
mimir
Python package for measuring memorization in LLMs.
Stars: 106
MIMIR is a Python package designed for measuring memorization in Large Language Models (LLMs). It provides functionalities for conducting experiments related to membership inference attacks on LLMs. The package includes implementations of various attacks such as Likelihood, Reference-based, Zlib Entropy, Neighborhood, Min-K% Prob, Min-K%++, Gradient Norm, and allows users to extend it by adding their own datasets and attacks.
README:
MIMIR - Python package for measuring memorization in LLMs.
Documentation is available here.
First install the python dependencies
pip install -r requirements.txt
Then, install our package
pip install -e .
To use, run the scripts in scripts/bash
Note: Intermediate results are saved in tmp_results/ and tmp_results_cross/ for bash scripts. If your experiment completes successfully, the results will be moved into the results/ and results_cross/ directory.
You can either provide the following environment variables, or pass them via your config/CLI:
MIMIR_CACHE_PATH: Path to cache directory
MIMIR_DATA_SOURCE: Path to data directory
The data we used for our experiments is available on Hugging Face Datasets. You can either choose to either load the data directly from Hugging Face with the load_from_hf flag in the config (preferred), or download the cache_100_200_.... folders into your MIMIR_CACHE_PATH directory.
python run.py --config configs/mi.json
We include and implement the following attacks, as described in our paper.
-
Likelihood (
loss). Works by simply using the likelihood of the target datapoint as score. -
Reference-based (
ref). Normalizes likelihood score with score obtained from a reference model. -
Zlib Entropy (
zlib). Uses the zlib compression size of a sample to approximate local difficulty of sample. -
Neighborhood (
ne). Generates neighbors using auxiliary model and measures change in likelihood. -
Min-K% Prob (
min_k). Uses k% of tokens with minimum likelihood for score computation. -
Min-K%++ (
min_k++). Uses k% of tokens with minimum normalized likelihood for score computation. -
Gradient Norm (
gradnorm). Uses gradient norm of the target datapoint as score. -
ReCaLL(
recall). Operates by comparing the unconditional and conditional log-likelihoods.
To extend the package for your own dataset, you can directly load your data inside load_cached() in data_utils.py, or add an additional if-else within load() in data_utils.py if it cannot be loaded from memory (or some source) easily. We will probably add a more general way to do this in the future.
To add an attack, create a file for your attack (e.g. attacks/my_attack.py) and implement the interface described in attacks/all_attacks.py.
Then, add a name for your attack to the dictionary in attacks/utils.py.
If you would like to submit your attack to the repository, please open a pull request describing your attack and the paper it is based on.
If you use MIMIR in your research, please cite our paper:
@inproceedings{duan2024membership,
title={Do Membership Inference Attacks Work on Large Language Models?},
author={Michael Duan and Anshuman Suri and Niloofar Mireshghallah and Sewon Min and Weijia Shi and Luke Zettlemoyer and Yulia Tsvetkov and Yejin Choi and David Evans and Hannaneh Hajishirzi},
year={2024},
booktitle={Conference on Language Modeling (COLM)},
}For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for mimir
Similar Open Source Tools

mimir
MIMIR is a Python package designed for measuring memorization in Large Language Models (LLMs). It provides functionalities for conducting experiments related to membership inference attacks on LLMs. The package includes implementations of various attacks such as Likelihood, Reference-based, Zlib Entropy, Neighborhood, Min-K% Prob, Min-K%++, Gradient Norm, and allows users to extend it by adding their own datasets and attacks.
probsem
ProbSem is a repository that provides a framework to leverage large language models (LLMs) for assigning context-conditional probability distributions over queried strings. It supports OpenAI engines and HuggingFace CausalLM models, and is flexible for research applications in linguistics, cognitive science, program synthesis, and NLP. Users can define prompts, contexts, and queries to derive probability distributions over possible completions, enabling tasks like cloze completion, multiple-choice QA, semantic parsing, and code completion. The repository offers CLI and API interfaces for evaluation, with options to customize models, normalize scores, and adjust temperature for probability distributions.
LayerSkip
LayerSkip is an implementation enabling early exit inference and self-speculative decoding. It provides a code base for running models trained using the LayerSkip recipe, offering speedup through self-speculative decoding. The tool integrates with Hugging Face transformers and provides checkpoints for various LLMs. Users can generate tokens, benchmark on datasets, evaluate tasks, and sweep over hyperparameters to optimize inference speed. The tool also includes correctness verification scripts and Docker setup instructions. Additionally, other implementations like gpt-fast and Native HuggingFace are available. Training implementation is a work-in-progress, and contributions are welcome under the CC BY-NC license.
LeanCopilot
Lean Copilot is a tool that enables the use of large language models (LLMs) in Lean for proof automation. It provides features such as suggesting tactics/premises, searching for proofs, and running inference of LLMs. Users can utilize built-in models from LeanDojo or bring their own models to run locally or on the cloud. The tool supports platforms like Linux, macOS, and Windows WSL, with optional CUDA and cuDNN for GPU acceleration. Advanced users can customize behavior using Tactic APIs and Model APIs. Lean Copilot also allows users to bring their own models through ExternalGenerator or ExternalEncoder. The tool comes with caveats such as occasional crashes and issues with premise selection and proof search. Users can get in touch through GitHub Discussions for questions, bug reports, feature requests, and suggestions. The tool is designed to enhance theorem proving in Lean using LLMs.
mosec
Mosec is a high-performance and flexible model serving framework for building ML model-enabled backend and microservices. It bridges the gap between any machine learning models you just trained and the efficient online service API. * **Highly performant** : web layer and task coordination built with Rust 🦀, which offers blazing speed in addition to efficient CPU utilization powered by async I/O * **Ease of use** : user interface purely in Python 🐍, by which users can serve their models in an ML framework-agnostic manner using the same code as they do for offline testing * **Dynamic batching** : aggregate requests from different users for batched inference and distribute results back * **Pipelined stages** : spawn multiple processes for pipelined stages to handle CPU/GPU/IO mixed workloads * **Cloud friendly** : designed to run in the cloud, with the model warmup, graceful shutdown, and Prometheus monitoring metrics, easily managed by Kubernetes or any container orchestration systems * **Do one thing well** : focus on the online serving part, users can pay attention to the model optimization and business logic
paper-qa
PaperQA is a minimal package for question and answering from PDFs or text files, providing very good answers with in-text citations. It uses OpenAI Embeddings to embed and search documents, and includes a process of embedding docs, queries, searching for top passages, creating summaries, using an LLM to re-score and select relevant summaries, putting summaries into prompt, and generating answers. The tool can be used to answer specific questions related to scientific research by leveraging citations and relevant passages from documents.
garak
Garak is a vulnerability scanner designed for LLMs (Large Language Models) that checks for various weaknesses such as hallucination, data leakage, prompt injection, misinformation, toxicity generation, and jailbreaks. It combines static, dynamic, and adaptive probes to explore vulnerabilities in LLMs. Garak is a free tool developed for red-teaming and assessment purposes, focusing on making LLMs or dialog systems fail. It supports various LLM models and can be used to assess their security and robustness.
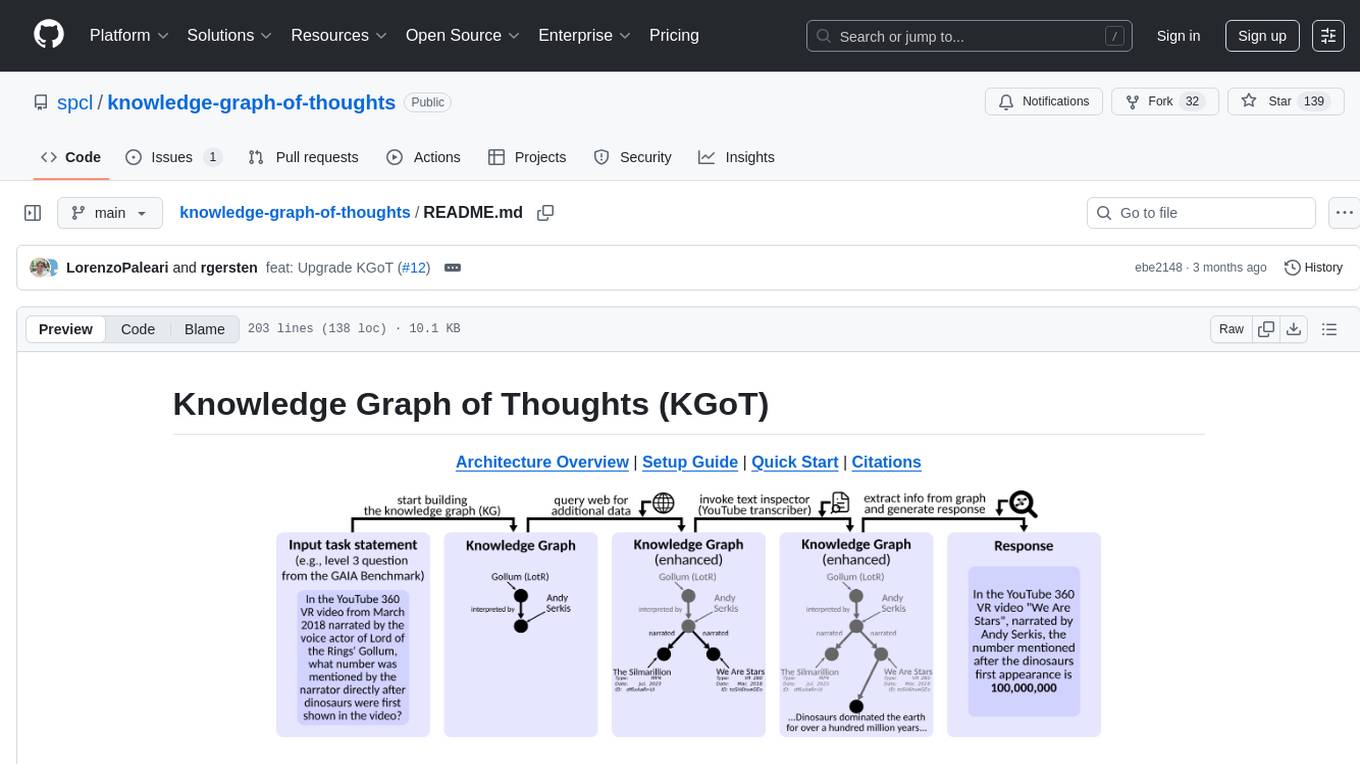
knowledge-graph-of-thoughts
Knowledge Graph of Thoughts (KGoT) is an innovative AI assistant architecture that integrates LLM reasoning with dynamically constructed knowledge graphs (KGs). KGoT extracts and structures task-relevant knowledge into a dynamic KG representation, iteratively enhanced through external tools such as math solvers, web crawlers, and Python scripts. Such structured representation of task-relevant knowledge enables low-cost models to solve complex tasks effectively. The KGoT system consists of three main components: the Controller, the Graph Store, and the Integrated Tools, each playing a critical role in the task-solving process.
safety-tooling
This repository, safety-tooling, is designed to be shared across various AI Safety projects. It provides an LLM API with a common interface for OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google models. The aim is to facilitate collaboration among AI Safety researchers, especially those with limited software engineering backgrounds, by offering a platform for contributing to a larger codebase. The repo can be used as a git submodule for easy collaboration and updates. It also supports pip installation for convenience. The repository includes features for installation, secrets management, linting, formatting, Redis configuration, testing, dependency management, inference, finetuning, API usage tracking, and various utilities for data processing and experimentation.
paper-qa
PaperQA is a minimal package for question and answering from PDFs or text files, providing very good answers with in-text citations. It uses OpenAI Embeddings to embed and search documents, and follows a process of embedding docs and queries, searching for top passages, creating summaries, scoring and selecting relevant summaries, putting summaries into prompt, and generating answers. Users can customize prompts and use various models for embeddings and LLMs. The tool can be used asynchronously and supports adding documents from paths, files, or URLs.
MultiPL-E
MultiPL-E is a system for translating unit test-driven neural code generation benchmarks to new languages. It is part of the BigCode Code Generation LM Harness and allows for evaluating Code LLMs using various benchmarks. The tool supports multiple versions with improvements and new language additions, providing a scalable and polyglot approach to benchmarking neural code generation. Users can access a tutorial for direct usage and explore the dataset of translated prompts on the Hugging Face Hub.

MegatronApp
MegatronApp is a toolchain built around the Megatron-LM training framework, offering performance tuning, slow-node detection, and training-process visualization. It includes modules like MegaScan for anomaly detection, MegaFBD for forward-backward decoupling, MegaDPP for dynamic pipeline planning, and MegaScope for visualization. The tool aims to enhance large-scale distributed training by providing valuable capabilities and insights.
strwythura
Strwythura is a library and tutorial focused on constructing a knowledge graph from unstructured data sources using state-of-the-art models for named entity recognition. It implements an enhanced GraphRAG approach and curates semantics for optimizing AI application outcomes within a specific domain. The tutorial emphasizes the use of sophisticated NLP pipelines based on spaCy, GLiNER, TextRank, and related libraries to provide better/faster/cheaper results with more control over the intentional arrangement of the knowledge graph. It leverages neurosymbolic AI methods and combines practices from natural language processing, graph data science, entity resolution, ontology pipeline, context engineering, and human-in-the-loop processes.
OlympicArena
OlympicArena is a comprehensive benchmark designed to evaluate advanced AI capabilities across various disciplines. It aims to push AI towards superintelligence by tackling complex challenges in science and beyond. The repository provides detailed data for different disciplines, allows users to run inference and evaluation locally, and offers a submission platform for testing models on the test set. Additionally, it includes an annotation interface and encourages users to cite their paper if they find the code or dataset helpful.

ontogpt
OntoGPT is a Python package for extracting structured information from text using large language models, instruction prompts, and ontology-based grounding. It provides a command line interface and a minimal web app for easy usage. The tool has been evaluated on test data and is used in related projects like TALISMAN for gene set analysis. OntoGPT enables users to extract information from text by specifying relevant terms and provides the extracted objects as output.
garak
Garak is a free tool that checks if a Large Language Model (LLM) can be made to fail in a way that is undesirable. It probes for hallucination, data leakage, prompt injection, misinformation, toxicity generation, jailbreaks, and many other weaknesses. Garak's a free tool. We love developing it and are always interested in adding functionality to support applications.
For similar tasks

mimir
MIMIR is a Python package designed for measuring memorization in Large Language Models (LLMs). It provides functionalities for conducting experiments related to membership inference attacks on LLMs. The package includes implementations of various attacks such as Likelihood, Reference-based, Zlib Entropy, Neighborhood, Min-K% Prob, Min-K%++, Gradient Norm, and allows users to extend it by adding their own datasets and attacks.
hume-python-sdk
The Hume AI Python SDK allows users to integrate Hume APIs directly into their Python applications. Users can access complete documentation, quickstart guides, and example notebooks to get started. The SDK is designed to provide support for Hume's expressive communication platform built on scientific research. Users are encouraged to create an account at beta.hume.ai and stay updated on changes through Discord. The SDK may undergo breaking changes to improve tooling and ensure reliable releases in the future.
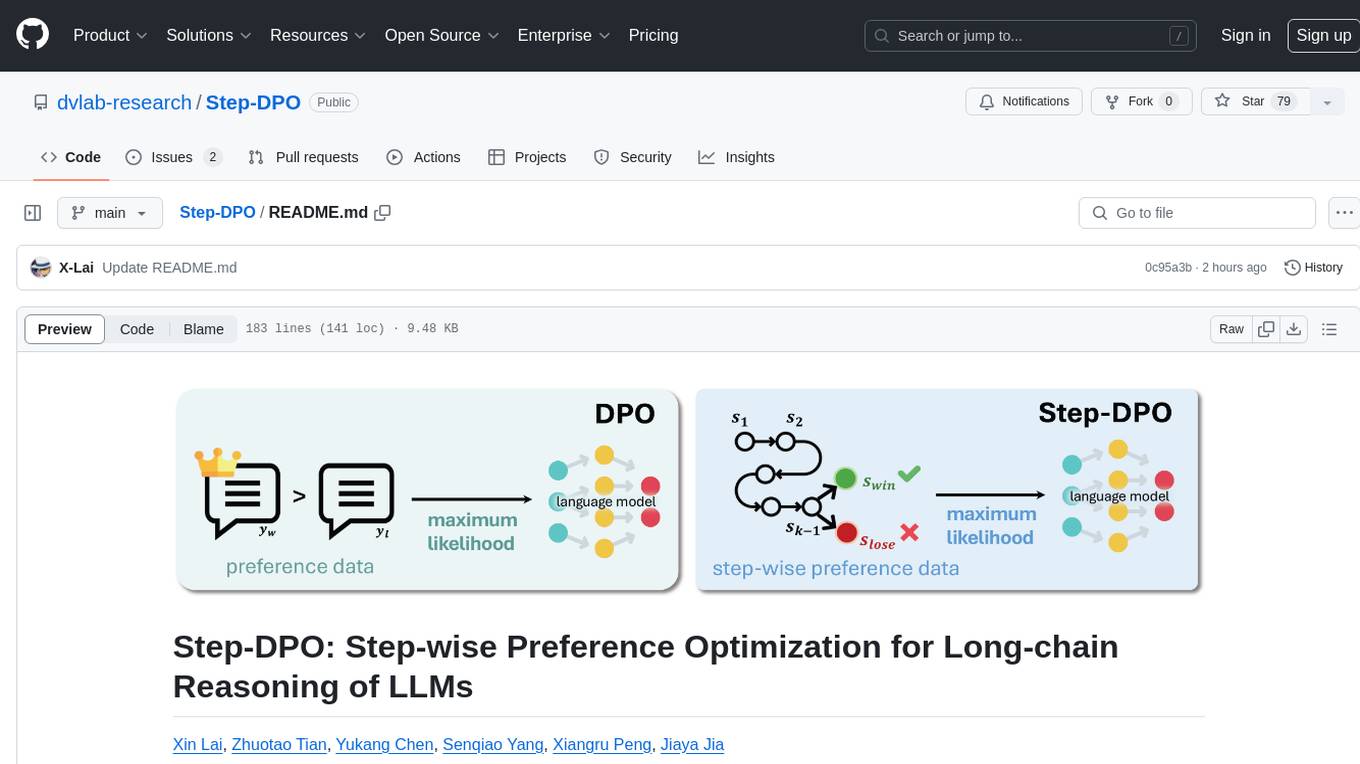
Step-DPO
Step-DPO is a method for enhancing long-chain reasoning ability of LLMs with a data construction pipeline creating a high-quality dataset. It significantly improves performance on math and GSM8K tasks with minimal data and training steps. The tool fine-tunes pre-trained models like Qwen2-7B-Instruct with Step-DPO, achieving superior results compared to other models. It provides scripts for training, evaluation, and deployment, along with examples and acknowledgements.
TriForce
TriForce is a training-free tool designed to accelerate long sequence generation. It supports long-context Llama models and offers both on-chip and offloading capabilities. Users can achieve a 2.2x speedup on a single A100 GPU. TriForce also provides options for offloading with tensor parallelism or without it, catering to different hardware configurations. The tool includes a baseline for comparison and is optimized for performance on RTX 4090 GPUs. Users can cite the associated paper if they find TriForce useful for their projects.
agentdojo
AgentDojo is a dynamic environment designed to evaluate prompt injection attacks and defenses for large language models (LLM) agents. It provides a benchmark script to run different suites and tasks with specified LLM models, defenses, and attacks. The tool is under active development, and users can inspect the results through dedicated documentation pages and the Invariant Benchmark Registry.
For similar jobs
awesome-MLSecOps
Awesome MLSecOps is a curated list of open-source tools, resources, and tutorials for MLSecOps (Machine Learning Security Operations). It includes a wide range of security tools and libraries for protecting machine learning models against adversarial attacks, as well as resources for AI security, data anonymization, model security, and more. The repository aims to provide a comprehensive collection of tools and information to help users secure their machine learning systems and infrastructure.

mimir
MIMIR is a Python package designed for measuring memorization in Large Language Models (LLMs). It provides functionalities for conducting experiments related to membership inference attacks on LLMs. The package includes implementations of various attacks such as Likelihood, Reference-based, Zlib Entropy, Neighborhood, Min-K% Prob, Min-K%++, Gradient Norm, and allows users to extend it by adding their own datasets and attacks.
openshield
OpenShield is a firewall designed for AI models to protect against various attacks such as prompt injection, insecure output handling, training data poisoning, model denial of service, supply chain vulnerabilities, sensitive information disclosure, insecure plugin design, excessive agency granting, overreliance, and model theft. It provides rate limiting, content filtering, and keyword filtering for AI models. The tool acts as a transparent proxy between AI models and clients, allowing users to set custom rate limits for OpenAI endpoints and perform tokenizer calculations for OpenAI models. OpenShield also supports Python and LLM based rules, with upcoming features including rate limiting per user and model, prompts manager, content filtering, keyword filtering based on LLM/Vector models, OpenMeter integration, and VectorDB integration. The tool requires an OpenAI API key, Postgres, and Redis for operation.
paig
PAIG is an open-source project focused on protecting Generative AI applications by ensuring security, safety, and observability. It offers a versatile framework to address the latest security challenges and integrate point security solutions without rewriting applications. The project aims to provide a secure environment for developing and deploying GenAI applications.
AI-Infra-Guard
A.I.G (AI-Infra-Guard) is an AI red teaming platform by Tencent Zhuque Lab that integrates capabilities such as AI infra vulnerability scan, MCP Server risk scan, and Jailbreak Evaluation. It aims to provide users with a comprehensive, intelligent, and user-friendly solution for AI security risk self-examination. The platform offers features like AI Infra Scan, AI Tool Protocol Scan, and Jailbreak Evaluation, along with a modern web interface, complete API, multi-language support, cross-platform deployment, and being free and open-source under the MIT license.
capsule
Capsule is a secure and durable runtime for AI agents, designed to coordinate tasks in isolated environments. It allows for long-running workflows, large-scale processing, autonomous decision-making, and multi-agent systems. Tasks run in WebAssembly sandboxes with isolated execution, resource limits, automatic retries, and lifecycle tracking. It enables safe execution of untrusted code within AI agent systems.

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

agentcloud
AgentCloud is an open-source platform that enables companies to build and deploy private LLM chat apps, empowering teams to securely interact with their data. It comprises three main components: Agent Backend, Webapp, and Vector Proxy. To run this project locally, clone the repository, install Docker, and start the services. The project is licensed under the GNU Affero General Public License, version 3 only. Contributions and feedback are welcome from the community.
