
vector-inference
Efficient LLM inference on Slurm clusters using vLLM.
Stars: 77
This repository provides an easy-to-use solution for running inference servers on Slurm-managed computing clusters using vLLM. All scripts in this repository run natively on the Vector Institute cluster environment. Users can deploy models as Slurm jobs, check server status and performance metrics, and shut down models. The repository also supports launching custom models with specific configurations. Additionally, users can send inference requests and set up an SSH tunnel to run inference from a local device.
README:
This repository provides an easy-to-use solution to run inference servers on Slurm-managed computing clusters using vLLM. This package runs natively on the Vector Institute cluster environments. To adapt to other environments, follow the instructions in Installation.
NOTE: Supported models on Killarney are tracked here
If you are using the Vector cluster environment, and you don't need any customization to the inference server environment, run the following to install package:
pip install vec-infOtherwise, we recommend using the provided Dockerfile to set up your own environment with the package. The latest image has vLLM version 0.10.1.1.
If you'd like to use vec-inf on your own Slurm cluster, you would need to update the configuration files, there are 3 ways to do it:
- Clone the repository and update the
environment.yamland themodels.yamlfile invec_inf/config, then install from source by runningpip install .. - The package would try to look for cached configuration files in your environment before using the default configuration. The default cached configuration directory path points to
/model-weights/vec-inf-shared, you would need to create anenvironment.yamland amodels.yamlfollowing the format of these files invec_inf/config. - The package would also look for an enviroment variable
VEC_INF_CONFIG_DIR. You can put yourenvironment.yamlandmodels.yamlin a directory of your choice and set the enviroment variableVEC_INF_CONFIG_DIRto point to that location.
Vector Inference provides 2 user interfaces, a CLI and an API
The launch command allows users to deploy a model as a slurm job. If the job successfully launches, a URL endpoint is exposed for the user to send requests for inference.
We will use the Llama 3.1 model as example, to launch an OpenAI compatible inference server for Meta-Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct, run:
vec-inf launch Meta-Llama-3.1-8B-InstructYou should see an output like the following:
NOTE: On Vector Killarney Cluster environment, the following fields are required:
-
--account,-A: The Slurm account, this argument can be set to default by setting environment variableVEC_INF_ACCOUNT. -
--work-dir,-D: A working directory other than your home directory, this argument can be set to default by seeting environment variableVEC_INF_WORK_DIR.
Models that are already supported by vec-inf would be launched using the cached configuration (set in slurm_vars.py) or default configuration. You can override these values by providing additional parameters. Use vec-inf launch --help to see the full list of parameters that can be overriden. You can also launch your own custom model as long as the model architecture is supported by vLLM. For detailed instructions on how to customize your model launch, check out the launch command section in User Guide
-
batch-launch: Launch multiple model inference servers at once, currently ONLY single node models supported, -
status: Check the model status by providing its Slurm job ID. -
metrics: Streams performance metrics to the console. -
shutdown: Shutdown a model by providing its Slurm job ID. -
list: List all available model names, or view the default/cached configuration of a specific model. -
cleanup: Remove old log directories, use--helpto see the supported filters. Use--dry-runto preview what would be deleted.
For more details on the usage of these commands, refer to the User Guide
Example:
>>> from vec_inf.api import VecInfClient
>>> client = VecInfClient()
>>> # Assume VEC_INF_ACCOUNT and VEC_INF_WORK_DIR is set
>>> response = client.launch_model("Meta-Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct")
>>> job_id = response.slurm_job_id
>>> status = client.get_status(job_id)
>>> if status.status == ModelStatus.READY:
... print(f"Model is ready at {status.base_url}")
>>> client.shutdown_model(job_id)For details on the usage of the API, refer to the API Reference
With every model launch, a Slurm script will be generated dynamically based on the job and model configuration. Once the Slurm job is queued, the generated Slurm script will be moved to the log directory for reproducibility, located at $log_dir/$model_family/$model_name.$slurm_job_id/$model_name.$slurm_job_id.slurm. In the same directory you can also find a JSON file with the same name that captures the launch configuration, and will have an entry of server URL once the server is ready.
Once the inference server is ready, you can start sending in inference requests. We provide example scripts for sending inference requests in examples folder. Make sure to update the model server URL and the model weights location in the scripts. For example, you can run python examples/inference/llm/chat_completions.py, and you should expect to see an output like the following:
{
"id":"chatcmpl-387c2579231948ffaf66cdda5439d3dc",
"choices": [
{
"finish_reason":"stop",
"index":0,
"logprobs":null,
"message": {
"content":"Arrr, I be Captain Chatbeard, the scurviest chatbot on the seven seas! Ye be wantin' to know me identity, eh? Well, matey, I be a swashbucklin' AI, here to provide ye with answers and swappin' tales, savvy?",
"role":"assistant",
"function_call":null,
"tool_calls":[],
"reasoning_content":null
},
"stop_reason":null
}
],
"created":1742496683,
"model":"Meta-Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct",
"object":"chat.completion",
"system_fingerprint":null,
"usage": {
"completion_tokens":66,
"prompt_tokens":32,
"total_tokens":98,
"prompt_tokens_details":null
},
"prompt_logprobs":null
}
NOTE: Certain models don't adhere to OpenAI's chat template, e.g. Mistral family. For these models, you can either change your prompt to follow the model's default chat template or provide your own chat template via --chat-template: TEMPLATE_PATH.
If you want to run inference from your local device, you can open a SSH tunnel to your cluster environment like the following:
ssh -L 8081:10.1.1.29:8081 [email protected] -NThe example provided above is for the Vector Killarney cluster, change the variables accordingly for your environment. The IP address for the compute nodes on Killarney follow 10.1.1.XX pattern, where XX is the GPU number (kn029 -> 29 in this example).
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for vector-inference
Similar Open Source Tools

vector-inference
This repository provides an easy-to-use solution for running inference servers on Slurm-managed computing clusters using vLLM. All scripts in this repository run natively on the Vector Institute cluster environment. Users can deploy models as Slurm jobs, check server status and performance metrics, and shut down models. The repository also supports launching custom models with specific configurations. Additionally, users can send inference requests and set up an SSH tunnel to run inference from a local device.
safety-tooling
This repository, safety-tooling, is designed to be shared across various AI Safety projects. It provides an LLM API with a common interface for OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google models. The aim is to facilitate collaboration among AI Safety researchers, especially those with limited software engineering backgrounds, by offering a platform for contributing to a larger codebase. The repo can be used as a git submodule for easy collaboration and updates. It also supports pip installation for convenience. The repository includes features for installation, secrets management, linting, formatting, Redis configuration, testing, dependency management, inference, finetuning, API usage tracking, and various utilities for data processing and experimentation.
llm-ollama
LLM-ollama is a plugin that provides access to models running on an Ollama server. It allows users to query the Ollama server for a list of models, register them with LLM, and use them for prompting, chatting, and embedding. The plugin supports image attachments, embeddings, JSON schemas, async models, model aliases, and model options. Users can interact with Ollama models through the plugin in a seamless and efficient manner.
termax
Termax is an LLM agent in your terminal that converts natural language to commands. It is featured by: - Personalized Experience: Optimize the command generation with RAG. - Various LLMs Support: OpenAI GPT, Anthropic Claude, Google Gemini, Mistral AI, and more. - Shell Extensions: Plugin with popular shells like `zsh`, `bash` and `fish`. - Cross Platform: Able to run on Windows, macOS, and Linux.
gpt-cli
gpt-cli is a command-line interface tool for interacting with various chat language models like ChatGPT, Claude, and others. It supports model customization, usage tracking, keyboard shortcuts, multi-line input, markdown support, predefined messages, and multiple assistants. Users can easily switch between different assistants, define custom assistants, and configure model parameters and API keys in a YAML file for easy customization and management.
web-llm
WebLLM is a modular and customizable javascript package that directly brings language model chats directly onto web browsers with hardware acceleration. Everything runs inside the browser with no server support and is accelerated with WebGPU. WebLLM is fully compatible with OpenAI API. That is, you can use the same OpenAI API on any open source models locally, with functionalities including json-mode, function-calling, streaming, etc. We can bring a lot of fun opportunities to build AI assistants for everyone and enable privacy while enjoying GPU acceleration.
vectorflow
VectorFlow is an open source, high throughput, fault tolerant vector embedding pipeline. It provides a simple API endpoint for ingesting large volumes of raw data, processing, and storing or returning the vectors quickly and reliably. The tool supports text-based files like TXT, PDF, HTML, and DOCX, and can be run locally with Kubernetes in production. VectorFlow offers functionalities like embedding documents, running chunking schemas, custom chunking, and integrating with vector databases like Pinecone, Qdrant, and Weaviate. It enforces a standardized schema for uploading data to a vector store and supports features like raw embeddings webhook, chunk validation webhook, S3 endpoint, and telemetry. The tool can be used with the Python client and provides detailed instructions for running and testing the functionalities.
hash
HASH is a self-building, open-source database which grows, structures and checks itself. With it, we're creating a platform for decision-making, which helps you integrate, understand and use data in a variety of different ways.
bedrock-claude-chat
This repository is a sample chatbot using the Anthropic company's LLM Claude, one of the foundational models provided by Amazon Bedrock for generative AI. It allows users to have basic conversations with the chatbot, personalize it with their own instructions and external knowledge, and analyze usage for each user/bot on the administrator dashboard. The chatbot supports various languages, including English, Japanese, Korean, Chinese, French, German, and Spanish. Deployment is straightforward and can be done via the command line or by using AWS CDK. The architecture is built on AWS managed services, eliminating the need for infrastructure management and ensuring scalability, reliability, and security.
magic-cli
Magic CLI is a command line utility that leverages Large Language Models (LLMs) to enhance command line efficiency. It is inspired by projects like Amazon Q and GitHub Copilot for CLI. The tool allows users to suggest commands, search across command history, and generate commands for specific tasks using local or remote LLM providers. Magic CLI also provides configuration options for LLM selection and response generation. The project is still in early development, so users should expect breaking changes and bugs.
LayerSkip
LayerSkip is an implementation enabling early exit inference and self-speculative decoding. It provides a code base for running models trained using the LayerSkip recipe, offering speedup through self-speculative decoding. The tool integrates with Hugging Face transformers and provides checkpoints for various LLMs. Users can generate tokens, benchmark on datasets, evaluate tasks, and sweep over hyperparameters to optimize inference speed. The tool also includes correctness verification scripts and Docker setup instructions. Additionally, other implementations like gpt-fast and Native HuggingFace are available. Training implementation is a work-in-progress, and contributions are welcome under the CC BY-NC license.
debug-gym
debug-gym is a text-based interactive debugging framework designed for debugging Python programs. It provides an environment where agents can interact with code repositories, use various tools like pdb and grep to investigate and fix bugs, and propose code patches. The framework supports different LLM backends such as OpenAI, Azure OpenAI, and Anthropic. Users can customize tools, manage environment states, and run agents to debug code effectively. debug-gym is modular, extensible, and suitable for interactive debugging tasks in a text-based environment.
hordelib
horde-engine is a wrapper around ComfyUI designed to run inference pipelines visually designed in the ComfyUI GUI. It enables users to design inference pipelines in ComfyUI and then call them programmatically, maintaining compatibility with the existing horde implementation. The library provides features for processing Horde payloads, initializing the library, downloading and validating models, and generating images based on input data. It also includes custom nodes for preprocessing and tasks such as face restoration and QR code generation. The project depends on various open source projects and bundles some dependencies within the library itself. Users can design ComfyUI pipelines, convert them to the backend format, and run them using the run_image_pipeline() method in hordelib.comfy.Comfy(). The project is actively developed and tested using git, tox, and a specific model directory structure.
garak
Garak is a vulnerability scanner designed for LLMs (Large Language Models) that checks for various weaknesses such as hallucination, data leakage, prompt injection, misinformation, toxicity generation, and jailbreaks. It combines static, dynamic, and adaptive probes to explore vulnerabilities in LLMs. Garak is a free tool developed for red-teaming and assessment purposes, focusing on making LLMs or dialog systems fail. It supports various LLM models and can be used to assess their security and robustness.
MCPJungle
MCPJungle is a self-hosted MCP Gateway for private AI agents, serving as a registry for Model Context Protocol Servers. Developers use it to manage servers and tools centrally, while clients discover and consume tools from a single 'Gateway' MCP Server. Suitable for developers using MCP Clients like Claude & Cursor, building production-grade AI Agents, and organizations managing client-server interactions. The tool allows quick start, installation, usage, server and client setup, connection to Claude and Cursor, enabling/disabling tools, managing tool groups, authentication, enterprise features like access control and OpenTelemetry metrics. Limitations include lack of long-running connections to servers and no support for OAuth flow. Contributions are welcome.
garak
Garak is a free tool that checks if a Large Language Model (LLM) can be made to fail in a way that is undesirable. It probes for hallucination, data leakage, prompt injection, misinformation, toxicity generation, jailbreaks, and many other weaknesses. Garak's a free tool. We love developing it and are always interested in adding functionality to support applications.
For similar tasks

vector-inference
This repository provides an easy-to-use solution for running inference servers on Slurm-managed computing clusters using vLLM. All scripts in this repository run natively on the Vector Institute cluster environment. Users can deploy models as Slurm jobs, check server status and performance metrics, and shut down models. The repository also supports launching custom models with specific configurations. Additionally, users can send inference requests and set up an SSH tunnel to run inference from a local device.
rho
Rho is an AI agent that runs on macOS, Linux, and Android, staying active, remembering past interactions, and checking in autonomously. It operates without cloud storage, allowing users to retain ownership of their data. Users can bring their own LLM provider and have full control over the agent's functionalities. Rho is built on the pi coding agent framework, offering features like persistent memory, scheduled tasks, and real email capabilities. The agent can be customized through checklists, scheduled triggers, and personalized voice and identity settings. Skills and extensions enhance the agent's capabilities, providing tools for notifications, clipboard management, text-to-speech, and more. Users can interact with Rho through commands and scripts, enabling tasks like checking status, triggering actions, and managing preferences.

vllm
vLLM is a fast and easy-to-use library for LLM inference and serving. It is designed to be efficient, flexible, and easy to use. vLLM can be used to serve a variety of LLM models, including Hugging Face models. It supports a variety of decoding algorithms, including parallel sampling, beam search, and more. vLLM also supports tensor parallelism for distributed inference and streaming outputs. It is open-source and available on GitHub.
bce-qianfan-sdk
The Qianfan SDK provides best practices for large model toolchains, allowing AI workflows and AI-native applications to access the Qianfan large model platform elegantly and conveniently. The core capabilities of the SDK include three parts: large model reasoning, large model training, and general and extension: * `Large model reasoning`: Implements interface encapsulation for reasoning of Yuyan (ERNIE-Bot) series, open source large models, etc., supporting dialogue, completion, Embedding, etc. * `Large model training`: Based on platform capabilities, it supports end-to-end large model training process, including training data, fine-tuning/pre-training, and model services. * `General and extension`: General capabilities include common AI development tools such as Prompt/Debug/Client. The extension capability is based on the characteristics of Qianfan to adapt to common middleware frameworks.

dstack
Dstack is an open-source orchestration engine for running AI workloads in any cloud. It supports a wide range of cloud providers (such as AWS, GCP, Azure, Lambda, TensorDock, Vast.ai, CUDO, RunPod, etc.) as well as on-premises infrastructure. With Dstack, you can easily set up and manage dev environments, tasks, services, and pools for your AI workloads.
tiny-llm-zh
Tiny LLM zh is a project aimed at building a small-parameter Chinese language large model for quick entry into learning large model-related knowledge. The project implements a two-stage training process for large models and subsequent human alignment, including tokenization, pre-training, instruction fine-tuning, human alignment, evaluation, and deployment. It is deployed on ModeScope Tiny LLM website and features open access to all data and code, including pre-training data and tokenizer. The project trains a tokenizer using 10GB of Chinese encyclopedia text to build a Tiny LLM vocabulary. It supports training with Transformers deepspeed, multiple machine and card support, and Zero optimization techniques. The project has three main branches: llama2_torch, main tiny_llm, and tiny_llm_moe, each with specific modifications and features.
examples
Cerebrium's official examples repository provides practical, ready-to-use examples for building Machine Learning / AI applications on the platform. The repository contains self-contained projects demonstrating specific use cases with detailed instructions on deployment. Examples cover a wide range of categories such as getting started, advanced concepts, endpoints, integrations, large language models, voice, image & video, migrations, application demos, batching, and Python apps.
HuaTuoAI
HuaTuoAI is an artificial intelligence image classification system specifically designed for traditional Chinese medicine. It utilizes deep learning techniques, such as Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN), to accurately classify Chinese herbs and ingredients based on input images. The project aims to unlock the secrets of plants, depict the unknown realm of Chinese medicine using technology and intelligence, and perpetuate ancient cultural heritage.
For similar jobs
LitServe
LitServe is a high-throughput serving engine designed for deploying AI models at scale. It generates an API endpoint for models, handles batching, streaming, and autoscaling across CPU/GPUs. LitServe is built for enterprise scale with a focus on minimal, hackable code-base without bloat. It supports various model types like LLMs, vision, time-series, and works with frameworks like PyTorch, JAX, Tensorflow, and more. The tool allows users to focus on model performance rather than serving boilerplate, providing full control and flexibility.
Lidar_AI_Solution
Lidar AI Solution is a highly optimized repository for self-driving 3D lidar, providing solutions for sparse convolution, BEVFusion, CenterPoint, OSD, and Conversion. It includes CUDA and TensorRT implementations for various tasks such as 3D sparse convolution, BEVFusion, CenterPoint, PointPillars, V2XFusion, cuOSD, cuPCL, and YUV to RGB conversion. The repository offers easy-to-use solutions, high accuracy, low memory usage, and quantization options for different tasks related to self-driving technology.
generative-ai-sagemaker-cdk-demo
This repository showcases how to deploy generative AI models from Amazon SageMaker JumpStart using the AWS CDK. Generative AI is a type of AI that can create new content and ideas, such as conversations, stories, images, videos, and music. The repository provides a detailed guide on deploying image and text generative AI models, utilizing pre-trained models from SageMaker JumpStart. The web application is built on Streamlit and hosted on Amazon ECS with Fargate. It interacts with the SageMaker model endpoints through Lambda functions and Amazon API Gateway. The repository also includes instructions on setting up the AWS CDK application, deploying the stacks, using the models, and viewing the deployed resources on the AWS Management Console.
cake
cake is a pure Rust implementation of the llama3 LLM distributed inference based on Candle. The project aims to enable running large models on consumer hardware clusters of iOS, macOS, Linux, and Windows devices by sharding transformer blocks. It allows running inferences on models that wouldn't fit in a single device's GPU memory by batching contiguous transformer blocks on the same worker to minimize latency. The tool provides a way to optimize memory and disk space by splitting the model into smaller bundles for workers, ensuring they only have the necessary data. cake supports various OS, architectures, and accelerations, with different statuses for each configuration.
Awesome-Robotics-3D
Awesome-Robotics-3D is a curated list of 3D Vision papers related to Robotics domain, focusing on large models like LLMs/VLMs. It includes papers on Policy Learning, Pretraining, VLM and LLM, Representations, and Simulations, Datasets, and Benchmarks. The repository is maintained by Zubair Irshad and welcomes contributions and suggestions for adding papers. It serves as a valuable resource for researchers and practitioners in the field of Robotics and Computer Vision.
tensorzero
TensorZero is an open-source platform that helps LLM applications graduate from API wrappers into defensible AI products. It enables a data & learning flywheel for LLMs by unifying inference, observability, optimization, and experimentation. The platform includes a high-performance model gateway, structured schema-based inference, observability, experimentation, and data warehouse for analytics. TensorZero Recipes optimize prompts and models, and the platform supports experimentation features and GitOps orchestration for deployment.

vector-inference
This repository provides an easy-to-use solution for running inference servers on Slurm-managed computing clusters using vLLM. All scripts in this repository run natively on the Vector Institute cluster environment. Users can deploy models as Slurm jobs, check server status and performance metrics, and shut down models. The repository also supports launching custom models with specific configurations. Additionally, users can send inference requests and set up an SSH tunnel to run inference from a local device.
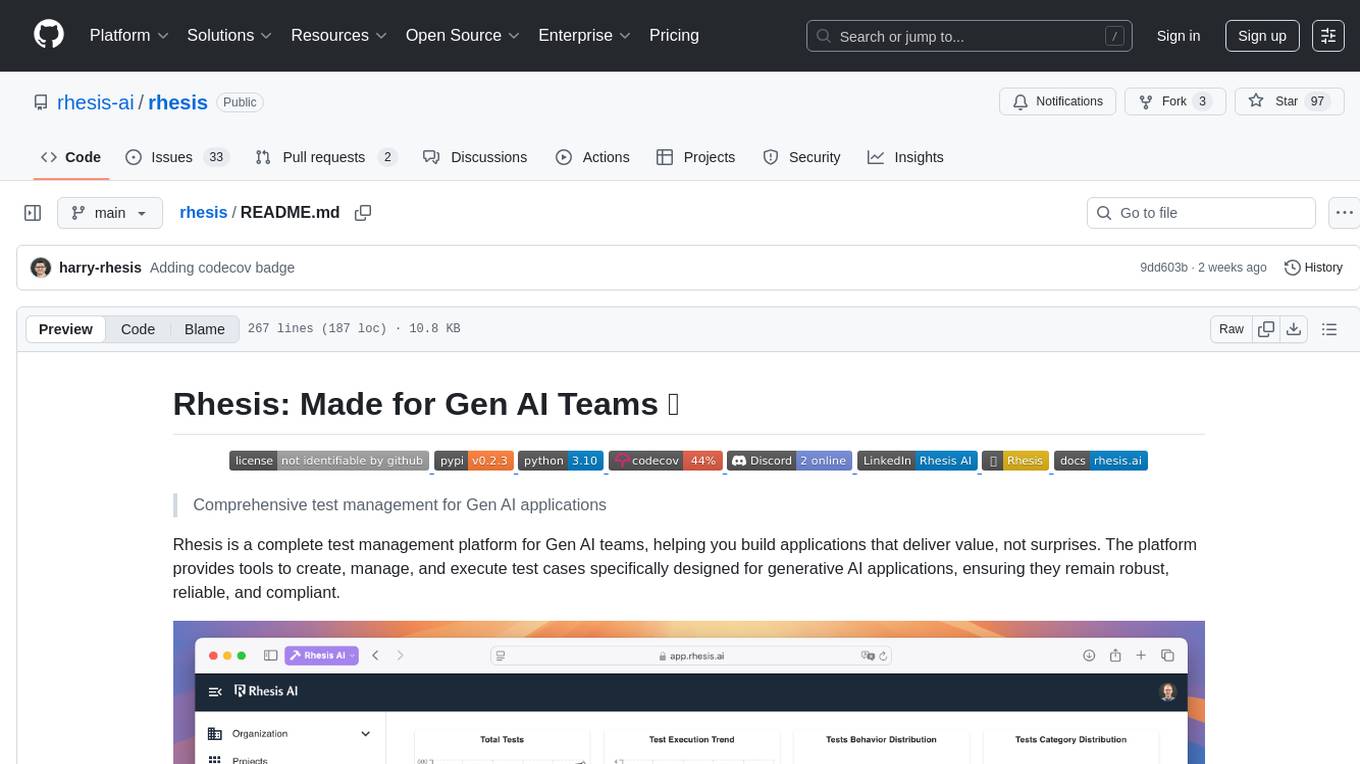
rhesis
Rhesis is a comprehensive test management platform designed for Gen AI teams, offering tools to create, manage, and execute test cases for generative AI applications. It ensures the robustness, reliability, and compliance of AI systems through features like test set management, automated test generation, edge case discovery, compliance validation, integration capabilities, and performance tracking. The platform is open source, emphasizing community-driven development, transparency, extensible architecture, and democratizing AI safety. It includes components such as backend services, frontend applications, SDK for developers, worker services, chatbot applications, and Polyphemus for uncensored LLM service. Rhesis enables users to address challenges unique to testing generative AI applications, such as non-deterministic outputs, hallucinations, edge cases, ethical concerns, and compliance requirements.



