
dir-assistant
Chat with your current directory's files using a local or API LLM.
Stars: 400
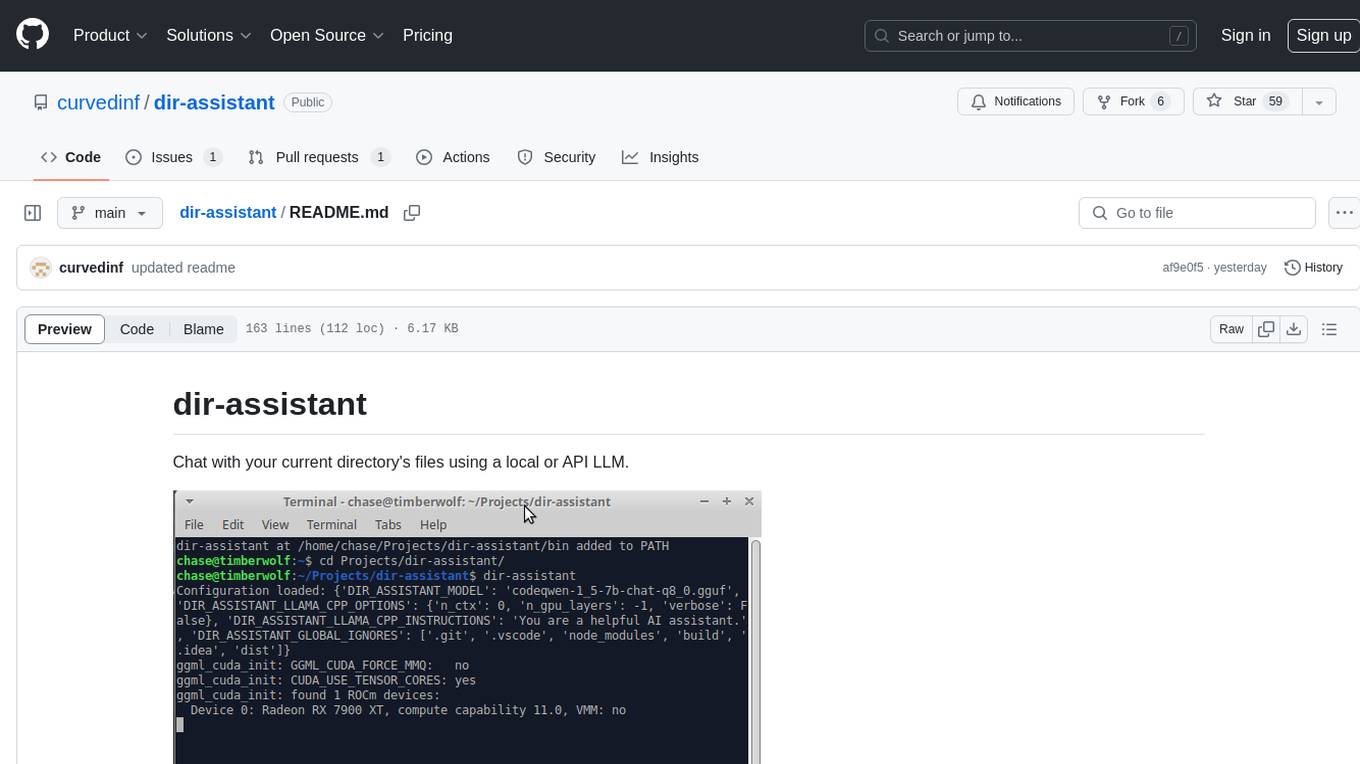
Dir-assistant is a tool that allows users to interact with their current directory's files using local or API Language Models (LLMs). It supports various platforms and provides API support for major LLM APIs. Users can configure and customize their local LLMs and API LLMs using the tool. Dir-assistant also supports model downloads and configurations for efficient usage. It is designed to enhance file interaction and retrieval using advanced language models.
README:
Chat with your current directory's files using a local or API LLM.
dir-assistant is a CLI python application available through pip that recursively indexes all text
files in the current working directory so you can chat with them using a local or API LLM. By
"chat with them", it is meant that their contents will automatically be included in the prompts sent
to the LLM, with the most contextually relevant files included first. dir-assistant is designed
primarily for use as a coding aid and automation tool.
- Includes an interactive chat mode and a single prompt non-interactive mode.
- When enabled, it will automatically make file updates and commit to git.
- Local platform support for CPU (OpenBLAS), Cuda, ROCm, Metal, Vulkan, and SYCL.
- API support for all major LLM APIs. More info in the LiteLLM Docs.
- Uses a unique method for finding the most important files to include when submitting your prompt to an LLM called CGRAG (Contextually Guided Retrieval-Augmented Generation). You can read this blog post for more information about how it works.
- Context caching optimization to reduce cost and latency.
- Optionally configure a separate, faster LLM for the CGRAG guidance step to reduce cost and latency.
- The embedding index is now separated by model in the database. This means you can switch between embedding models without needing to re-index files.
- Indexing is now parallelized and faster.
- Fixed a bug where the context optimizer was not utilizing the whole context
In this section are recipes to run dir-assistant in basic capacity to get you started quickly.
To get started locally, you can download a default llm model. Default configuration with this model requires 3GB of memory on most hardware. You will be able to adjust the configuration to fit higher or lower memory requirements. To run via CPU:
pip install dir-assistant[recommended]
dir-assistant models download-embed
dir-assistant models download-llm
cd directory/to/chat/with
dir-assistantTo run with hardware acceleration, use the platform subcommand:
...
dir-assistant platform cuda
cd directory/to/chat/with
dir-assistantSee which platforms are supported using -h:
dir-assistant platform -hIt is not recommended to use dir-assistant directly with local LLMs on Windows. This is because
llama-cpp-python requires a C compiler for installation via pip, and setting one up is not
a trivial task on Windows like it is on other platforms. Instead, it is recommended to
use another LLM server such as LMStudio and configure dir-assistant to use it as
a custom API server. To do this, ensure you are installing dir-assistant without
the recommended dependencies:
pip install dir-assistantThen configure dir-assistant to connect to your custom LLM API server:
Connecting to a Custom API Server
For instructions on setting up LMStudio to host an API, follow their guide:
https://lmstudio.ai/docs/app/api
pip3 has been replaced with pipx starting in Ubuntu 24.04.
pipx install dir-assistant[recommended]
...
dir-assistant platform cuda --pipxTo get started using an API model, you can use Google Gemini 1.5 Flash, which is currently free. To begin, you need to sign up for Google AI Studio and create an API key. After you create your API key, enter the following commands:
pip install dir-assistant
dir-assistant setkey GEMINI_API_KEY xxxxxYOURAPIKEYHERExxxxx
cd directory/to/chat/with
dir-assistantNote: The Python.org installer is recommended for Windows. The Windows
Store installer does not add dir-assistant to your PATH so you will need to call it
with python -m dir_assistant if you decide to go that route.
pip install dir-assistant
dir-assistant setkey GEMINI_API_KEY xxxxxYOURAPIKEYHERExxxxx
cd directory/to/chat/with
dir-assistantpip3 has been replaced with pipx starting in Ubuntu 24.04.
pipx install dir-assistant
dir-assistant setkey GEMINI_API_KEY xxxxxYOURAPIKEYHERExxxxx
cd directory/to/chat/with
dir-assistantTo get started quickly with Anthropic's Claude models (e.g., Claude 3.7 Sonnet):
- Obtain an API key from Anthropic.
- Install
dir-assistantand set your API key:pip install dir-assistant dir-assistant setkey ANTHROPIC_API_KEY xxxxxYOURAPIKEYHERExxxxx
- Configure
dir-assistantto use Claude. Open the config file withdir-assistant config openand make sure these settings are present:[DIR_ASSISTANT] ACTIVE_MODEL_IS_LOCAL = false LITELLM_MODEL_USES_SYSTEM_MESSAGE = true LITELLM_CONTEXT_SIZE = 200000 [DIR_ASSISTANT.LITELLM_COMPLETION_OPTIONS] model = "anthropic/claude-3-7-sonnet-20240729"
- Navigate to your project directory and run:
cd directory/to/chat/with dir-assistant
pip install dir-assistant
dir-assistant setkey ANTHROPIC_API_KEY xxxxxYOURAPIKEYHERExxxxx
# Then, configure the model as shown above using 'dir-assistant config open'
cd directory/to/chat/with
dir-assistantpipx install dir-assistant
dir-assistant setkey ANTHROPIC_API_KEY xxxxxYOURAPIKEYHERExxxxx
# Then, configure the model as shown above using 'dir-assistant config open'
cd directory/to/chat/with
dir-assistantTo get started quickly with OpenAI's models (e.g., GPT-4o):
- Obtain an API key from OpenAI.
- Install
dir-assistantand set your API key:pip install dir-assistant dir-assistant setkey OPENAI_API_KEY xxxxxYOURAPIKEYHERExxxxx
- Configure
dir-assistantto use an OpenAI model. Open the config file withdir-assistant config openand make sure these settings are present:[DIR_ASSISTANT] ACTIVE_MODEL_IS_LOCAL = false LITELLM_MODEL_USES_SYSTEM_MESSAGE = true LITELLM_CONTEXT_SIZE = 128000 [DIR_ASSISTANT.LITELLM_COMPLETION_OPTIONS] model = "gpt-4o"
- Navigate to your project directory and run:
cd directory/to/chat/with dir-assistant
pip install dir-assistant
dir-assistant setkey OPENAI_API_KEY xxxxxYOURAPIKEYHERExxxxx
# Then, configure the model as shown above using 'dir-assistant config open'
cd directory/to/chat/with
dir-assistantpipx install dir-assistant
dir-assistant setkey OPENAI_API_KEY xxxxxYOURAPIKEYHERExxxxx
# Then, configure the model as shown above using 'dir-assistant config open'
cd directory/to/chat/with
dir-assistantThe non-interactive mode of dir-assistant allows you to create scripts which analyze
your files without user interaction.
To get started using an API model, you can use Google Gemini 1.5 Flash, which is currently free.
To begin, you need to sign up for Google AI Studio and
create an API key. After you create your API key,
enter the following commands:
pip install dir-assistant
dir-assistant setkey GEMINI_API_KEY xxxxxYOURAPIKEYHERExxxxx
cd directory/to/chat/with
dir-assistant -s "Describe the files in this directory"pip3 has been replaced with pipx starting in Ubuntu 24.04.
pipx install dir-assistant
dir-assistant setkey GEMINI_API_KEY xxxxxYOURAPIKEYHERExxxxx
cd directory/to/chat/with
dir-assistant -s "Describe the files in this directory"For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for dir-assistant
Similar Open Source Tools

dir-assistant
Dir-assistant is a tool that allows users to interact with their current directory's files using local or API Language Models (LLMs). It supports various platforms and provides API support for major LLM APIs. Users can configure and customize their local LLMs and API LLMs using the tool. Dir-assistant also supports model downloads and configurations for efficient usage. It is designed to enhance file interaction and retrieval using advanced language models.
backend.ai-webui
Backend.AI Web UI is a user-friendly web and app interface designed to make AI accessible for end-users, DevOps, and SysAdmins. It provides features for session management, inference service management, pipeline management, storage management, node management, statistics, configurations, license checking, plugins, help & manuals, kernel management, user management, keypair management, manager settings, proxy mode support, service information, and integration with the Backend.AI Web Server. The tool supports various devices, offers a built-in websocket proxy feature, and allows for versatile usage across different platforms. Users can easily manage resources, run environment-supported apps, access a web-based terminal, use Visual Studio Code editor, manage experiments, set up autoscaling, manage pipelines, handle storage, monitor nodes, view statistics, configure settings, and more.
frontend
Nuclia frontend apps and libraries repository contains various frontend applications and libraries for the Nuclia platform. It includes components such as Dashboard, Widget, SDK, Sistema (design system), NucliaDB admin, CI/CD Deployment, and Maintenance page. The repository provides detailed instructions on installation, dependencies, and usage of these components for both Nuclia employees and external developers. It also covers deployment processes for different components and tools like ArgoCD for monitoring deployments and logs. The repository aims to facilitate the development, testing, and deployment of frontend applications within the Nuclia ecosystem.
QA-Pilot
QA-Pilot is an interactive chat project that leverages online/local LLM for rapid understanding and navigation of GitHub code repository. It allows users to chat with GitHub public repositories using a git clone approach, store chat history, configure settings easily, manage multiple chat sessions, and quickly locate sessions with a search function. The tool integrates with `codegraph` to view Python files and supports various LLM models such as ollama, openai, mistralai, and localai. The project is continuously updated with new features and improvements, such as converting from `flask` to `fastapi`, adding `localai` API support, and upgrading dependencies like `langchain` and `Streamlit` to enhance performance.
shortest
Shortest is a project for local development that helps set up environment variables and services for a web application. It provides a guide for setting up Node.js and pnpm dependencies, configuring services like Clerk, Vercel Postgres, Anthropic, Stripe, and GitHub OAuth, and running the application and tests locally.
elyra
Elyra is a set of AI-centric extensions to JupyterLab Notebooks that includes features like Visual Pipeline Editor, running notebooks/scripts as batch jobs, reusable code snippets, hybrid runtime support, script editors with execution capabilities, debugger, version control using Git, and more. It provides a comprehensive environment for data scientists and AI practitioners to develop, test, and deploy machine learning models and workflows efficiently.
desktop
ComfyUI Desktop is a packaged desktop application that allows users to easily use ComfyUI with bundled features like ComfyUI source code, ComfyUI-Manager, and uv. It automatically installs necessary Python dependencies and updates with stable releases. The app comes with Electron, Chromium binaries, and node modules. Users can store ComfyUI files in a specified location and manage model paths. The tool requires Python 3.12+ and Visual Studio with Desktop C++ workload for Windows. It uses nvm to manage node versions and yarn as the package manager. Users can install ComfyUI and dependencies using comfy-cli, download uv, and build/launch the code. Troubleshooting steps include rebuilding modules and installing missing libraries. The tool supports debugging in VSCode and provides utility scripts for cleanup. Crash reports can be sent to help debug issues, but no personal data is included.
jupyter-quant
Jupyter Quant is a dockerized environment tailored for quantitative research, equipped with essential tools like statsmodels, pymc, arch, py_vollib, zipline-reloaded, PyPortfolioOpt, numpy, pandas, sci-py, scikit-learn, yellowbricks, shap, optuna, and more. It provides Interactive Broker connectivity via ib_async and includes major Python packages for statistical and time series analysis. The image is optimized for size, includes jedi language server, jupyterlab-lsp, and common command line utilities. Users can install new packages with sudo, leverage apt cache, and bring their own dot files and SSH keys. The tool is designed for ephemeral containers, ensuring data persistence and flexibility for quantitative analysis tasks.
trieve
Trieve is an advanced relevance API for hybrid search, recommendations, and RAG. It offers a range of features including self-hosting, semantic dense vector search, typo tolerant full-text/neural search, sub-sentence highlighting, recommendations, convenient RAG API routes, the ability to bring your own models, hybrid search with cross-encoder re-ranking, recency biasing, tunable popularity-based ranking, filtering, duplicate detection, and grouping. Trieve is designed to be flexible and customizable, allowing users to tailor it to their specific needs. It is also easy to use, with a simple API and well-documented features.
sandvault
SandVault is a tool that manages a limited user account to sandbox shell commands and AI agents on macOS, providing a lightweight alternative to application isolation using virtual machines. It allows for running Claude Code, OpenAI Codex, Google Gemini, and shell commands safely within a sandboxed environment. SandVault offers features like fast context switching, passwordless account switching, shared workspace access, and clean uninstallation. The tool operates with limited access to the user's computer, ensuring security by restricting access to certain directories and system files.
snipkit
SnipKit is a CLI tool designed to manage snippets efficiently, allowing users to execute saved scripts or generate new ones with the help of AI directly from the terminal. It supports loading snippets from various sources, parameter substitution, different parameter types, themes, and customization options. The tool includes an interactive chat-style interface called SnipKit Assistant for generating parameterized scripts. Users can also work with different AI providers like OpenAI, Anthropic, Google Gemini, and more. SnipKit aims to streamline script execution and script generation workflows for developers and users who frequently work with code snippets.
openai-kotlin
OpenAI Kotlin API client is a Kotlin client for OpenAI's API with multiplatform and coroutines capabilities. It allows users to interact with OpenAI's API using Kotlin programming language. The client supports various features such as models, chat, images, embeddings, files, fine-tuning, moderations, audio, assistants, threads, messages, and runs. It also provides guides on getting started, chat & function call, file source guide, and assistants. Sample apps are available for reference, and troubleshooting guides are provided for common issues. The project is open-source and licensed under the MIT license, allowing contributions from the community.
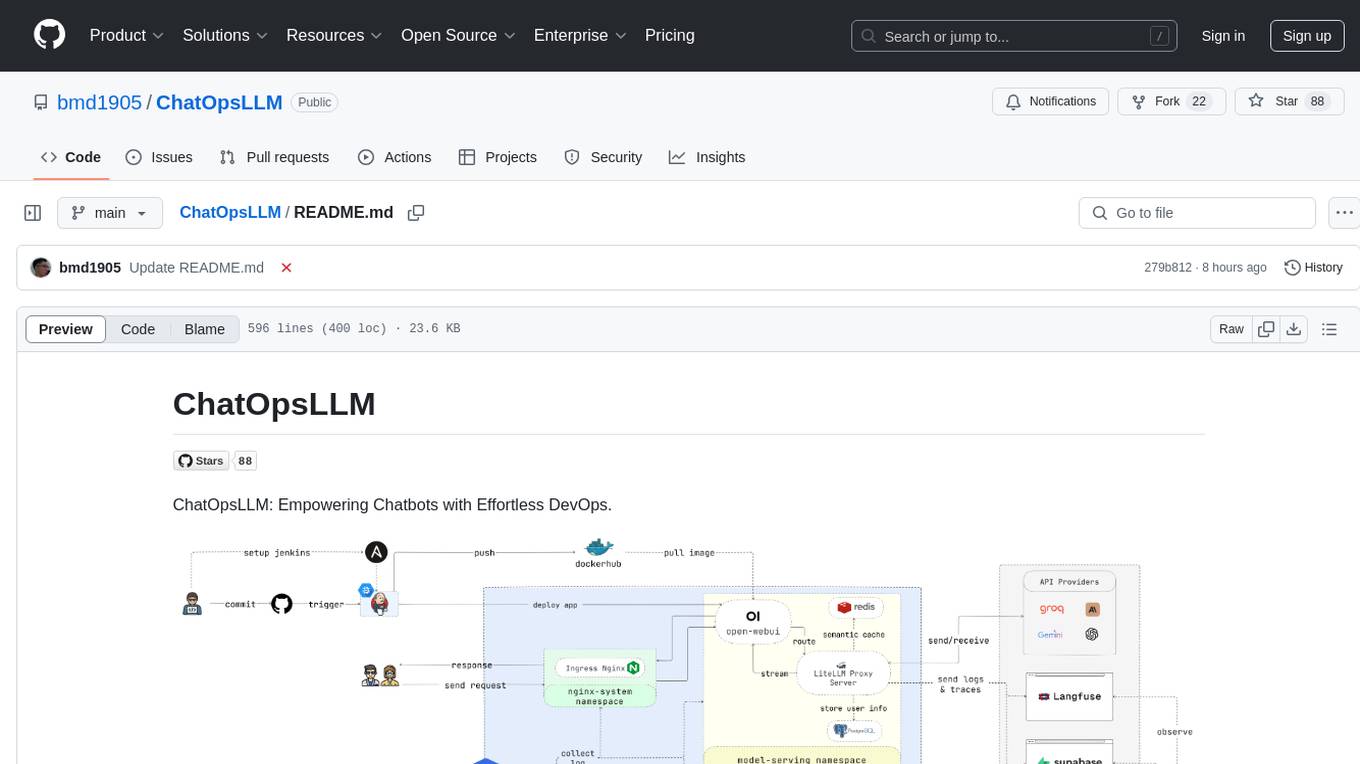
ChatOpsLLM
ChatOpsLLM is a project designed to empower chatbots with effortless DevOps capabilities. It provides an intuitive interface and streamlined workflows for managing and scaling language models. The project incorporates robust MLOps practices, including CI/CD pipelines with Jenkins and Ansible, monitoring with Prometheus and Grafana, and centralized logging with the ELK stack. Developers can find detailed documentation and instructions on the project's website.
gitingest
GitIngest is a tool that allows users to turn any Git repository into a prompt-friendly text ingest for LLMs. It provides easy code context by generating a text digest from a git repository URL or directory. The tool offers smart formatting for optimized output format for LLM prompts and provides statistics about file and directory structure, size of the extract, and token count. GitIngest can be used as a CLI tool on Linux and as a Python package for code integration. The tool is built using Tailwind CSS for frontend, FastAPI for backend framework, tiktoken for token estimation, and apianalytics.dev for simple analytics. Users can self-host GitIngest by building the Docker image and running the container. Contributions to the project are welcome, and the tool aims to be beginner-friendly for first-time contributors with a simple Python and HTML codebase.
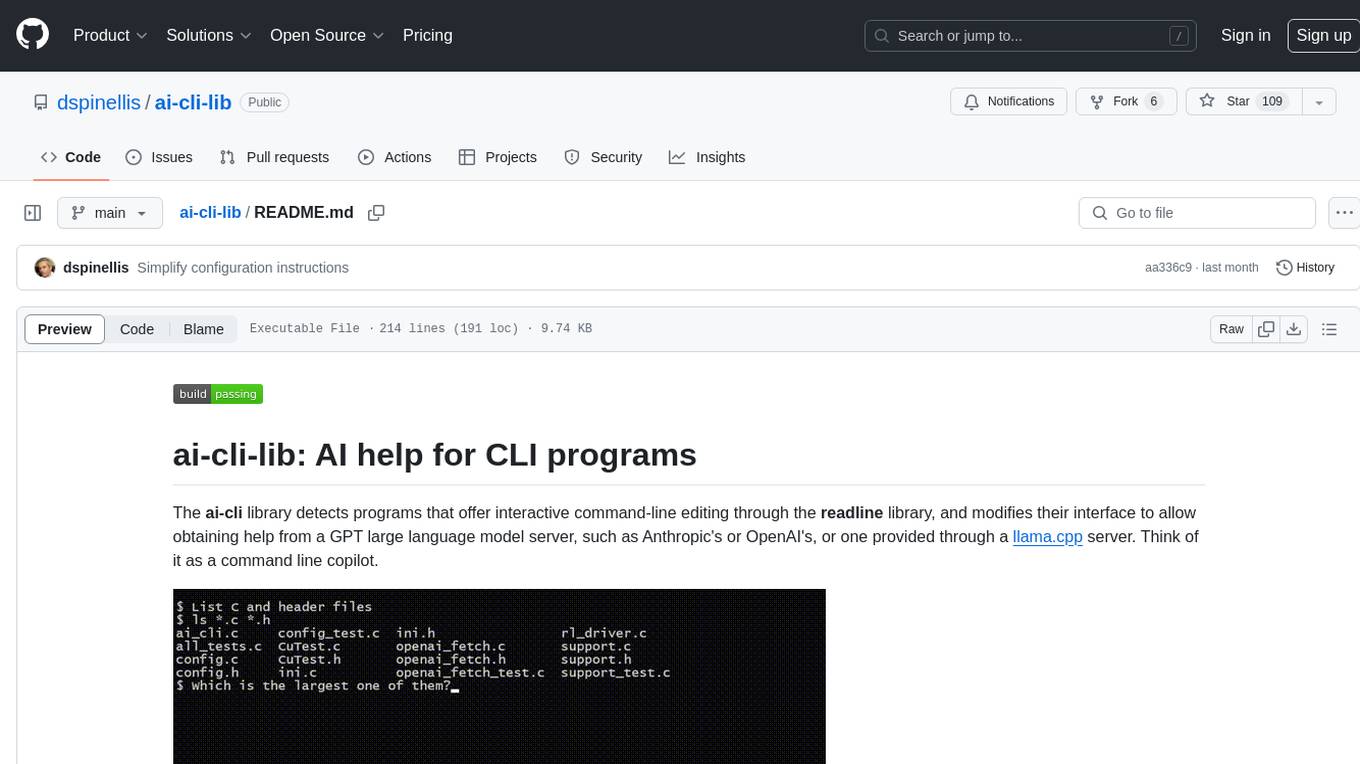
ai-cli-lib
The ai-cli-lib is a library designed to enhance interactive command-line editing programs by integrating with GPT large language model servers. It allows users to obtain AI help from servers like Anthropic's or OpenAI's, or a llama.cpp server. The library acts as a command line copilot, providing natural language prompts and responses to enhance user experience and productivity. It supports various platforms such as Debian GNU/Linux, macOS, and Cygwin, and requires specific packages for installation and operation. Users can configure the library to activate during shell startup and interact with command-line programs like bash, mysql, psql, gdb, sqlite3, and bc. Additionally, the library provides options for configuring API keys, setting up llama.cpp servers, and ensuring data privacy by managing context settings.
ollama4j-web-ui
Ollama4j Web UI is a Java-based web interface built using Spring Boot and Vaadin framework for Ollama users with Java and Spring background. It allows users to interact with various models running on Ollama servers, providing a fully functional web UI experience. The project offers multiple ways to run the application, including via Docker, Docker Compose, or as a standalone JAR. Users can configure the environment variables and access the web UI through a browser. The project also includes features for error handling on the UI and settings pane for customizing default parameters.
For similar tasks
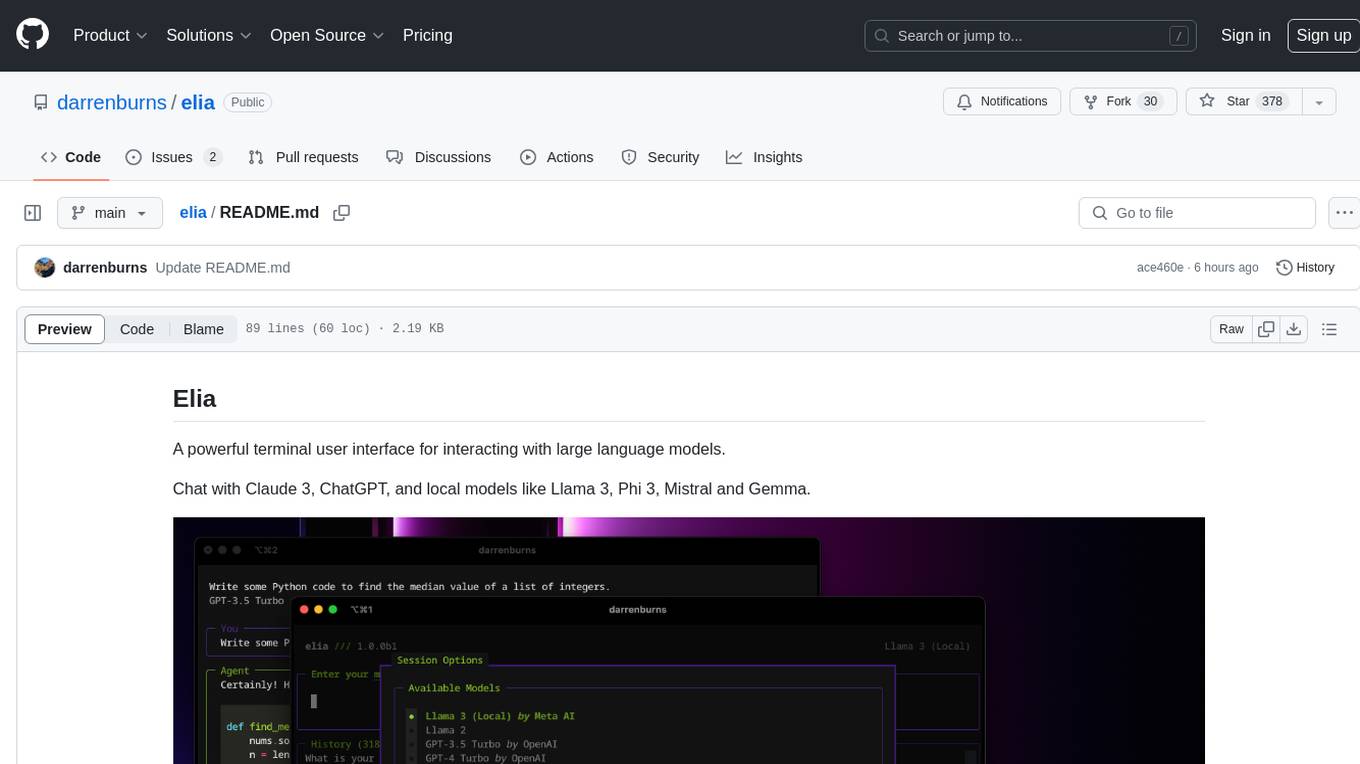
elia
Elia is a powerful terminal user interface designed for interacting with large language models. It allows users to chat with models like Claude 3, ChatGPT, Llama 3, Phi 3, Mistral, and Gemma. Conversations are stored locally in a SQLite database, ensuring privacy. Users can run local models through 'ollama' without data leaving their machine. Elia offers easy installation with pipx and supports various environment variables for different models. It provides a quick start to launch chats and manage local models. Configuration options are available to customize default models, system prompts, and add new models. Users can import conversations from ChatGPT and wipe the database when needed. Elia aims to enhance user experience in interacting with language models through a user-friendly interface.
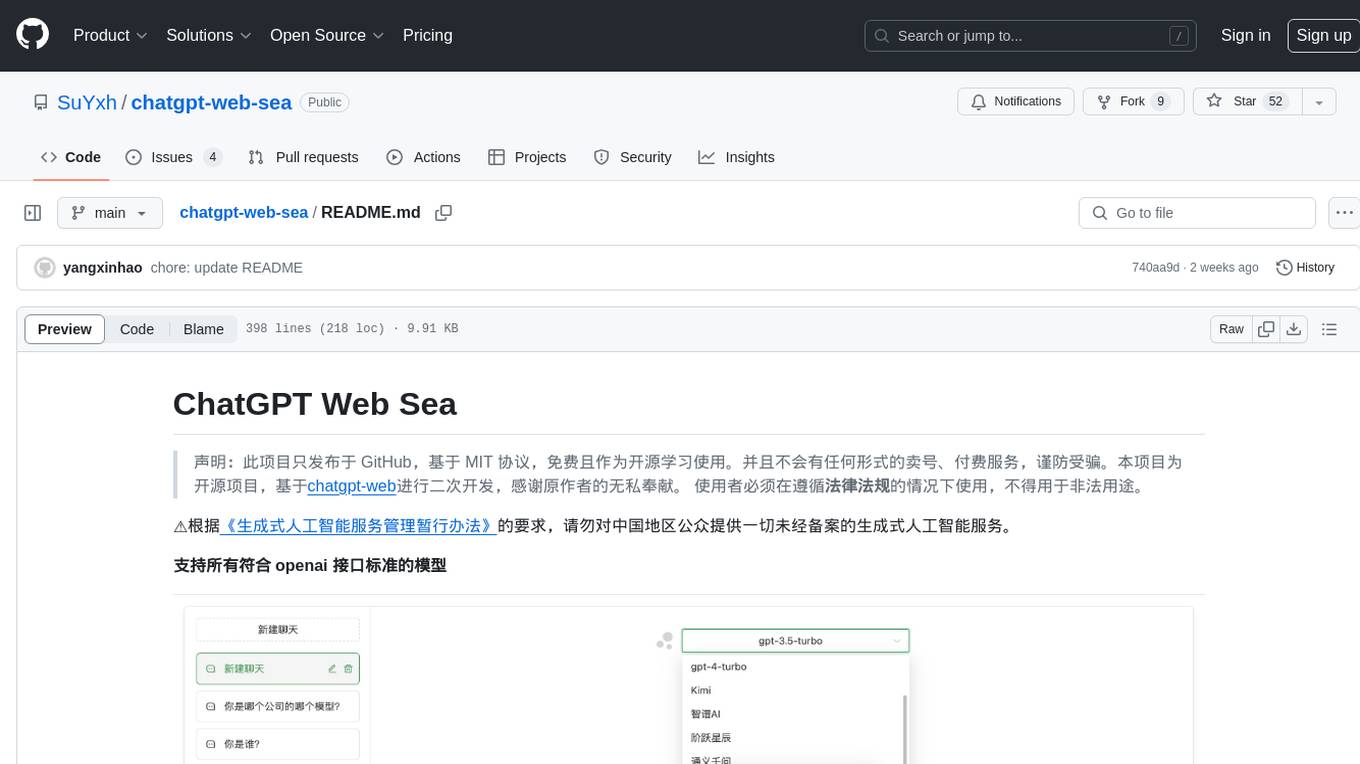
chatgpt-web-sea
ChatGPT Web Sea is an open-source project based on ChatGPT-web for secondary development. It supports all models that comply with the OpenAI interface standard, allows for model selection, configuration, and extension, and is compatible with OneAPI. The tool includes a Chinese ChatGPT tuning guide, supports file uploads, and provides model configuration options. Users can interact with the tool through a web interface, configure models, and perform tasks such as model selection, API key management, and chat interface setup. The project also offers Docker deployment options and instructions for manual packaging.

dir-assistant
Dir-assistant is a tool that allows users to interact with their current directory's files using local or API Language Models (LLMs). It supports various platforms and provides API support for major LLM APIs. Users can configure and customize their local LLMs and API LLMs using the tool. Dir-assistant also supports model downloads and configurations for efficient usage. It is designed to enhance file interaction and retrieval using advanced language models.
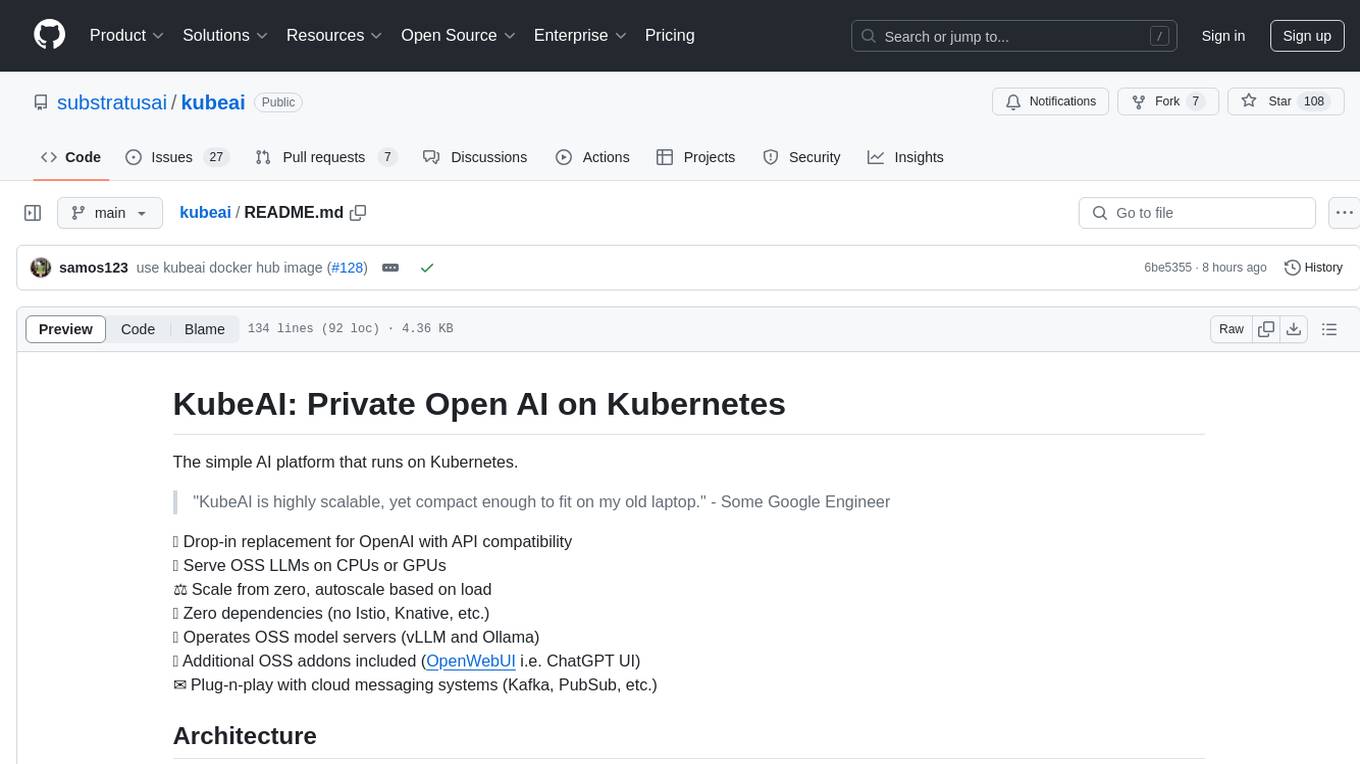
kubeai
KubeAI is a highly scalable AI platform that runs on Kubernetes, serving as a drop-in replacement for OpenAI with API compatibility. It can operate OSS model servers like vLLM and Ollama, with zero dependencies and additional OSS addons included. Users can configure models via Kubernetes Custom Resources and interact with models through a chat UI. KubeAI supports serving various models like Llama v3.1, Gemma2, and Qwen2, and has plans for model caching, LoRA finetuning, and image generation.
renumics-rag
Renumics RAG is a retrieval-augmented generation assistant demo that utilizes LangChain and Streamlit. It provides a tool for indexing documents and answering questions based on the indexed data. Users can explore and visualize RAG data, configure OpenAI and Hugging Face models, and interactively explore questions and document snippets. The tool supports GPU and CPU setups, offers a command-line interface for retrieving and answering questions, and includes a web application for easy access. It also allows users to customize retrieval settings, embeddings models, and database creation. Renumics RAG is designed to enhance the question-answering process by leveraging indexed documents and providing detailed answers with sources.
llm-term
LLM-Term is a Rust-based CLI tool that generates and executes terminal commands using OpenAI's language models or local Ollama models. It offers configurable model and token limits, works on both PowerShell and Unix-like shells, and provides a seamless user experience for generating commands based on prompts. Users can easily set up the tool, customize configurations, and leverage different models for command generation.
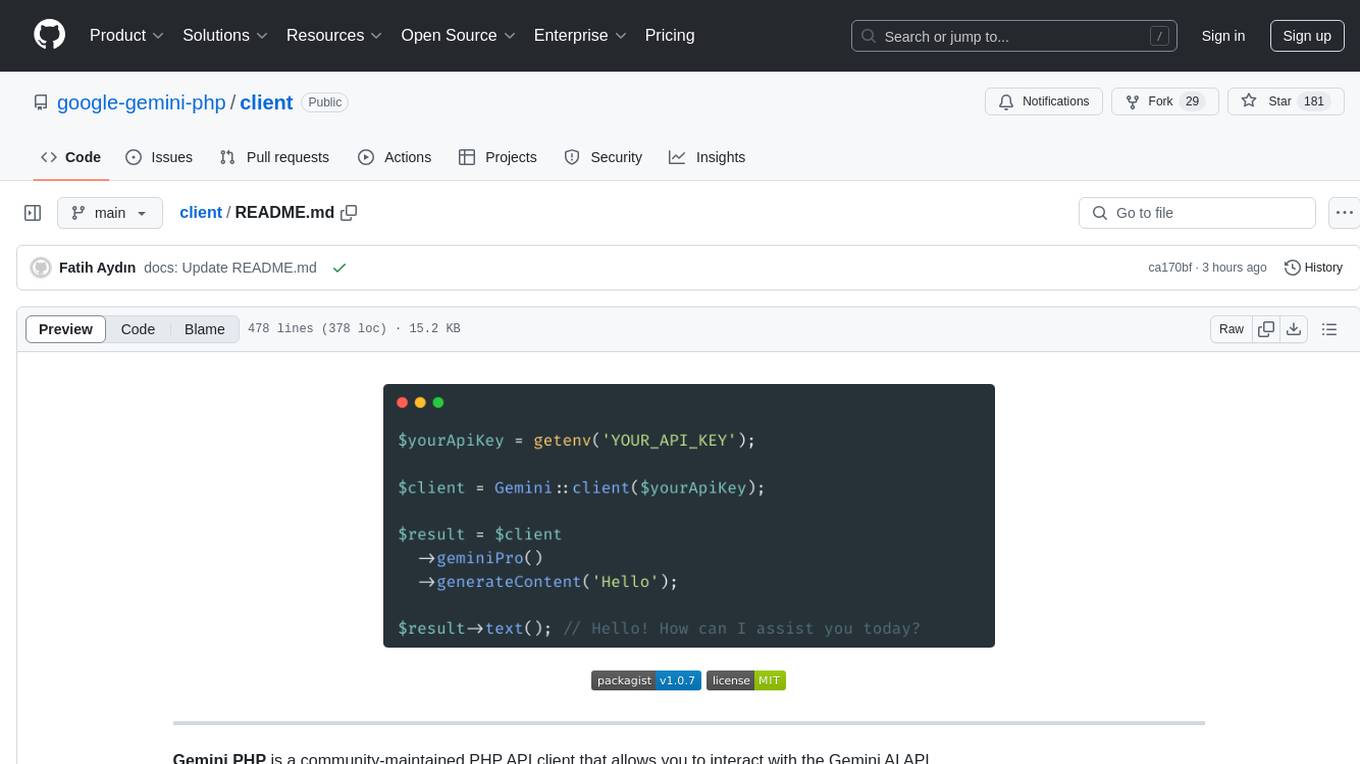
client
Gemini PHP is a PHP API client for interacting with the Gemini AI API. It allows users to generate content, chat, count tokens, configure models, embed resources, list models, get model information, troubleshoot timeouts, and test API responses. The client supports various features such as text-only input, text-and-image input, multi-turn conversations, streaming content generation, token counting, model configuration, and embedding techniques. Users can interact with Gemini's API to perform tasks related to natural language generation and text analysis.
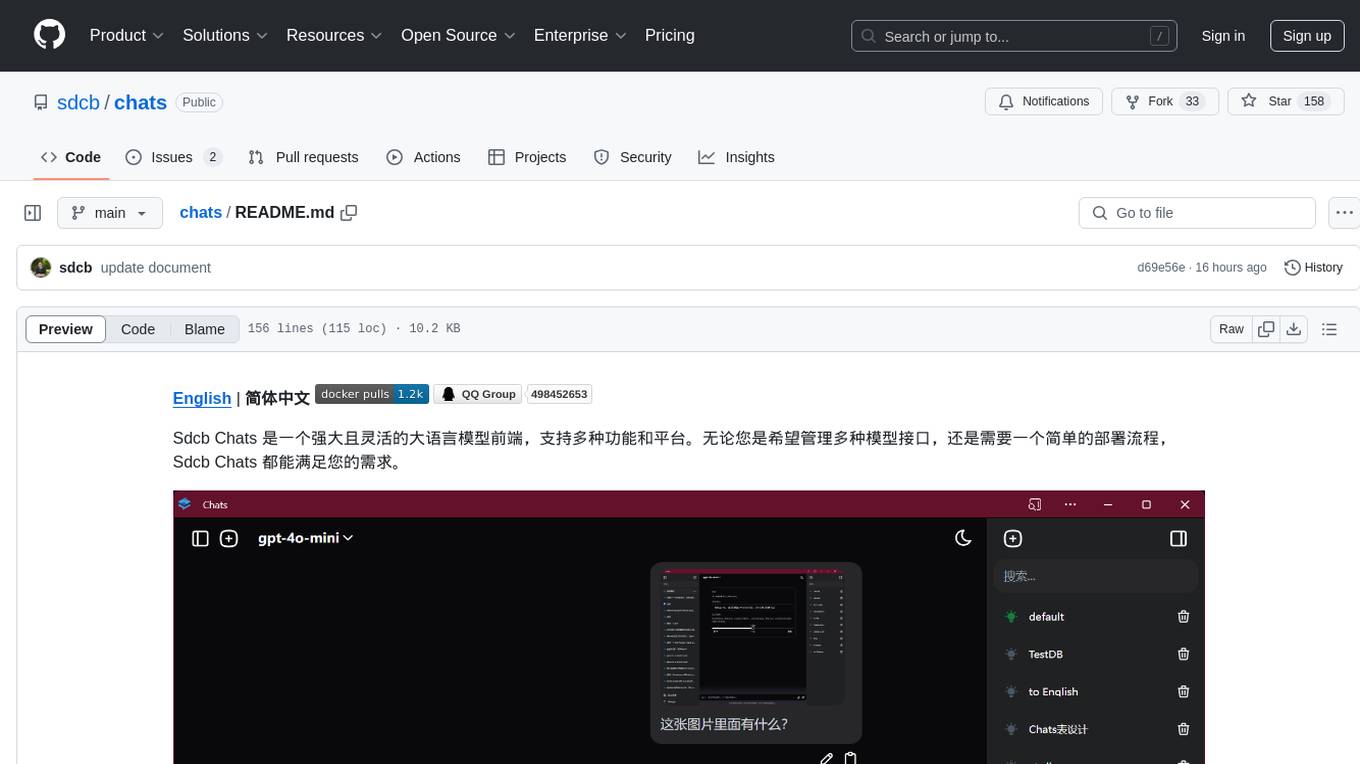
chats
Sdcb Chats is a powerful and flexible frontend for large language models, supporting multiple functions and platforms. Whether you want to manage multiple model interfaces or need a simple deployment process, Sdcb Chats can meet your needs. It supports dynamic management of multiple large language model interfaces, integrates visual models to enhance user interaction experience, provides fine-grained user permission settings for security, real-time tracking and management of user account balances, easy addition, deletion, and configuration of models, transparently forwards user chat requests based on the OpenAI protocol, supports multiple databases including SQLite, SQL Server, and PostgreSQL, compatible with various file services such as local files, AWS S3, Minio, Aliyun OSS, Azure Blob Storage, and supports multiple login methods including Keycloak SSO and phone SMS verification.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.






