
code2prompt
A CLI tool to convert your codebase into a single LLM prompt with source tree, prompt templating, and token counting.
Stars: 6560
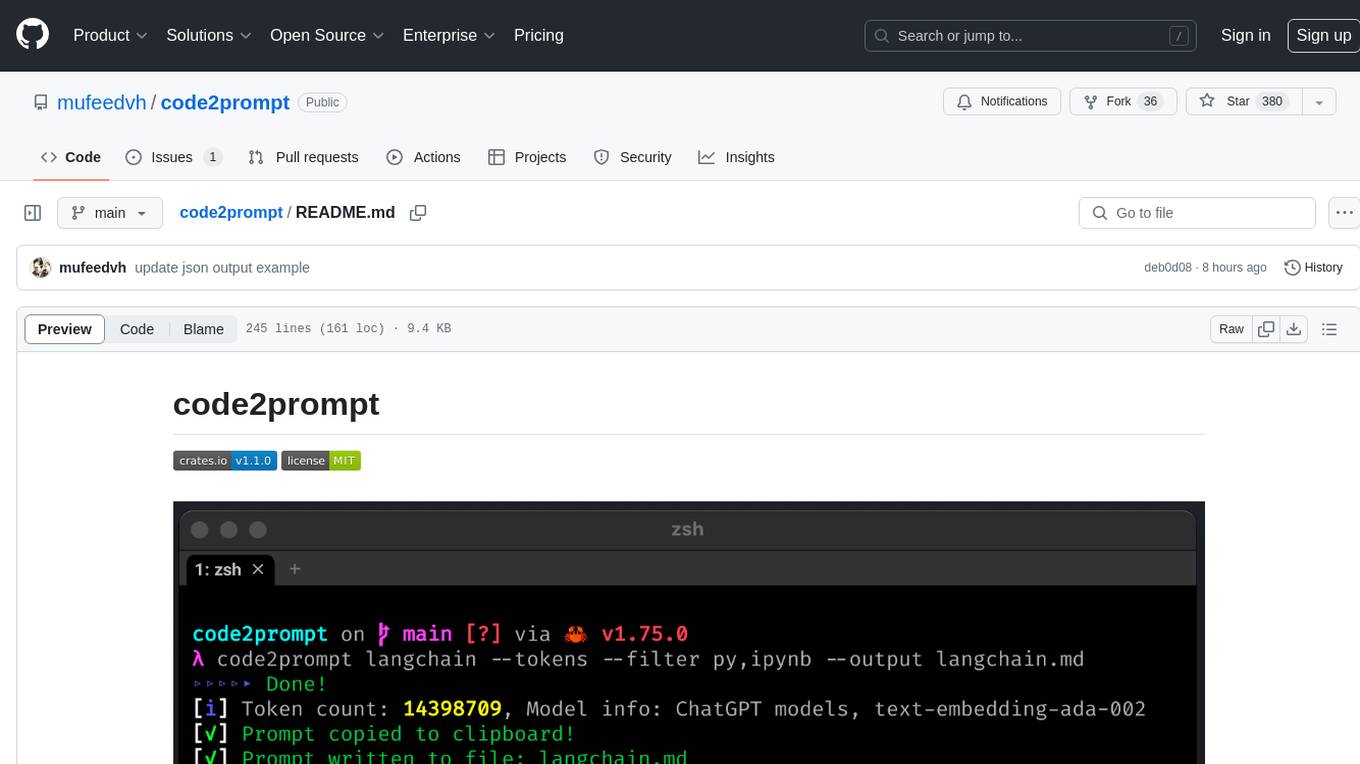
code2prompt is a command-line tool that converts your codebase into a single LLM prompt with a source tree, prompt templating, and token counting. It automates generating LLM prompts from codebases of any size, customizing prompt generation with Handlebars templates, respecting .gitignore, filtering and excluding files using glob patterns, displaying token count, including Git diff output, copying prompt to clipboard, saving prompt to an output file, excluding files and folders, adding line numbers to source code blocks, and more. It helps streamline the process of creating LLM prompts for code analysis, generation, and other tasks.
README:
Want to engage with us ? Join our Discord channel!
Stay updated on new features 📢
Give your insight and suggestion 💬
Get help with configuration and usage 🛠️
Report Bug 🐛
cargo install code2prompt To enable optional Wayland support (e.g., for clipboard integration on Wayland-based systems), use the wayland feature flag:
cargo install --features wayland code2promptbrew install code2promptpip install code2prompt-rsCore
code2prompt is a code ingestion tool that streamline the process of creating LLM prompts for code analysis, generation, and other tasks. It works by traversing directories, building a tree structure, and gathering informations about each file. The core library can easily be integrated into other applications.
CLI
code2prompt command line interface (CLI) was designed for humans to generate prompts directly from your codebase. The generated prompt is automatically copied to your clipboard and can also be saved to an output file. Furthermore, you can customize the prompt generation using Handlebars templates. Check out the provided prompts in the doc !
SDK
code2prompt software development kit (SDK) offers python binding to the core library. This is perfect for AI agents or automation scripts that want to interact with codebase seamlessly. The SDK is hosted on Pypi and can be installed via pip.
MCP
code2prompt is also available as a Model Context Protocol (MCP) server, which allows you to run it as a local service. This enables LLMs on steroids by providing them a tool to automatically gather a well-structured context of your codebase.
Check our online documentation for detailed instructions
Code2Prompt transforms your entire codebase into a well-structured prompt for large language models. Key features include:
- Automatic Code Processing: Convert codebases of any size into readable, formatted prompts
-
Smart Filtering: Include/exclude files using glob patterns and respect
.gitignorerules - Flexible Templating: Customize prompts with Handlebars templates for different use cases
- Token Tracking: Track token usage to stay within LLM context limits
- Git Integration: Include diffs, logs, and branch comparisons in your prompts
- Developer Experience: Automatic clipboard copy, line numbers, and file organization options
Stop manually copying files and formatting code for LLMs. Code2Prompt handles the tedious work so you can focus on getting insights and solutions from AI models.
Refer to the documentation for detailed installation instructions.
Download the latest binary for your OS from Releases.
Requires:
git clone https://github.com/mufeedvh/code2prompt.git
cd code2prompt/
cargo install --path crates/code2promptLicensed under the MIT License, see LICENSE for more information.
If you liked the project and found it useful, please give it a ⭐ !
Ways to contribute:
- Suggest a feature
- Report a bug
- Fix something and open a pull request
- Help me document the code
- Spread the word
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for code2prompt
Similar Open Source Tools

code2prompt
code2prompt is a command-line tool that converts your codebase into a single LLM prompt with a source tree, prompt templating, and token counting. It automates generating LLM prompts from codebases of any size, customizing prompt generation with Handlebars templates, respecting .gitignore, filtering and excluding files using glob patterns, displaying token count, including Git diff output, copying prompt to clipboard, saving prompt to an output file, excluding files and folders, adding line numbers to source code blocks, and more. It helps streamline the process of creating LLM prompts for code analysis, generation, and other tasks.
langmanus
LangManus is a community-driven AI automation framework that combines language models with specialized tools for tasks like web search, crawling, and Python code execution. It implements a hierarchical multi-agent system with agents like Coordinator, Planner, Supervisor, Researcher, Coder, Browser, and Reporter. The framework supports LLM integration, search and retrieval tools, Python integration, workflow management, and visualization. LangManus aims to give back to the open-source community and welcomes contributions in various forms.

swark
Swark is a VS Code extension that automatically generates architecture diagrams from code using large language models (LLMs). It is directly integrated with GitHub Copilot, requires no authentication or API key, and supports all languages. Swark helps users learn new codebases, review AI-generated code, improve documentation, understand legacy code, spot design flaws, and gain test coverage insights. It saves output in a 'swark-output' folder with diagram and log files. Source code is only shared with GitHub Copilot for privacy. The extension settings allow customization for file reading, file extensions, exclusion patterns, and language model selection. Swark is open source under the GNU Affero General Public License v3.0.
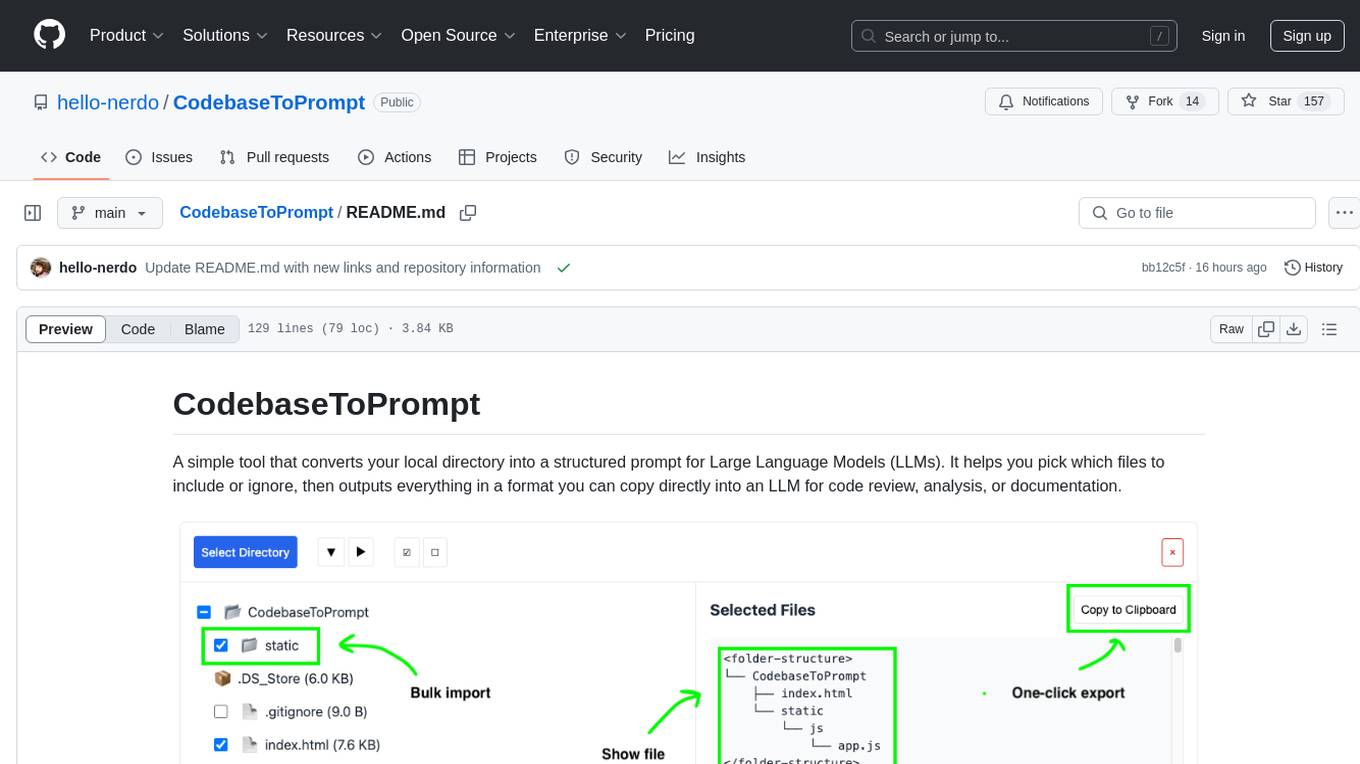
CodebaseToPrompt
CodebaseToPrompt is a tool that converts a local directory into a structured prompt for Large Language Models (LLMs). It allows users to select specific files for code review, analysis, or documentation by exploring and filtering through the file tree in an interactive interface. The tool generates a formatted output that can be directly used with LLMs, estimates token count, and supports flexible text selection. Users can deploy the tool using Docker for self-contained usage and can contribute to the project by opening issues or submitting pull requests.

CodebaseToPrompt
CodebaseToPrompt is a simple tool that converts a local directory into a structured prompt for Large Language Models (LLMs). It allows users to select specific files for code review, analysis, or documentation by exploring and filtering through the file tree in a browser-based interface. The tool generates a formatted output that can be directly used with AI tools, provides token count estimates, and supports local storage for saving selections. Users can easily copy the selected files in the desired format for further use.
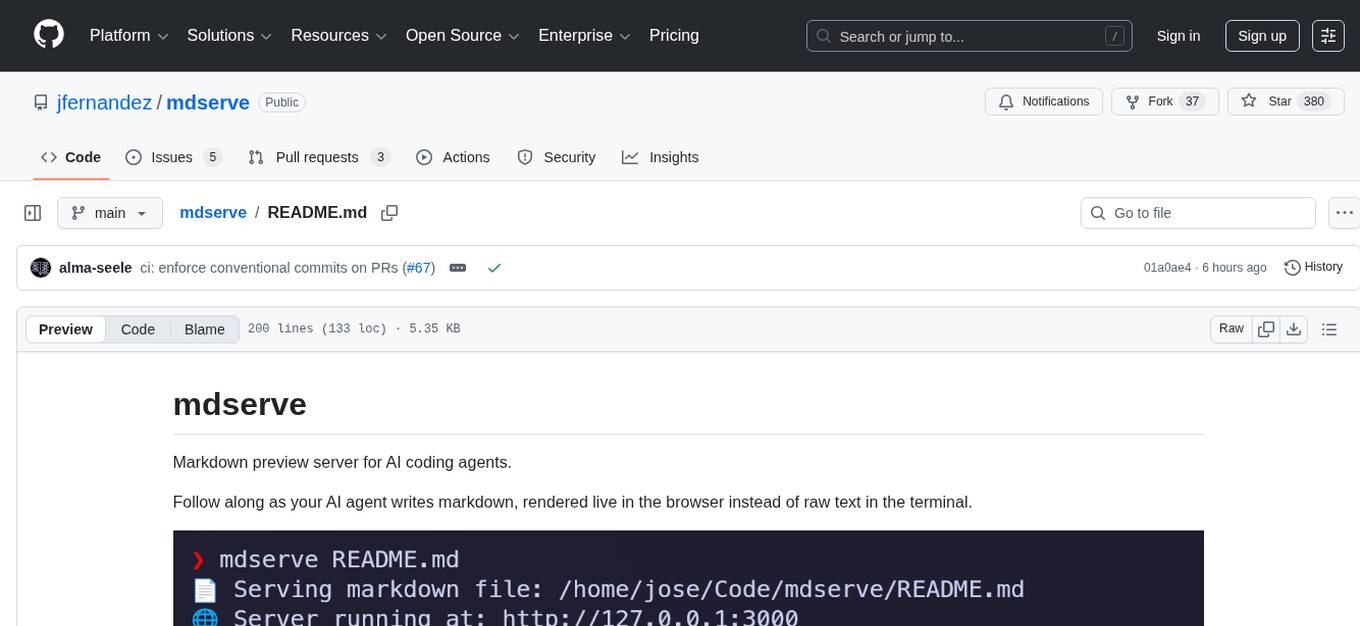
mdserve
Markdown preview server for AI coding agents. mdserve is a tool that allows AI agents to write markdown and see it rendered live in the browser. It features zero configuration, single binary installation, instant live reload via WebSocket, ephemeral sessions, and agent-friendly content support. It is not a documentation site generator, static site server, or general-purpose markdown authoring tool. mdserve is designed for AI coding agents to produce content like tables, diagrams, and code blocks.
panda-etl
PandaETL is an open-source, no-code ETL tool designed to extract and parse data from various document types including PDFs, emails, websites, audio files, and more. With an intuitive interface and powerful backend, PandaETL simplifies the process of data extraction and transformation, making it accessible to users without programming skills.

gptme
GPTMe is a tool that allows users to interact with an LLM assistant directly in their terminal in a chat-style interface. The tool provides features for the assistant to run shell commands, execute code, read/write files, and more, making it suitable for various development and terminal-based tasks. It serves as a local alternative to ChatGPT's 'Code Interpreter,' offering flexibility and privacy when using a local model. GPTMe supports code execution, file manipulation, context passing, self-correction, and works with various AI models like GPT-4. It also includes a GitHub Bot for requesting changes and operates entirely in GitHub Actions. In progress features include handling long contexts intelligently, a web UI and API for conversations, web and desktop vision, and a tree-based conversation structure.
AgentPilot
Agent Pilot is an open source desktop app for creating, managing, and chatting with AI agents. It features multi-agent, branching chats with various providers through LiteLLM. Users can combine models from different providers, configure interactions, and run code using the built-in Open Interpreter. The tool allows users to create agents, manage chats, work with multi-agent workflows, branching workflows, context blocks, tools, and plugins. It also supports a code interpreter, scheduler, voice integration, and integration with various AI providers. Contributions to the project are welcome, and users can report known issues for improvement.

cline-based-code-generator
HAI Code Generator is a cutting-edge tool designed to simplify and automate task execution while enhancing code generation workflows. Leveraging Specif AI, it streamlines processes like task execution, file identification, and code documentation through intelligent automation and AI-driven capabilities. Built on Cline's powerful foundation for AI-assisted development, HAI Code Generator boosts productivity and precision by automating task execution and integrating file management capabilities. It combines intelligent file indexing, context generation, and LLM-driven automation to minimize manual effort and ensure task accuracy. Perfect for developers and teams aiming to enhance their workflows.
AiTextDetectionBypass
ParaGenie is a script designed to automate the process of paraphrasing articles using the undetectable.ai platform. It allows users to convert lengthy content into unique paraphrased versions by splitting the input text into manageable chunks and processing each chunk individually. The script offers features such as automated paraphrasing, multi-file support for TXT, DOCX, and PDF formats, customizable chunk splitting methods, Gmail-based registration for seamless paraphrasing, purpose-specific writing support, readability level customization, anonymity features for user privacy, error handling and recovery, and output management for easy access and organization of paraphrased content.
PyWxDump
PyWxDump is a powerful tool designed to help extract and manage WeChat data efficiently. It allows users to read local databases, view chat histories, and export data in various formats such as CSV and HTML. With features like multi-account support, version compatibility, data export, AI training, and automated responses, PyWxDump offers flexibility for training AI models and developing automated replies.
CodeGPT
CodeGPT is an extension for JetBrains IDEs that provides access to state-of-the-art large language models (LLMs) for coding assistance. It offers a range of features to enhance the coding experience, including code completions, a ChatGPT-like interface for instant coding advice, commit message generation, reference file support, name suggestions, and offline development support. CodeGPT is designed to keep privacy in mind, ensuring that user data remains secure and private.

UltraRAG
The UltraRAG framework is a researcher and developer-friendly RAG system solution that simplifies the process from data construction to model fine-tuning in domain adaptation. It introduces an automated knowledge adaptation technology system, supporting no-code programming, one-click synthesis and fine-tuning, multidimensional evaluation, and research-friendly exploration work integration. The architecture consists of Frontend, Service, and Backend components, offering flexibility in customization and optimization. Performance evaluation in the legal field shows improved results compared to VanillaRAG, with specific metrics provided. The repository is licensed under Apache-2.0 and encourages citation for support.

mattermost-plugin-agents
The Mattermost Agents Plugin integrates AI capabilities directly into your Mattermost workspace, allowing users to run local LLMs on their infrastructure or connect to cloud providers. It offers multiple AI assistants with specialized personalities, thread and channel summarization, action item extraction, meeting transcription, semantic search, smart reactions, direct conversations with AI assistants, and flexible LLM support. The plugin comes with comprehensive documentation, installation instructions, system requirements, and development guidelines for users to interact with AI features and configure LLM providers.
aisdk-prompt-optimizer
AISDK Prompt Optimizer is an open-source tool designed to transform AI interactions by optimizing prompts. It utilizes the GEPA reflective optimizer to evolve textual components of AI systems, providing features such as reflective prompt mutation, rich textual feedback, and Pareto-based selection. Users can teach their AI desired behaviors, collect ideal samples, run optimization to generate optimized prompts, and deploy the results in their applications. The tool leverages advanced optimization algorithms to guide AI through interactive conversations and refine prompt candidates for improved performance.
For similar tasks
cody
Cody is a free, open-source AI coding assistant that can write and fix code, provide AI-generated autocomplete, and answer your coding questions. Cody fetches relevant code context from across your entire codebase to write better code that uses more of your codebase's APIs, impls, and idioms, with less hallucination.
auto-dev-vscode
AutoDev for VSCode is an AI-powered coding wizard with multilingual support, auto code generation, and a bug-slaying assistant. It offers customizable prompts and features like Auto Dev/Testing/Document/Agent. The tool aims to enhance coding productivity and efficiency by providing intelligent assistance and automation capabilities within the Visual Studio Code environment.
bia-bob
BIA `bob` is a Jupyter-based assistant for interacting with data using large language models to generate Python code. It can utilize OpenAI's chatGPT, Google's Gemini, Helmholtz' blablador, and Ollama. Users need respective accounts to access these services. Bob can assist in code generation, bug fixing, code documentation, GPU-acceleration, and offers a no-code custom Jupyter Kernel. It provides example notebooks for various tasks like bio-image analysis, model selection, and bug fixing. Installation is recommended via conda/mamba environment. Custom endpoints like blablador and ollama can be used. Google Cloud AI API integration is also supported. The tool is extensible for Python libraries to enhance Bob's functionality.

code2prompt
code2prompt is a command-line tool that converts your codebase into a single LLM prompt with a source tree, prompt templating, and token counting. It automates generating LLM prompts from codebases of any size, customizing prompt generation with Handlebars templates, respecting .gitignore, filtering and excluding files using glob patterns, displaying token count, including Git diff output, copying prompt to clipboard, saving prompt to an output file, excluding files and folders, adding line numbers to source code blocks, and more. It helps streamline the process of creating LLM prompts for code analysis, generation, and other tasks.
fittencode.nvim
Fitten Code AI Programming Assistant for Neovim provides fast completion using AI, asynchronous I/O, and support for various actions like document code, edit code, explain code, find bugs, generate unit test, implement features, optimize code, refactor code, start chat, and more. It offers features like accepting suggestions with Tab, accepting line with Ctrl + Down, accepting word with Ctrl + Right, undoing accepted text, automatic scrolling, and multiple HTTP/REST backends. It can run as a coc.nvim source or nvim-cmp source.
chatgpt
The ChatGPT R package provides a set of features to assist in R coding. It includes addins like Ask ChatGPT, Comment selected code, Complete selected code, Create unit tests, Create variable name, Document code, Explain selected code, Find issues in the selected code, Optimize selected code, and Refactor selected code. Users can interact with ChatGPT to get code suggestions, explanations, and optimizations. The package helps in improving coding efficiency and quality by providing AI-powered assistance within the RStudio environment.
VimLM
VimLM is an AI-powered coding assistant for Vim that integrates AI for code generation, refactoring, and documentation directly into your Vim workflow. It offers native Vim integration with split-window responses and intuitive keybindings, offline first execution with MLX-compatible models, contextual awareness with seamless integration with codebase and external resources, conversational workflow for iterating on responses, project scaffolding for generating and deploying code blocks, and extensibility for creating custom LLM workflows with command chains.
jupyter-mcp-server
Jupyter MCP Server is a Model Context Protocol (MCP) server implementation that enables real-time interaction with Jupyter Notebooks. It allows AI to edit, document, and execute code for data analysis and visualization. The server offers features like real-time control, smart execution, and MCP compatibility. Users can use tools such as insert_execute_code_cell, append_markdown_cell, get_notebook_info, and read_cell for advanced interactions with Jupyter notebooks.
For similar jobs

sourcegraph
Sourcegraph is a code search and navigation tool that helps developers read, write, and fix code in large, complex codebases. It provides features such as code search across all repositories and branches, code intelligence for navigation and refactoring, and the ability to fix and refactor code across multiple repositories at once.
pr-agent
PR-Agent is a tool that helps to efficiently review and handle pull requests by providing AI feedbacks and suggestions. It supports various commands such as generating PR descriptions, providing code suggestions, answering questions about the PR, and updating the CHANGELOG.md file. PR-Agent can be used via CLI, GitHub Action, GitHub App, Docker, and supports multiple git providers and models. It emphasizes real-life practical usage, with each tool having a single GPT-4 call for quick and affordable responses. The PR Compression strategy enables effective handling of both short and long PRs, while the JSON prompting strategy allows for modular and customizable tools. PR-Agent Pro, the hosted version by CodiumAI, provides additional benefits such as full management, improved privacy, priority support, and extra features.
code-review-gpt
Code Review GPT uses Large Language Models to review code in your CI/CD pipeline. It helps streamline the code review process by providing feedback on code that may have issues or areas for improvement. It should pick up on common issues such as exposed secrets, slow or inefficient code, and unreadable code. It can also be run locally in your command line to review staged files. Code Review GPT is in alpha and should be used for fun only. It may provide useful feedback but please check any suggestions thoroughly.
DevoxxGenieIDEAPlugin
Devoxx Genie is a Java-based IntelliJ IDEA plugin that integrates with local and cloud-based LLM providers to aid in reviewing, testing, and explaining project code. It supports features like code highlighting, chat conversations, and adding files/code snippets to context. Users can modify REST endpoints and LLM parameters in settings, including support for cloud-based LLMs. The plugin requires IntelliJ version 2023.3.4 and JDK 17. Building and publishing the plugin is done using Gradle tasks. Users can select an LLM provider, choose code, and use commands like review, explain, or generate unit tests for code analysis.

code2prompt
code2prompt is a command-line tool that converts your codebase into a single LLM prompt with a source tree, prompt templating, and token counting. It automates generating LLM prompts from codebases of any size, customizing prompt generation with Handlebars templates, respecting .gitignore, filtering and excluding files using glob patterns, displaying token count, including Git diff output, copying prompt to clipboard, saving prompt to an output file, excluding files and folders, adding line numbers to source code blocks, and more. It helps streamline the process of creating LLM prompts for code analysis, generation, and other tasks.
ai-codereviewer
AI Code Reviewer is a GitHub Action that utilizes OpenAI's GPT-4 API to provide intelligent feedback and suggestions on pull requests. It helps enhance code quality and streamline the code review process by offering insightful comments and filtering out specified files. The tool is easy to set up and integrate into GitHub workflows.
github-pr-summary
github-pr-summary is a bot designed to summarize GitHub Pull Requests, helping open source contributors make faster decisions. It automatically summarizes commits and changed files in PRs, triggered by new commits or a magic trigger phrase. Users can deploy their own code review bot in 3 steps: create a bot from their GitHub repo, configure it to review PRs, and connect to GitHub for access to the target repo. The bot runs on flows.network using Rust and WasmEdge Runtimes. It utilizes ChatGPT/4 to review and summarize PR content, posting the result back as a comment on the PR. The bot can be used on multiple repos by creating new flows and importing the source code repo, specifying the target repo using flow config. Users can also change the magic phrase to trigger a review from a PR comment.

fittencode.nvim
Fitten Code AI Programming Assistant for Neovim provides fast completion using AI, asynchronous I/O, and support for various actions like document code, edit code, explain code, find bugs, generate unit test, implement features, optimize code, refactor code, start chat, and more. It offers features like accepting suggestions with Tab, accepting line with Ctrl + Down, accepting word with Ctrl + Right, undoing accepted text, automatic scrolling, and multiple HTTP/REST backends. It can run as a coc.nvim source or nvim-cmp source.




