
ell
A language model programming library.
Stars: 4879
ell is a lightweight, functional prompt engineering framework that treats prompts as programs rather than strings. It provides tools for prompt versioning, monitoring, and visualization, as well as support for multimodal inputs and outputs. The framework aims to simplify the process of prompt engineering for language models.
README:
pip install -U "ell-ai[all]"ell is a lightweight, functional prompt engineering framework built on a few core principles:
Prompts aren't just strings; they are all the code that leads to strings being sent to a language model. In ell we think of one particular way of using a language model as a discrete subroutine called a language model program.
import ell
@ell.simple(model="gpt-4o")
def hello(world : str):
"""You are a helpful assistant that writes in lower case.""" # System Message
return f"Say hello to {world[::-1]} with a poem." # User Message
hello("sama")The process of prompt engineering involves many iterations, similar to the optimization processes in machine learning. Because LMPs are just functions, ell provides rich tooling for this process.
ell provides automatic versioning and serialization of prompts through static and dynamic analysis and gpt-4o-mini autogenerated commit messages directly to a local store. This process is similar to checkpointing in a machine learning training loop, but it doesn't require any special IDE or editor - it's all done with regular Python code.
Prompt engineering goes from a dark art to a science with the right tools. Ell Studio is a local, open source tool for prompt version control, monitoring, visualization. With Ell Studio you can empiricize your prompt optimization process over time and catch regressions before it's too late.

ell-studio --storage ./logdir LLMs can process and generate various types of content, including text, images, audio, and video. Prompt engineering with these data types should be as easy as it is with text.
from PIL import Image
import ell
@ell.simple(model="gpt-4o", temperature=0.1)
def describe_activity(image: Image.Image):
return [
ell.system("You are VisionGPT. Answer <5 words all lower case."),
ell.user(["Describe what the person in the image is doing:", image])
]
# Capture an image from the webcam
describe_activity(capture_webcam_image()) # "they are holding a book"ell supports rich type coercion for multimodal inputs and outputs. You can use PIL images, audio, and other multimodal inputs inline in Message objects returned by LMPs.
Read more in the docs!
To install ell and ell studio, you can use pip. Follow these steps:
-
Open your terminal or command prompt.
-
Run the following command to install the
ell-aipackage from PyPI:pip install ell-ai
-
Verify the installation by checking the version of
ell:python -c "import ell; print(ell.__version__)"
This will install both ell and ell studio on your system, allowing you to start using the tools for prompt engineering and visualization.
Explore the documentation to learn more about ell and its features. Follow the Getting Started guide to create your first Language Model Program. Join our Discord community to connect with other users and get support.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for ell
Similar Open Source Tools

ell
ell is a lightweight, functional prompt engineering framework that treats prompts as programs rather than strings. It provides tools for prompt versioning, monitoring, and visualization, as well as support for multimodal inputs and outputs. The framework aims to simplify the process of prompt engineering for language models.
LeanCopilot
Lean Copilot is a tool that enables the use of large language models (LLMs) in Lean for proof automation. It provides features such as suggesting tactics/premises, searching for proofs, and running inference of LLMs. Users can utilize built-in models from LeanDojo or bring their own models to run locally or on the cloud. The tool supports platforms like Linux, macOS, and Windows WSL, with optional CUDA and cuDNN for GPU acceleration. Advanced users can customize behavior using Tactic APIs and Model APIs. Lean Copilot also allows users to bring their own models through ExternalGenerator or ExternalEncoder. The tool comes with caveats such as occasional crashes and issues with premise selection and proof search. Users can get in touch through GitHub Discussions for questions, bug reports, feature requests, and suggestions. The tool is designed to enhance theorem proving in Lean using LLMs.
truss
Truss is a tool that simplifies the process of serving AI/ML models in production. It provides a consistent and easy-to-use interface for packaging, testing, and deploying models, regardless of the framework they were created with. Truss also includes a live reload server for fast feedback during development, and a batteries-included model serving environment that eliminates the need for Docker and Kubernetes configuration.
py-vectara-agentic
The `vectara-agentic` Python library is designed for developing powerful AI assistants using Vectara and Agentic-RAG. It supports various agent types, includes pre-built tools for domains like finance and legal, and enables easy creation of custom AI assistants and agents. The library provides tools for summarizing text, rephrasing text, legal tasks like summarizing legal text and critiquing as a judge, financial tasks like analyzing balance sheets and income statements, and database tools for inspecting and querying databases. It also supports observability via LlamaIndex and Arize Phoenix integration.
web-llm
WebLLM is a modular and customizable javascript package that directly brings language model chats directly onto web browsers with hardware acceleration. Everything runs inside the browser with no server support and is accelerated with WebGPU. WebLLM is fully compatible with OpenAI API. That is, you can use the same OpenAI API on any open source models locally, with functionalities including json-mode, function-calling, streaming, etc. We can bring a lot of fun opportunities to build AI assistants for everyone and enable privacy while enjoying GPU acceleration.
mflux
MFLUX is a line-by-line port of the FLUX implementation in the Huggingface Diffusers library to Apple MLX. It aims to run powerful FLUX models from Black Forest Labs locally on Mac machines. The codebase is minimal and explicit, prioritizing readability over generality and performance. Models are implemented from scratch in MLX, with tokenizers from the Huggingface Transformers library. Dependencies include Numpy and Pillow for image post-processing. Installation can be done using `uv tool` or classic virtual environment setup. Command-line arguments allow for image generation with specified models, prompts, and optional parameters. Quantization options for speed and memory reduction are available. LoRA adapters can be loaded for fine-tuning image generation. Controlnet support provides more control over image generation with reference images. Current limitations include generating images one by one, lack of support for negative prompts, and some LoRA adapters not working.
HuggingFaceGuidedTourForMac
HuggingFaceGuidedTourForMac is a guided tour on how to install optimized pytorch and optionally Apple's new MLX, JAX, and TensorFlow on Apple Silicon Macs. The repository provides steps to install homebrew, pytorch with MPS support, MLX, JAX, TensorFlow, and Jupyter lab. It also includes instructions on running large language models using HuggingFace transformers. The repository aims to help users set up their Macs for deep learning experiments with optimized performance.
paper-qa
PaperQA is a minimal package for question and answering from PDFs or text files, providing very good answers with in-text citations. It uses OpenAI Embeddings to embed and search documents, and includes a process of embedding docs, queries, searching for top passages, creating summaries, using an LLM to re-score and select relevant summaries, putting summaries into prompt, and generating answers. The tool can be used to answer specific questions related to scientific research by leveraging citations and relevant passages from documents.
elmer
Elmer is a user-friendly wrapper over common APIs for calling llm’s, with support for streaming and easy registration and calling of R functions. Users can interact with Elmer in various ways, such as interactive chat console, interactive method call, programmatic chat, and streaming results. Elmer also supports async usage for running multiple chat sessions concurrently, useful for Shiny applications. The tool calling feature allows users to define external tools that Elmer can request to execute, enhancing the capabilities of the chat model.
termax
Termax is an LLM agent in your terminal that converts natural language to commands. It is featured by: - Personalized Experience: Optimize the command generation with RAG. - Various LLMs Support: OpenAI GPT, Anthropic Claude, Google Gemini, Mistral AI, and more. - Shell Extensions: Plugin with popular shells like `zsh`, `bash` and `fish`. - Cross Platform: Able to run on Windows, macOS, and Linux.
garak
Garak is a vulnerability scanner designed for LLMs (Large Language Models) that checks for various weaknesses such as hallucination, data leakage, prompt injection, misinformation, toxicity generation, and jailbreaks. It combines static, dynamic, and adaptive probes to explore vulnerabilities in LLMs. Garak is a free tool developed for red-teaming and assessment purposes, focusing on making LLMs or dialog systems fail. It supports various LLM models and can be used to assess their security and robustness.
paper-qa
PaperQA is a minimal package for question and answering from PDFs or text files, providing very good answers with in-text citations. It uses OpenAI Embeddings to embed and search documents, and follows a process of embedding docs and queries, searching for top passages, creating summaries, scoring and selecting relevant summaries, putting summaries into prompt, and generating answers. Users can customize prompts and use various models for embeddings and LLMs. The tool can be used asynchronously and supports adding documents from paths, files, or URLs.
LLM-Merging
LLM-Merging is a repository containing starter code for the LLM-Merging competition. It provides a platform for efficiently building LLMs through merging methods. Users can develop new merging methods by creating new files in the specified directory and extending existing classes. The repository includes instructions for setting up the environment, developing new merging methods, testing the methods on specific datasets, and submitting solutions for evaluation. It aims to facilitate the development and evaluation of merging methods for LLMs.
garak
Garak is a free tool that checks if a Large Language Model (LLM) can be made to fail in a way that is undesirable. It probes for hallucination, data leakage, prompt injection, misinformation, toxicity generation, jailbreaks, and many other weaknesses. Garak's a free tool. We love developing it and are always interested in adding functionality to support applications.
EuroEval
EuroEval is a robust European language model benchmark tool, formerly known as ScandEval. It provides a platform to benchmark pretrained models on various tasks across different languages. Users can evaluate models, datasets, and metrics both online and offline. The tool supports benchmarking from the command line, script, and Docker. Additionally, users can reproduce datasets used in the project using provided scripts. EuroEval welcomes contributions and offers guidelines for general contributions and adding new datasets.
turnkeyml
TurnkeyML is a tools framework that integrates models, toolchains, and hardware backends to simplify the evaluation and actuation of deep learning models. It supports use cases like exporting ONNX files, performance validation, functional coverage measurement, stress testing, and model insights analysis. The framework consists of analysis, build, runtime, reporting tools, and a models corpus, seamlessly integrated to provide comprehensive functionality with simple commands. Extensible through plugins, it offers support for various export and optimization tools and AI runtimes. The project is actively seeking collaborators and is licensed under Apache 2.0.
For similar tasks

HPT
Hyper-Pretrained Transformers (HPT) is a novel multimodal LLM framework from HyperGAI, trained for vision-language models capable of understanding both textual and visual inputs. The repository contains the open-source implementation of inference code to reproduce the evaluation results of HPT Air on different benchmarks. HPT has achieved competitive results with state-of-the-art models on various multimodal LLM benchmarks. It offers models like HPT 1.5 Air and HPT 1.0 Air, providing efficient solutions for vision-and-language tasks.
learnopencv
LearnOpenCV is a repository containing code for Computer Vision, Deep learning, and AI research articles shared on the blog LearnOpenCV.com. It serves as a resource for individuals looking to enhance their expertise in AI through various courses offered by OpenCV. The repository includes a wide range of topics such as image inpainting, instance segmentation, robotics, deep learning models, and more, providing practical implementations and code examples for readers to explore and learn from.
spark-free-api
Spark AI Free 服务 provides high-speed streaming output, multi-turn dialogue support, AI drawing support, long document interpretation, and image parsing. It offers zero-configuration deployment, multi-token support, and automatic session trace cleaning. It is fully compatible with the ChatGPT interface. The repository includes multiple free-api projects for various AI services. Users can access the API for tasks such as chat completions, AI drawing, document interpretation, image analysis, and ssoSessionId live checking. The project also provides guidelines for deployment using Docker, Docker-compose, Render, Vercel, and native deployment methods. It recommends using custom clients for faster and simpler access to the free-api series projects.
mlx-vlm
MLX-VLM is a package designed for running Vision LLMs on Mac systems using MLX. It provides a convenient way to install and utilize the package for processing large language models related to vision tasks. The tool simplifies the process of running LLMs on Mac computers, offering a seamless experience for users interested in leveraging MLX for vision-related projects.
clarifai-python-grpc
This is the official Clarifai gRPC Python client for interacting with their recognition API. Clarifai offers a platform for data scientists, developers, researchers, and enterprises to utilize artificial intelligence for image, video, and text analysis through computer vision and natural language processing. The client allows users to authenticate, predict concepts in images, and access various functionalities provided by the Clarifai API. It follows a versioning scheme that aligns with the backend API updates and includes specific instructions for installation and troubleshooting. Users can explore the Clarifai demo, sign up for an account, and refer to the documentation for detailed information.
horde-worker-reGen
This repository provides the latest implementation for the AI Horde Worker, allowing users to utilize their graphics card(s) to generate, post-process, or analyze images for others. It offers a platform where users can create images and earn 'kudos' in return, granting priority for their own image generations. The repository includes important details for setup, recommendations for system configurations, instructions for installation on Windows and Linux, basic usage guidelines, and information on updating the AI Horde Worker. Users can also run the worker with multiple GPUs and receive notifications for updates through Discord. Additionally, the repository contains models that are licensed under the CreativeML OpenRAIL License.
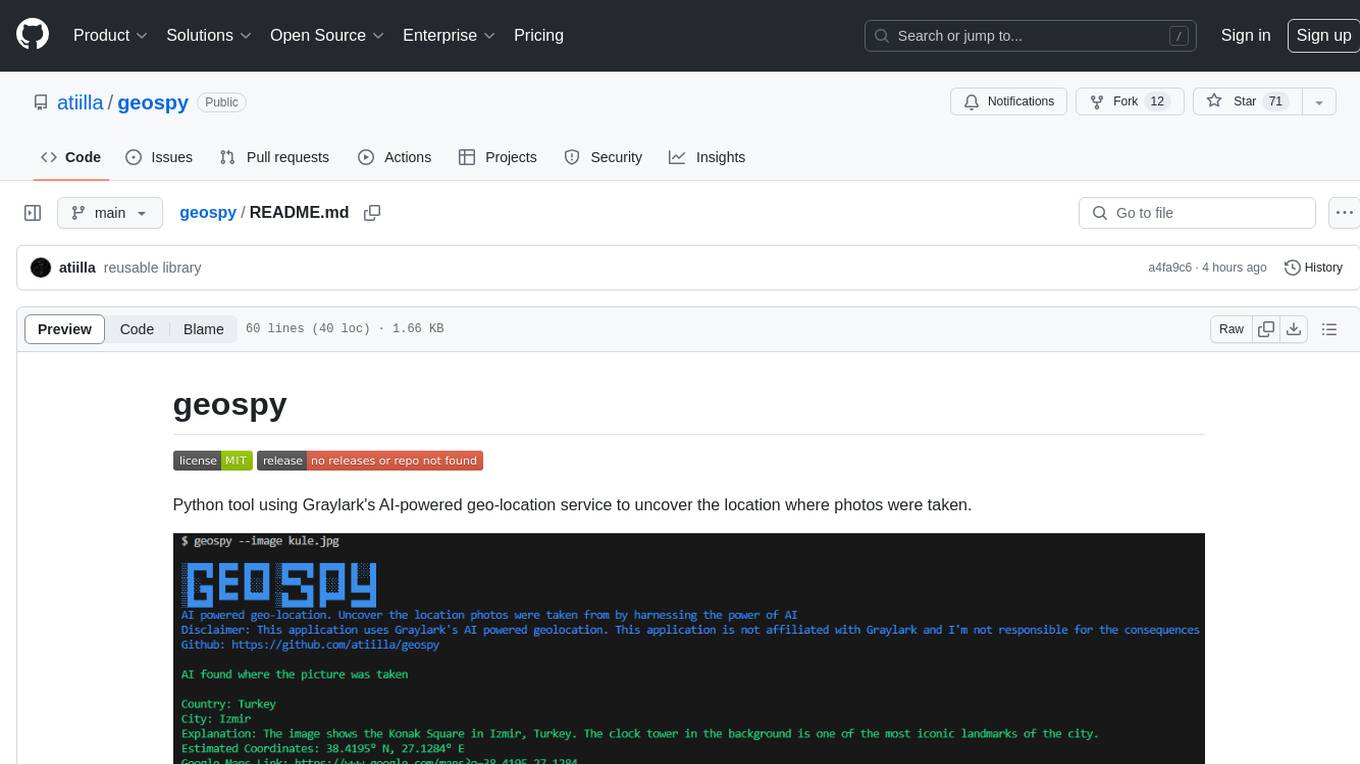
geospy
Geospy is a Python tool that utilizes Graylark's AI-powered geolocation service to determine the location where photos were taken. It allows users to analyze images and retrieve information such as country, city, explanation, coordinates, and Google Maps links. The tool provides a seamless way to integrate geolocation services into various projects and applications.
Awesome-Colorful-LLM
Awesome-Colorful-LLM is a meticulously assembled anthology of vibrant multimodal research focusing on advancements propelled by large language models (LLMs) in domains such as Vision, Audio, Agent, Robotics, and Fundamental Sciences like Mathematics. The repository contains curated collections of works, datasets, benchmarks, projects, and tools related to LLMs and multimodal learning. It serves as a comprehensive resource for researchers and practitioners interested in exploring the intersection of language models and various modalities for tasks like image understanding, video pretraining, 3D modeling, document understanding, audio analysis, agent learning, robotic applications, and mathematical research.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.






