
elmer
Call LLM APIs from R
Stars: 71
Elmer is a user-friendly wrapper over common APIs for calling llm’s, with support for streaming and easy registration and calling of R functions. Users can interact with Elmer in various ways, such as interactive chat console, interactive method call, programmatic chat, and streaming results. Elmer also supports async usage for running multiple chat sessions concurrently, useful for Shiny applications. The tool calling feature allows users to define external tools that Elmer can request to execute, enhancing the capabilities of the chat model.
README:
The goal of elmer is to provide a user friendly wrapper over the most common llm providers. Major design goals include support for streaming and making it easy to register and call R functions.
You can install the development version of elmer from GitHub with:
# install.packages("pak")
pak::pak("hadley/elmer")Depending on which backend you use, you’ll need to set the appropriate
environment variable in your ~/.Renviron (an easy way to open that
file is to call usethis::edit_r_environ()):
- For
chat_claude(), setANTHROPIC_API_KEYusing the key from https://console.anthropic.com/account/keys. - For
chat_gemini(), setGOOGLE_API_KEYusing the key from https://aistudio.google.com/app/apikey. - For
chat_openai()setOPENAI_API_KEYusing the key from https://platform.openai.com/account/api-keys.
You chat with elmer in several different ways, depending on whether you are working interactively or programmatically. They all start with creating a new chat object:
library(elmer)
chat <- chat_openai(
model = "gpt-4o-mini",
system_prompt = "You are a friendly but terse assistant.",
echo = TRUE
)Chat objects are stateful: they retain the context of the conversation, so each new query can build on the previous ones. This is true regardless of which of the various ways of chatting you use.
The most interactive, least programmatic way of using elmer is to chat
with it directly in your R console with live_console(chat) or in your
browser with live_browser().
live_console(chat)
#> ╔════════════════════════════════════════════════════════╗
#> ║ Entering chat console. Use """ for multi-line input. ║
#> ║ Press Ctrl+C to quit. ║
#> ╚════════════════════════════════════════════════════════╝
#> >>> Who were the original creators of R?
#> R was originally created by Ross Ihaka and Robert Gentleman at the University of
#> Auckland, New Zealand.
#>
#> >>> When was that?
#> R was initially released in 1995. Development began a few years prior to that,
#> in the early 1990s.The chat console is useful for quickly exploring the capabilities of the model, especially when you’ve customized the chat object with tool integrations (see below).
Again, keep in mind that the chat object retains state, so when you enter the chat console, any previous interactions with that chat object are still part of the conversation, and any interactions you have in the chat console will persist even after you exit back to the R prompt.
The second most interactive way to chat using elmer is to call the
chat() method.
chat$chat("What preceding languages most influenced R?")
#> R was primarily influenced by the S programming language, particularly S-PLUS.
#> Other languages that had an impact include Scheme and various data analysis
#> languages.If you initialize the chat object with echo = TRUE, as we did above,
the chat method streams the response to the console as it arrives.
When the entire response is received, it is returned as a character
vector (invisibly, so it’s not printed twice).
This mode is useful when you want to see the response as it arrives, but you don’t want to enter the chat console.
If you want to ask a question about an image, you can pass one or more
additional input arguments using content_image_file() and/or
content_image_url().
chat$chat(
content_image_url("https://www.r-project.org/Rlogo.png"),
"Can you explain this logo?"
)
#> The logo of R features a stylized letter "R" in blue, enclosed in an oval shape that resembles the letter "O,"
#> signifying the programming language's name. The design conveys a modern and professional look, reflecting its use
#> in statistical computing and data analysis. The blue color often represents trust and reliability, which aligns
#> with R's role in data science.The content_image_url function takes a URL to an image file and sends
that URL directly to the API. The content_image_file function takes a
path to a local image file and encodes it as a base64 string to send to
the API. Note that by default, content_image_file automatically
resizes the image to fit within 512x512 pixels; set the resize
parameter to "high" if higher resolution is needed.
If you don’t want to see the response as it arrives, you can turn off
echoing by leaving off the echo = TRUE argument to chat_openai().
chat <- chat_openai(
model = "gpt-4o-mini",
system_prompt = "You are a friendly but terse assistant."
)
chat$chat("Is R a functional programming language?")
#> [1] "Yes, R supports functional programming concepts. It allows functions to be first-class objects, supports higher-order functions, and encourages the use of functions as core components of code. However, it also supports procedural and object-oriented programming styles."This mode is useful for programming using elmer, when the result is either not intended for human consumption or when you want to process the response before displaying it.
- Learn more about streaming and async APIs in
vignette("streaming-async"). - Learn more about tool calling (aka function calling) in
vignette("tool-calling").
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for elmer
Similar Open Source Tools

elmer
Elmer is a user-friendly wrapper over common APIs for calling llm’s, with support for streaming and easy registration and calling of R functions. Users can interact with Elmer in various ways, such as interactive chat console, interactive method call, programmatic chat, and streaming results. Elmer also supports async usage for running multiple chat sessions concurrently, useful for Shiny applications. The tool calling feature allows users to define external tools that Elmer can request to execute, enhancing the capabilities of the chat model.
ellmer
ellmer is a tool that facilitates the use of large language models (LLM) from R. It supports various LLM providers and offers features such as streaming outputs, tool/function calling, and structured data extraction. Users can interact with ellmer in different ways, including interactive chat console, interactive method call, and programmatic chat. The tool provides support for multiple model providers and offers recommendations for different use cases, such as exploration or organizational use.

appworld
AppWorld is a high-fidelity execution environment of 9 day-to-day apps, operable via 457 APIs, populated with digital activities of ~100 people living in a simulated world. It provides a benchmark of natural, diverse, and challenging autonomous agent tasks requiring rich and interactive coding. The repository includes implementations of AppWorld apps and APIs, along with tests. It also introduces safety features for code execution and provides guides for building agents and extending the benchmark.
node_characterai
Node.js client for the unofficial Character AI API, an awesome website which brings characters to life with AI! This repository is inspired by RichardDorian's unofficial node API. Though, I found it hard to use and it was not really stable and archived. So I remade it in javascript. This project is not affiliated with Character AI in any way! It is a community project. The purpose of this project is to bring and build projects powered by Character AI. If you like this project, please check their website.
smartcat
Smartcat is a CLI interface that brings language models into the Unix ecosystem, allowing power users to leverage the capabilities of LLMs in their daily workflows. It features a minimalist design, seamless integration with terminal and editor workflows, and customizable prompts for specific tasks. Smartcat currently supports OpenAI, Mistral AI, and Anthropic APIs, providing access to a range of language models. With its ability to manipulate file and text streams, integrate with editors, and offer configurable settings, Smartcat empowers users to automate tasks, enhance code quality, and explore creative possibilities.
llamabot
LlamaBot is a Pythonic bot interface to Large Language Models (LLMs), providing an easy way to experiment with LLMs in Jupyter notebooks and build Python apps utilizing LLMs. It supports all models available in LiteLLM. Users can access LLMs either through local models with Ollama or by using API providers like OpenAI and Mistral. LlamaBot offers different bot interfaces like SimpleBot, ChatBot, QueryBot, and ImageBot for various tasks such as rephrasing text, maintaining chat history, querying documents, and generating images. The tool also includes CLI demos showcasing its capabilities and supports contributions for new features and bug reports from the community.
SirChatalot
A Telegram bot that proves you don't need a body to have a personality. It can use various text and image generation APIs to generate responses to user messages. For text generation, the bot can use: * OpenAI's ChatGPT API (or other compatible API). Vision capabilities can be used with GPT-4 models. Function calling can be used with Function calling. * Anthropic's Claude API. Vision capabilities can be used with Claude 3 models. Function calling can be used with tool use. * YandexGPT API Bot can also generate images with: * OpenAI's DALL-E * Stability AI * Yandex ART This bot can also be used to generate responses to voice messages. Bot will convert the voice message to text and will then generate a response. Speech recognition can be done using the OpenAI's Whisper model. To use this feature, you need to install the ffmpeg library. This bot is also support working with files, see Files section for more details. If function calling is enabled, bot can generate images and search the web (limited).
Discord-AI-Selfbot
Discord-AI-Selfbot is a Python-based Discord selfbot that uses the `discord.py-self` library to automatically respond to messages mentioning its trigger word using Groq API's Llama-3 model. It functions as a normal Discord bot on a real Discord account, enabling interactions in DMs, servers, and group chats without needing to invite a bot. The selfbot comes with features like custom AI instructions, free LLM model usage, mention and reply recognition, message handling, channel-specific responses, and a psychoanalysis command to analyze user messages for insights on personality.
kwaak
Kwaak is a tool that allows users to run a team of autonomous AI agents locally from their own machine. It enables users to write code, improve test coverage, update documentation, and enhance code quality while focusing on building innovative projects. Kwaak is designed to run multiple agents in parallel, interact with codebases, answer questions about code, find examples, write and execute code, create pull requests, and more. It is free and open-source, allowing users to bring their own API keys or models via Ollama. Kwaak is part of the bosun.ai project, aiming to be a platform for autonomous code improvement.
garak
Garak is a free tool that checks if a Large Language Model (LLM) can be made to fail in a way that is undesirable. It probes for hallucination, data leakage, prompt injection, misinformation, toxicity generation, jailbreaks, and many other weaknesses. Garak's a free tool. We love developing it and are always interested in adding functionality to support applications.
Discord-AI-Chatbot
Discord AI Chatbot is a versatile tool that seamlessly integrates into your Discord server, offering a wide range of capabilities to enhance your communication and engagement. With its advanced language model, the bot excels at imaginative generation, providing endless possibilities for creative expression. Additionally, it offers secure credential management, ensuring the privacy of your data. The bot's hybrid command system combines the best of slash and normal commands, providing flexibility and ease of use. It also features mention recognition, ensuring prompt responses whenever you mention it or use its name. The bot's message handling capabilities prevent confusion by recognizing when you're replying to others. You can customize the bot's behavior by selecting from a range of pre-existing personalities or creating your own. The bot's web access feature unlocks a new level of convenience, allowing you to interact with it from anywhere. With its open-source nature, you have the freedom to modify and adapt the bot to your specific needs.
fabric
Fabric is an open-source framework for augmenting humans using AI. It provides a structured approach to breaking down problems into individual components and applying AI to them one at a time. Fabric includes a collection of pre-defined Patterns (prompts) that can be used for a variety of tasks, such as extracting the most interesting parts of YouTube videos and podcasts, writing essays, summarizing academic papers, creating AI art prompts, and more. Users can also create their own custom Patterns. Fabric is designed to be easy to use, with a command-line interface and a variety of helper apps. It is also extensible, allowing users to integrate it with their own AI applications and infrastructure.
LeanAide
LeanAide is a work in progress AI tool designed to assist with development using the Lean Theorem Prover. It currently offers a tool that translates natural language statements to Lean types, including theorem statements. The tool is based on GPT 3.5-turbo/GPT 4 and requires an OpenAI key for usage. Users can include LeanAide as a dependency in their projects to access the translation functionality.
garak
Garak is a vulnerability scanner designed for LLMs (Large Language Models) that checks for various weaknesses such as hallucination, data leakage, prompt injection, misinformation, toxicity generation, and jailbreaks. It combines static, dynamic, and adaptive probes to explore vulnerabilities in LLMs. Garak is a free tool developed for red-teaming and assessment purposes, focusing on making LLMs or dialog systems fail. It supports various LLM models and can be used to assess their security and robustness.
mentals-ai
Mentals AI is a tool designed for creating and operating agents that feature loops, memory, and various tools, all through straightforward markdown syntax. This tool enables you to concentrate solely on the agent’s logic, eliminating the necessity to compose underlying code in Python or any other language. It redefines the foundational frameworks for future AI applications by allowing the creation of agents with recursive decision-making processes, integration of reasoning frameworks, and control flow expressed in natural language. Key concepts include instructions with prompts and references, working memory for context, short-term memory for storing intermediate results, and control flow from strings to algorithms. The tool provides a set of native tools for message output, user input, file handling, Python interpreter, Bash commands, and short-term memory. The roadmap includes features like a web UI, vector database tools, agent's experience, and tools for image generation and browsing. The idea behind Mentals AI originated from studies on psychoanalysis executive functions and aims to integrate 'System 1' (cognitive executor) with 'System 2' (central executive) to create more sophisticated agents.
MultiPL-E
MultiPL-E is a system for translating unit test-driven neural code generation benchmarks to new languages. It is part of the BigCode Code Generation LM Harness and allows for evaluating Code LLMs using various benchmarks. The tool supports multiple versions with improvements and new language additions, providing a scalable and polyglot approach to benchmarking neural code generation. Users can access a tutorial for direct usage and explore the dataset of translated prompts on the Hugging Face Hub.
For similar tasks
call-gpt
Call GPT is a voice application that utilizes Deepgram for Speech to Text, elevenlabs for Text to Speech, and OpenAI for GPT prompt completion. It allows users to chat with ChatGPT on the phone, providing better transcription, understanding, and speaking capabilities than traditional IVR systems. The app returns responses with low latency, allows user interruptions, maintains chat history, and enables GPT to call external tools. It coordinates data flow between Deepgram, OpenAI, ElevenLabs, and Twilio Media Streams, enhancing voice interactions.

elmer
Elmer is a user-friendly wrapper over common APIs for calling llm’s, with support for streaming and easy registration and calling of R functions. Users can interact with Elmer in various ways, such as interactive chat console, interactive method call, programmatic chat, and streaming results. Elmer also supports async usage for running multiple chat sessions concurrently, useful for Shiny applications. The tool calling feature allows users to define external tools that Elmer can request to execute, enhancing the capabilities of the chat model.
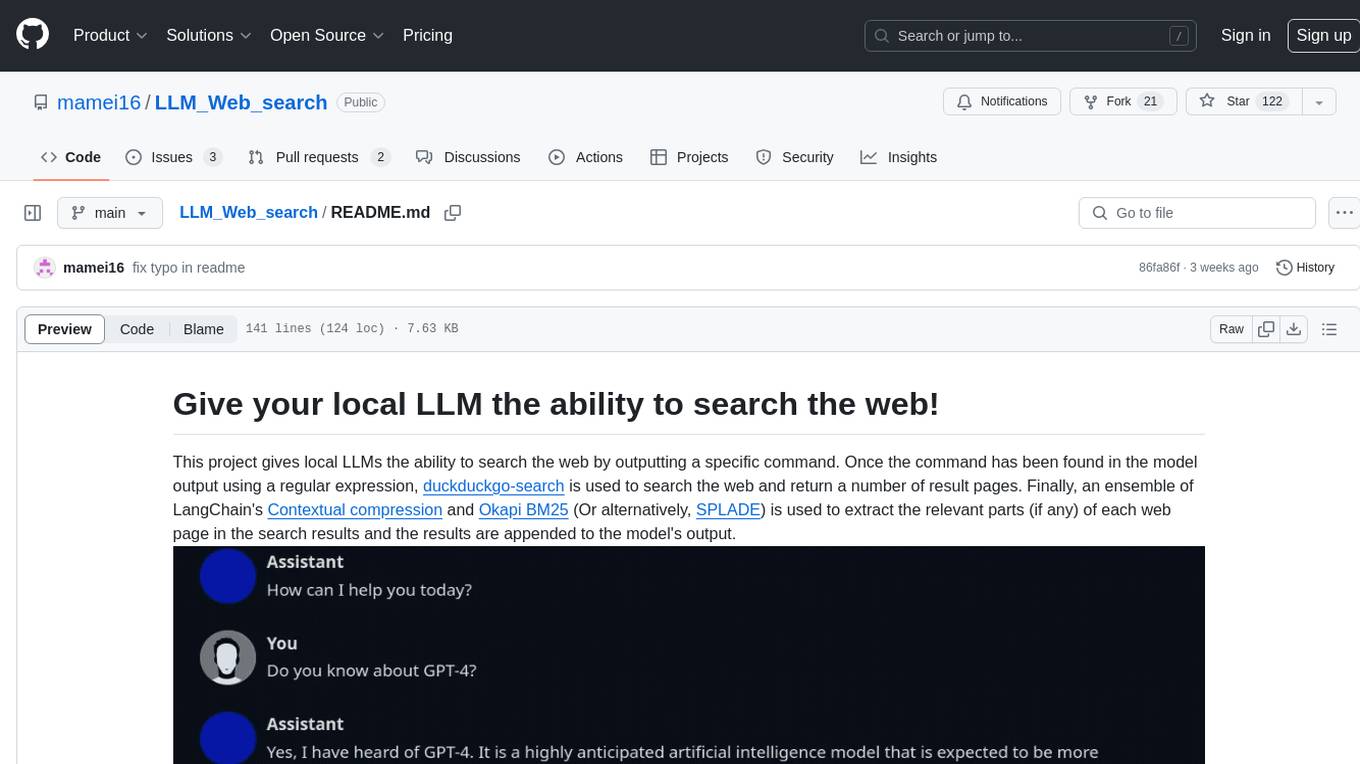
LLM_Web_search
LLM_Web_search project gives local LLMs the ability to search the web by outputting a specific command. It uses regular expressions to extract search queries from model output and then utilizes duckduckgo-search to search the web. LangChain's Contextual compression and Okapi BM25 or SPLADE are used to extract relevant parts of web pages in search results. The extracted results are appended to the model's output.
node-llama-cpp
node-llama-cpp is a tool that allows users to run AI models locally on their machines. It provides pre-built bindings with the option to build from source using cmake. Users can interact with text generation models, chat with models using a chat wrapper, and force models to generate output in a parseable format like JSON. The tool supports Metal and CUDA, offers CLI functionality for chatting with models without coding, and ensures up-to-date compatibility with the latest version of llama.cpp. Installation includes pre-built binaries for macOS, Linux, and Windows, with the option to build from source if binaries are not available for the platform.
Jlama
Jlama is a modern Java inference engine designed for large language models. It supports various model types such as Gemma, Llama, Mistral, GPT-2, BERT, and more. The tool implements features like Flash Attention, Mixture of Experts, and supports different model quantization formats. Built with Java 21 and utilizing the new Vector API for faster inference, Jlama allows users to add LLM inference directly to their Java applications. The tool includes a CLI for running models, a simple UI for chatting with LLMs, and examples for different model types.
torchchat
torchchat is a codebase showcasing the ability to run large language models (LLMs) seamlessly. It allows running LLMs using Python in various environments such as desktop, server, iOS, and Android. The tool supports running models via PyTorch, chatting, generating text, running chat in the browser, and running models on desktop/server without Python. It also provides features like AOT Inductor for faster execution, running in C++ using the runner, and deploying and running on iOS and Android. The tool supports popular hardware and OS including Linux, Mac OS, Android, and iOS, with various data types and execution modes available.
chatgpt-cli
ChatGPT CLI provides a powerful command-line interface for seamless interaction with ChatGPT models via OpenAI and Azure. It features streaming capabilities, extensive configuration options, and supports various modes like streaming, query, and interactive mode. Users can manage thread-based context, sliding window history, and provide custom context from any source. The CLI also offers model and thread listing, advanced configuration options, and supports GPT-4, GPT-3.5-turbo, and Perplexity's models. Installation is available via Homebrew or direct download, and users can configure settings through default values, a config.yaml file, or environment variables.
mlx-lm
MLX LM is a Python package designed for generating text and fine-tuning large language models on Apple silicon using MLX. It offers integration with the Hugging Face Hub for easy access to thousands of LLMs, support for quantizing and uploading models to the Hub, low-rank and full model fine-tuning capabilities, and distributed inference and fine-tuning with `mx.distributed`. Users can interact with the package through command line options or the Python API, enabling tasks such as text generation, chatting with language models, model conversion, streaming generation, and sampling. MLX LM supports various Hugging Face models and provides tools for efficient scaling to long prompts and generations, including a rotating key-value cache and prompt caching. It requires macOS 15.0 or higher for optimal performance.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.

