
LeanCopilot
LLMs as Copilots for Theorem Proving in Lean
Stars: 1014
Lean Copilot is a tool that enables the use of large language models (LLMs) in Lean for proof automation. It provides features such as suggesting tactics/premises, searching for proofs, and running inference of LLMs. Users can utilize built-in models from LeanDojo or bring their own models to run locally or on the cloud. The tool supports platforms like Linux, macOS, and Windows WSL, with optional CUDA and cuDNN for GPU acceleration. Advanced users can customize behavior using Tactic APIs and Model APIs. Lean Copilot also allows users to bring their own models through ExternalGenerator or ExternalEncoder. The tool comes with caveats such as occasional crashes and issues with premise selection and proof search. Users can get in touch through GitHub Discussions for questions, bug reports, feature requests, and suggestions. The tool is designed to enhance theorem proving in Lean using LLMs.
README:
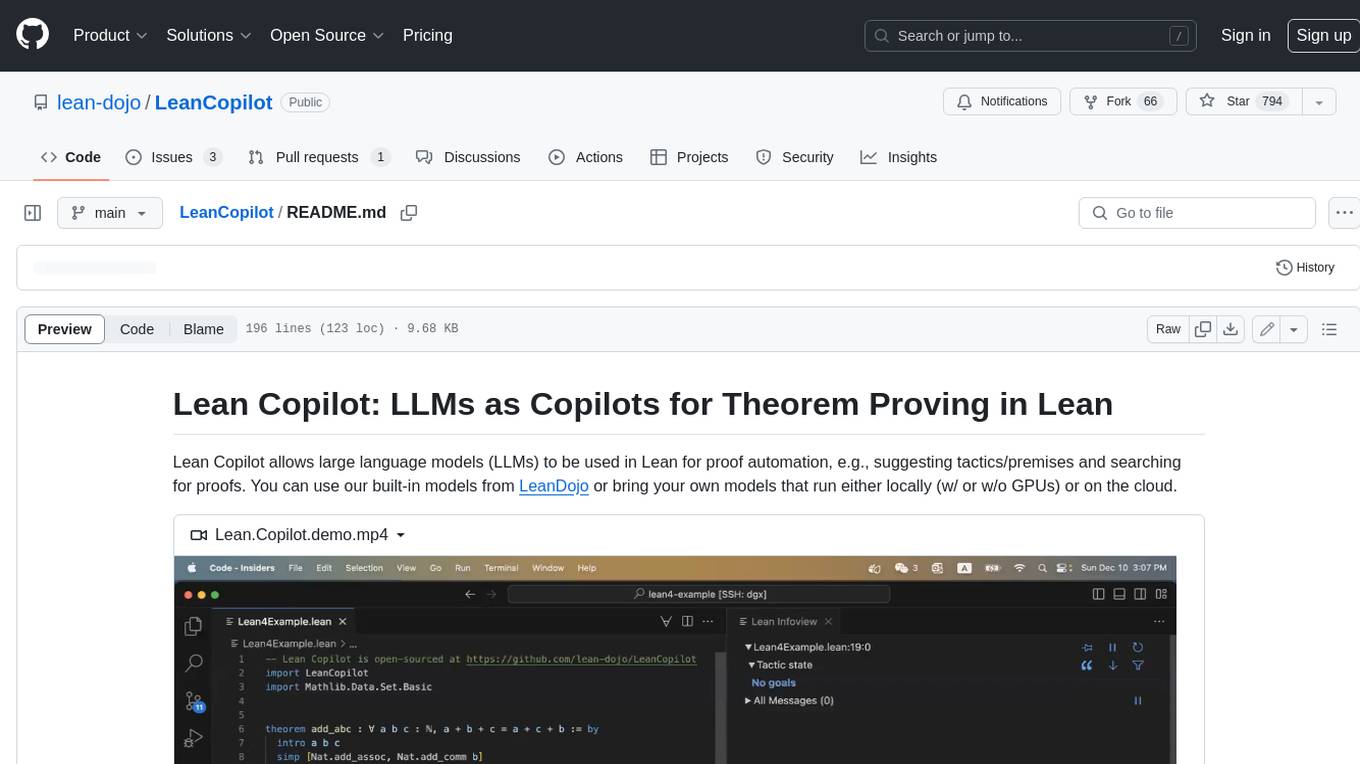
Lean Copilot allows large language models (LLMs) to be used in Lean for proof automation, e.g., suggesting tactics/premises and searching for proofs. You can use our built-in models from LeanDojo or bring your own models that run either locally (w/ or w/o GPUs) or on the cloud.
https://github.com/lean-dojo/LeanCopilot/assets/114432581/ee0f56f8-849e-4099-9284-d8092cbd22a3
- Requirements
- Using Lean Copilot in Your Project
- Advanced Usage
- Caveats
- Getting in Touch
- Acknowledgements
- Citation
- Supported platforms: Linux, macOS, and Windows WSL;
⚠️ Native Windows currently not supported. - Git LFS
- Optional (recommended if you have a CUDA-enabled GPU): CUDA and cuDNN
- Required for building Lean Copilot itself (rather than a downstream package): CMake >= 3.7 and a C++17 compatible compiler
lean4:v4.3.0-rc2.
- Add the package configuration option
moreLinkArgs := #["-L./.lake/packages/LeanCopilot/.lake/build/lib", "-lctranslate2"]to lakefile.lean. For example,
package «my-package» {
moreLinkArgs := #[
"-L./.lake/packages/LeanCopilot/.lake/build/lib",
"-lctranslate2"
]
}Alternatively, if your project uses lakefile.toml, it should include:
moreLinkArgs = ["-L./.lake/packages/LeanCopilot/.lake/build/lib", "-lctranslate2"]- Add the following line to lakefile.lean, including the quotation marks:
require LeanCopilot from git "https://github.com/lean-dojo/LeanCopilot.git" @ "LEAN_COPILOT_VERSION"For stable Lean versions (e.g., v4.15.0), set LEAN_COPILOT_VERSION to be that version. For the latest unstable Lean versions (e.g., v4.16.0-rc1), set LEAN_COPILOT_VERSION to main. In either case, make sure the version is compatible with other dependencies such as mathlib. If your project uses lakefile.toml instead of lakefile.lean, it should include:
[[require]]
name = "LeanCopilot"
git = "https://github.com/lean-dojo/LeanCopilot.git"
rev = "LEAN_COPILOT_VERSION"-
Run
lake update LeanCopilot. -
Run
lake exe LeanCopilot/downloadto download the built-in models from Hugging Face to~/.cache/lean_copilot/. Alternatively, you can download the models from Hugging Face manually from
- ct2-leandojo-lean4-tacgen-byt5-small
- ct2-leandojo-lean4-retriever-byt5-small
- premise-embeddings-leandojo-lean4-retriever-byt5-small
- ct2-byt5-small
- Run
lake build.
Here is an example of a Lean package depending on Lean Copilot. If you have problems building the project, our Dockerfile, build.sh or build_example.sh may be helpful.
After import LeanCopilot, you can use the tactic suggest_tactics to generate tactic suggestions. You can click on any of the suggested tactics to use it in the proof.
You can provide a prefix (e.g., simp) to constrain the generated tactics:
The tactic search_proof combines LLM-generated tactics with aesop to search for multi-tactic proofs. When a proof is found, you can click on it to insert it into the editor.
The select_premises tactic retrieves a list of potentially useful premises. Currently, it uses the retriever in LeanDojo to select premises from a fixed snapshot of Lean and mathlib4.
You can also run the inference of any LLMs in Lean, which can be used to build customized proof automation or other LLM-based applications (not limited to theorem proving). It's possible to run arbitrary models either locally or remotely (see Bring Your Own Model).
This section is only for advanced users who would like to change the default behavior of suggest_tactics, search_proof, or select_premises, e.g., to use different models or hyperparameters.
- Examples in TacticSuggestion.lean showcase how to configure
suggest_tactics, e.g., to use different models or generate different numbers of tactics. - Examples in ProofSearch.lean showcase how to configure
search_proofusing options provided by aesop. - Examples in PremiseSelection.lean showcase how to set the number of retrieved premises for
select_premises.
Examples in ModelAPIs.lean showcase how to run the inference of different models and configure their parameters (temperature, beam size, etc.).
Lean Copilot supports two kinds of models: generators and encoders. Generators must implement the TextToText interface:
class TextToText (τ : Type) where
generate (model : τ) (input : String) (targetPrefix : String) : IO $ Array (String × Float)-
inputis the input string -
targetPrefixis used to constrain the generator's output.""means no constraint. -
generateshould return an array ofString × Float. EachStringis an output from the model, andFloatis the corresponding score.
We provide three types of Generators:
-
NativeGeneratorruns locally powered by CTranslate2 and is linked to Lean using Foreign Function Interface (FFI). -
ExternalGeneratoris hosted either locally or remotely. See Bring Your Own Model for details. -
GenericGeneratorcan be anything that implements thegeneratefunction in theTextToTexttypeclass.
Encoders must implement TextToVec:
class TextToVec (τ : Type) where
encode : τ → String → IO FloatArray-
inputis the input string -
encodeshould return a vector embedding produced by the model.
Similar to generators, we have NativeEncoder, ExternalEncoder, and GenericEncoder.
In principle, it is possible to run any model using Lean Copilot through ExternalGenerator or ExternalEncoder (examples in ModelAPIs.lean). To use a model, you need to wrap it properly to expose the APIs in external_model_api.yaml. As an example, we provide a Python API server and use it to run a few models, including llmstep-mathlib4-pythia2.8b.
- Lean may occasionally crash when restarting or editing a file. Restarting the file again should fix the problem.
-
select_premisesalways retrieves the original form of a premise. For example,Nat.add_left_commis a result of the theorem below. In this case,select_premisesretrievesNat.mul_left_comminstead ofNat.add_left_comm.
@[to_additive]
theorem mul_left_comm : ∀ a b c : G, a * (b * c) = b * (a * c)- In some cases,
search_proofproduces an erroneous proof with error messages likefail to show termination for .... A temporary workaround is changing the theorem's name before applyingsearch_proof. You can change it back aftersearch_proofcompletes.
- For general questions and discussions, please use GitHub Discussions.
- To report a potential bug, please open an issue. In the issue, please include your OS information and the exact steps to reproduce the error. The more details you provide, the better we will be able to help you.
- Feature requests and other suggestions are extremely welcome. Please feel free to start a discussion!
- We thank Scott Morrison for suggestions on simplifying Lean Copilot's installation and Mac Malone for helping implement it. Both Scott and Mac work for the Lean FRO.
- We thank Jannis Limperg for supporting our LLM-generated tactics in Aesop (https://github.com/leanprover-community/aesop/pull/70).
If you find our work useful, please consider citing our paper:
@misc{song2024largelanguagemodelscopilots,
title={Towards Large Language Models as Copilots for Theorem Proving in Lean},
author={Peiyang Song and Kaiyu Yang and Anima Anandkumar},
year={2024},
eprint={2404.12534},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.AI},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2404.12534},
}For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for LeanCopilot
Similar Open Source Tools

LeanCopilot
Lean Copilot is a tool that enables the use of large language models (LLMs) in Lean for proof automation. It provides features such as suggesting tactics/premises, searching for proofs, and running inference of LLMs. Users can utilize built-in models from LeanDojo or bring their own models to run locally or on the cloud. The tool supports platforms like Linux, macOS, and Windows WSL, with optional CUDA and cuDNN for GPU acceleration. Advanced users can customize behavior using Tactic APIs and Model APIs. Lean Copilot also allows users to bring their own models through ExternalGenerator or ExternalEncoder. The tool comes with caveats such as occasional crashes and issues with premise selection and proof search. Users can get in touch through GitHub Discussions for questions, bug reports, feature requests, and suggestions. The tool is designed to enhance theorem proving in Lean using LLMs.
garak
Garak is a vulnerability scanner designed for LLMs (Large Language Models) that checks for various weaknesses such as hallucination, data leakage, prompt injection, misinformation, toxicity generation, and jailbreaks. It combines static, dynamic, and adaptive probes to explore vulnerabilities in LLMs. Garak is a free tool developed for red-teaming and assessment purposes, focusing on making LLMs or dialog systems fail. It supports various LLM models and can be used to assess their security and robustness.
garak
Garak is a free tool that checks if a Large Language Model (LLM) can be made to fail in a way that is undesirable. It probes for hallucination, data leakage, prompt injection, misinformation, toxicity generation, jailbreaks, and many other weaknesses. Garak's a free tool. We love developing it and are always interested in adding functionality to support applications.
HuggingFaceGuidedTourForMac
HuggingFaceGuidedTourForMac is a guided tour on how to install optimized pytorch and optionally Apple's new MLX, JAX, and TensorFlow on Apple Silicon Macs. The repository provides steps to install homebrew, pytorch with MPS support, MLX, JAX, TensorFlow, and Jupyter lab. It also includes instructions on running large language models using HuggingFace transformers. The repository aims to help users set up their Macs for deep learning experiments with optimized performance.
paper-qa
PaperQA is a minimal package for question and answering from PDFs or text files, providing very good answers with in-text citations. It uses OpenAI Embeddings to embed and search documents, and includes a process of embedding docs, queries, searching for top passages, creating summaries, using an LLM to re-score and select relevant summaries, putting summaries into prompt, and generating answers. The tool can be used to answer specific questions related to scientific research by leveraging citations and relevant passages from documents.
paper-qa
PaperQA is a minimal package for question and answering from PDFs or text files, providing very good answers with in-text citations. It uses OpenAI Embeddings to embed and search documents, and follows a process of embedding docs and queries, searching for top passages, creating summaries, scoring and selecting relevant summaries, putting summaries into prompt, and generating answers. Users can customize prompts and use various models for embeddings and LLMs. The tool can be used asynchronously and supports adding documents from paths, files, or URLs.
LayerSkip
LayerSkip is an implementation enabling early exit inference and self-speculative decoding. It provides a code base for running models trained using the LayerSkip recipe, offering speedup through self-speculative decoding. The tool integrates with Hugging Face transformers and provides checkpoints for various LLMs. Users can generate tokens, benchmark on datasets, evaluate tasks, and sweep over hyperparameters to optimize inference speed. The tool also includes correctness verification scripts and Docker setup instructions. Additionally, other implementations like gpt-fast and Native HuggingFace are available. Training implementation is a work-in-progress, and contributions are welcome under the CC BY-NC license.
ray-llm
RayLLM (formerly known as Aviary) is an LLM serving solution that makes it easy to deploy and manage a variety of open source LLMs, built on Ray Serve. It provides an extensive suite of pre-configured open source LLMs, with defaults that work out of the box. RayLLM supports Transformer models hosted on Hugging Face Hub or present on local disk. It simplifies the deployment of multiple LLMs, the addition of new LLMs, and offers unique autoscaling support, including scale-to-zero. RayLLM fully supports multi-GPU & multi-node model deployments and offers high performance features like continuous batching, quantization and streaming. It provides a REST API that is similar to OpenAI's to make it easy to migrate and cross test them. RayLLM supports multiple LLM backends out of the box, including vLLM and TensorRT-LLM.
generative-models
Generative Models by Stability AI is a repository that provides various generative models for research purposes. It includes models like Stable Video 4D (SV4D) for video synthesis, Stable Video 3D (SV3D) for multi-view synthesis, SDXL-Turbo for text-to-image generation, and more. The repository focuses on modularity and implements a config-driven approach for building and combining submodules. It supports training with PyTorch Lightning and offers inference demos for different models. Users can access pre-trained models like SDXL-base-1.0 and SDXL-refiner-1.0 under a CreativeML Open RAIL++-M license. The codebase also includes tools for invisible watermark detection in generated images.
MultiPL-E
MultiPL-E is a system for translating unit test-driven neural code generation benchmarks to new languages. It is part of the BigCode Code Generation LM Harness and allows for evaluating Code LLMs using various benchmarks. The tool supports multiple versions with improvements and new language additions, providing a scalable and polyglot approach to benchmarking neural code generation. Users can access a tutorial for direct usage and explore the dataset of translated prompts on the Hugging Face Hub.
py-vectara-agentic
The `vectara-agentic` Python library is designed for developing powerful AI assistants using Vectara and Agentic-RAG. It supports various agent types, includes pre-built tools for domains like finance and legal, and enables easy creation of custom AI assistants and agents. The library provides tools for summarizing text, rephrasing text, legal tasks like summarizing legal text and critiquing as a judge, financial tasks like analyzing balance sheets and income statements, and database tools for inspecting and querying databases. It also supports observability via LlamaIndex and Arize Phoenix integration.
ScandEval
ScandEval is a framework for evaluating pretrained language models on mono- or multilingual language tasks. It provides a unified interface for benchmarking models on a variety of tasks, including sentiment analysis, question answering, and machine translation. ScandEval is designed to be easy to use and extensible, making it a valuable tool for researchers and practitioners alike.
mosec
Mosec is a high-performance and flexible model serving framework for building ML model-enabled backend and microservices. It bridges the gap between any machine learning models you just trained and the efficient online service API. * **Highly performant** : web layer and task coordination built with Rust 🦀, which offers blazing speed in addition to efficient CPU utilization powered by async I/O * **Ease of use** : user interface purely in Python 🐍, by which users can serve their models in an ML framework-agnostic manner using the same code as they do for offline testing * **Dynamic batching** : aggregate requests from different users for batched inference and distribute results back * **Pipelined stages** : spawn multiple processes for pipelined stages to handle CPU/GPU/IO mixed workloads * **Cloud friendly** : designed to run in the cloud, with the model warmup, graceful shutdown, and Prometheus monitoring metrics, easily managed by Kubernetes or any container orchestration systems * **Do one thing well** : focus on the online serving part, users can pay attention to the model optimization and business logic
mflux
MFLUX is a line-by-line port of the FLUX implementation in the Huggingface Diffusers library to Apple MLX. It aims to run powerful FLUX models from Black Forest Labs locally on Mac machines. The codebase is minimal and explicit, prioritizing readability over generality and performance. Models are implemented from scratch in MLX, with tokenizers from the Huggingface Transformers library. Dependencies include Numpy and Pillow for image post-processing. Installation can be done using `uv tool` or classic virtual environment setup. Command-line arguments allow for image generation with specified models, prompts, and optional parameters. Quantization options for speed and memory reduction are available. LoRA adapters can be loaded for fine-tuning image generation. Controlnet support provides more control over image generation with reference images. Current limitations include generating images one by one, lack of support for negative prompts, and some LoRA adapters not working.
mimir
MIMIR is a Python package designed for measuring memorization in Large Language Models (LLMs). It provides functionalities for conducting experiments related to membership inference attacks on LLMs. The package includes implementations of various attacks such as Likelihood, Reference-based, Zlib Entropy, Neighborhood, Min-K% Prob, Min-K%++, Gradient Norm, and allows users to extend it by adding their own datasets and attacks.
mentals-ai
Mentals AI is a tool designed for creating and operating agents that feature loops, memory, and various tools, all through straightforward markdown syntax. This tool enables you to concentrate solely on the agent’s logic, eliminating the necessity to compose underlying code in Python or any other language. It redefines the foundational frameworks for future AI applications by allowing the creation of agents with recursive decision-making processes, integration of reasoning frameworks, and control flow expressed in natural language. Key concepts include instructions with prompts and references, working memory for context, short-term memory for storing intermediate results, and control flow from strings to algorithms. The tool provides a set of native tools for message output, user input, file handling, Python interpreter, Bash commands, and short-term memory. The roadmap includes features like a web UI, vector database tools, agent's experience, and tools for image generation and browsing. The idea behind Mentals AI originated from studies on psychoanalysis executive functions and aims to integrate 'System 1' (cognitive executor) with 'System 2' (central executive) to create more sophisticated agents.
For similar tasks

LeanCopilot
Lean Copilot is a tool that enables the use of large language models (LLMs) in Lean for proof automation. It provides features such as suggesting tactics/premises, searching for proofs, and running inference of LLMs. Users can utilize built-in models from LeanDojo or bring their own models to run locally or on the cloud. The tool supports platforms like Linux, macOS, and Windows WSL, with optional CUDA and cuDNN for GPU acceleration. Advanced users can customize behavior using Tactic APIs and Model APIs. Lean Copilot also allows users to bring their own models through ExternalGenerator or ExternalEncoder. The tool comes with caveats such as occasional crashes and issues with premise selection and proof search. Users can get in touch through GitHub Discussions for questions, bug reports, feature requests, and suggestions. The tool is designed to enhance theorem proving in Lean using LLMs.
langflow
Langflow is an open-source Python-powered visual framework designed for building multi-agent and RAG applications. It is fully customizable, language model agnostic, and vector store agnostic. Users can easily create flows by dragging components onto the canvas, connect them, and export the flow as a JSON file. Langflow also provides a command-line interface (CLI) for easy management and configuration, allowing users to customize the behavior of Langflow for development or specialized deployment scenarios. The tool can be deployed on various platforms such as Google Cloud Platform, Railway, and Render. Contributors are welcome to enhance the project on GitHub by following the contributing guidelines.
TypeGPT
TypeGPT is a Python application that enables users to interact with ChatGPT or Google Gemini from any text field in their operating system using keyboard shortcuts. It provides global accessibility, keyboard shortcuts for communication, and clipboard integration for larger text inputs. Users need to have Python 3.x installed along with specific packages and API keys from OpenAI for ChatGPT access. The tool allows users to run the program normally or in the background, manage processes, and stop the program. Users can use keyboard shortcuts like `/ask`, `/see`, `/stop`, `/chatgpt`, `/gemini`, `/check`, and `Shift + Cmd + Enter` to interact with the application in any text field. Customization options are available by modifying files like `keys.txt` and `system_prompt.txt`. Contributions are welcome, and future plans include adding support for other APIs and a user-friendly GUI.
HookPHP
HookPHP is an open-source project that provides a PHP extension for hooking into various aspects of PHP applications. It allows developers to easily extend and customize the behavior of their PHP applications by providing hooks at key points in the execution flow. With HookPHP, developers can efficiently add custom functionality, modify existing behavior, and enhance the overall performance of their PHP applications. The project is licensed under the MIT license, making it accessible for developers to use and contribute to.
flutter_gemma
Flutter Gemma is a family of lightweight, state-of-the art open models that bring the power of Google's Gemma language models directly to Flutter applications. It allows for local execution on user devices, supports both iOS and Android platforms, and offers LoRA support for tailored AI behavior. The tool provides a simple interface for integrating Gemma models into Flutter projects, enabling advanced AI capabilities without relying on external servers. Users can easily download pre-trained Gemma models, fine-tune them for specific use cases, and customize behavior using LoRA weights. The tool supports model and LoRA weight management, model initialization, response generation, and chat scenarios, with considerations for model size, LoRA weights, and production app deployment.
tiledesk-chatbot
Tiledesk Chatbot Engine is a Node.js-based framework for creating and managing interactive chatbots. It is designed to work seamlessly with the Tiledesk Design Studio, allowing easy design and customization of chatbot behavior. The engine is scalable, performant, and encourages collaboration and innovation through its open-source nature under the MIT license.
claude-code-settings
A repository collecting best practices for Claude Code settings and customization. It provides configuration files for customizing Claude Code's behavior and building an efficient development environment. The repository includes custom agents and skills for specific domains, interactive development workflow features, efficient development rules, and team workflow with Codex MCP. Users can leverage the provided configuration files and tools to enhance their development process and improve code quality.

djl
Deep Java Library (DJL) is an open-source, high-level, engine-agnostic Java framework for deep learning. It is designed to be easy to get started with and simple to use for Java developers. DJL provides a native Java development experience and allows users to integrate machine learning and deep learning models with their Java applications. The framework is deep learning engine agnostic, enabling users to switch engines at any point for optimal performance. DJL's ergonomic API interface guides users with best practices to accomplish deep learning tasks, such as running inference and training neural networks.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

agentcloud
AgentCloud is an open-source platform that enables companies to build and deploy private LLM chat apps, empowering teams to securely interact with their data. It comprises three main components: Agent Backend, Webapp, and Vector Proxy. To run this project locally, clone the repository, install Docker, and start the services. The project is licensed under the GNU Affero General Public License, version 3 only. Contributions and feedback are welcome from the community.

oss-fuzz-gen
This framework generates fuzz targets for real-world `C`/`C++` projects with various Large Language Models (LLM) and benchmarks them via the `OSS-Fuzz` platform. It manages to successfully leverage LLMs to generate valid fuzz targets (which generate non-zero coverage increase) for 160 C/C++ projects. The maximum line coverage increase is 29% from the existing human-written targets.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement
The Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement repository provides packaged Industry Scenario DREAM Demos with ARM templates (Containing a demo web application, Power BI reports, Synapse resources, AML Notebooks etc.) that can be deployed in a customer’s subscription using the CAPE tool within a matter of few hours. Partners can also deploy DREAM Demos in their own subscriptions using DPoC.