Academic_LLM_Sec_Papers
Academic Papers about LLM Application on Security
Stars: 54
Academic_LLM_Sec_Papers is a curated collection of academic papers related to LLM Security Application. The repository includes papers sorted by conference name and published year, covering topics such as large language models for blockchain security, software engineering, machine learning, and more. Developers and researchers are welcome to contribute additional published papers to the list. The repository also provides information on listed conferences and journals related to security, networking, software engineering, and cryptography. The papers cover a wide range of topics including privacy risks, ethical concerns, vulnerabilities, threat modeling, code analysis, fuzzing, and more.
README:
A curated LLM Security Application related academic papers. All papers are sorted based on the conference name and published year.
Welcome developers or researchers to add more published papers to this list.
The cryptocurrency donation address: 0xCC28B05fE858CDbc8692E3272A4451111bDCf700.
Welcome to visit my homepage and Google Scholar.
| Security & Crypto | Networking & Database | Software Engineering & Programming Language | Machine Learning |
|---|---|---|---|
| IEEE S&P | SIGMETRICS | ICSE | AAAI |
| ACM CCS | ICDE | ESEC/FSE | ACL |
| USENIX Security | VLDB | ASE | ICML |
| NDSS | ACM SIGMOD | ACM PLDI | NeurIPS |
| IEEE DSN | IEEE INFOCOM | ACM OOPSLA | |
| SRCS | IMC | ISSTA | |
| RAID | WWW | ACM POPL | |
| CAV |
Large Language Models for Blockchain Security: A Systematic Literature Review.
A survey on large language model (llm) security and privacy: The good, the bad, and the ugly.
Large language models for software engineering: A systematic literature review.
Securing Large Language Models: Threats, Vulnerabilities and Responsible Practices.
Unveiling security, privacy, and ethical concerns of chatgpt.
On Large Language Models’ Resilience to Coercive Interrogation.
Combing for Credentials: Active Pattern Extraction from Smart Reply.
DrSec: Flexible Distributed Representations for Efficient Endpoint Security.
Moderating New Waves of Online Hate with Chain-of-Thought Reasoning in LargeLanguage Models.
TROJANPUZZLE: Covertly Poisoning Code-Suggestion Models.
Transferable Multimoda!Attack on Vision-LanguagePre-Training Models.
SMARTINV: Multimodal Learning for Smart Contract Invariant Inference.
LLMIF: Augmented Large Language Model for Fuzzing IoT Devices.
Examining zero-shot vulnerability repair with large language models.
Analyzing Leakage of Personally Identifiable Information in Language Models.
Asleep at the Keyboard? Assessing the Security of GitHub Copilot's Code Contributions.
Spinning language models: Risks of propaganda-as-a-service and countermeasures.
Privacy risks of general-purpose language models
PromptFuzz: Prompt Fuzzing for Fuzz Driver Generation.
Stealing the Decoding Algorithms of Language Models.
Large Language Models for Code: Security Hardening and Adversarial Testing.
Protecting intellectual property of large language model-based code generation apis via watermarks.
Dp-forward: Fine-tuning and inference on language models with differential privacy in forward pass.
Rapid Adoption, Hidden Risks: The Dual Impact of Large Language Model Customization.
PENTESTGPT: An LLM-empowered Automatic Penetration Testing Tool
Don't Listen To Me: Understanding and Exploring Jailbreak Prompts of Large Language Models.
Large Language Models for Code Analysis: Do LLMs Really Do Their Job?.
EaTVul: ChatGPT-based Evasion Attack Against Software Vulnerability Detection.
Fuzzing BusyBox: Leveraging LLM and Crash Reuse for Embedded Bug Unearthing.
Prompt Stealing Attacks Against Text-to-Image Generation Models.
Lost at c: A user study on the security implications of large language model code assistants.
CodexLeaks: Privacy Leaks from Code Generation Language Models in GitHub Copilot.
{Two-in-One}: A Model Hijacking Attack Against Text Generation Models.
Extracting Training Data from Large Language Models.
You Autocomplete Me: Poisoning Vulnerabilities in Neural Code Completion.
LMSanitator: Defending Prompt-Tuning Against Task-Agnostic Backdoors
MASTERKEY: Automated Jailbreaking of Large Language Model Chatbots.
DeGPT: Optimizing Decompiler Output with LLM.
DEMASQ: Unmasking the ChatGPT Wordsmith.
Large Language Model guided Protocol Fuzzing.
Facilitating Threat Modeling by Leveraging Large Language Models
Enhancing Static Analysis for Practical Bug Detection: An LLM-Integrated Approach.
PyDex: Repairing Bugs in Introductory Python Assignments using LLMs.
Large Language Models are Edge-Case Fuzzers: Testing Deep Learning Libraries via FuzzGPT
Fuzz4All: Universal Fuzzing with Large Language Models.
LLMParser: An Exploratory Study on Using Large Language Models for Log Parsing.
Exploring the Potential of ChatGPT in Automated Code Refinement: An Empirical Study.
Large Language Models are Edge-Case Fuzzers: Testing Deep Learning Libraries via FuzzGPT.
UniLog: Automatic Logging via LLM and In-Context Learning.
Prompting Is All You Need: Automated Android Bug Replay with Large Language Models.
Large Language Models for Test-Free Fault Localization.
Large language models are few-shot testers: Exploring llm-based general bug reproduction.
GPTScan: Detecting Logic Vulnerabilities in Smart Contracts by Combining GPT with Program Analysis.
Automated Program Repair in the Era of Large Pre-trained Language Models.
Does data sampling improve deep learning-based vulnerability detection? Yeas! and Nays!.
An Empirical Study of Deep Learning Models for Vulnerability Detection.
RepresentThemAll: A Universal Learning Representation of Bug Reports.
Contrabert: Enhancing code pre-trained models via contrastive learning.
On the robustness of code generation techniques: An empirical study on github copilot.
Two sides of the same coin: Exploiting the impact of identifiers in neural code comprehension.
Automated repair of programs from large language models.
Cctest: Testing and repairing code completion systems.
CodaMosa: Escaping Coverage Plateaus in Test Generation with Pre-trained Large Language Models.
Impact of Code Language Models on Automated Program Repair.
ReCode: Robustness Evaluation of Code Generation Models.
Better Patching Using LLM Prompting, via Self-Consistency.
Towards Autonomous Testing Agents via Conversational Large Language Models.
Let's Chat to Find the APIs: Connecting Human, LLM and Knowledge Graph through AI Chain.
Log Parsing: How Far Can ChatGPT Go?.
Robust Learning of Deep Predictive Models from Noisy and Imbalanced Software Engineering Datasets.
How Effective Are Neural Networks for Fixing Security Vulnerabilities.
InferFix: End-to-End Program Repair with LLMs.
Getting pwn'd by ai: Penetration testing with large language models.
Llm-based code generation method for golang compiler testing.
Assisting static analysis with large language models: A chatgpt experiment.
Assess and Summarize: Improve Outage Understanding with Large Language Models.
Generating realistic vulnerabilities via neural code editing: an empirical study.
You see what I want you to see: poisoning vulnerabilities in neural code search.
Vulnerability detection with fine-grained interpretations.
Not the end of story: An evaluation of chatgpt-driven vulnerability description mappings.
Understanding Programs by Exploiting (Fuzzing) Test Cases.
Backdooring Neural Code Search.
Membership inference attacks against language models via neighbourhood comparison.
ReCode: Robustness Evaluation of Code Generation Models.
Knowledge unlearning for mitigating privacy risks in language models.
Contamination attacks and mitigation in multi-party machine learning.
Adversarial Robustness of Deep Code Comment Generation.
Bag of tricks for training data extraction from language models.
Deduplicating training data mitigates privacy risks in language models.
Recovering private text in federated learning of language models.
ZipZap: Efficient Training of Language Models for Large-Scale Fraud Detection on Blockchain.
Coprotector: Protect open-source code against unauthorized training usage with data poisoning.
(Security) Assertions by Large Language Models.
A Performance-Sensitive Malware Detection System Using Deep Learning on Mobile DevicesA Performance-Sensitive Malware Detection System Using Deep Learning on Mobile Devices.
PrivacyAsst: Safeguarding User Privacy in Tool-Using Large Language Model Agents.
CD-VulD: Cross-Domain Vulnerability Discovery Based on Deep Domain Adaptation.
Software Testing with Large Language Models: Survey, Landscape, and Vision.
An Empirical Evaluation of Using Large Language Models for Automated Unit Test Generation.
Deep Learning Based Vulnerability Detection: Are We There Yet?.
On the Value of Oversampling for Deep Learning in Software Defect Prediction.
Prompt Sapper: A LLM-Empowered Production Tool for Building AI Chains.
Adversarial Robustness of Deep Code Comment Generation .
LLM4Fuzz: Guided Fuzzing of Smart Contracts with Large Language Models
CHEMFUZZ: Large Language Models-assisted Fuzzing for Quantum Chemistry Software Bug Detection
Attack Prompt Generation for Red Teaming and Defending Large Language Models
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for Academic_LLM_Sec_Papers
Similar Open Source Tools

Academic_LLM_Sec_Papers
Academic_LLM_Sec_Papers is a curated collection of academic papers related to LLM Security Application. The repository includes papers sorted by conference name and published year, covering topics such as large language models for blockchain security, software engineering, machine learning, and more. Developers and researchers are welcome to contribute additional published papers to the list. The repository also provides information on listed conferences and journals related to security, networking, software engineering, and cryptography. The papers cover a wide range of topics including privacy risks, ethical concerns, vulnerabilities, threat modeling, code analysis, fuzzing, and more.
awesome-MLSecOps
Awesome MLSecOps is a curated list of open-source tools, resources, and tutorials for MLSecOps (Machine Learning Security Operations). It includes a wide range of security tools and libraries for protecting machine learning models against adversarial attacks, as well as resources for AI security, data anonymization, model security, and more. The repository aims to provide a comprehensive collection of tools and information to help users secure their machine learning systems and infrastructure.
Prompt_Engineering
Prompt Engineering Techniques is a comprehensive repository for learning, building, and sharing prompt engineering techniques, from basic concepts to advanced strategies for leveraging large language models. It provides step-by-step tutorials, practical implementations, and a platform for showcasing innovative prompt engineering techniques. The repository covers fundamental concepts, core techniques, advanced strategies, optimization and refinement, specialized applications, and advanced applications in prompt engineering.

LMOps
LMOps is a research initiative focusing on fundamental research and technology for building AI products with foundation models, particularly enabling AI capabilities with Large Language Models (LLMs) and Generative AI models. The project explores various aspects such as prompt optimization, longer context handling, LLM alignment, acceleration of LLMs, LLM customization, and understanding in-context learning. It also includes tools like Promptist for automatic prompt optimization, Structured Prompting for efficient long-sequence prompts consumption, and X-Prompt for extensible prompts beyond natural language. Additionally, LLMA accelerators are developed to speed up LLM inference by referencing and copying text spans from documents. The project aims to advance technologies that facilitate prompting language models and enhance the performance of LLMs in various scenarios.
Next-Generation-LLM-based-Recommender-Systems-Survey
The Next-Generation LLM-based Recommender Systems Survey is a comprehensive overview of the latest advancements in recommender systems leveraging Large Language Models (LLMs). The survey covers various paradigms, approaches, and applications of LLMs in recommendation tasks, including generative and non-generative models, multimodal recommendations, personalized explanations, and industrial deployment. It discusses the comparison with existing surveys, different paradigms, and specific works in the field. The survey also addresses challenges and future directions in the domain of LLM-based recommender systems.
GenAI_Agents
GenAI Agents is a comprehensive repository for developing and implementing Generative AI (GenAI) agents, ranging from simple conversational bots to complex multi-agent systems. It serves as a valuable resource for learning, building, and sharing GenAI agents, offering tutorials, implementations, and a platform for showcasing innovative agent creations. The repository covers a wide range of agent architectures and applications, providing step-by-step tutorials, ready-to-use implementations, and regular updates on advancements in GenAI technology.
FATE-LLM
FATE-LLM is a framework supporting federated learning for large and small language models. It promotes training efficiency of federated LLMs using Parameter-Efficient methods, protects the IP of LLMs using FedIPR, and ensures data privacy during training and inference through privacy-preserving mechanisms.

fenic
fenic is an opinionated DataFrame framework from typedef.ai for building AI and agentic applications. It transforms unstructured and structured data into insights using familiar DataFrame operations enhanced with semantic intelligence. With support for markdown, transcripts, and semantic operators, plus efficient batch inference across various model providers. fenic is purpose-built for LLM inference, providing a query engine designed for AI workloads, semantic operators as first-class citizens, native unstructured data support, production-ready infrastructure, and a familiar DataFrame API.
long-llms-learning
A repository sharing the panorama of the methodology literature on Transformer architecture upgrades in Large Language Models for handling extensive context windows, with real-time updating the newest published works. It includes a survey on advancing Transformer architecture in long-context large language models, flash-ReRoPE implementation, latest news on data engineering, lightning attention, Kimi AI assistant, chatglm-6b-128k, gpt-4-turbo-preview, benchmarks like InfiniteBench and LongBench, long-LLMs-evals for evaluating methods for enhancing long-context capabilities, and LLMs-learning for learning technologies and applicated tasks about Large Language Models.
llm-course
The LLM course is divided into three parts: 1. 🧩 **LLM Fundamentals** covers essential knowledge about mathematics, Python, and neural networks. 2. 🧑🔬 **The LLM Scientist** focuses on building the best possible LLMs using the latest techniques. 3. 👷 **The LLM Engineer** focuses on creating LLM-based applications and deploying them. For an interactive version of this course, I created two **LLM assistants** that will answer questions and test your knowledge in a personalized way: * 🤗 **HuggingChat Assistant**: Free version using Mixtral-8x7B. * 🤖 **ChatGPT Assistant**: Requires a premium account. ## 📝 Notebooks A list of notebooks and articles related to large language models. ### Tools | Notebook | Description | Notebook | |----------|-------------|----------| | 🧐 LLM AutoEval | Automatically evaluate your LLMs using RunPod |  | | 🥱 LazyMergekit | Easily merge models using MergeKit in one click. |  | | 🦎 LazyAxolotl | Fine-tune models in the cloud using Axolotl in one click. |  | | ⚡ AutoQuant | Quantize LLMs in GGUF, GPTQ, EXL2, AWQ, and HQQ formats in one click. |  | | 🌳 Model Family Tree | Visualize the family tree of merged models. |  | | 🚀 ZeroSpace | Automatically create a Gradio chat interface using a free ZeroGPU. |  |
awesome-lifelong-llm-agent
This repository is a collection of papers and resources related to Lifelong Learning of Large Language Model (LLM) based Agents. It focuses on continual learning and incremental learning of LLM agents, identifying key modules such as Perception, Memory, and Action. The repository serves as a roadmap for understanding lifelong learning in LLM agents and provides a comprehensive overview of related research and surveys.
langkit
LangKit is an open-source text metrics toolkit for monitoring language models. It offers methods for extracting signals from input/output text, compatible with whylogs. Features include text quality, relevance, security, sentiment, toxicity analysis. Installation via PyPI. Modules contain UDFs for whylogs. Benchmarks show throughput on AWS instances. FAQs available.
BitMat
BitMat is a Python package designed to optimize matrix multiplication operations by utilizing custom kernels written in Triton. It leverages the principles outlined in the "1bit-LLM Era" paper, specifically utilizing packed int8 data to enhance computational efficiency and performance in deep learning and numerical computing tasks.
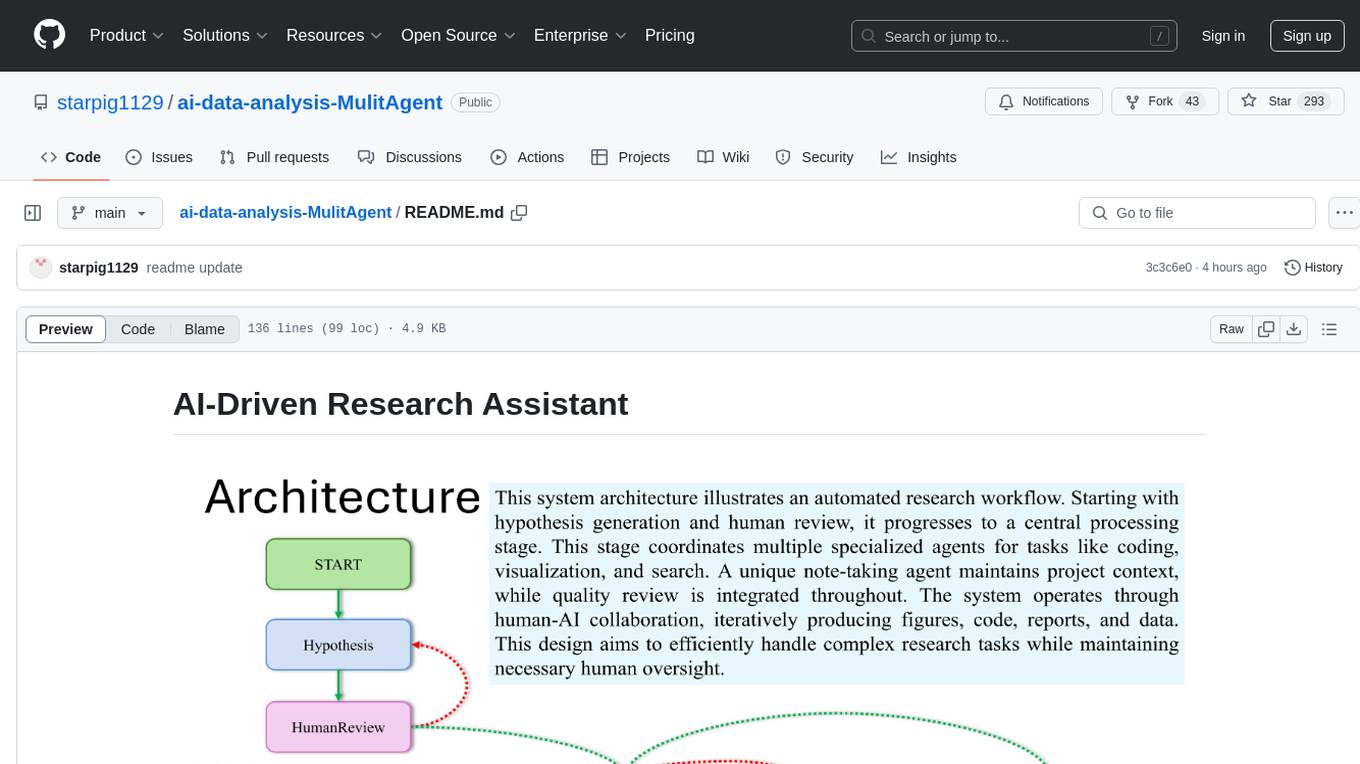
ai-data-analysis-MulitAgent
AI-Driven Research Assistant is an advanced AI-powered system utilizing specialized agents for data analysis, visualization, and report generation. It integrates LangChain, OpenAI's GPT models, and LangGraph for complex research processes. Key features include hypothesis generation, data processing, web search, code generation, and report writing. The system's unique Note Taker agent maintains project state, reducing overhead and improving context retention. System requirements include Python 3.10+ and Jupyter Notebook environment. Installation involves cloning the repository, setting up a Conda virtual environment, installing dependencies, and configuring environment variables. Usage instructions include setting data, running Jupyter Notebook, customizing research tasks, and viewing results. Main components include agents for hypothesis generation, process supervision, visualization, code writing, search, report writing, quality review, and note-taking. Workflow involves hypothesis generation, processing, quality review, and revision. Customization is possible by modifying agent creation and workflow definition. Current issues include OpenAI errors, NoteTaker efficiency, runtime optimization, and refiner improvement. Contributions via pull requests are welcome under the MIT License.

agentUniverse
agentUniverse is a multi-agent framework based on large language models, providing flexible capabilities for building individual agents. It focuses on collaborative pattern components to solve problems in various fields and integrates domain experience. The framework supports LLM model integration and offers various pattern components like PEER and DOE. Users can easily configure models and set up agents for tasks. agentUniverse aims to assist developers and enterprises in constructing domain-expert-level intelligent agents for seamless collaboration.
For similar tasks

Academic_LLM_Sec_Papers
Academic_LLM_Sec_Papers is a curated collection of academic papers related to LLM Security Application. The repository includes papers sorted by conference name and published year, covering topics such as large language models for blockchain security, software engineering, machine learning, and more. Developers and researchers are welcome to contribute additional published papers to the list. The repository also provides information on listed conferences and journals related to security, networking, software engineering, and cryptography. The papers cover a wide range of topics including privacy risks, ethical concerns, vulnerabilities, threat modeling, code analysis, fuzzing, and more.

HackBot
HackBot is an AI-powered cybersecurity chatbot designed to provide accurate answers to cybersecurity-related queries, conduct code analysis, and scan analysis. It utilizes the Meta-LLama2 AI model through the 'LlamaCpp' library to respond coherently. The chatbot offers features like local AI/Runpod deployment support, cybersecurity chat assistance, interactive interface, clear output presentation, static code analysis, and vulnerability analysis. Users can interact with HackBot through a command-line interface and utilize it for various cybersecurity tasks.
vulnerability-analysis
The NVIDIA AI Blueprint for Vulnerability Analysis for Container Security showcases accelerated analysis on common vulnerabilities and exposures (CVE) at an enterprise scale, reducing mitigation time from days to seconds. It enables security analysts to determine software package vulnerabilities using large language models (LLMs) and retrieval-augmented generation (RAG). The blueprint is designed for security analysts, IT engineers, and AI practitioners in cybersecurity. It requires NVAIE developer license and API keys for vulnerability databases, search engines, and LLM model services. Hardware requirements include L40 GPU for pipeline operation and optional LLM NIM and Embedding NIM. The workflow involves LLM pipeline for CVE impact analysis, utilizing LLM planner, agent, and summarization nodes. The blueprint uses NVIDIA NIM microservices and Morpheus Cybersecurity AI SDK for vulnerability analysis.
Mirror-Flowers
Mirror Flowers is an out-of-the-box code security auditing tool that integrates local static scanning (line-level taint tracking + AST) with AI verification to help quickly discover and locate high-risk issues, providing repair suggestions. It supports multiple languages such as PHP, Python, JavaScript/TypeScript, and Java. The tool offers both single-file and project modes, with features like concurrent acceleration, integrated UI for visual results, and compatibility with multiple OpenAI interface providers. Users can configure the tool through environment variables or API, and can utilize it through a web UI or HTTP API for tasks like single-file auditing or project auditing.
run-gemini-cli
run-gemini-cli is a GitHub Action that integrates Gemini into your development workflow via the Gemini CLI. It acts as an autonomous agent for routine coding tasks and an on-demand collaborator. Use it for GitHub pull request reviews, triaging issues, code analysis, and more. It provides automation, on-demand collaboration, extensibility with tools, and customization options.
For similar jobs
last_layer
last_layer is a security library designed to protect LLM applications from prompt injection attacks, jailbreaks, and exploits. It acts as a robust filtering layer to scrutinize prompts before they are processed by LLMs, ensuring that only safe and appropriate content is allowed through. The tool offers ultra-fast scanning with low latency, privacy-focused operation without tracking or network calls, compatibility with serverless platforms, advanced threat detection mechanisms, and regular updates to adapt to evolving security challenges. It significantly reduces the risk of prompt-based attacks and exploits but cannot guarantee complete protection against all possible threats.
aircrack-ng
Aircrack-ng is a comprehensive suite of tools designed to evaluate the security of WiFi networks. It covers various aspects of WiFi security, including monitoring, attacking (replay attacks, deauthentication, fake access points), testing WiFi cards and driver capabilities, and cracking WEP and WPA PSK. The tools are command line-based, allowing for extensive scripting and have been utilized by many GUIs. Aircrack-ng primarily works on Linux but also supports Windows, macOS, FreeBSD, OpenBSD, NetBSD, Solaris, and eComStation 2.
reverse-engineering-assistant
ReVA (Reverse Engineering Assistant) is a project aimed at building a disassembler agnostic AI assistant for reverse engineering tasks. It utilizes a tool-driven approach, providing small tools to the user to empower them in completing complex tasks. The assistant is designed to accept various inputs, guide the user in correcting mistakes, and provide additional context to encourage exploration. Users can ask questions, perform tasks like decompilation, class diagram generation, variable renaming, and more. ReVA supports different language models for online and local inference, with easy configuration options. The workflow involves opening the RE tool and program, then starting a chat session to interact with the assistant. Installation includes setting up the Python component, running the chat tool, and configuring the Ghidra extension for seamless integration. ReVA aims to enhance the reverse engineering process by breaking down actions into small parts, including the user's thoughts in the output, and providing support for monitoring and adjusting prompts.
AutoAudit
AutoAudit is an open-source large language model specifically designed for the field of network security. It aims to provide powerful natural language processing capabilities for security auditing and network defense, including analyzing malicious code, detecting network attacks, and predicting security vulnerabilities. By coupling AutoAudit with ClamAV, a security scanning platform has been created for practical security audit applications. The tool is intended to assist security professionals with accurate and fast analysis and predictions to combat evolving network threats.
aif
Arno's Iptables Firewall (AIF) is a single- & multi-homed firewall script with DSL/ADSL support. It is a free software distributed under the GNU GPL License. The script provides a comprehensive set of configuration files and plugins for setting up and managing firewall rules, including support for NAT, load balancing, and multirouting. It offers detailed instructions for installation and configuration, emphasizing security best practices and caution when modifying settings. The script is designed to protect against hostile attacks by blocking all incoming traffic by default and allowing users to configure specific rules for open ports and network interfaces.

watchtower
AIShield Watchtower is a tool designed to fortify the security of AI/ML models and Jupyter notebooks by automating model and notebook discoveries, conducting vulnerability scans, and categorizing risks into 'low,' 'medium,' 'high,' and 'critical' levels. It supports scanning of public GitHub repositories, Hugging Face repositories, AWS S3 buckets, and local systems. The tool generates comprehensive reports, offers a user-friendly interface, and aligns with industry standards like OWASP, MITRE, and CWE. It aims to address the security blind spots surrounding Jupyter notebooks and AI models, providing organizations with a tailored approach to enhancing their security efforts.

Academic_LLM_Sec_Papers
Academic_LLM_Sec_Papers is a curated collection of academic papers related to LLM Security Application. The repository includes papers sorted by conference name and published year, covering topics such as large language models for blockchain security, software engineering, machine learning, and more. Developers and researchers are welcome to contribute additional published papers to the list. The repository also provides information on listed conferences and journals related to security, networking, software engineering, and cryptography. The papers cover a wide range of topics including privacy risks, ethical concerns, vulnerabilities, threat modeling, code analysis, fuzzing, and more.
DeGPT
DeGPT is a tool designed to optimize decompiler output using Large Language Models (LLM). It requires manual installation of specific packages and setting up API key for OpenAI. The tool provides functionality to perform optimization on decompiler output by running specific scripts.