
mlx-lm
Run LLMs with MLX
Stars: 2477
MLX LM is a Python package designed for generating text and fine-tuning large language models on Apple silicon using MLX. It offers integration with the Hugging Face Hub for easy access to thousands of LLMs, support for quantizing and uploading models to the Hub, low-rank and full model fine-tuning capabilities, and distributed inference and fine-tuning with `mx.distributed`. Users can interact with the package through command line options or the Python API, enabling tasks such as text generation, chatting with language models, model conversion, streaming generation, and sampling. MLX LM supports various Hugging Face models and provides tools for efficient scaling to long prompts and generations, including a rotating key-value cache and prompt caching. It requires macOS 15.0 or higher for optimal performance.
README:
MLX LM is a Python package for generating text and fine-tuning large language models on Apple silicon with MLX.
Some key features include:
- Integration with the Hugging Face Hub to easily use thousands of LLMs with a single command.
- Support for quantizing and uploading models to the Hugging Face Hub.
- Low-rank and full model fine-tuning with support for quantized models.
- Distributed inference and fine-tuning with
mx.distributed
The easiest way to get started is to install the mlx-lm package:
With pip:
pip install mlx-lmWith conda:
conda install -c conda-forge mlx-lmTo generate text with an LLM use:
mlx_lm.generate --prompt "How tall is Mt Everest?"To chat with an LLM use:
mlx_lm.chatThis will give you a chat REPL that you can use to interact with the LLM. The chat context is preserved during the lifetime of the REPL.
Commands in mlx-lm typically take command line options which let you specify
the model, sampling parameters, and more. Use -h to see a list of available
options for a command, e.g.:
mlx_lm.generate -hThe default model for generation and chat is
mlx-community/Llama-3.2-3B-Instruct-4bit. You can specify any MLX-compatible
model with the --model flag. Thousands are available in the
MLX Community Hugging Face
organization.
You can use mlx-lm as a module:
from mlx_lm import load, generate
model, tokenizer = load("mlx-community/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.3-4bit")
prompt = "Write a story about Einstein"
messages = [{"role": "user", "content": prompt}]
prompt = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(
messages, add_generation_prompt=True
)
text = generate(model, tokenizer, prompt=prompt, verbose=True)To see a description of all the arguments you can do:
>>> help(generate)
Check out the generation example to see how to use the API in more detail. Check out the batch generation example to see how to efficiently generate continuations for a batch of prompts.
The mlx-lm package also comes with functionality to quantize and optionally
upload models to the Hugging Face Hub.
You can convert models using the Python API:
from mlx_lm import convert
repo = "mistralai/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.3"
upload_repo = "mlx-community/My-Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.3-4bit"
convert(repo, quantize=True, upload_repo=upload_repo)This will generate a 4-bit quantized Mistral 7B and upload it to the repo
mlx-community/My-Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.3-4bit. It will also save the
converted model in the path mlx_model by default.
To see a description of all the arguments you can do:
>>> help(convert)
For streaming generation, use the stream_generate function. This yields
a generation response object.
For example,
from mlx_lm import load, stream_generate
repo = "mlx-community/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.3-4bit"
model, tokenizer = load(repo)
prompt = "Write a story about Einstein"
messages = [{"role": "user", "content": prompt}]
prompt = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(
messages, add_generation_prompt=True
)
for response in stream_generate(model, tokenizer, prompt, max_tokens=512):
print(response.text, end="", flush=True)
print()The generate and stream_generate functions accept sampler and
logits_processors keyword arguments. A sampler is any callable which accepts
a possibly batched logits array and returns an array of sampled tokens. The
logits_processors must be a list of callables which take the token history
and current logits as input and return the processed logits. The logits
processors are applied in order.
Some standard sampling functions and logits processors are provided in
mlx_lm.sample_utils.
You can also use mlx-lm from the command line with:
mlx_lm.generate --model mistralai/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.3 --prompt "hello"
This will download a Mistral 7B model from the Hugging Face Hub and generate text using the given prompt.
For a full list of options run:
mlx_lm.generate --help
To quantize a model from the command line run:
mlx_lm.convert --hf-path mistralai/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.3 -q
For more options run:
mlx_lm.convert --help
You can upload new models to Hugging Face by specifying --upload-repo to
convert. For example, to upload a quantized Mistral-7B model to the
MLX Hugging Face community you can do:
mlx_lm.convert \
--hf-path mistralai/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.3 \
-q \
--upload-repo mlx-community/my-4bit-mistral
Models can also be converted and quantized directly in the mlx-my-repo Hugging Face Space.
mlx-lm has some tools to scale efficiently to long prompts and generations:
- A rotating fixed-size key-value cache.
- Prompt caching
To use the rotating key-value cache pass the argument --max-kv-size n where
n can be any integer. Smaller values like 512 will use very little RAM but
result in worse quality. Larger values like 4096 or higher will use more RAM
but have better quality.
Caching prompts can substantially speedup reusing the same long context with
different queries. To cache a prompt use mlx_lm.cache_prompt. For example:
cat prompt.txt | mlx_lm.cache_prompt \
--model mistralai/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.3 \
--prompt - \
--prompt-cache-file mistral_prompt.safetensorsThen use the cached prompt with mlx_lm.generate:
mlx_lm.generate \
--prompt-cache-file mistral_prompt.safetensors \
--prompt "\nSummarize the above text."
The cached prompt is treated as a prefix to the supplied prompt. Also notice when using a cached prompt, the model to use is read from the cache and need not be supplied explicitly.
Prompt caching can also be used in the Python API in order to avoid recomputing the prompt. This is useful in multi-turn dialogues or across requests that use the same context. See the example for more usage details.
mlx-lm supports thousands of Hugging Face format LLMs. If the model you want to
run is not supported, file an
issue or better yet,
submit a pull request.
Here are a few examples of Hugging Face models that work with this example:
- mistralai/Mistral-7B-v0.1
- meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-hf
- deepseek-ai/deepseek-coder-6.7b-instruct
- 01-ai/Yi-6B-Chat
- microsoft/phi-2
- mistralai/Mixtral-8x7B-Instruct-v0.1
- Qwen/Qwen-7B
- pfnet/plamo-13b
- pfnet/plamo-13b-instruct
- stabilityai/stablelm-2-zephyr-1_6b
- internlm/internlm2-7b
- tiiuae/falcon-mamba-7b-instruct
Most Mistral, Llama, Phi-2, and Mixtral style models should work out of the box.
For some models (such as Qwen and plamo) the tokenizer requires you to
enable the trust_remote_code option. You can do this by passing
--trust-remote-code in the command line. If you don't specify the flag
explicitly, you will be prompted to trust remote code in the terminal when
running the model.
For Qwen models you must also specify the eos_token. You can do this by
passing --eos-token "<|endoftext|>" in the command
line.
These options can also be set in the Python API. For example:
model, tokenizer = load(
"qwen/Qwen-7B",
tokenizer_config={"eos_token": "<|endoftext|>", "trust_remote_code": True},
)[!NOTE] This requires macOS 15.0 or higher to work.
Models which are large relative to the total RAM available on the machine can
be slow. mlx-lm will attempt to make them faster by wiring the memory
occupied by the model and cache. This requires macOS 15 or higher to
work.
If you see the following warning message:
[WARNING] Generating with a model that requires ...
then the model will likely be slow on the given machine. If the model fits in
RAM then it can often be sped up by increasing the system wired memory limit.
To increase the limit, set the following sysctl:
sudo sysctl iogpu.wired_limit_mb=NThe value N should be larger than the size of the model in megabytes but
smaller than the memory size of the machine.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for mlx-lm
Similar Open Source Tools

mlx-lm
MLX LM is a Python package designed for generating text and fine-tuning large language models on Apple silicon using MLX. It offers integration with the Hugging Face Hub for easy access to thousands of LLMs, support for quantizing and uploading models to the Hub, low-rank and full model fine-tuning capabilities, and distributed inference and fine-tuning with `mx.distributed`. Users can interact with the package through command line options or the Python API, enabling tasks such as text generation, chatting with language models, model conversion, streaming generation, and sampling. MLX LM supports various Hugging Face models and provides tools for efficient scaling to long prompts and generations, including a rotating key-value cache and prompt caching. It requires macOS 15.0 or higher for optimal performance.
vector-inference
This repository provides an easy-to-use solution for running inference servers on Slurm-managed computing clusters using vLLM. All scripts in this repository run natively on the Vector Institute cluster environment. Users can deploy models as Slurm jobs, check server status and performance metrics, and shut down models. The repository also supports launching custom models with specific configurations. Additionally, users can send inference requests and set up an SSH tunnel to run inference from a local device.
llm-ollama
LLM-ollama is a plugin that provides access to models running on an Ollama server. It allows users to query the Ollama server for a list of models, register them with LLM, and use them for prompting, chatting, and embedding. The plugin supports image attachments, embeddings, JSON schemas, async models, model aliases, and model options. Users can interact with Ollama models through the plugin in a seamless and efficient manner.
LayerSkip
LayerSkip is an implementation enabling early exit inference and self-speculative decoding. It provides a code base for running models trained using the LayerSkip recipe, offering speedup through self-speculative decoding. The tool integrates with Hugging Face transformers and provides checkpoints for various LLMs. Users can generate tokens, benchmark on datasets, evaluate tasks, and sweep over hyperparameters to optimize inference speed. The tool also includes correctness verification scripts and Docker setup instructions. Additionally, other implementations like gpt-fast and Native HuggingFace are available. Training implementation is a work-in-progress, and contributions are welcome under the CC BY-NC license.
turnkeyml
TurnkeyML is a tools framework that integrates models, toolchains, and hardware backends to simplify the evaluation and actuation of deep learning models. It supports use cases like exporting ONNX files, performance validation, functional coverage measurement, stress testing, and model insights analysis. The framework consists of analysis, build, runtime, reporting tools, and a models corpus, seamlessly integrated to provide comprehensive functionality with simple commands. Extensible through plugins, it offers support for various export and optimization tools and AI runtimes. The project is actively seeking collaborators and is licensed under Apache 2.0.
garak
Garak is a free tool that checks if a Large Language Model (LLM) can be made to fail in a way that is undesirable. It probes for hallucination, data leakage, prompt injection, misinformation, toxicity generation, jailbreaks, and many other weaknesses. Garak's a free tool. We love developing it and are always interested in adding functionality to support applications.
garak
Garak is a vulnerability scanner designed for LLMs (Large Language Models) that checks for various weaknesses such as hallucination, data leakage, prompt injection, misinformation, toxicity generation, and jailbreaks. It combines static, dynamic, and adaptive probes to explore vulnerabilities in LLMs. Garak is a free tool developed for red-teaming and assessment purposes, focusing on making LLMs or dialog systems fail. It supports various LLM models and can be used to assess their security and robustness.
paper-qa
PaperQA is a minimal package for question and answering from PDFs or text files, providing very good answers with in-text citations. It uses OpenAI Embeddings to embed and search documents, and includes a process of embedding docs, queries, searching for top passages, creating summaries, using an LLM to re-score and select relevant summaries, putting summaries into prompt, and generating answers. The tool can be used to answer specific questions related to scientific research by leveraging citations and relevant passages from documents.
HuggingFaceGuidedTourForMac
HuggingFaceGuidedTourForMac is a guided tour on how to install optimized pytorch and optionally Apple's new MLX, JAX, and TensorFlow on Apple Silicon Macs. The repository provides steps to install homebrew, pytorch with MPS support, MLX, JAX, TensorFlow, and Jupyter lab. It also includes instructions on running large language models using HuggingFace transformers. The repository aims to help users set up their Macs for deep learning experiments with optimized performance.
py-vectara-agentic
The `vectara-agentic` Python library is designed for developing powerful AI assistants using Vectara and Agentic-RAG. It supports various agent types, includes pre-built tools for domains like finance and legal, and enables easy creation of custom AI assistants and agents. The library provides tools for summarizing text, rephrasing text, legal tasks like summarizing legal text and critiquing as a judge, financial tasks like analyzing balance sheets and income statements, and database tools for inspecting and querying databases. It also supports observability via LlamaIndex and Arize Phoenix integration.

reader
Reader is a tool that converts any URL to an LLM-friendly input with a simple prefix `https://r.jina.ai/`. It improves the output for your agent and RAG systems at no cost. Reader supports image reading, captioning all images at the specified URL and adding `Image [idx]: [caption]` as an alt tag. This enables downstream LLMs to interact with the images in reasoning, summarizing, etc. Reader offers a streaming mode, useful when the standard mode provides an incomplete result. In streaming mode, Reader waits a bit longer until the page is fully rendered, providing more complete information. Reader also supports a JSON mode, which contains three fields: `url`, `title`, and `content`. Reader is backed by Jina AI and licensed under Apache-2.0.
verifiers
Verifiers is a library of modular components for creating RL environments and training LLM agents. It includes an async GRPO implementation built around the `transformers` Trainer, is supported by `prime-rl` for large-scale FSDP training, and can easily be integrated into any RL framework which exposes an OpenAI-compatible inference client. The library provides tools for creating and evaluating RL environments, training LLM agents, and leveraging OpenAI-compatible models for various tasks. Verifiers aims to be a reliable toolkit for building on top of, minimizing fork proliferation in the RL infrastructure ecosystem.
mflux
MFLUX is a line-by-line port of the FLUX implementation in the Huggingface Diffusers library to Apple MLX. It aims to run powerful FLUX models from Black Forest Labs locally on Mac machines. The codebase is minimal and explicit, prioritizing readability over generality and performance. Models are implemented from scratch in MLX, with tokenizers from the Huggingface Transformers library. Dependencies include Numpy and Pillow for image post-processing. Installation can be done using `uv tool` or classic virtual environment setup. Command-line arguments allow for image generation with specified models, prompts, and optional parameters. Quantization options for speed and memory reduction are available. LoRA adapters can be loaded for fine-tuning image generation. Controlnet support provides more control over image generation with reference images. Current limitations include generating images one by one, lack of support for negative prompts, and some LoRA adapters not working.
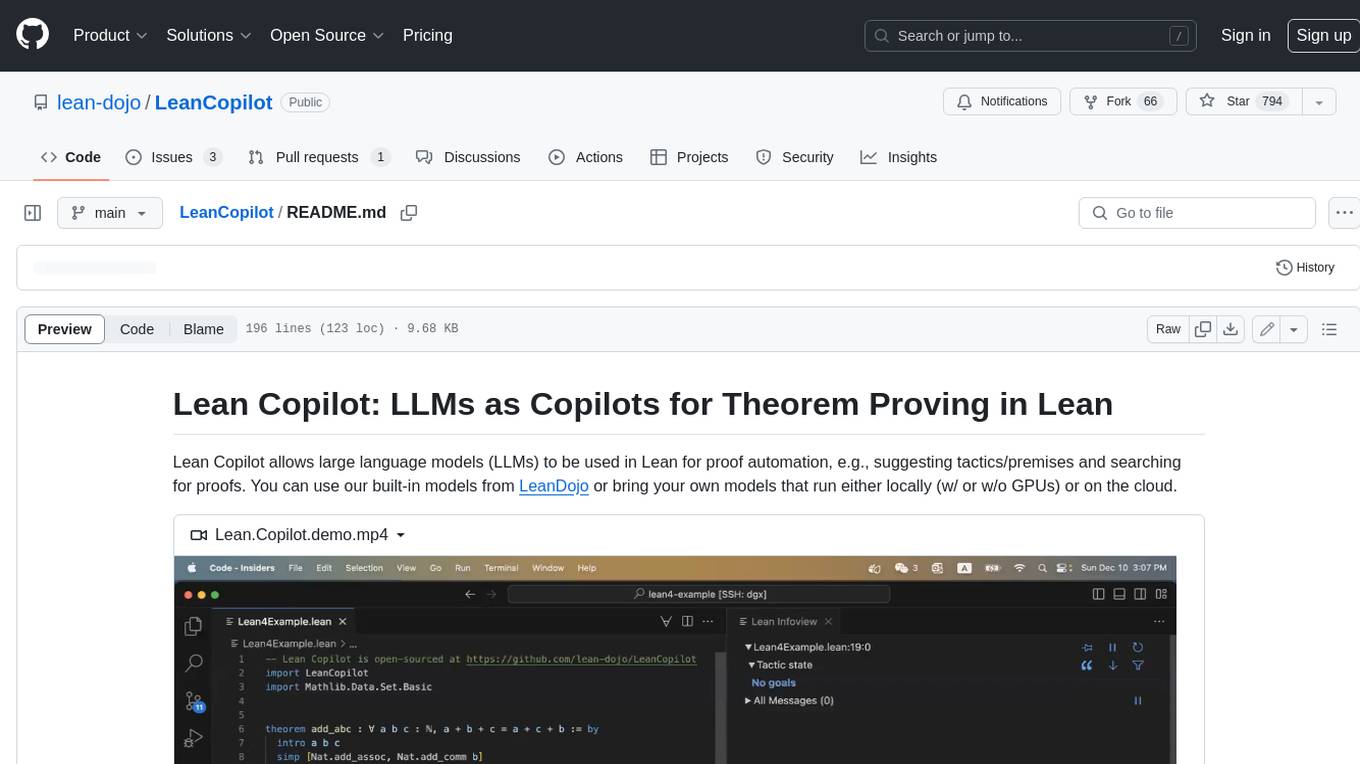
LeanCopilot
Lean Copilot is a tool that enables the use of large language models (LLMs) in Lean for proof automation. It provides features such as suggesting tactics/premises, searching for proofs, and running inference of LLMs. Users can utilize built-in models from LeanDojo or bring their own models to run locally or on the cloud. The tool supports platforms like Linux, macOS, and Windows WSL, with optional CUDA and cuDNN for GPU acceleration. Advanced users can customize behavior using Tactic APIs and Model APIs. Lean Copilot also allows users to bring their own models through ExternalGenerator or ExternalEncoder. The tool comes with caveats such as occasional crashes and issues with premise selection and proof search. Users can get in touch through GitHub Discussions for questions, bug reports, feature requests, and suggestions. The tool is designed to enhance theorem proving in Lean using LLMs.
llm-verified-with-monte-carlo-tree-search
This prototype synthesizes verified code with an LLM using Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS). It explores the space of possible generation of a verified program and checks at every step that it's on the right track by calling the verifier. This prototype uses Dafny, Coq, Lean, Scala, or Rust. By using this technique, weaker models that might not even know the generated language all that well can compete with stronger models.
gpt-cli
gpt-cli is a command-line interface tool for interacting with various chat language models like ChatGPT, Claude, and others. It supports model customization, usage tracking, keyboard shortcuts, multi-line input, markdown support, predefined messages, and multiple assistants. Users can easily switch between different assistants, define custom assistants, and configure model parameters and API keys in a YAML file for easy customization and management.
For similar tasks
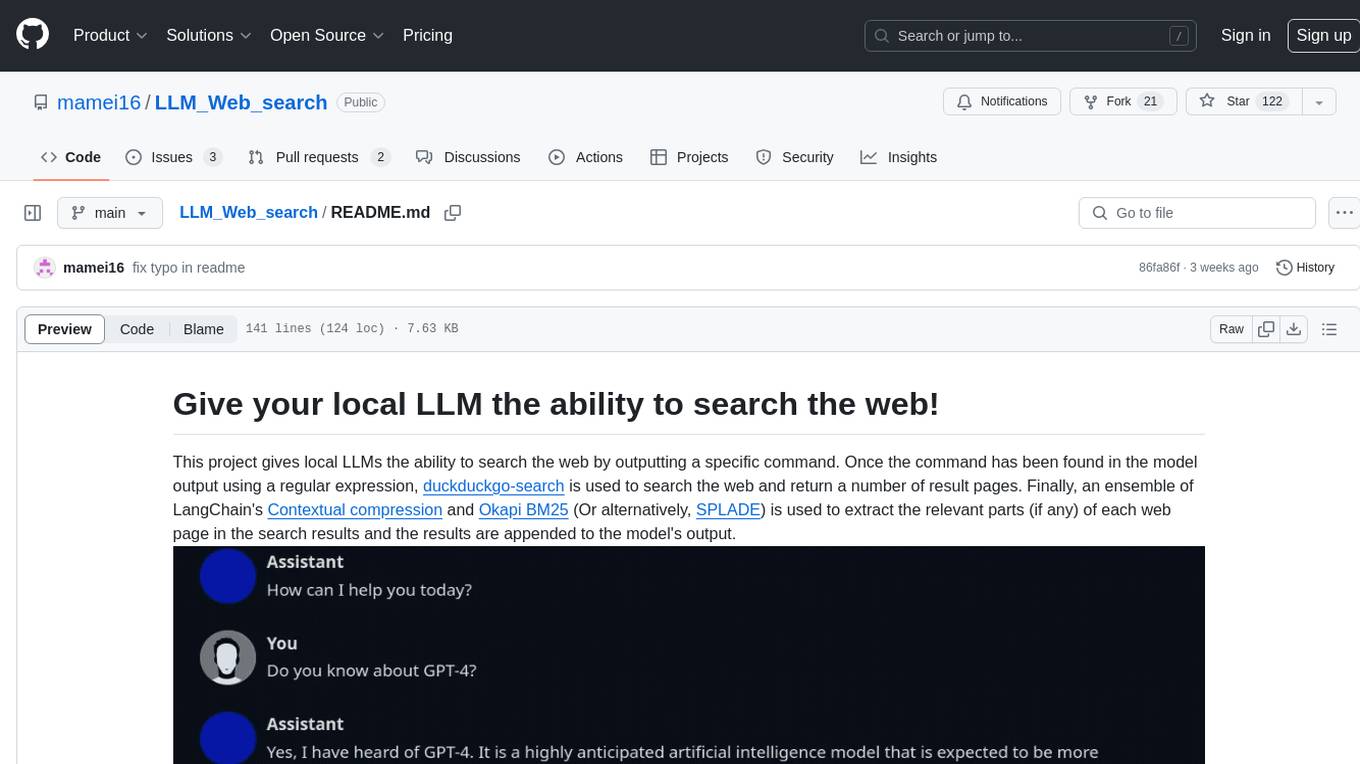
LLM_Web_search
LLM_Web_search project gives local LLMs the ability to search the web by outputting a specific command. It uses regular expressions to extract search queries from model output and then utilizes duckduckgo-search to search the web. LangChain's Contextual compression and Okapi BM25 or SPLADE are used to extract relevant parts of web pages in search results. The extracted results are appended to the model's output.
node-llama-cpp
node-llama-cpp is a tool that allows users to run AI models locally on their machines. It provides pre-built bindings with the option to build from source using cmake. Users can interact with text generation models, chat with models using a chat wrapper, and force models to generate output in a parseable format like JSON. The tool supports Metal and CUDA, offers CLI functionality for chatting with models without coding, and ensures up-to-date compatibility with the latest version of llama.cpp. Installation includes pre-built binaries for macOS, Linux, and Windows, with the option to build from source if binaries are not available for the platform.
Jlama
Jlama is a modern Java inference engine designed for large language models. It supports various model types such as Gemma, Llama, Mistral, GPT-2, BERT, and more. The tool implements features like Flash Attention, Mixture of Experts, and supports different model quantization formats. Built with Java 21 and utilizing the new Vector API for faster inference, Jlama allows users to add LLM inference directly to their Java applications. The tool includes a CLI for running models, a simple UI for chatting with LLMs, and examples for different model types.
torchchat
torchchat is a codebase showcasing the ability to run large language models (LLMs) seamlessly. It allows running LLMs using Python in various environments such as desktop, server, iOS, and Android. The tool supports running models via PyTorch, chatting, generating text, running chat in the browser, and running models on desktop/server without Python. It also provides features like AOT Inductor for faster execution, running in C++ using the runner, and deploying and running on iOS and Android. The tool supports popular hardware and OS including Linux, Mac OS, Android, and iOS, with various data types and execution modes available.
chatgpt-cli
ChatGPT CLI provides a powerful command-line interface for seamless interaction with ChatGPT models via OpenAI and Azure. It features streaming capabilities, extensive configuration options, and supports various modes like streaming, query, and interactive mode. Users can manage thread-based context, sliding window history, and provide custom context from any source. The CLI also offers model and thread listing, advanced configuration options, and supports GPT-4, GPT-3.5-turbo, and Perplexity's models. Installation is available via Homebrew or direct download, and users can configure settings through default values, a config.yaml file, or environment variables.
elmer
Elmer is a user-friendly wrapper over common APIs for calling llm’s, with support for streaming and easy registration and calling of R functions. Users can interact with Elmer in various ways, such as interactive chat console, interactive method call, programmatic chat, and streaming results. Elmer also supports async usage for running multiple chat sessions concurrently, useful for Shiny applications. The tool calling feature allows users to define external tools that Elmer can request to execute, enhancing the capabilities of the chat model.

mlx-lm
MLX LM is a Python package designed for generating text and fine-tuning large language models on Apple silicon using MLX. It offers integration with the Hugging Face Hub for easy access to thousands of LLMs, support for quantizing and uploading models to the Hub, low-rank and full model fine-tuning capabilities, and distributed inference and fine-tuning with `mx.distributed`. Users can interact with the package through command line options or the Python API, enabling tasks such as text generation, chatting with language models, model conversion, streaming generation, and sampling. MLX LM supports various Hugging Face models and provides tools for efficient scaling to long prompts and generations, including a rotating key-value cache and prompt caching. It requires macOS 15.0 or higher for optimal performance.
Ollama-Colab-Integration
Ollama Colab Integration V4 is a tool designed to enhance the interaction and management of large language models. It allows users to quantize models within their notebook environment, access a variety of models through a user-friendly interface, and manage public endpoints efficiently. The tool also provides features like LiteLLM proxy control, model insights, and customizable model file templating. Users can troubleshoot model loading issues, CPU fallback strategies, and manage VRAM and RAM effectively. Additionally, the tool offers functionalities for downloading model files from Hugging Face, model conversion with high precision, model quantization using Q and Kquants, and securely uploading converted models to Hugging Face.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.