman -Sy base-devel libnl openssl ethtool util-linux zlib libpcap sqlite pcre2 hwloc cmocka hostapd wpa_supplicant tcpdump screen iw usbutils pciutils expect
sudo apt-get install build-essential autoconf automake libtool pkg-config libnl-3-dev libnl-genl-3-dev libssl-dev ethtool shtool rfkill zlib1g-dev libpcap-dev libsqlite3-dev libpcre2-dev libhwloc-dev libcmocka-dev hostapd wpasupplicant tcpdump screen iw usbutils expect
sudo yum install libtool pkgconfig sqlite-devel autoconf automake openssl-devel libpcap-devel pcre2-devel rfkill libnl3-devel gcc gcc-c++ ethtool hwloc-devel libcmocka-devel make file expect hostapd wpa_supplicant iw usbutils tcpdump screen zlib-devel expect
sudo yum install epel-release
sudo ./centos_autotools.sh
# Remove older installation of automake/autoconf
sudo yum remove autoconf automake
sudo yum install sqlite-devel openssl-devel libpcap-devel pcre2-devel rfkill libnl3-devel ethtool hwloc-devel libcmocka-devel make file expect hostapd wpa_supplicant iw usbutils tcpdump screen zlib-devel
Note: autoconf, automake, libtool, and pkgconfig in the repositories are too old. The script centos_autotools.sh automatically installs dependencies to compile then install the tools.
sudo yum config-manager --set-enabled powertools
sudo yum install epel-release
sudo yum install libtool pkgconfig sqlite-devel autoconf automake openssl-devel libpcap-devel pcre2-devel rfkill libnl3-devel gcc gcc-c++ ethtool hwloc-devel libcmocka-devel make file expect hostapd wpa_supplicant iw usbutils tcpdump screen zlib-devel
sudo zypper install autoconf automake libtool pkg-config libnl3-devel libopenssl-1_1-devel zlib-devel libpcap-devel sqlite3-devel pcre2-devel hwloc-devel libcmocka-devel hostapd wpa_supplicant tcpdump screen iw gcc-c++ gcc ethtool pciutils usbutils expect
sudo urpmi autoconf automake libtool pkgconfig libnl3-devel libopenssl-devel zlib-devel libpcap-devel sqlite3-devel pcre2-devel hwloc-devel libcmocka-devel hostapd wpa_supplicant tcpdump screen iw gcc-c++ gcc make expect
sudo apk add gcc g++ make autoconf automake libtool libnl3-dev openssl-dev ethtool libpcap-dev cmocka-dev hostapd wpa_supplicant tcpdump screen iw pkgconf util-linux sqlite-dev pcre2-dev linux-headers zlib-dev pciutils usbutils expect
Note: Community repository needs to be enabled for iw
sudo swupd bundle-add c-basic devpkg-openssl devpkg-libgcrypt devpkg-libnl devpkg-hwloc devpkg-libpcap devpkg-pcre2 devpkg-sqlite-autoconf ethtool wget network-basic software-testing sysadmin-basic wpa_supplicant os-testsuite
Note: hostapd must be compiled manually, it is not present in the repository
pkg install pkgconf shtool libtool gcc9 automake autoconf pcre2 sqlite3 openssl gmake hwloc cmocka
pkg install pkgconf shtool libtool gcc8 automake autoconf pcre2 sqlite3 libgcrypt gmake cmocka
pkg_add pkgconf shtool libtool gcc automake autoconf pcre2 sqlite3 openssl gmake cmocka
pkg_add pkgconf libtool gcc7 automake autoconf pcre2 sqlite3 openssl gmake cmocka
XCode, Xcode command line tools and HomeBrew are required.
brew install autoconf automake libtool openssl shtool pkg-config hwloc pcre2 sqlite3 libpcap cmocka
Cygwin requires the full path to the setup.exe utility, in order to
automate the installation of the necessary packages. In addition, it
requires the location of your installation, a path to the cached
packages download location, and a mirror URL.
An example of automatically installing all the dependencies is as follows:
c:\cygwin\setup-x86.exe -qnNdO -R C:/cygwin -s http://cygwin.mirror.constant.com -l C:/cygwin/var/cache/setup -P autoconf -P automake -P bison -P gcc-core -P gcc-g++ -P mingw-runtime -P mingw-binutils -P mingw-gcc-core -P mingw-gcc-g++ -P mingw-pthreads -P mingw-w32api -P libtool -P make -P python -P gettext-devel -P gettext -P intltool -P libiconv -P pkg-config -P git -P wget -P curl -P libpcre2-devel -P libssl-devel -P libsqlite3-devel
pacman -Sy autoconf automake-wrapper libtool msys2-w32api-headers msys2-w32api-runtime gcc pkg-config git python openssl-devel openssl libopenssl msys2-runtime-devel gcc binutils make pcre2-devel libsqlite-devel
apt-get install build-essential autoconf automake libtool pkg-config libssl-dev shtool zlib1g-dev libpcap-dev libsqlite3-dev libpcre2-dev libhwloc-dev libcmocka-dev screen expect libbsd-dev
We have two repositories on DockerHub:
- aircrackng/release: Each release
- aircrackng/git: every commit in the git repository
Base command for the git version:
sudo docker run --rm -it aircrackng/git
Available platforms/CPU architectures:
- linux/386 (base image: debian:unstable-slim)
- linux/amd64 (base image: debian:unstable-slim)
- linux/arm/v5 (base image: debian:unstable-slim)
- linux/arm/v6 (base image: alpine:3)
- linux/arm/v7 (base image: debian:unstable-slim)
- linux/arm64/v8 (base image: debian:unstable-slim)
- linux/mips64le (base image: debian:unstable-slim)
- linux/ppc64le (base image: debian:unstable-slim)
- linux/riscv64 (base image: debian:unstable-slim)
- linux/s390x (base image: debian:unstable-slim)
To build aircrack-ng, the Autotools build system is utilized. Autotools replaces
the older method of compilation.
NOTE: If utilizing a developer version, eg: one checked out from source control,
you will need to run a pre-configure script. The script to use is one of the
following: autoreconf -i or env NOCONFIGURE=1 ./autogen.sh.
First, ./configure the project for building with the appropriate options specified
for your environment:
./configure <options>
TIP: If the above fails, please see above about developer source control versions.
Next, compile the project (respecting if make or gmake is needed):
-
Compilation:
make -
Compilation on *BSD or Solaris:
gmake
Finally, the additional targets listed below may be of use in your environment:
-
Execute all unit testing:
make check -
Execute all integration testing (requires root):
make integration -
Installing:
make install -
Uninstall:
make uninstall
When configuring, the following flags can be used and combined to adjust the suite to your choosing:
-
with-airpcap=DIR: needed for supporting airpcap devices on Windows (Cygwin or MSYS2 only). Replace DIR above with the absolute location to the root of the extracted source code from the Airpcap CD or downloaded SDK available online. Required on Windows to build
besside-ng,besside-ng-crawler,easside-ng,tkiptun-ngandwesside-ngwhen building experimental tools. The developer pack (Compatible with version 4.1.1 and 4.1.3) can be downloaded at https://support.riverbed.com/content/support/software/steelcentral-npm/airpcap.html -
with-experimental: needed to compile
tkiptun-ng,easside-ng,buddy-ng,buddy-ng-crawler,airventriloquistandwesside-ng. libpcap development package is also required to compile most of the tools. If not present, not all experimental tools will be built. On Cygwin, libpcap is not present and the Airpcap SDK replaces it. See --with-airpcap option above. -
with-ext-scripts: needed to build
airoscript-ng,versuck-ng,airgraph-ngandairdrop-ng. Note: Each script has its own dependencies. -
with-gcrypt: Use libgcrypt crypto library instead of the default OpenSSL. And also use internal fast sha1 implementation (borrowed from GIT). Dependency (Debian): libgcrypt20-dev
-
with-duma: Compile with DUMA support. DUMA is a library to detect buffer overruns and underruns. Dependency (Debian): duma
-
disable-libnl: Set up the project to be compiled without libnl (1 or 3). Linux option only.
-
without-opt: Do not enable -O3 optimizations.
-
enable-shared: Make OSdep a shared library.
-
disable-shared: When combined with enable-static, it will statically compile Aircrack-ng.
-
with-avx512: On x86, add support for AVX512 instructions in aircrack-ng. Only use it when the current CPU supports AVX512.
-
with-static-simd=: Compile a single optimization in aircrack-ng binary. Useful when compiling statically and/or for space-constrained devices. Valid SIMD options: x86-sse2, x86-avx, x86-avx2, x86-avx512, ppc-altivec, ppc-power8, arm-neon, arm-asimd. Must be used with --enable-static --disable-shared. When using those 2 options, the default is to compile the generic optimization in the binary. --with-static-simd merely allows to choose another one.
-
enable-maintainer-mode: It is important to enable this flag when developing with Aircrack-ng. This flag enables additional compile warnings and safety features.
-
Configure and compiling:
./configure --with-experimental make -
Compiling with gcrypt:
./configure --with-gcrypt make -
Installing:
make install -
Installing (strip binaries):
make install-strip -
Installing, with external scripts:
./configure --with-experimental --with-ext-scripts make make install -
Testing (with sqlite, experimental and pcre2)
./configure --with-experimental make make check -
Compiling on OS X with macports (and all options):
./configure --with-experimental gmake -
Compiling on macOS running on M1/AARCH64 and Homebrew:
autoreconf -vif env CPPFLAGS="-Wno-deprecated-declarations" ./configure --with-experimental make make check -
Compiling on OS X 10.10 with XCode 7.1 and Homebrew:
env CC=gcc-4.9 CXX=g++-4.9 ./configure make make checkNOTE: Older XCode ships with a version of LLVM that does not support CPU feature detection; which causes the
./configureto fail. To work around this older LLVM, it is required that a different compile suite is used, such as GCC or a newer LLVM from Homebrew.If you wish to use OpenSSL from Homebrew, you may need to specify the location to its installation. To figure out where OpenSSL lives, run:
brew --prefix opensslUse the output above as the DIR for
--with-openssl=DIRin the./configureline:env CC=gcc-4.9 CXX=g++-4.9 ./configure --with-openssl=DIR make make check -
Compiling on FreeBSD with gcc9
env CC=gcc9 CXX=g++9 MAKE=gmake ./configure gmake -
Compiling on Cygwin with Airpcap (assuming Airpcap devpack is unpacked in Aircrack-ng directory)
cp -vfp Airpcap_Devpack/bin/x86/airpcap.dll src cp -vfp Airpcap_Devpack/bin/x86/airpcap.dll src/aircrack-osdep cp -vfp Airpcap_Devpack/bin/x86/airpcap.dll src/aircrack-crypto cp -vfp Airpcap_Devpack/bin/x86/airpcap.dll src/aircrack-util dlltool -D Airpcap_Devpack/bin/x86/airpcap.dll -d build/airpcap.dll.def -l Airpcap_Devpack/bin/x86/libairpcap.dll.a autoreconf -i ./configure --with-experimental --with-airpcap=$(pwd) make -
Compiling on DragonflyBSD with gcrypt using GCC 8
autoreconf -i env CC=gcc8 CXX=g++8 MAKE=gmake ./configure --with-experimental --with-gcrypt gmake -
Compiling on OpenBSD (with autoconf 2.69 and automake 1.16)
export AUTOCONF_VERSION=2.69 export AUTOMAKE_VERSION=1.16 autoreconf -i env MAKE=gmake CC=cc CXX=c++ ./configure gmake -
Compiling and debugging aircrack-ng
export CFLAGS='-O0 -g' export CXXFLAGS='-O0 -g' ./configure --with-experimental --enable-maintainer-mode --without-opt make LD_LIBRARY_PATH=.libs gdb --args ./aircrack-ng [PARAMETERS]
A VS Code development environment is provided, as is, for rapid setup of a development environment. This additionally adds support for GitHub Codespaces.
The first requirement is a working Docker Engine environment.
Next, an installation of VS Code with the following extension(s):
-
Remote - Containersby Microsoft.
The "Remote - Containers" extension will refuse to work with OSS Code.
- Clone this repository to your working folder:
$ git clone --recursive https://github.com/aircrack-ng/aircrack-ng.git
$ cd aircrack-ng
- After cloning this repository, open the folder inside VS Code.
$ code .
IMPORTANT: You should answer "Yes", if it asks if the folder should be opened inside a remote container. If it does not ask, then press
Ctrl+Shift+Pand typeopen in container. This should bring up the correct command, for which pressing enter will run said command.
- A number of warnings might appear about a missing
compile_commands.jsonfile. These are safe to ignore for a moment, as this file is automatically generated after the initial compilation. - Now build the entire project by pressing
Ctrl+Rand selectingBuild Fullfrom the pop-up menu that appears. - VS Code should detect the
compile_commands.jsonfile and ask if it should be used; selecting "Yes, always" will complete the initial setup of a fully working IDE.
IMPORTANT: If it doesn't detect the file, pressing
Ctrl+Shift+Pand typingreload windowwill bring up the selection to fully reload the environment.
- At this point, nearly all features of VS Code will function; from Intellisense, auto-completion, live documentation, to code formatting. Additionally, there are pre-configured tasks for builds and tests, as well as an example GDB/LLDB configuration for debugging
aircrack-ng.
Automatic detection of CPU optimization is done at run time. This behavior is desirable when packaging Aircrack-ng (for a Linux or other distribution.)
Also, in some cases it may be desired to provide your own flags completely and
not having the suite auto-detect a number of optimizations. To do this, add
the additional flag --without-opt to the ./configure line:
./configure --without-opt
Aircrack-ng is available in most distributions repositories. However, it is not always up-to-date.
- Install the appropriate "monitor" driver for your card; standard drivers don't work for capturing data.
- Aircrack-ng suite is command line tools. So, you have to open a command-line
Start menu -> Run... -> cmd.exethen use them - Run the executables without any parameters to have help
Some more information is present in the README file.
Documentation, tutorials, ... can be found on https://aircrack-ng.org
Support is available in the GitHub Discussions and on IRC (in #aircrack-ng on Libera Chat).
Every tool has its own manpage. For aircrack-ng, man aircrack-ng
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for aircrack-ng
Similar Open Source Tools

aircrack-ng
Aircrack-ng is a comprehensive suite of tools designed to evaluate the security of WiFi networks. It covers various aspects of WiFi security, including monitoring, attacking (replay attacks, deauthentication, fake access points), testing WiFi cards and driver capabilities, and cracking WEP and WPA PSK. The tools are command line-based, allowing for extensive scripting and have been utilized by many GUIs. Aircrack-ng primarily works on Linux but also supports Windows, macOS, FreeBSD, OpenBSD, NetBSD, Solaris, and eComStation 2.
KsanaLLM
KsanaLLM is a high-performance engine for LLM inference and serving. It utilizes optimized CUDA kernels for high performance, efficient memory management, and detailed optimization for dynamic batching. The tool offers flexibility with seamless integration with popular Hugging Face models, support for multiple weight formats, and high-throughput serving with various decoding algorithms. It enables multi-GPU tensor parallelism, streaming outputs, and an OpenAI-compatible API server. KsanaLLM supports NVIDIA GPUs and Huawei Ascend NPU, and seamlessly integrates with verified Hugging Face models like LLaMA, Baichuan, and Qwen. Users can create a docker container, clone the source code, compile for Nvidia or Huawei Ascend NPU, run the tool, and distribute it as a wheel package. Optional features include a model weight map JSON file for models with different weight names.
Flowise
Flowise is a tool that allows users to build customized LLM flows with a drag-and-drop UI. It is open-source and self-hostable, and it supports various deployments, including AWS, Azure, Digital Ocean, GCP, Railway, Render, HuggingFace Spaces, Elestio, Sealos, and RepoCloud. Flowise has three different modules in a single mono repository: server, ui, and components. The server module is a Node backend that serves API logics, the ui module is a React frontend, and the components module contains third-party node integrations. Flowise supports different environment variables to configure your instance, and you can specify these variables in the .env file inside the packages/server folder.
WilliamButcherBot
WilliamButcherBot is a Telegram Group Manager Bot and Userbot written in Python using Pyrogram. It provides features for managing Telegram groups and users, with ready-to-use methods available. The bot requires Python 3.9, Telegram API Key, Telegram Bot Token, and MongoDB URI. Users can install it locally or on a VPS, run it directly, generate Pyrogram session for Heroku, or use Docker for deployment. Additionally, users can write new modules to extend the bot's functionality by adding them to the wbb/modules/ directory.
yams
YAMS (Yet Another Memory System) is a persistent memory system designed for Large Language Models (LLMs) and applications. It provides content-addressed storage with features such as deduplication, compression, full-text search, and vector search. The system is built with SHA-256 content-addressed store, block-level deduplication, full-text search using SQLite FTS5, semantic search with embeddings, WAL-backed durability, high-throughput I/O, and thread-safe operations. YAMS supports Linux x86_64/ARM64 and macOS x86_64/ARM64 platforms. It is recommended to build using Conan for managing dependencies and ensuring proper installation. Users can interact with YAMS through a command-line interface for tasks like initialization, adding content, searching, and retrieving data. Additionally, YAMS provides LLM-friendly patterns for caching web content, storing code diffs, and integrating with other systems through an API in C++. Troubleshooting tips include creating a default Conan profile and handling PDF support issues during the build process. The project is licensed under Apache-2.0.
Airshipper
Airshipper is a cross-platform Veloren launcher that allows users to update/download and start nightly builds of the game. It features a fancy UI with self-updating capabilities on Windows. Users can compile it from source and also have the option to install Airshipper-Server for advanced configurations. Note that Airshipper is still in development and may not be stable for all users.
codemie-code
Unified AI Coding Assistant CLI for managing multiple AI agents like Claude Code, Google Gemini, OpenCode, and custom AI agents. Supports OpenAI, Azure OpenAI, AWS Bedrock, LiteLLM, Ollama, and Enterprise SSO. Features built-in LangGraph agent with file operations, command execution, and planning tools. Cross-platform support for Windows, Linux, and macOS. Ideal for developers seeking a powerful alternative to GitHub Copilot or Cursor.

fiftyone
FiftyOne is an open-source tool designed for building high-quality datasets and computer vision models. It supercharges machine learning workflows by enabling users to visualize datasets, interpret models faster, and improve efficiency. With FiftyOne, users can explore scenarios, identify failure modes, visualize complex labels, evaluate models, find annotation mistakes, and much more. The tool aims to streamline the process of improving machine learning models by providing a comprehensive set of features for data analysis and model interpretation.
pianotrans
ByteDance's Piano Transcription is a PyTorch implementation for transcribing piano recordings into MIDI files with pedals. This repository provides a simple GUI and packaging for Windows and Nix on Linux/macOS. It supports using GPU for inference and includes CLI usage. Users can upgrade the tool and report issues to the upstream project. The tool focuses on providing MIDI files, and any other improvements to transcription results should be directed to the original project.
obs-localvocal
LocalVocal is a Speech AI assistant OBS Plugin that enables users to transcribe speech into text and translate it into any language locally on their machine. The plugin runs OpenAI's Whisper for real-time speech processing and prediction. It supports features like transcribing audio in real-time, displaying captions on screen, sending captions to files, syncing captions with recordings, and translating captions to major languages. Users can bring their own Whisper model, filter or replace captions, and experience partial transcriptions for streaming. The plugin is privacy-focused, requiring no GPU, cloud costs, network, or downtime.
ppl.llm.kernel.cuda
Primitive cuda kernel library for ppl.nn.llm, part of PPL.LLM system, tested on Ampere and Hopper, requires Linux on x86_64 or arm64 CPUs, GCC >= 9.4.0, CMake >= 3.18, Git >= 2.7.0, CUDA Toolkit >= 11.4. 11.6 recommended. Provides cuda kernel functionalities for deep learning tasks.

comp
Comp AI is an open-source compliance automation platform designed to assist companies in achieving compliance with standards like SOC 2, ISO 27001, and GDPR. It transforms compliance into an engineering problem solved through code, automating evidence collection, policy management, and control implementation while maintaining data and infrastructure control.
claude-code.nvim
Claude Code Neovim Plugin is a seamless integration between Claude Code AI assistant and Neovim. It allows users to toggle Claude Code in a terminal window with a single key press, automatically detect and reload files modified by Claude Code, provide real-time buffer updates when files are changed externally, offer customizable window position and size, integrate with which-key, use git project root as working directory, maintain a modular code structure, provide type annotations with LuaCATS for better IDE support, offer configuration validation, and include a testing framework for reliability. The plugin creates a terminal buffer running the Claude Code CLI, sets up autocommands to detect file changes on disk, automatically reloads files modified by Claude Code, provides keymaps and commands for toggling the terminal, and detects git repositories to set the working directory to the git root.
airstore
Airstore is a filesystem for AI agents that adds any source of data into a virtual filesystem, allowing users to connect services like Gmail, GitHub, Linear, and more, and describe data needs in plain English. Results are presented as files that can be read by Claude Code. Features include smart folders for natural language queries, integrations with various services, executable MCP servers, team workspaces, and local mode operation on user infrastructure. Users can sign up, connect integrations, create smart folders, install the CLI, mount the filesystem, and use with Claude Code to perform tasks like summarizing invoices, identifying unpaid invoices, and extracting data into CSV format.
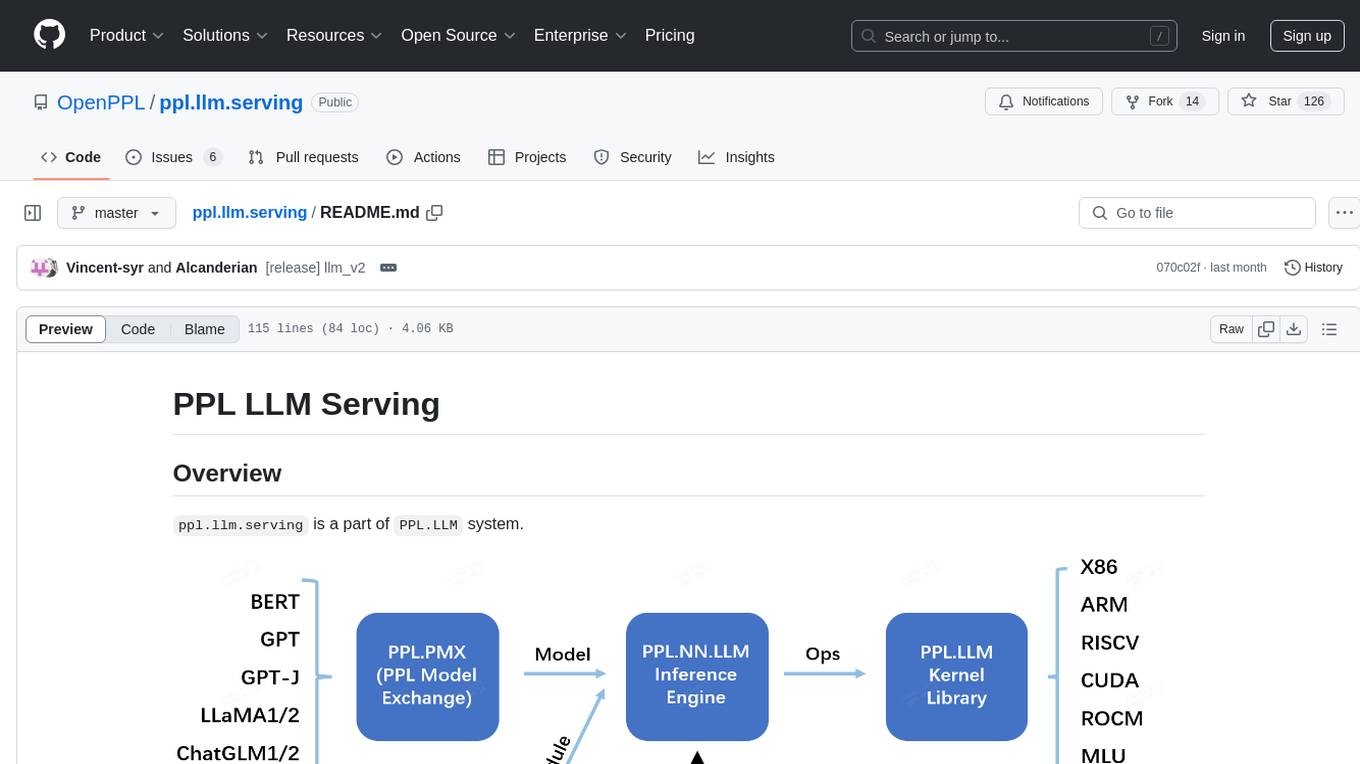
ppl.llm.serving
ppl.llm.serving is a serving component for Large Language Models (LLMs) within the PPL.LLM system. It provides a server based on gRPC and supports inference for LLaMA. The repository includes instructions for prerequisites, quick start guide, model exporting, server setup, client usage, benchmarking, and offline inference. Users can refer to the LLaMA Guide for more details on using this serving component.

sim
Sim is a platform that allows users to build and deploy AI agent workflows quickly and easily. It provides cloud-hosted and self-hosted options, along with support for local AI models. Users can set up the application using Docker Compose, Dev Containers, or manual setup with PostgreSQL and pgvector extension. The platform utilizes technologies like Next.js, Bun, PostgreSQL with Drizzle ORM, Better Auth for authentication, Shadcn and Tailwind CSS for UI, Zustand for state management, ReactFlow for flow editor, Fumadocs for documentation, Turborepo for monorepo management, Socket.io for real-time communication, and Trigger.dev for background jobs.
For similar tasks

aircrack-ng
Aircrack-ng is a comprehensive suite of tools designed to evaluate the security of WiFi networks. It covers various aspects of WiFi security, including monitoring, attacking (replay attacks, deauthentication, fake access points), testing WiFi cards and driver capabilities, and cracking WEP and WPA PSK. The tools are command line-based, allowing for extensive scripting and have been utilized by many GUIs. Aircrack-ng primarily works on Linux but also supports Windows, macOS, FreeBSD, OpenBSD, NetBSD, Solaris, and eComStation 2.
For similar jobs
last_layer
last_layer is a security library designed to protect LLM applications from prompt injection attacks, jailbreaks, and exploits. It acts as a robust filtering layer to scrutinize prompts before they are processed by LLMs, ensuring that only safe and appropriate content is allowed through. The tool offers ultra-fast scanning with low latency, privacy-focused operation without tracking or network calls, compatibility with serverless platforms, advanced threat detection mechanisms, and regular updates to adapt to evolving security challenges. It significantly reduces the risk of prompt-based attacks and exploits but cannot guarantee complete protection against all possible threats.

aircrack-ng
Aircrack-ng is a comprehensive suite of tools designed to evaluate the security of WiFi networks. It covers various aspects of WiFi security, including monitoring, attacking (replay attacks, deauthentication, fake access points), testing WiFi cards and driver capabilities, and cracking WEP and WPA PSK. The tools are command line-based, allowing for extensive scripting and have been utilized by many GUIs. Aircrack-ng primarily works on Linux but also supports Windows, macOS, FreeBSD, OpenBSD, NetBSD, Solaris, and eComStation 2.
reverse-engineering-assistant
ReVA (Reverse Engineering Assistant) is a project aimed at building a disassembler agnostic AI assistant for reverse engineering tasks. It utilizes a tool-driven approach, providing small tools to the user to empower them in completing complex tasks. The assistant is designed to accept various inputs, guide the user in correcting mistakes, and provide additional context to encourage exploration. Users can ask questions, perform tasks like decompilation, class diagram generation, variable renaming, and more. ReVA supports different language models for online and local inference, with easy configuration options. The workflow involves opening the RE tool and program, then starting a chat session to interact with the assistant. Installation includes setting up the Python component, running the chat tool, and configuring the Ghidra extension for seamless integration. ReVA aims to enhance the reverse engineering process by breaking down actions into small parts, including the user's thoughts in the output, and providing support for monitoring and adjusting prompts.
AutoAudit
AutoAudit is an open-source large language model specifically designed for the field of network security. It aims to provide powerful natural language processing capabilities for security auditing and network defense, including analyzing malicious code, detecting network attacks, and predicting security vulnerabilities. By coupling AutoAudit with ClamAV, a security scanning platform has been created for practical security audit applications. The tool is intended to assist security professionals with accurate and fast analysis and predictions to combat evolving network threats.
aif
Arno's Iptables Firewall (AIF) is a single- & multi-homed firewall script with DSL/ADSL support. It is a free software distributed under the GNU GPL License. The script provides a comprehensive set of configuration files and plugins for setting up and managing firewall rules, including support for NAT, load balancing, and multirouting. It offers detailed instructions for installation and configuration, emphasizing security best practices and caution when modifying settings. The script is designed to protect against hostile attacks by blocking all incoming traffic by default and allowing users to configure specific rules for open ports and network interfaces.

watchtower
AIShield Watchtower is a tool designed to fortify the security of AI/ML models and Jupyter notebooks by automating model and notebook discoveries, conducting vulnerability scans, and categorizing risks into 'low,' 'medium,' 'high,' and 'critical' levels. It supports scanning of public GitHub repositories, Hugging Face repositories, AWS S3 buckets, and local systems. The tool generates comprehensive reports, offers a user-friendly interface, and aligns with industry standards like OWASP, MITRE, and CWE. It aims to address the security blind spots surrounding Jupyter notebooks and AI models, providing organizations with a tailored approach to enhancing their security efforts.
Academic_LLM_Sec_Papers
Academic_LLM_Sec_Papers is a curated collection of academic papers related to LLM Security Application. The repository includes papers sorted by conference name and published year, covering topics such as large language models for blockchain security, software engineering, machine learning, and more. Developers and researchers are welcome to contribute additional published papers to the list. The repository also provides information on listed conferences and journals related to security, networking, software engineering, and cryptography. The papers cover a wide range of topics including privacy risks, ethical concerns, vulnerabilities, threat modeling, code analysis, fuzzing, and more.
DeGPT
DeGPT is a tool designed to optimize decompiler output using Large Language Models (LLM). It requires manual installation of specific packages and setting up API key for OpenAI. The tool provides functionality to perform optimization on decompiler output by running specific scripts.












