
kubeai
AI Inference Operator for Kubernetes. The easiest way to serve ML models in production. Supports VLMs, LLMs, embeddings, and speech-to-text.
Stars: 873
KubeAI is a highly scalable AI platform that runs on Kubernetes, serving as a drop-in replacement for OpenAI with API compatibility. It can operate OSS model servers like vLLM and Ollama, with zero dependencies and additional OSS addons included. Users can configure models via Kubernetes Custom Resources and interact with models through a chat UI. KubeAI supports serving various models like Llama v3.1, Gemma2, and Qwen2, and has plans for model caching, LoRA finetuning, and image generation.
README:
Deploy and scale machine learning models on Kubernetes. Built for LLMs, embeddings, and speech-to-text.
What is it for?
🚀 LLM Inferencing - Operate vLLM and Ollama servers
🎙️ Speech Processing - Transcribe audio with FasterWhisper
🔢 Vector Embeddings - Generate embeddings with Infinity
What do you get?
⚡️ Intelligent Scaling - Scale from zero to meet demand
📊 Optimized Routing - Dramatically improves performance at scale (see paper)
💾 Model Caching - Automates downloading & mounting (EFS, etc.)
🧩 Dynamic Adapters - Orchestrates LoRA adapters across replicas
📨 Event Streaming - Integrates with Kafka, PubSub, and more
We strive for an "it justs works" experience:
🔗 OpenAI Compatible - Works with OpenAI client libraries
🛠️ Zero Dependencies - Does not require Istio, Knative, etc.
🖥 Hardware Flexible - Runs on CPU, GPU, or TPU
Quotes from the community:
reusable, well abstracted solution to run LLMs - Mike Ensor, Google
When running multiple replicas of vLLM, the random load balancing strategy built into kube-proxy that backs standard Kubernetes Services performs poorly (TTFT & throughput). This is because vLLM isn't stateless, its performance is heavily influenced by the state of its KV cache.
The KubeAI proxy includes a prefix-aware load balancing strategy that optimizes KV cache utilization - resulting in dramatic improvements to overall system performance.
See the full paper for more details.
KubeAI does not depend on other systems like Istio & Knative (for scale-from-zero), or the Prometheus metrics adapter (for autoscaling). This allows KubeAI to work out of the box in almost any Kubernetes cluster. Day-two operations is greatly simplified as well - don't worry about inter-project version and configuration mismatches.
The project ships with a catalog of popular models, pre-configured for common GPU types. This means you can spend less time tweaking vLLM-specific flags. As we expand, we plan to build out an extensive model optimization pipeline that will ensure you get the most out of your hardware.
No need to change your client libraries, KubeAI supports the following endpoints:
/v1/chat/completions
/v1/completions
/v1/embeddings
/v1/models
/v1/audio/transcriptionsKubeAI consists of two primary sub-components:
1. The model proxy: the KubeAI proxy provides an OpenAI-compatible API. Behind this API, the proxy implements a prefix-aware load balancing strategy that optimizes for KV the cache utilization of the backend serving engines (i.e. vLLM). The proxy also implements request queueing (while the system scales from zero replicas) and request retries (to seamlessly handle bad backends).
2. The model operator: the KubeAI model operator manages backend server Pods directly. It automates common operations such as downloading models, mounting volumes, and loading dynamic LoRA adapters via the KubeAI Model CRD.
Both of these components are co-located in the same deployment, but could be deployed independently.
List of known adopters:
| Name | Description | Link |
|---|---|---|
| Telescope | Telescope uses KubeAI for multi-region large scale batch LLM inference. | trytelescope.ai |
| Google Cloud Distributed Edge | KubeAI is included as a reference architecture for inferencing at the edge. | LinkedIn, GitLab |
| Lambda | You can try KubeAI on the Lambda AI Developer Cloud. See Lambda's tutorial and video. | Lambda |
| Vultr | KubeAI can be deployed on Vultr Managed Kubernetes using the application marketplace. | Vultr |
| Arcee | Arcee uses KubeAI for multi-region, multi-tenant SLM inference. | Arcee |
| Seeweb | Seeweb leverages KubeAI for direct and client-facing GPU inference workloads. KubeAI can be deployed on any GPU server and SKS | Seeweb |
If you are using KubeAI and would like to be listed as an adopter, please make a PR.
Create a local cluster using kind or minikube.
TIP: If you are using Podman for kind...
Make sure your Podman machine can use up to 6G of memory (by default it is capped at 2G):# You might need to stop and remove the existing machine:
podman machine stop
podman machine rm
# Init and start a new machine:
podman machine init --memory 6144 --disk-size 120
podman machine startkind create cluster # OR: minikube startAdd the KubeAI Helm repository.
helm repo add kubeai https://www.kubeai.org
helm repo updateInstall KubeAI and wait for all components to be ready (may take a minute).
helm install kubeai kubeai/kubeai --wait --timeout 10mInstall some predefined models.
cat <<EOF > kubeai-models.yaml
catalog:
deepseek-r1-1.5b-cpu:
enabled: true
features: [TextGeneration]
url: 'ollama://deepseek-r1:1.5b'
engine: OLlama
minReplicas: 1
resourceProfile: 'cpu:1'
qwen2-500m-cpu:
enabled: true
nomic-embed-text-cpu:
enabled: true
EOF
helm install kubeai-models kubeai/models \
-f ./kubeai-models.yamlBefore progressing to the next steps, start a watch on Pods in a standalone terminal to see how KubeAI deploys models.
kubectl get pods --watchBecause we set minReplicas: 1 for the Deepseek model you should see a model Pod already coming up.
Start a local port-forward to the bundled chat UI.
kubectl port-forward svc/open-webui 8000:80Now open your browser to localhost:8000 and select the Deepseek model to start chatting with.
If you go back to the browser and start a chat with Qwen2, you will notice that it will take a while to respond at first. This is because we set minReplicas: 0 for this model and KubeAI needs to spin up a new Pod (you can verify with kubectl get models -oyaml qwen2-500m-cpu).
Read about concepts, guides, and API documentation on kubeai.org.
🌟 Don't forget to drop us a star on GitHub and follow the repo to stay up to date!
Let us know about features you are interested in seeing or reach out with questions. Visit our Discord channel to join the discussion!
Or just reach out on LinkedIn if you want to connect:
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for kubeai
Similar Open Source Tools

kubeai
KubeAI is a highly scalable AI platform that runs on Kubernetes, serving as a drop-in replacement for OpenAI with API compatibility. It can operate OSS model servers like vLLM and Ollama, with zero dependencies and additional OSS addons included. Users can configure models via Kubernetes Custom Resources and interact with models through a chat UI. KubeAI supports serving various models like Llama v3.1, Gemma2, and Qwen2, and has plans for model caching, LoRA finetuning, and image generation.
podman-desktop-extension-ai-lab
Podman AI Lab is an open source extension for Podman Desktop designed to work with Large Language Models (LLMs) on a local environment. It features a recipe catalog with common AI use cases, a curated set of open source models, and a playground for learning, prototyping, and experimentation. Users can quickly and easily get started bringing AI into their applications without depending on external infrastructure, ensuring data privacy and security.
OpenLLM
OpenLLM is a platform that helps developers run any open-source Large Language Models (LLMs) as OpenAI-compatible API endpoints, locally and in the cloud. It supports a wide range of LLMs, provides state-of-the-art serving and inference performance, and simplifies cloud deployment via BentoML. Users can fine-tune, serve, deploy, and monitor any LLMs with ease using OpenLLM. The platform also supports various quantization techniques, serving fine-tuning layers, and multiple runtime implementations. OpenLLM seamlessly integrates with other tools like OpenAI Compatible Endpoints, LlamaIndex, LangChain, and Transformers Agents. It offers deployment options through Docker containers, BentoCloud, and provides a community for collaboration and contributions.
SalesGPT
SalesGPT is an open-source AI agent designed for sales, utilizing context-awareness and LLMs to work across various communication channels like voice, email, and texting. It aims to enhance sales conversations by understanding the stage of the conversation and providing tools like product knowledge base to reduce errors. The agent can autonomously generate payment links, handle objections, and close sales. It also offers features like automated email communication, meeting scheduling, and integration with various LLMs for customization. SalesGPT is optimized for low latency in voice channels and ensures human supervision where necessary. The tool provides enterprise-grade security and supports LangSmith tracing for monitoring and evaluation of intelligent agents built on LLM frameworks.
piccolo
Piccolo AI is an open-source software development toolkit for constructing sensor-based AI inference models optimized to run on low-power microcontrollers and IoT edge platforms. It includes SensiML's ML Engine, Embedded ML SDK, Analytic Studio UI, and SensiML Python Client. The tool is intended for individual developers, researchers, and AI enthusiasts, offering support for time-series sensor data classification and various applications such as acoustic event detection, activity recognition, gesture detection, anomaly detection, keyword spotting, and vibration classification.
llocal
LLocal is an Electron application focused on providing a seamless and privacy-driven chatting experience using open-sourced technologies, particularly open-sourced LLM's. It allows users to store chats locally, switch between models, pull new models, upload images, perform web searches, and render responses as markdown. The tool also offers multiple themes, seamless integration with Ollama, and upcoming features like chat with images, web search improvements, retrieval augmented generation, multiple PDF chat, text to speech models, community wallpapers, lofi music, speech to text, and more. LLocal's builds are currently unsigned, requiring manual builds or using the universal build for stability.

lollms-webui
LoLLMs WebUI (Lord of Large Language Multimodal Systems: One tool to rule them all) is a user-friendly interface to access and utilize various LLM (Large Language Models) and other AI models for a wide range of tasks. With over 500 AI expert conditionings across diverse domains and more than 2500 fine tuned models over multiple domains, LoLLMs WebUI provides an immediate resource for any problem, from car repair to coding assistance, legal matters, medical diagnosis, entertainment, and more. The easy-to-use UI with light and dark mode options, integration with GitHub repository, support for different personalities, and features like thumb up/down rating, copy, edit, and remove messages, local database storage, search, export, and delete multiple discussions, make LoLLMs WebUI a powerful and versatile tool.
lingo
Lingo is a lightweight ML model proxy that runs on Kubernetes, allowing you to run text-completion and embedding servers without changing OpenAI client code. It supports serving OSS LLMs, is compatible with OpenAI API, plug-and-play with messaging systems, scales from zero based on load, and has zero dependencies. Namespaced with no cluster privileges needed.
OpenDAN-Personal-AI-OS
OpenDAN is an open source Personal AI OS that consolidates various AI modules for personal use. It empowers users to create powerful AI agents like assistants, tutors, and companions. The OS allows agents to collaborate, integrate with services, and control smart devices. OpenDAN offers features like rapid installation, AI agent customization, connectivity via Telegram/Email, building a local knowledge base, distributed AI computing, and more. It aims to simplify life by putting AI in users' hands. The project is in early stages with ongoing development and future plans for user and kernel mode separation, home IoT device control, and an official OpenDAN SDK release.
phosphobot
Phosphobot is a software tool designed to control robots, record data, train and use VLA (vision language action) models. It allows users to control robots using various input methods, train action models with ease, and is compatible with a range of robots and cameras. The tool runs on multiple operating systems and provides a user-friendly API for developers. Users can purchase a starter pack or use supported robots, record datasets, train action models, and control robots using the webapp or Python package. Phosphobot is open source, allowing users to extend its functionality with their own robots and cameras.
langdrive
LangDrive is an open-source AI library that simplifies training, deploying, and querying open-source large language models (LLMs) using private data. It supports data ingestion, fine-tuning, and deployment via a command-line interface, YAML file, or API, with a quick, easy setup. Users can build AI applications such as question/answering systems, chatbots, AI agents, and content generators. The library provides features like data connectors for ingestion, fine-tuning of LLMs, deployment to Hugging Face hub, inference querying, data utilities for CRUD operations, and APIs for model access. LangDrive is designed to streamline the process of working with LLMs and making AI development more accessible.
LlamaPen
LlamaPen is a no-install needed GUI tool for Ollama, featuring a web-based interface accessible on both desktop and mobile. It allows easy setup and configuration, renders markdown, text, and LaTeX math, provides keyboard shortcuts for quick navigation, includes a built-in model and download manager, supports offline and PWA, and is 100% free and open-source. Users can chat with complete privacy as all chats are stored locally in the browser, ensuring near-instant chat load times. The tool also offers an optional cloud service, LlamaPen API, for running up-to-date models if unable to run locally, with a subscription option for increased rate limits and access to more expensive models.
BeamNGpy
BeamNGpy is an official Python library providing an API to interact with BeamNG.tech, a video game focused on academia and industry. It allows remote control of vehicles, AI-controlled vehicles, dynamic sensor models, access to road network and scenario objects, and multiple clients. The library comes with low-level functions and higher-level interfaces for complex actions. BeamNGpy requires BeamNG.tech for usage and offers compatibility information for different versions. It also provides troubleshooting tips and encourages user contributions.
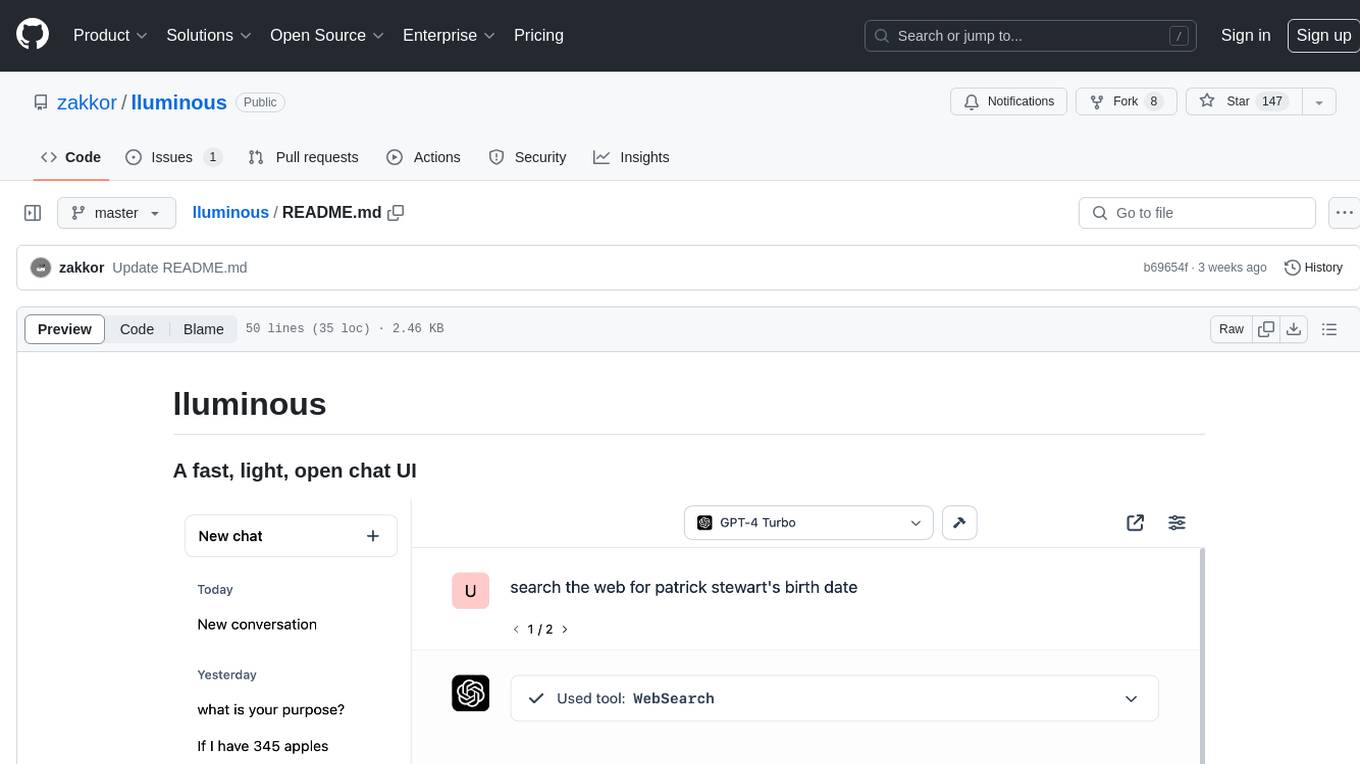
lluminous
lluminous is a fast and light open chat UI that supports multiple providers such as OpenAI, Anthropic, and Groq models. Users can easily plug in their API keys locally to access various models for tasks like multimodal input, image generation, multi-shot prompting, pre-filled responses, and more. The tool ensures privacy by storing all conversation history and keys locally on the user's device. Coming soon features include memory tool, file ingestion/embedding, embeddings-based web search, and prompt templates.
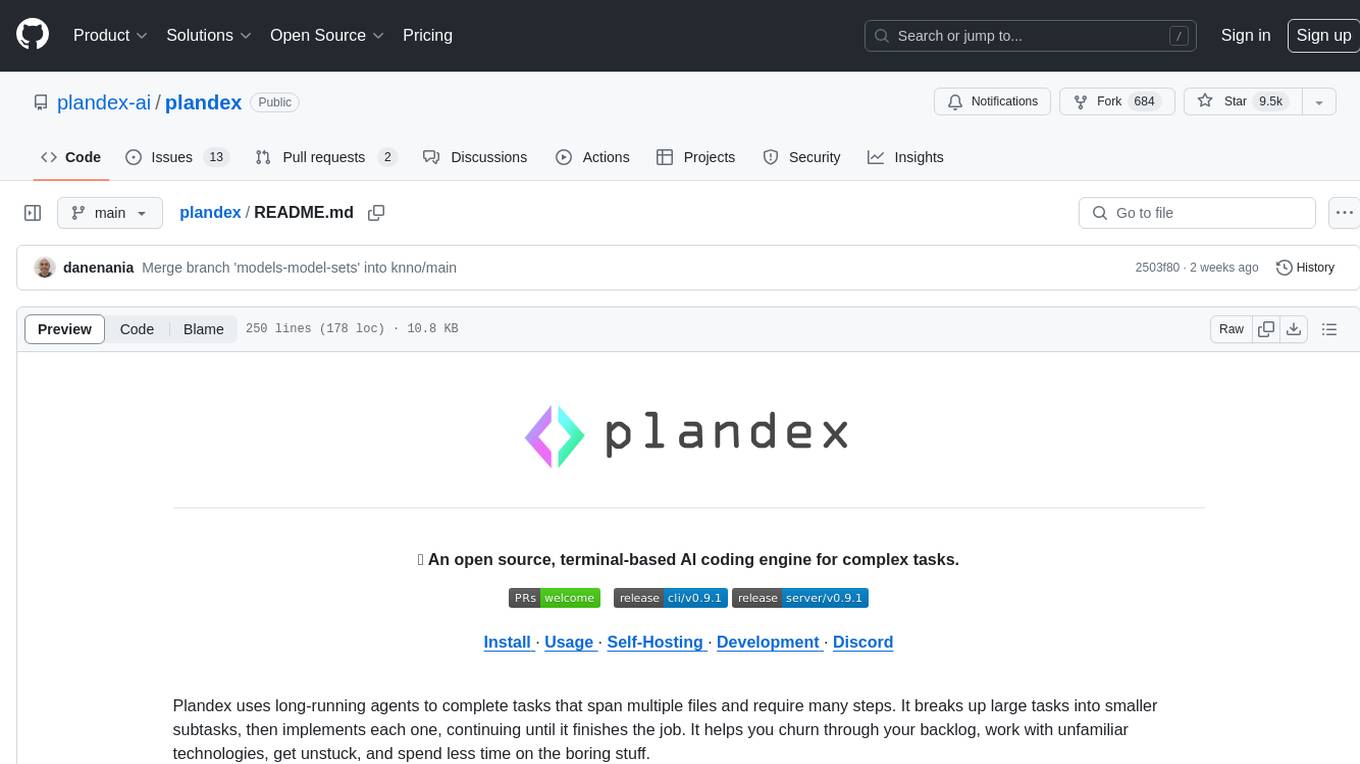
plandex
Plandex is an open source, terminal-based AI coding engine designed for complex tasks. It uses long-running agents to break up large tasks into smaller subtasks, helping users work through backlogs, navigate unfamiliar technologies, and save time on repetitive tasks. Plandex supports various AI models, including OpenAI, Anthropic Claude, Google Gemini, and more. It allows users to manage context efficiently in the terminal, experiment with different approaches using branches, and review changes before applying them. The tool is platform-independent and runs from a single binary with no dependencies.
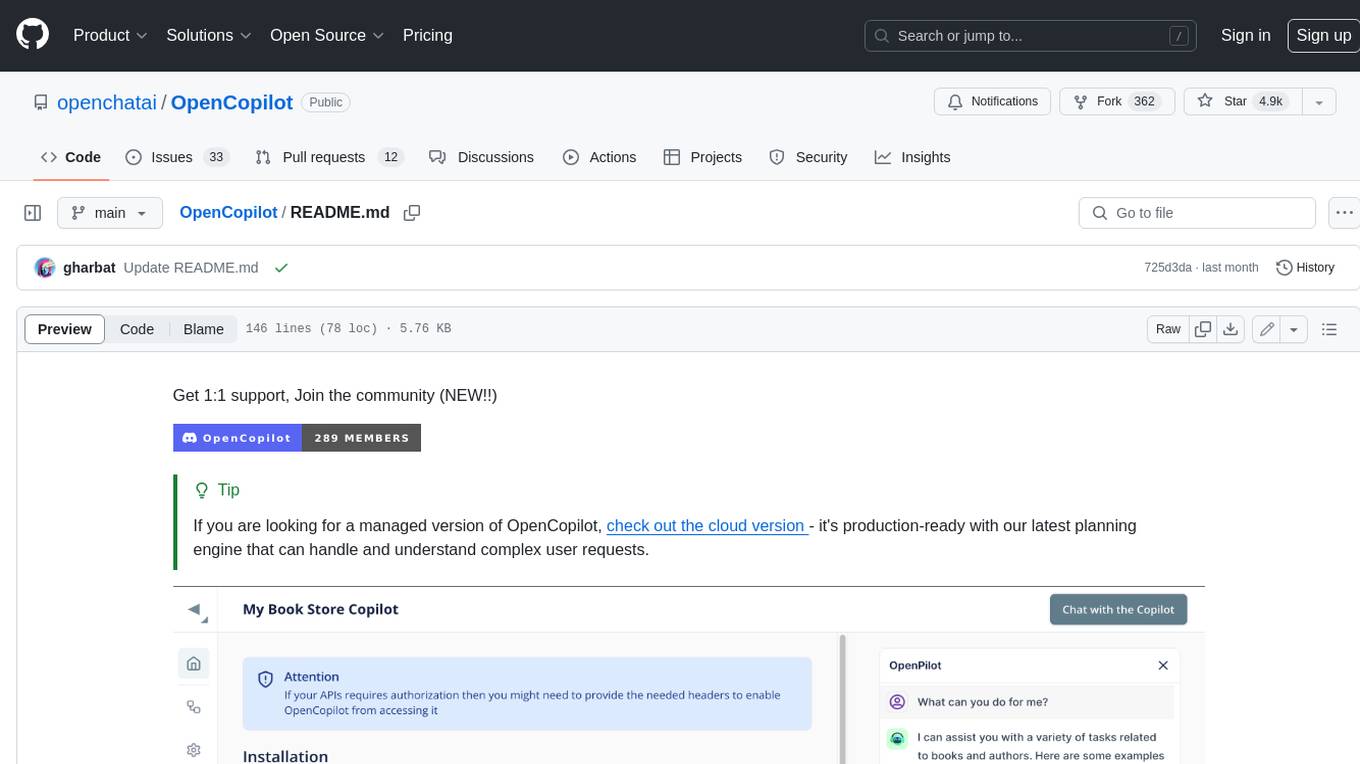
OpenCopilot
OpenCopilot allows you to have your own product's AI copilot. It integrates with your underlying APIs and can execute API calls whenever needed. It uses LLMs to determine if the user's request requires calling an API endpoint. Then, it decides which endpoint to call and passes the appropriate payload based on the given API definition.
For similar tasks
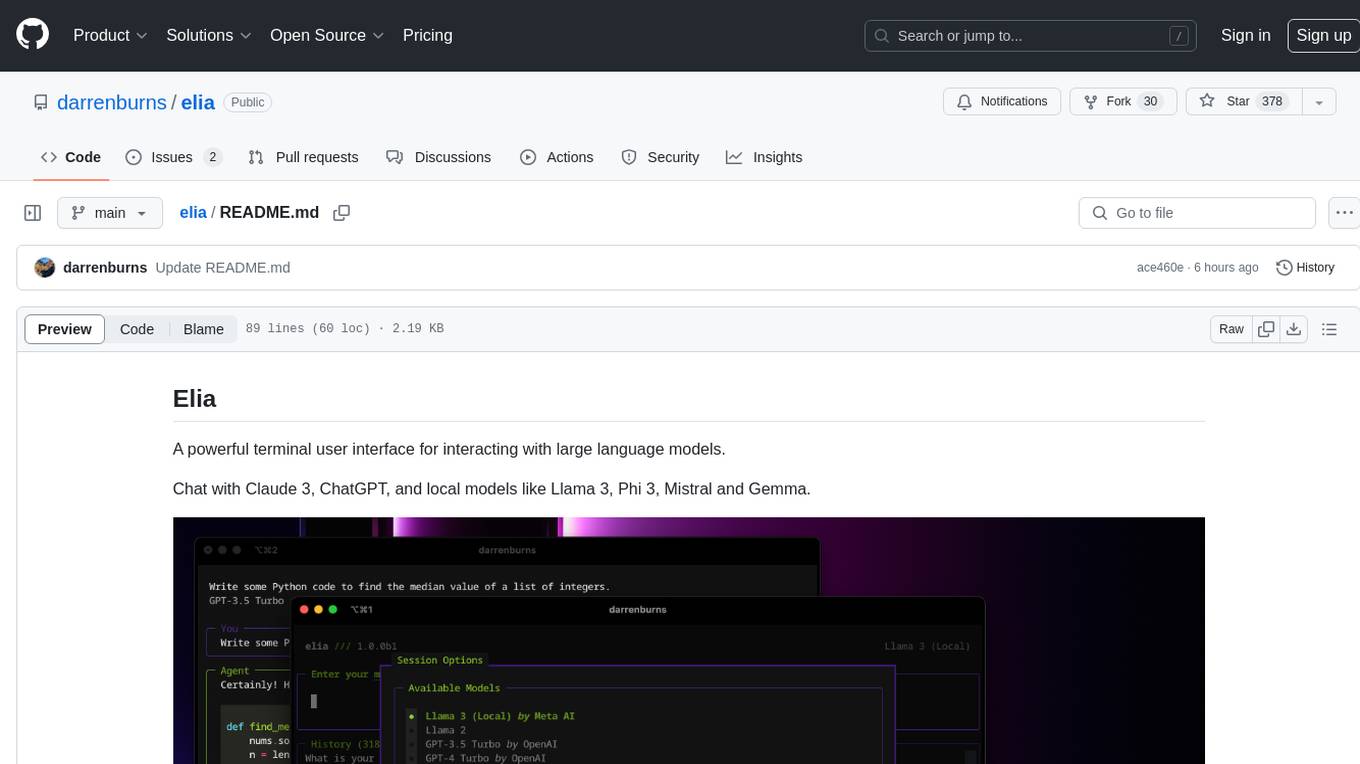
elia
Elia is a powerful terminal user interface designed for interacting with large language models. It allows users to chat with models like Claude 3, ChatGPT, Llama 3, Phi 3, Mistral, and Gemma. Conversations are stored locally in a SQLite database, ensuring privacy. Users can run local models through 'ollama' without data leaving their machine. Elia offers easy installation with pipx and supports various environment variables for different models. It provides a quick start to launch chats and manage local models. Configuration options are available to customize default models, system prompts, and add new models. Users can import conversations from ChatGPT and wipe the database when needed. Elia aims to enhance user experience in interacting with language models through a user-friendly interface.
mistral-inference
Mistral Inference repository contains minimal code to run 7B, 8x7B, and 8x22B models. It provides model download links, installation instructions, and usage guidelines for running models via CLI or Python. The repository also includes information on guardrailing, model platforms, deployment, and references. Users can interact with models through commands like mistral-demo, mistral-chat, and mistral-common. Mistral AI models support function calling and chat interactions for tasks like testing models, chatting with models, and using Codestral as a coding assistant. The repository offers detailed documentation and links to blogs for further information.
LLMFlex
LLMFlex is a python package designed for developing AI applications with local Large Language Models (LLMs). It provides classes to load LLM models, embedding models, and vector databases to create AI-powered solutions with prompt engineering and RAG techniques. The package supports multiple LLMs with different generation configurations, embedding toolkits, vector databases, chat memories, prompt templates, custom tools, and a chatbot frontend interface. Users can easily create LLMs, load embeddings toolkit, use tools, chat with models in a Streamlit web app, and serve an OpenAI API with a GGUF model. LLMFlex aims to offer a simple interface for developers to work with LLMs and build private AI solutions using local resources.
minimal-chat
MinimalChat is a minimal and lightweight open-source chat application with full mobile PWA support that allows users to interact with various language models, including GPT-4 Omni, Claude Opus, and various Local/Custom Model Endpoints. It focuses on simplicity in setup and usage while being fully featured and highly responsive. The application supports features like fully voiced conversational interactions, multiple language models, markdown support, code syntax highlighting, DALL-E 3 integration, conversation importing/exporting, and responsive layout for mobile use.
chat-with-mlx
Chat with MLX is an all-in-one Chat Playground using Apple MLX on Apple Silicon Macs. It provides privacy-enhanced AI for secure conversations with various models, easy integration of HuggingFace and MLX Compatible Open-Source Models, and comes with default models like Llama-3, Phi-3, Yi, Qwen, Mistral, Codestral, Mixtral, StableLM. The tool is designed for developers and researchers working with machine learning models on Apple Silicon.
transformerlab-app
Transformer Lab is an app that allows users to experiment with Large Language Models by providing features such as one-click download of popular models, finetuning across different hardware, RLHF and Preference Optimization, working with LLMs across different operating systems, chatting with models, using different inference engines, evaluating models, building datasets for training, calculating embeddings, providing a full REST API, running in the cloud, converting models across platforms, supporting plugins, embedded Monaco code editor, prompt editing, inference logs, all through a simple cross-platform GUI.
ell
ell is a command-line interface for Language Model Models (LLMs) written in Bash. It allows users to interact with LLMs from the terminal, supports piping, context bringing, and chatting with LLMs. Users can also call functions and use templates. The tool requires bash, jq for JSON parsing, curl for HTTPS requests, and perl for PCRE. Configuration involves setting variables for different LLM models and APIs. Usage examples include asking questions, specifying models, recording input/output, running in interactive mode, and using templates. The tool is lightweight, easy to install, and pipe-friendly, making it suitable for interacting with LLMs in a terminal environment.
Ollama-SwiftUI
Ollama-SwiftUI is a user-friendly interface for Ollama.ai created in Swift. It allows seamless chatting with local Large Language Models on Mac. Users can change models mid-conversation, restart conversations, send system prompts, and use multimodal models with image + text. The app supports managing models, including downloading, deleting, and duplicating them. It offers light and dark mode, multiple conversation tabs, and a localized interface in English and Arabic.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.

