
inference
Replace OpenAI GPT with another LLM in your app by changing a single line of code. Xinference gives you the freedom to use any LLM you need. With Xinference, you're empowered to run inference with any open-source language models, speech recognition models, and multimodal models, whether in the cloud, on-premises, or even on your laptop.
Stars: 8561
Xorbits Inference (Xinference) is a powerful and versatile library designed to serve language, speech recognition, and multimodal models. With Xorbits Inference, you can effortlessly deploy and serve your or state-of-the-art built-in models using just a single command. Whether you are a researcher, developer, or data scientist, Xorbits Inference empowers you to unleash the full potential of cutting-edge AI models.
README:
Xorbits Inference(Xinference) is a powerful and versatile library designed to serve language, speech recognition, and multimodal models. With Xorbits Inference, you can effortlessly deploy and serve your or state-of-the-art built-in models using just a single command. Whether you are a researcher, developer, or data scientist, Xorbits Inference empowers you to unleash the full potential of cutting-edge AI models.
- Xllamacpp: New llama.cpp Python binding, maintained by Xinference team, supports continuous batching and is more production-ready.: #2997
- Distributed inference: running models across workers: #2877
- VLLM enhancement: Shared KV cache across multiple replicas: #2732
- Support Continuous batching for Transformers engine: #1724
- Support MLX backend for Apple Silicon chips: #1765
- Support specifying worker and GPU indexes for launching models: #1195
- Support SGLang backend: #1161
- Support LoRA for LLM and image models: #1080
- Built-in support for Deepseek-V3.1: #4022
- Built-in support for Qwen-Image-Edit: #3989
- Built-in support for Wan2.2: #3996
- Built-in support for seed-oss: #4020
- Built-in support for gpt-oss: #3924
- Built-in support for GLM-4.5v: #3957
- Built-in support for Qwen-Image: #3916
- Built-in support for GLM-4.5: #3882
- Dify: an LLMOps platform that enables developers (and even non-developers) to quickly build useful applications based on large language models, ensuring they are visual, operable, and improvable.
- FastGPT: a knowledge-based platform built on the LLM, offers out-of-the-box data processing and model invocation capabilities, allows for workflow orchestration through Flow visualization.
- RAGFlow: is an open-source RAG engine based on deep document understanding.
- MaxKB: MaxKB = Max Knowledge Base, it is a chatbot based on Large Language Models (LLM) and Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG).
- Chatbox: a desktop client for multiple cutting-edge LLM models, available on Windows, Mac and Linux.
🌟 Model Serving Made Easy: Simplify the process of serving large language, speech recognition, and multimodal models. You can set up and deploy your models for experimentation and production with a single command.
⚡️ State-of-the-Art Models: Experiment with cutting-edge built-in models using a single command. Inference provides access to state-of-the-art open-source models!
🖥 Heterogeneous Hardware Utilization: Make the most of your hardware resources with ggml. Xorbits Inference intelligently utilizes heterogeneous hardware, including GPUs and CPUs, to accelerate your model inference tasks.
⚙️ Flexible API and Interfaces: Offer multiple interfaces for interacting with your models, supporting OpenAI compatible RESTful API (including Function Calling API), RPC, CLI and WebUI for seamless model management and interaction.
🌐 Distributed Deployment: Excel in distributed deployment scenarios, allowing the seamless distribution of model inference across multiple devices or machines.
🔌 Built-in Integration with Third-Party Libraries: Xorbits Inference seamlessly integrates with popular third-party libraries including LangChain, LlamaIndex, Dify, and Chatbox.
| Feature | Xinference | FastChat | OpenLLM | RayLLM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OpenAI-Compatible RESTful API | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| vLLM Integrations | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| More Inference Engines (GGML, TensorRT) | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ |
| More Platforms (CPU, Metal) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Multi-node Cluster Deployment | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ |
| Image Models (Text-to-Image) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Text Embedding Models | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Multimodal Models | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Audio Models | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
| More OpenAI Functionalities (Function Calling) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
-
Cloud We host a Xinference Cloud service for anyone to try with zero setup.
-
Self-hosting Xinference Community Edition Quickly get Xinference running in your environment with this starter guide. Use our documentation for further references and more in-depth instructions.
-
Xinference for enterprise / organizations We provide additional enterprise-centric features. send us an email to discuss enterprise needs.
Star Xinference on GitHub and be instantly notified of new releases.
The lightest way to experience Xinference is to try our Jupyter Notebook on Google Colab.
Nvidia GPU users can start Xinference server using Xinference Docker Image. Prior to executing the installation command, ensure that both Docker and CUDA are set up on your system.
docker run --name xinference -d -p 9997:9997 -e XINFERENCE_HOME=/data -v </on/your/host>:/data --gpus all xprobe/xinference:latest xinference-local -H 0.0.0.0Ensure that you have GPU support in your Kubernetes cluster, then install as follows.
# add repo
helm repo add xinference https://xorbitsai.github.io/xinference-helm-charts
# update indexes and query xinference versions
helm repo update xinference
helm search repo xinference/xinference --devel --versions
# install xinference
helm install xinference xinference/xinference -n xinference --version 0.0.1-v<xinference_release_version>
For more customized installation methods on K8s, please refer to the documentation.
Install Xinference by using pip as follows. (For more options, see Installation page.)
pip install "xinference[all]"To start a local instance of Xinference, run the following command:
$ xinference-localOnce Xinference is running, there are multiple ways you can try it: via the web UI, via cURL, via the command line, or via the Xinference’s python client. Check out our docs for the guide.
| Platform | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Github Issues | Reporting bugs and filing feature requests. |
| Discord | Collaborating with other Xinference users. |
| Staying up-to-date on new features. |
If this work is helpful, please kindly cite as:
@inproceedings{lu2024xinference,
title = "Xinference: Making Large Model Serving Easy",
author = "Lu, Weizheng and Xiong, Lingfeng and Zhang, Feng and Qin, Xuye and Chen, Yueguo",
booktitle = "Proceedings of the 2024 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing: System Demonstrations",
month = nov,
year = "2024",
address = "Miami, Florida, USA",
publisher = "Association for Computational Linguistics",
url = "https://aclanthology.org/2024.emnlp-demo.30",
pages = "291--300",
}For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for inference
Similar Open Source Tools

inference
Xorbits Inference (Xinference) is a powerful and versatile library designed to serve language, speech recognition, and multimodal models. With Xorbits Inference, you can effortlessly deploy and serve your or state-of-the-art built-in models using just a single command. Whether you are a researcher, developer, or data scientist, Xorbits Inference empowers you to unleash the full potential of cutting-edge AI models.

openrl
OpenRL is an open-source general reinforcement learning research framework that supports training for various tasks such as single-agent, multi-agent, offline RL, self-play, and natural language. Developed based on PyTorch, the goal of OpenRL is to provide a simple-to-use, flexible, efficient and sustainable platform for the reinforcement learning research community. It supports a universal interface for all tasks/environments, single-agent and multi-agent tasks, offline RL training with expert dataset, self-play training, reinforcement learning training for natural language tasks, DeepSpeed, Arena for evaluation, importing models and datasets from Hugging Face, user-defined environments, models, and datasets, gymnasium environments, callbacks, visualization tools, unit testing, and code coverage testing. It also supports various algorithms like PPO, DQN, SAC, and environments like Gymnasium, MuJoCo, Atari, and more.
beeai-framework
BeeAI Framework is a versatile tool for building production-ready multi-agent systems. It offers flexibility in orchestrating agents, seamless integration with various models and tools, and production-grade controls for scaling. The framework supports Python and TypeScript libraries, enabling users to implement simple to complex multi-agent patterns, connect with AI services, and optimize token usage and resource management.
FlagEmbedding
FlagEmbedding focuses on retrieval-augmented LLMs, consisting of the following projects currently: * **Long-Context LLM** : Activation Beacon * **Fine-tuning of LM** : LM-Cocktail * **Embedding Model** : Visualized-BGE, BGE-M3, LLM Embedder, BGE Embedding * **Reranker Model** : llm rerankers, BGE Reranker * **Benchmark** : C-MTEB
SimAI
SimAI is the industry's first full-stack, high-precision simulator for AI large-scale training. It provides detailed modeling and simulation of the entire LLM training process, encompassing framework, collective communication, network layers, and more. This comprehensive approach offers end-to-end performance data, enabling researchers to analyze training process details, evaluate time consumption of AI tasks under specific conditions, and assess performance gains from various algorithmic optimizations.
PURE
PURE (Process-sUpervised Reinforcement lEarning) is a framework that trains a Process Reward Model (PRM) on a dataset and fine-tunes a language model to achieve state-of-the-art mathematical reasoning capabilities. It uses a novel credit assignment method to calculate return and supports multiple reward types. The final model outperforms existing methods with minimal RL data or compute resources, achieving high accuracy on various benchmarks. The tool addresses reward hacking issues and aims to enhance long-range decision-making and reasoning tasks using large language models.
Dokugen
Dokugen is a lightweight README.md file Generator Command Line Interface Tool that simplifies the process of writing README.md files by generating professional READMEs for projects, saving time and ensuring consistency using AI. It automates the most neglected part of a repo, resulting in cleaner projects and happier contributors.
MiniCPM-V
MiniCPM-V is a series of end-side multimodal LLMs designed for vision-language understanding. The models take image and text inputs to provide high-quality text outputs. The series includes models like MiniCPM-Llama3-V 2.5 with 8B parameters surpassing proprietary models, and MiniCPM-V 2.0, a lighter model with 2B parameters. The models support over 30 languages, efficient deployment on end-side devices, and have strong OCR capabilities. They achieve state-of-the-art performance on various benchmarks and prevent hallucinations in text generation. The models can process high-resolution images efficiently and support multilingual capabilities.
NSMusicS
NSMusicS is a local music software that is expected to support multiple platforms with AI capabilities and multimodal features. The goal of NSMusicS is to integrate various functions (such as artificial intelligence, streaming, music library management, cross platform, etc.), which can be understood as similar to Navidrome but with more features than Navidrome. It wants to become a plugin integrated application that can almost have all music functions.
LLaVA-MORE
LLaVA-MORE is a new family of Multimodal Language Models (MLLMs) that integrates recent language models with diverse visual backbones. The repository provides a unified training protocol for fair comparisons across all architectures and releases training code and scripts for distributed training. It aims to enhance Multimodal LLM performance and offers various models for different tasks. Users can explore different visual backbones like SigLIP and methods for managing image resolutions (S2) to improve the connection between images and language. The repository is a starting point for expanding the study of Multimodal LLMs and enhancing new features in the field.
InternLM-XComposer
InternLM-XComposer2 is a groundbreaking vision-language large model (VLLM) based on InternLM2-7B excelling in free-form text-image composition and comprehension. It boasts several amazing capabilities and applications: * **Free-form Interleaved Text-Image Composition** : InternLM-XComposer2 can effortlessly generate coherent and contextual articles with interleaved images following diverse inputs like outlines, detailed text requirements and reference images, enabling highly customizable content creation. * **Accurate Vision-language Problem-solving** : InternLM-XComposer2 accurately handles diverse and challenging vision-language Q&A tasks based on free-form instructions, excelling in recognition, perception, detailed captioning, visual reasoning, and more. * **Awesome performance** : InternLM-XComposer2 based on InternLM2-7B not only significantly outperforms existing open-source multimodal models in 13 benchmarks but also **matches or even surpasses GPT-4V and Gemini Pro in 6 benchmarks** We release InternLM-XComposer2 series in three versions: * **InternLM-XComposer2-4KHD-7B** 🤗: The high-resolution multi-task trained VLLM model with InternLM-7B as the initialization of the LLM for _High-resolution understanding_ , _VL benchmarks_ and _AI assistant_. * **InternLM-XComposer2-VL-7B** 🤗 : The multi-task trained VLLM model with InternLM-7B as the initialization of the LLM for _VL benchmarks_ and _AI assistant_. **It ranks as the most powerful vision-language model based on 7B-parameter level LLMs, leading across 13 benchmarks.** * **InternLM-XComposer2-VL-1.8B** 🤗 : A lightweight version of InternLM-XComposer2-VL based on InternLM-1.8B. * **InternLM-XComposer2-7B** 🤗: The further instruction tuned VLLM for _Interleaved Text-Image Composition_ with free-form inputs. Please refer to Technical Report and 4KHD Technical Reportfor more details.
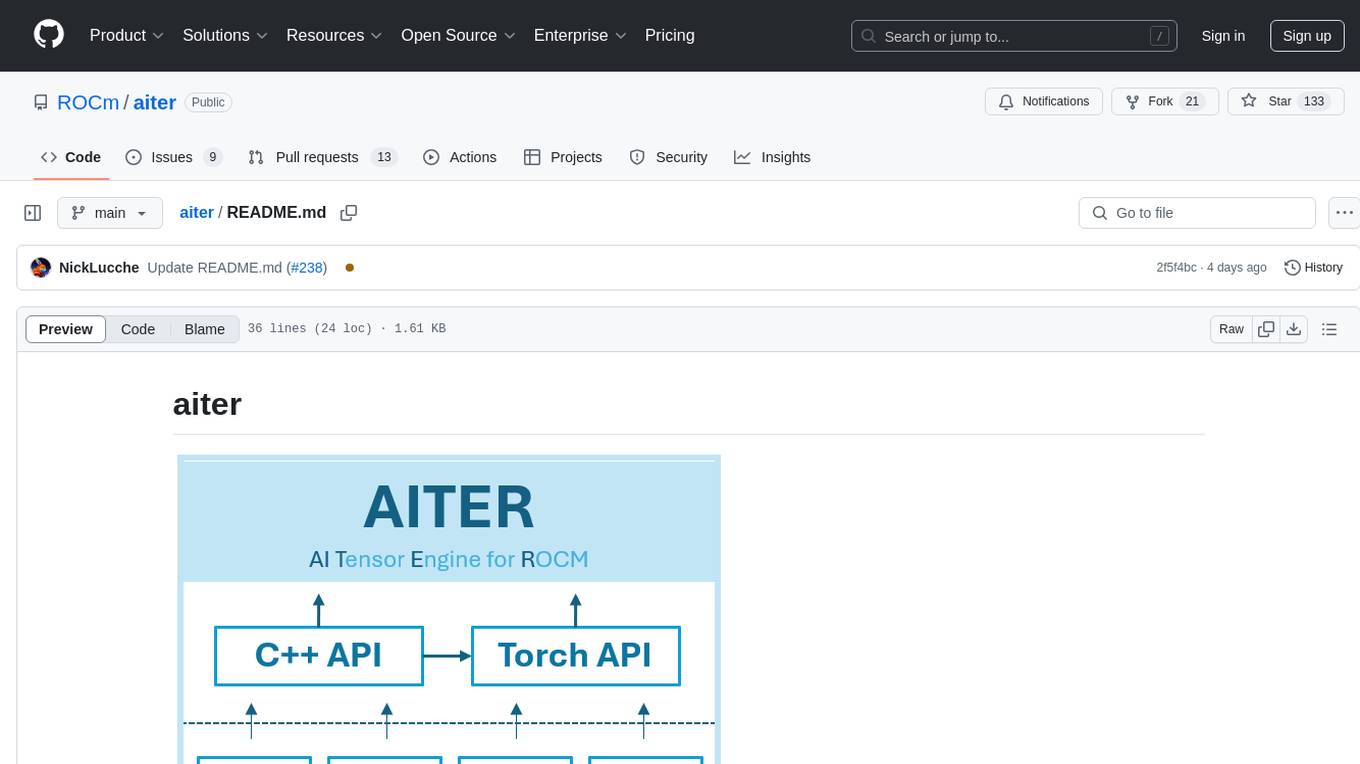
aiter
AITER is AMD’s centralized repository that supports various high performance AI operators for AI workloads acceleration. It serves as a unified platform for customer operator-level requests, catering to different customer needs. Developers can focus on operators and customers can integrate this collection into their own frameworks. Features include C++ and Python level APIs, kernels from triton/ck/asm, support for inference, training, GEMM, and communication kernels for workarounds in any kernel-framework combination for any architecture limitation.
BitBLAS
BitBLAS is a library for mixed-precision BLAS operations on GPUs, for example, the $W_{wdtype}A_{adtype}$ mixed-precision matrix multiplication where $C_{cdtype}[M, N] = A_{adtype}[M, K] \times W_{wdtype}[N, K]$. BitBLAS aims to support efficient mixed-precision DNN model deployment, especially the $W_{wdtype}A_{adtype}$ quantization in large language models (LLMs), for example, the $W_{UINT4}A_{FP16}$ in GPTQ, the $W_{INT2}A_{FP16}$ in BitDistiller, the $W_{INT2}A_{INT8}$ in BitNet-b1.58. BitBLAS is based on techniques from our accepted submission at OSDI'24.
VILA
VILA is a family of open Vision Language Models optimized for efficient video understanding and multi-image understanding. It includes models like NVILA, LongVILA, VILA-M3, VILA-U, and VILA-1.5, each offering specific features and capabilities. The project focuses on efficiency, accuracy, and performance in various tasks related to video, image, and language understanding and generation. VILA models are designed to be deployable on diverse NVIDIA GPUs and support long-context video understanding, medical applications, and multi-modal design.
aichat
Aichat is an AI-powered CLI chat and copilot tool that seamlessly integrates with over 10 leading AI platforms, providing a powerful combination of chat-based interaction, context-aware conversations, and AI-assisted shell capabilities, all within a customizable and user-friendly environment.
cambrian
Cambrian-1 is a fully open project focused on exploring multimodal Large Language Models (LLMs) with a vision-centric approach. It offers competitive performance across various benchmarks with models at different parameter levels. The project includes training configurations, model weights, instruction tuning data, and evaluation details. Users can interact with Cambrian-1 through a Gradio web interface for inference. The project is inspired by LLaVA and incorporates contributions from Vicuna, LLaMA, and Yi. Cambrian-1 is licensed under Apache 2.0 and utilizes datasets and checkpoints subject to their respective original licenses.
For similar tasks

ai-on-gke
This repository contains assets related to AI/ML workloads on Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE). Run optimized AI/ML workloads with Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) platform orchestration capabilities. A robust AI/ML platform considers the following layers: Infrastructure orchestration that support GPUs and TPUs for training and serving workloads at scale Flexible integration with distributed computing and data processing frameworks Support for multiple teams on the same infrastructure to maximize utilization of resources

ray
Ray is a unified framework for scaling AI and Python applications. It consists of a core distributed runtime and a set of AI libraries for simplifying ML compute, including Data, Train, Tune, RLlib, and Serve. Ray runs on any machine, cluster, cloud provider, and Kubernetes, and features a growing ecosystem of community integrations. With Ray, you can seamlessly scale the same code from a laptop to a cluster, making it easy to meet the compute-intensive demands of modern ML workloads.

labelbox-python
Labelbox is a data-centric AI platform for enterprises to develop, optimize, and use AI to solve problems and power new products and services. Enterprises use Labelbox to curate data, generate high-quality human feedback data for computer vision and LLMs, evaluate model performance, and automate tasks by combining AI and human-centric workflows. The academic & research community uses Labelbox for cutting-edge AI research.

djl
Deep Java Library (DJL) is an open-source, high-level, engine-agnostic Java framework for deep learning. It is designed to be easy to get started with and simple to use for Java developers. DJL provides a native Java development experience and allows users to integrate machine learning and deep learning models with their Java applications. The framework is deep learning engine agnostic, enabling users to switch engines at any point for optimal performance. DJL's ergonomic API interface guides users with best practices to accomplish deep learning tasks, such as running inference and training neural networks.

mlflow
MLflow is a platform to streamline machine learning development, including tracking experiments, packaging code into reproducible runs, and sharing and deploying models. MLflow offers a set of lightweight APIs that can be used with any existing machine learning application or library (TensorFlow, PyTorch, XGBoost, etc), wherever you currently run ML code (e.g. in notebooks, standalone applications or the cloud). MLflow's current components are:
* `MLflow Tracking
tt-metal
TT-NN is a python & C++ Neural Network OP library. It provides a low-level programming model, TT-Metalium, enabling kernel development for Tenstorrent hardware.
burn
Burn is a new comprehensive dynamic Deep Learning Framework built using Rust with extreme flexibility, compute efficiency and portability as its primary goals.
awsome-distributed-training
This repository contains reference architectures and test cases for distributed model training with Amazon SageMaker Hyperpod, AWS ParallelCluster, AWS Batch, and Amazon EKS. The test cases cover different types and sizes of models as well as different frameworks and parallel optimizations (Pytorch DDP/FSDP, MegatronLM, NemoMegatron...).
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.










