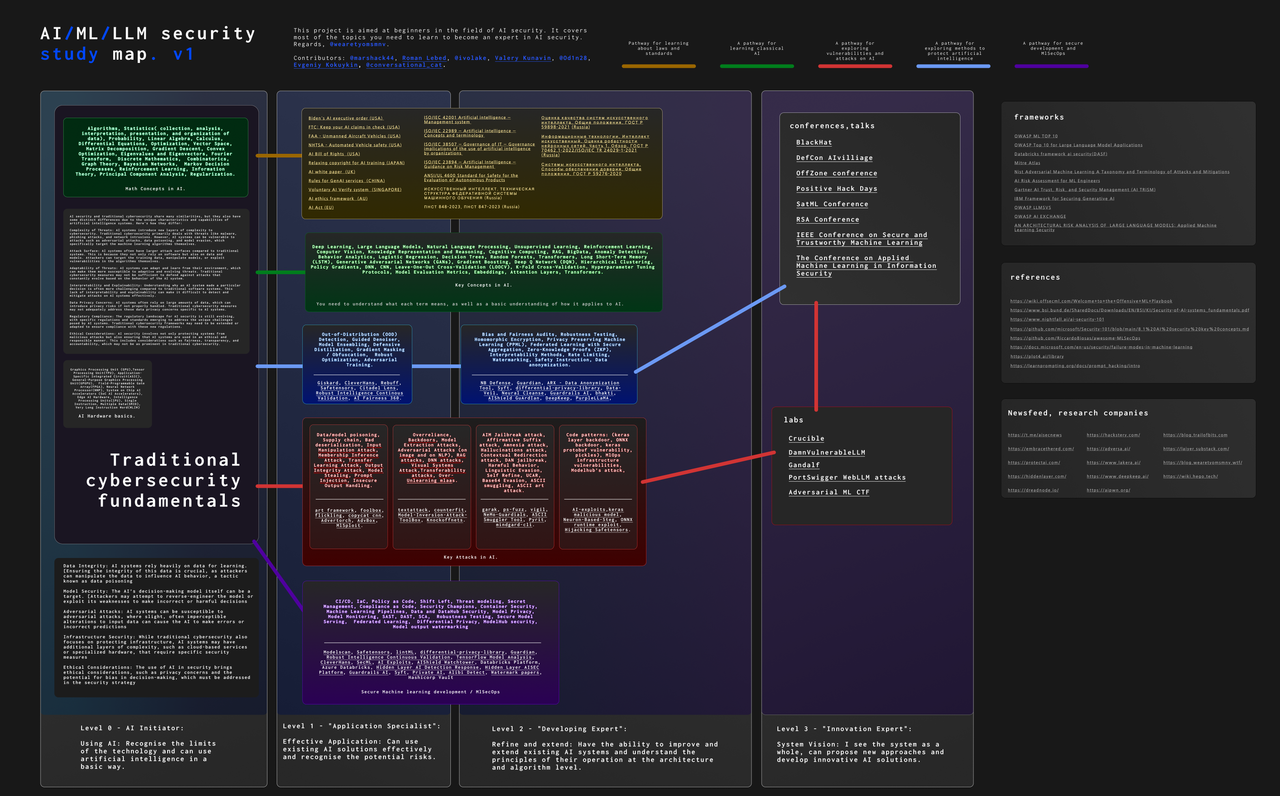
awesome-MLSecOps
A curated list of MLSecOps tools, articles and other resources on security applied to Machine Learning and MLOps systems.
Stars: 204
Awesome MLSecOps is a curated list of open-source tools, resources, and tutorials for MLSecOps (Machine Learning Security Operations). It includes a wide range of security tools and libraries for protecting machine learning models against adversarial attacks, as well as resources for AI security, data anonymization, model security, and more. The repository aims to provide a comprehensive collection of tools and information to help users secure their machine learning systems and infrastructure.
README:
A curated list of awesome open-source tools, resources, and tutorials for MLSecOps (Machine Learning Security Operations).
- Open Source Security Tools
- Commercial Tools
- DATA
- ML Code Security
- 101 Resources
- Attack Vectors
- Blogs and Publications
- MLOps Infrastructure Vulnerabilities
- Community Resources
- Infographics
- Contributions
- Contributors
In this section, you and I can take a look at what opensource solutions and PoCs, exist to accomplish the task of ML protection. Of course, some of them are unsupported or will have difficulties to run. However, not mentioning them is a big crime.
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| ModelScan | Protection Against ML Model Serialization Attacks |
| NB Defense | Secure Jupyter Notebooks |
| Garak | LLM vulnerability scanner |
| Adversarial Robustness Toolbox | Library of defense methods for ML models against adversarial attacks |
| MLSploit | Cloud framework for interactive experimentation with adversarial machine learning research |
| TensorFlow Privacy | Library of privacy-preserving machine learning algorithms and tools |
| Foolbox | Python toolbox for creating and evaluating adversarial attacks and defenses |
| Advertorch | Python toolbox for adversarial robustness research |
| Artificial Intelligence Threat Matrix | Framework for identifying and mitigating threats to machine learning systems |
| Adversarial ML Threat Matrix | Adversarial Threat Landscape for AI Systems |
| CleverHans | A library of adversarial examples and defenses for machine learning models |
| AdvBox | Advbox is a toolbox to generate adversarial examples that fool neural networks in PaddlePaddle、PyTorch、Caffe2、MxNet、Keras、TensorFlow |
| Audit AI | Bias Testing for Generalized Machine Learning Applications |
| Deep Pwning | Deep-pwning is a lightweight framework for experimenting with machine learning models with the goal of evaluating their robustness against a motivated adversary |
| Privacy Meter | An open-source library to audit data privacy in statistical and machine learning algorithms |
| TensorFlow Model Analysis | A library for analyzing, validating, and monitoring machine learning models in production |
| PromptInject | A framework that assembles adversarial prompts |
| TextAttack | TextAttack is a Python framework for adversarial attacks, data augmentation, and model training in NLP |
| OpenAttack | An Open-Source Package for Textual Adversarial Attack |
| TextFooler | A Model for Natural Language Attack on Text Classification and Inference |
| Flawed Machine Learning Security | Practical examples of "Flawed Machine Learning Security" together with ML Security best practice across the end to end stages of the machine learning model lifecycle from training, to packaging, to deployment |
| Adversarial Machine Learning CTF | This repository is a CTF challenge, showing a security flaw in most (all?) common artificial neural networks. They are vulnerable for adversarial images |
| Damn Vulnerable LLM Project | A Large Language Model designed for getting hacked |
| Gandalf Lakera | Prompt Injection CTF playground |
| Vigil | LLM prompt injection and security scanner |
| PALLMs (Payloads for Attacking Large Language Models) | list of various payloads for attacking LLMs collected in one place |
| AI-exploits | exploits for MlOps systems. It's not just in the inputs given to LLMs such as ChatGPT |
| Offensive ML Playbook | Offensive ML Playbook. Notes on machine learning attacks and pentesting |
| AnonLLM | Anonymize Personally Identifiable Information (PII) for Large Language Model APIs |
| AI Goat | vulnerable LLM CTF challenges |
| Pyrit | The Python Risk Identification Tool for generative AI |
| Raze to the Ground: Query-Efficient Adversarial HTML Attacks on Machine-Learning Phishing Webpage Detectors | Source code of the paper "Raze to the Ground: Query-Efficient Adversarial HTML Attacks on Machine-Learning Phishing Webpage Detectors" accepted at AISec '23 |
| Giskard | Open-source testing tool for LLM applications |
| Safetensors | Convert pickle to a safe serialization option |
| Citadel Lens | Quality testing of models according to industry standards |
| Model-Inversion-Attack-ToolBox | A framework for implementing Model Inversion attacks |
| NeMo-Guardials | NeMo Guardrails allow developers building LLM-based applications to easily add programmable guardrails between the application code and the LLM |
| AugLy | A tool for generating adversarial attacks |
| Knockoffnets | PoC to implement BlackBox attacks to steal model data |
| Robust Intelligence Continous Validation | Tool for continuous model validation for compliance with standards |
| VGER | Jupyter Attack framework |
| AIShield Watchtower | An open source tool from AIShield for studying AI models and scanning for vulnerabilities |
| PS-fuzz | tool for scanning LLM vulnerabilities |
| Mindgard-cli | Check security of you AI via CLI |
| PurpleLLama3 | Check LLM security with Meta LLM Benchmark |
| Model transparency | generate model signing |
| ARTkit | Automated prompt-based testing and evaluation of Gen AI applications |
| LangBiTe | A Bias Tester framework for LLMs |
| OpenDP | The core library of differential privacy algorithms powering the OpenDP Project |
| TF-encrypted | Encryption for tensorflow |
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| Databricks Platform, Azure Databricks | Datalake data management and implementation tool |
| Hidden Layer AI Detection Response | Tool for detecting and responding to incidents |
| Guardian | Model protection in CI/CD |
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| ARX - Data Anonymization Tool | Tool for anonymizing datasets |
| Data-Veil | Data masking and anonymization tool |
| Tool for IMG anonymization | Image anonymization |
| Tool for DATA anonymization | Data anonymization |
| BMW-Anonymization-Api | This repository allows you to anonymize sensitive information in images/videos. The solution is fully compatible with the DL-based training/inference solutions that we already published/will publish for Object Detection and Semantic Segmentation |
| DeepPrivacy2 | A Toolbox for Realistic Image Anonymization |
| PPAP | Latent-space-level Image Anonymization with Adversarial Protector Networks |
- lintML - Security linter for ML, by Nvidia
- HiddenLayer: Model as Code - Research about some vectors in ML libraries
- Copycat CNN - Proof-of-concept on how to generate a copy of a Convolutional Neural Network
- differential-privacy-library - Library designed for differential privacy and machine learning
You can find here a list of resources to help you get into the topic of AI security. Understand what attacks exist and how they can be used by an attacker.
- AI Security 101
- Web LLM attacks
- Microsoft AI Red Team
- AI Risk Assessment for ML Engineers
- Microsoft - Generative AI Security for beginners
Full size map in this repository
more in Adversarial AI Attacks, Mitigations, and Defense Strategies: A cybersecurity professional's guide to AI attacks, threat modeling, and securing AI with MLSecOps
🌱 The AI security community is growing. New blogs and many researchers are emerging. In this paragraph you can see examples of some blogs.
- 🛡️ Red-Teaming Large Language Models
- 🔍 Google's AI red-team
- 🔒 The MLSecOps Top 10 vulnerabilities
- 🏴☠️ Token Smuggling Jailbreak via Adversarial Prompt
- ☣️ Just How Toxic is Data Poisoning? A Unified Benchmark for Backdoor and Data Poisoning Attacks
- 📊 We need a new way to measure AI security
- 🕵️ PrivacyRaven: Implementing a proof of concept for model inversion
- 🧠 Adversarial Prompts Engineering
- 🔫 TextAttack: A Framework for Adversarial Attacks, Data Augmentation, and Adversarial Training in NLP
- 📋 Trail Of Bits' audit of Hugging Face's safetensors library
- 🔝 OWASP Top 10 for Large Language Model Applications
- 🔐 LLM Security
- 🔑 Is you MLOps infrastructure leaking secrets?
- 🚩 Embrace The Red, blog where show how u can hack LLM's.
- 🎙️ Audio-jacking: Using generative AI to distort live audio transactions
- 🌐 HADESS - Web LLM Attacks
- 🧰 WTF-blog - MlSecOps frameworks ... Which ones are available and what is the difference?
- 📚 DreadNode Paper Stack
Very interesting articles on MlOps infrastructure vulnerabilities. In some of them you can even find ready-made exploits.
- SILENT SABOTAGE - Study on bot compromise for converting Pickle to SafeTensors
- NOT SO CLEAR: HOW MLOPS SOLUTIONS CAN MUDDY THE WATERS OF YOUR SUPPLY CHAIN - Study on vulnerabilities for the ClearML platform
- Uncovering Azure's Silent Threats: A Journey into Cloud Vulnerabilities - Study on security issues of Azure MLAAS
- The MLOps Security Landscape
- Confused Learning: Supply Chain Attacks through Machine Learning Models
Official implementation of "AgentPoison: Red-teaming LLM Agents via Memory or Knowledge Base Backdoor Poisoning". This project explores methods of data poisoning and backdoor insertion in LLM agents to assess their resilience against such attacks.
Research on methods of embedding malicious payloads into deep neural networks.
Investigation of backdoor attacks on deep learning models, focusing on creating undetectable vulnerabilities within models.
Techniques for stealing deep learning models through various attack vectors, enabling adversaries to replicate or access models.
Model extraction without using data, allowing for the recovery of models without access to the original data.
Tool for mapping and analyzing large language models (LLMs), exploring the structure and behavior of various LLMs.
Federated learning pipeline using Google Cloud infrastructure, enabling model training on distributed data.
Attack using ensemble class activation maps to introduce errors in models by manipulating activation maps.
Methods for attacking deep models under various conditions and constraints, focusing on creating more resilient attacks.
Research on adaptive attacks on machine learning models, enabling the creation of attacks that can adapt to model defenses.
Knowledge transfer in zero-shot scenarios, exploring methods to transfer knowledge between models without prior training on target data.
Attack for generating informative labels, aimed at covertly extracting data from trained models.
Enhancing DMI (Data Mining and Integration) methods using additional knowledge to improve accuracy and efficiency.
Research on methods for visualizing and interpreting machine learning models, providing insights into model workings.
Attacks that can be "plugged and played" without needing model modifications, offering flexible and universal attack methods.
Tool for analyzing and processing snapshot data, enabling efficient handling of data snapshots.
Research on the trade-offs between privacy and robustness in models, aiming to balance these two aspects in machine learning.
Methods for data leakage from trained models, exploring ways to extract private information from machine learning models.
Research on blind information extraction attacks, enabling data retrieval without access to the model's internal structure.
Differential privacy methods for deep learning, ensuring data privacy during model training.
Defense methods using MMD-mixup, aimed at improving model robustness against attacks.
Tools for protecting memory from attacks, exploring ways to prevent data leaks from model memory.
Methods for merging and splitting data to improve training, optimizing the use of heterogeneous data in models.
Attacks on face recognition models using attributes, exploring ways to manipulate facial attributes to induce errors.
Attacks on face verification models, aimed at disrupting authentication systems based on face recognition.
Using GANs to create malware, exploring methods for generating malicious code with generative models.
Methods for generating adversarial perturbations using generative models, aimed at introducing errors in deep models.
Adversarial attacks using Relativistic AdvGAN, exploring methods for creating more realistic and effective attacks.
Attacks on large language models, exploring vulnerabilities and protection methods for LLMs.
Safe fine-tuning of large language models, aiming to prevent data leaks and ensure security during LLM tuning.
Methods for evaluating trust in models, exploring ways to determine the reliability and safety of machine learning models.
Benchmark for evaluating prompts, providing tools for testing and optimizing queries to large language models.
Tool for analyzing and evaluating models based on ROM codes, exploring various aspects of model performance and resilience.
Research on privacy in large language models, aiming to protect data and prevent leaks from LLMs.
- MLSecOps
- MLSecOps Podcast
- MITRE ATLAS™ and SLACK COMMUNITY
- MlSecOps communtiy and SLACK COMMUNITY
- MITRE ATLAS™ (Adversarial Threat Landscape for Artificial-Intelligence Systems)
- OWASP AI Exchange
- OWASP Machine Learning Security Top Ten
- OWASP Top 10 for Large Language Model Applications
- OWASP LLMSVS
- OWASP Periodic Table of AI Security
- OWASP SLACK
- Awesome LLM Security
- Hackstery
- PWNAI
- AiSec_X_Feed
- HUNTR Discord community
- AIRSK
- AI Vulnerability Database
- Incident AI Database
- Defcon AI Village CTF
- Awesome AI Security
- MLSecOps Reference Repository
- Awesome LVLM Attack
- Awesome MLLM Safety
- Adversarial AI Attacks, Mitigations, and Defense Strategies: A cybersecurity professional's guide to AI attacks, threat modeling, and securing AI with MLSecOps
- Privacy-Preserving Machine Learning
- Generative AI Security: Theories and Practices (Future of Business and Finance)
All contributions to this list are welcome! Please feel free to submit a pull request with any additions or improvements.
 @riccardobiosas |
 @badarahmed |
 @deadbits |
 @wearetyomsmnv |
 @anmorgan24 |
 @mik0w |
 @alexcombessie |
If you find this project useful, please consider giving it a star ⭐️
This project is licensed under the MIT License - see the LICENSE file for details.
Made with ❤️
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for awesome-MLSecOps
Similar Open Source Tools

awesome-MLSecOps
Awesome MLSecOps is a curated list of open-source tools, resources, and tutorials for MLSecOps (Machine Learning Security Operations). It includes a wide range of security tools and libraries for protecting machine learning models against adversarial attacks, as well as resources for AI security, data anonymization, model security, and more. The repository aims to provide a comprehensive collection of tools and information to help users secure their machine learning systems and infrastructure.
mcp-for-security
MCP for Security is a repository that contains Model Context Protocol (MCP) server implementations for various security testing tools, making them accessible through a standardized interface. It aims to provide automated threat detection and reduce human latency in cybersecurity by combining artificial intelligence and security tools. Users can access a variety of tools for subdomain enumeration, reconnaissance, vulnerability scanning, web crawling, HTTP security analysis, mobile application security testing, network scanning, SSL/TLS configuration analysis, DNS brute-forcing, HTTP request smuggling detection, SQL injection testing, historical URL retrieval, and WordPress vulnerability scanning. The repository encourages collaboration and rapid evolution through open-source projects.
inference
Xorbits Inference (Xinference) is a powerful and versatile library designed to serve language, speech recognition, and multimodal models. With Xorbits Inference, you can effortlessly deploy and serve your or state-of-the-art built-in models using just a single command. Whether you are a researcher, developer, or data scientist, Xorbits Inference empowers you to unleash the full potential of cutting-edge AI models.
rai
RAI is a framework designed to bring general multi-agent system capabilities to robots, enhancing human interactivity, flexibility in problem-solving, and out-of-the-box AI features. It supports multi-modalities, incorporates an advanced database for agent memory, provides ROS 2-oriented tooling, and offers a comprehensive task/mission orchestrator. The framework includes features such as voice interaction, customizable robot identity, camera sensor access, reasoning through ROS logs, and integration with LangChain for AI tools. RAI aims to support various AI vendors, improve human-robot interaction, provide an SDK for developers, and offer a user interface for configuration.
SimAI
SimAI is the industry's first full-stack, high-precision simulator for AI large-scale training. It provides detailed modeling and simulation of the entire LLM training process, encompassing framework, collective communication, network layers, and more. This comprehensive approach offers end-to-end performance data, enabling researchers to analyze training process details, evaluate time consumption of AI tasks under specific conditions, and assess performance gains from various algorithmic optimizations.
unoplat-code-confluence
Unoplat-CodeConfluence is a universal code context engine that aims to extract, understand, and provide precise code context across repositories tied through domains. It combines deterministic code grammar with state-of-the-art LLM pipelines to achieve human-like understanding of codebases in minutes. The tool offers smart summarization, graph-based embedding, enhanced onboarding, graph-based intelligence, deep dependency insights, and seamless integration with existing development tools and workflows. It provides a precise context API for knowledge engine and AI coding assistants, enabling reliable code understanding through bottom-up code summarization, graph-based querying, and deep package and dependency analysis.
Dokugen
Dokugen is a lightweight README.md file Generator Command Line Interface Tool that simplifies the process of writing README.md files by generating professional READMEs for projects, saving time and ensuring consistency using AI. It automates the most neglected part of a repo, resulting in cleaner projects and happier contributors.
PURE
PURE (Process-sUpervised Reinforcement lEarning) is a framework that trains a Process Reward Model (PRM) on a dataset and fine-tunes a language model to achieve state-of-the-art mathematical reasoning capabilities. It uses a novel credit assignment method to calculate return and supports multiple reward types. The final model outperforms existing methods with minimal RL data or compute resources, achieving high accuracy on various benchmarks. The tool addresses reward hacking issues and aims to enhance long-range decision-making and reasoning tasks using large language models.
Academic_LLM_Sec_Papers
Academic_LLM_Sec_Papers is a curated collection of academic papers related to LLM Security Application. The repository includes papers sorted by conference name and published year, covering topics such as large language models for blockchain security, software engineering, machine learning, and more. Developers and researchers are welcome to contribute additional published papers to the list. The repository also provides information on listed conferences and journals related to security, networking, software engineering, and cryptography. The papers cover a wide range of topics including privacy risks, ethical concerns, vulnerabilities, threat modeling, code analysis, fuzzing, and more.
cambrian
Cambrian-1 is a fully open project focused on exploring multimodal Large Language Models (LLMs) with a vision-centric approach. It offers competitive performance across various benchmarks with models at different parameter levels. The project includes training configurations, model weights, instruction tuning data, and evaluation details. Users can interact with Cambrian-1 through a Gradio web interface for inference. The project is inspired by LLaVA and incorporates contributions from Vicuna, LLaMA, and Yi. Cambrian-1 is licensed under Apache 2.0 and utilizes datasets and checkpoints subject to their respective original licenses.
LLaVA-MORE
LLaVA-MORE is a new family of Multimodal Language Models (MLLMs) that integrates recent language models with diverse visual backbones. The repository provides a unified training protocol for fair comparisons across all architectures and releases training code and scripts for distributed training. It aims to enhance Multimodal LLM performance and offers various models for different tasks. Users can explore different visual backbones like SigLIP and methods for managing image resolutions (S2) to improve the connection between images and language. The repository is a starting point for expanding the study of Multimodal LLMs and enhancing new features in the field.
Clean-Coder-AI
Clean Coder is an AI tool that serves as a 2-in-1 Scrum Master and Developer. It helps users delegate planning, managing, and coding tasks to AI agents. These agents create tasks within Todoist, write code, and test it, enabling users to work on projects with minimal effort and stress. The tool offers features like project supervision, task execution by programming agents, frontend feedback, automatic file linting, file researcher agent, and sensitive files protection. Users can interact with Clean Coder through speech and benefit from advanced techniques for intelligent task execution.
camel
CAMEL is an open-source library designed for the study of autonomous and communicative agents. We believe that studying these agents on a large scale offers valuable insights into their behaviors, capabilities, and potential risks. To facilitate research in this field, we implement and support various types of agents, tasks, prompts, models, and simulated environments.
beeai-framework
BeeAI Framework is a versatile tool for building production-ready multi-agent systems. It offers flexibility in orchestrating agents, seamless integration with various models and tools, and production-grade controls for scaling. The framework supports Python and TypeScript libraries, enabling users to implement simple to complex multi-agent patterns, connect with AI services, and optimize token usage and resource management.
livekit
LiveKit is an open source project providing scalable, multi-user conferencing based on WebRTC. It offers a server written in Go, client SDKs, and advanced features like speaker detection, end-to-end encryption, and SVC codecs. The tool is easy to deploy with support for JWT authentication and robust networking. LiveKit ecosystem includes agents for AI applications, tools like CLI and Docker image, and SDKs for both client and server-side development.

openrl
OpenRL is an open-source general reinforcement learning research framework that supports training for various tasks such as single-agent, multi-agent, offline RL, self-play, and natural language. Developed based on PyTorch, the goal of OpenRL is to provide a simple-to-use, flexible, efficient and sustainable platform for the reinforcement learning research community. It supports a universal interface for all tasks/environments, single-agent and multi-agent tasks, offline RL training with expert dataset, self-play training, reinforcement learning training for natural language tasks, DeepSpeed, Arena for evaluation, importing models and datasets from Hugging Face, user-defined environments, models, and datasets, gymnasium environments, callbacks, visualization tools, unit testing, and code coverage testing. It also supports various algorithms like PPO, DQN, SAC, and environments like Gymnasium, MuJoCo, Atari, and more.
For similar tasks

awesome-MLSecOps
Awesome MLSecOps is a curated list of open-source tools, resources, and tutorials for MLSecOps (Machine Learning Security Operations). It includes a wide range of security tools and libraries for protecting machine learning models against adversarial attacks, as well as resources for AI security, data anonymization, model security, and more. The repository aims to provide a comprehensive collection of tools and information to help users secure their machine learning systems and infrastructure.
For similar jobs

awesome-MLSecOps
Awesome MLSecOps is a curated list of open-source tools, resources, and tutorials for MLSecOps (Machine Learning Security Operations). It includes a wide range of security tools and libraries for protecting machine learning models against adversarial attacks, as well as resources for AI security, data anonymization, model security, and more. The repository aims to provide a comprehensive collection of tools and information to help users secure their machine learning systems and infrastructure.
mimir
MIMIR is a Python package designed for measuring memorization in Large Language Models (LLMs). It provides functionalities for conducting experiments related to membership inference attacks on LLMs. The package includes implementations of various attacks such as Likelihood, Reference-based, Zlib Entropy, Neighborhood, Min-K% Prob, Min-K%++, Gradient Norm, and allows users to extend it by adding their own datasets and attacks.
openshield
OpenShield is a firewall designed for AI models to protect against various attacks such as prompt injection, insecure output handling, training data poisoning, model denial of service, supply chain vulnerabilities, sensitive information disclosure, insecure plugin design, excessive agency granting, overreliance, and model theft. It provides rate limiting, content filtering, and keyword filtering for AI models. The tool acts as a transparent proxy between AI models and clients, allowing users to set custom rate limits for OpenAI endpoints and perform tokenizer calculations for OpenAI models. OpenShield also supports Python and LLM based rules, with upcoming features including rate limiting per user and model, prompts manager, content filtering, keyword filtering based on LLM/Vector models, OpenMeter integration, and VectorDB integration. The tool requires an OpenAI API key, Postgres, and Redis for operation.
paig
PAIG is an open-source project focused on protecting Generative AI applications by ensuring security, safety, and observability. It offers a versatile framework to address the latest security challenges and integrate point security solutions without rewriting applications. The project aims to provide a secure environment for developing and deploying GenAI applications.