aiid
The AI Incident Database seeks to identify, define, and catalog artificial intelligence incidents.
Stars: 183
The Artificial Intelligence Incident Database (AIID) is a collection of incidents involving the development and use of artificial intelligence (AI). The database is designed to help researchers, policymakers, and the public understand the potential risks and benefits of AI, and to inform the development of policies and practices to mitigate the risks and promote the benefits of AI. The AIID is a collaborative project involving researchers from the University of California, Berkeley, the University of Washington, and the University of Toronto.
README:
Information about the goals and organization of the AI Incident Database can be found on the production website. This page concentrates on onboarding for the following types of contributions to the database,
- Contribute changes to the current AI Incident Database.
- Contribute a new summary to the AI Incident Database. A "summary" is a programmatically generated summary of the database contents. Examples are available here.
- Contribute a new taxonomy to the AI Incident Database. Details on taxonomies are available in the arXiv paper.
- Contribute a new application facilitating a new use case for the database.
In most cases unless you are contributing quick fixes, we recommend opening an issue before contributing to the project. You can also Contact us for an invitation to the project's Slack installation. Lurking is encouraged. Finally, for major announcements you can join the announcements-only mailing list.
The AI Incident Database is an open source project inviting contributions from the global community. Anyone with code changes that advance the change thesis of making the world better in the future by remembering the negative outcomes of the past are welcome to submit pull requests. To ensure that submitted changes are likely to be accepted, we recommend becoming familiar with the manner in which we organize our work items and open an issue on GitHub.
The process of completing work through GitHub issues at the highest level is:
Create Issue -> Assign Issue -> Review and Publish
Labels help streamline the process and ensure issues do not get lost or neglected. Label descriptions are on GitHub. The following describes when/how to use a label.
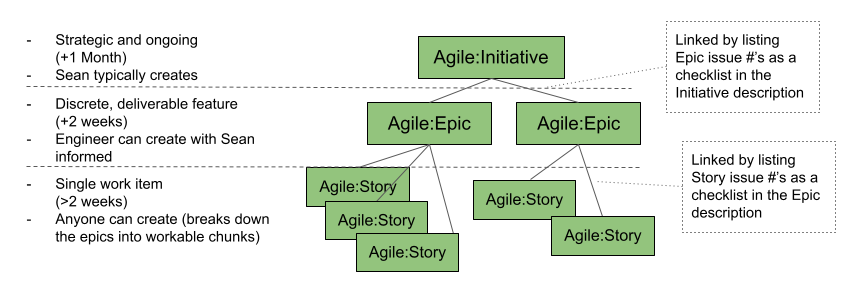
- Consider if the issue is an Initiative, Epic, or Story. All engineering issues aside from Bugs should fall in one of these categories and be assigned a label. Other types of issues (ex: Data Editor-related) may not have this label.
- Apply a descriptor label (when applicable):
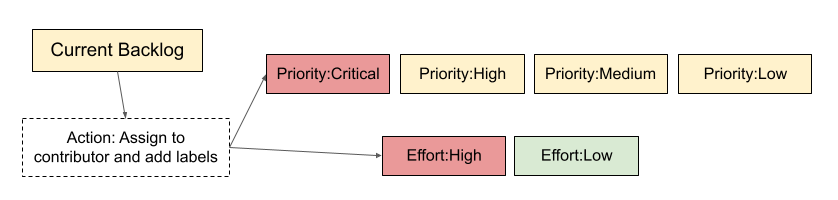
Add the label Current Backlog to trigger assigning a contributor. Either the assigner or the contributor adds the issue’s priority and effort labels.
Once the issue has a deliverable output(s), use the Pull Request process to have the contribution reviewed and accepted.
The person opening the PR should create it in a draft status until the work is finished, then they should click on "Ready for review" button and assign it to someone as a reviewer as soon the PR is ready to be reviewed.
In general, PR reviews can be assigned to any member of the @responsible-ai-collaboraite/aiid-dev team, or to the team alias itself. Don't be shy! Above all, contributors and reviewers should assume good intentions. As such, reviewers are also encouraged to re-assign PR reviews based on familiarity and time constraints.
When something is mergeable, then someone else with maintainer permissions (not the implementer or reviewer) can merge it to staging. They can optionally do a final review.
After merging to staging, the code quality is everyone’s responsibility.
For more information on how to create built-in draft pull requests, please refer to the GitHub blog.
Anyone can contribute code to the project. The system is being built as a "do-ocracy", meaning those who "do" have influence over the development of the code.
The steps for contributing changes are the following,
- Create a fork of the repository.
- Clone the fork to your local environment.
- Open a feature branch from whichever branch you would like to change. This is typically the
stagingbranch, so you can dogit checkout stagingthengit checkout -b feature-cool-new-thing. - Make your changes, commit them, then push them remote.
- Open a pull request to the
stagingbranch. - Update the pull request based on the review.
- See the pull request get pulled. :)
Please make sure your code is well organized and commented before opening the pull request.
The site architecture consists of these main components:
-
Deployment Pipeline:
- Hosted in a GitHub repository
- Automated through GitHub Actions workflows that handle building, testing, and deploying the application
- Ensures code quality and successful deployment through automated checks
-
Frontend Hosting: A Gatsby-based static web application hosted on Netlify, along with Netlify Functions for serverless API functionality.
-
Search: Algolia provides the search index functionality, enabling fast and efficient content discovery.
-
Content Management: Prismic CMS allows for dynamic content management including blog posts and other updateable content.
-
Database: A MongoDB database stores the core application data. The database content can be synced periodically to update the Algolia search index, allowing for storage of documents and details that may be either unsupported by or too costly to host in Algolia.
Additional services integrated into the architecture include:
- MailerSend for email communication
- Cloudinary for image hosting and optimization
- Rollbar for error logging and monitoring
- Google Translate API for content translation capabilities
This architecture maintains a serverless approach, with no need for a traditional dynamic backend server, while leveraging specialized services for specific functionalities. The deployment process is fully automated through GitHub Actions, ensuring consistent and reliable deployments with proper testing and validation steps.
More details are available on our documentation.
The site exposes a read-only GraphQL endpoint at /api/graphql.
You can check the endpoint https://incidentdatabase.ai/api/graphql
The endpoint can be queried using any GraphQL client, but for example, if using Apollo:
import { ApolloClient, HttpLink, InMemoryCache, gql } from '@apollo/client';
const client = new ApolloClient({
link: new HttpLink({
uri: `https://incidentdatabase.ai/api/graphql`,
}),
cache: new InMemoryCache()
});
client.query({query: gql`{
reports {
title
report_number
}
}`}).then(result => console.log(result));
For inquiries, you are encouraged to open an issue on this repository or visit the contact page.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for aiid
Similar Open Source Tools

aiid
The Artificial Intelligence Incident Database (AIID) is a collection of incidents involving the development and use of artificial intelligence (AI). The database is designed to help researchers, policymakers, and the public understand the potential risks and benefits of AI, and to inform the development of policies and practices to mitigate the risks and promote the benefits of AI. The AIID is a collaborative project involving researchers from the University of California, Berkeley, the University of Washington, and the University of Toronto.

OpenBB
The OpenBB Platform is the first financial platform that is free and fully open source, offering access to equity, options, crypto, forex, macro economy, fixed income, and more. It provides a broad range of extensions to enhance the user experience according to their needs. Users can sign up to the OpenBB Hub to maximize the benefits of the OpenBB ecosystem. Additionally, the platform includes an AI-powered Research and Analytics Workspace for free. There is also an open source AI financial analyst agent available that can access all the data within OpenBB.
LaVague
LaVague is an open-source Large Action Model framework that uses advanced AI techniques to compile natural language instructions into browser automation code. It leverages Selenium or Playwright for browser actions. Users can interact with LaVague through an interactive Gradio interface to automate web interactions. The tool requires an OpenAI API key for default examples and offers a Playwright integration guide. Contributors can help by working on outlined tasks, submitting PRs, and engaging with the community on Discord. The project roadmap is available to track progress, but users should exercise caution when executing LLM-generated code using 'exec'.
hackingBuddyGPT
hackingBuddyGPT is a framework for testing LLM-based agents for security testing. It aims to create common ground truth by creating common security testbeds and benchmarks, evaluating multiple LLMs and techniques against those, and publishing prototypes and findings as open-source/open-access reports. The initial focus is on evaluating the efficiency of LLMs for Linux privilege escalation attacks, but the framework is being expanded to evaluate the use of LLMs for web penetration-testing and web API testing. hackingBuddyGPT is released as open-source to level the playing field for blue teams against APTs that have access to more sophisticated resources.
hi-ml
The Microsoft Health Intelligence Machine Learning Toolbox is a repository that provides low-level and high-level building blocks for Machine Learning / AI researchers and practitioners. It simplifies and streamlines work on deep learning models for healthcare and life sciences by offering tested components such as data loaders, pre-processing tools, deep learning models, and cloud integration utilities. The repository includes two Python packages, 'hi-ml-azure' for helper functions in AzureML, 'hi-ml' for ML components, and 'hi-ml-cpath' for models and workflows related to histopathology images.

project_alice
Alice is an agentic workflow framework that integrates task execution and intelligent chat capabilities. It provides a flexible environment for creating, managing, and deploying AI agents for various purposes, leveraging a microservices architecture with MongoDB for data persistence. The framework consists of components like APIs, agents, tasks, and chats that interact to produce outputs through files, messages, task results, and URL references. Users can create, test, and deploy agentic solutions in a human-language framework, making it easy to engage with by both users and agents. The tool offers an open-source option, user management, flexible model deployment, and programmatic access to tasks and chats.
ersilia
The Ersilia Model Hub is a unified platform of pre-trained AI/ML models dedicated to infectious and neglected disease research. It offers an open-source, low-code solution that provides seamless access to AI/ML models for drug discovery. Models housed in the hub come from two sources: published models from literature (with due third-party acknowledgment) and custom models developed by the Ersilia team or contributors.
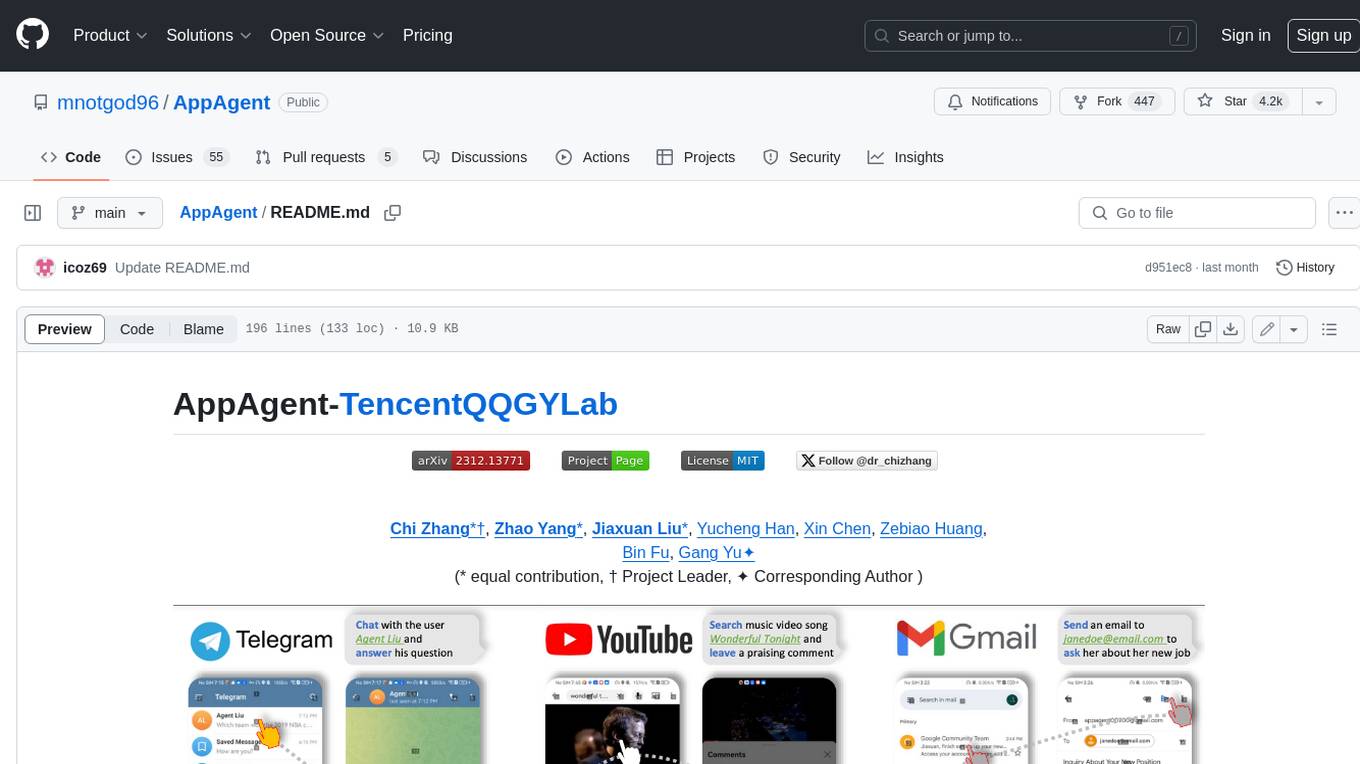
AppAgent
AppAgent is a novel LLM-based multimodal agent framework designed to operate smartphone applications. Our framework enables the agent to operate smartphone applications through a simplified action space, mimicking human-like interactions such as tapping and swiping. This novel approach bypasses the need for system back-end access, thereby broadening its applicability across diverse apps. Central to our agent's functionality is its innovative learning method. The agent learns to navigate and use new apps either through autonomous exploration or by observing human demonstrations. This process generates a knowledge base that the agent refers to for executing complex tasks across different applications.

promptflow
**Prompt flow** is a suite of development tools designed to streamline the end-to-end development cycle of LLM-based AI applications, from ideation, prototyping, testing, evaluation to production deployment and monitoring. It makes prompt engineering much easier and enables you to build LLM apps with production quality.

sdk
Vikit.ai SDK is a software development kit that enables easy development of video generators using generative AI and other AI models. It serves as a langchain to orchestrate AI models and video editing tools. The SDK allows users to create videos from text prompts with background music and voice-over narration. It also supports generating composite videos from multiple text prompts. The tool requires Python 3.8+, specific dependencies, and tools like FFMPEG and ImageMagick for certain functionalities. Users can contribute to the project by following the contribution guidelines and standards provided.

HackBot
HackBot is an AI-powered cybersecurity chatbot designed to provide accurate answers to cybersecurity-related queries, conduct code analysis, and scan analysis. It utilizes the Meta-LLama2 AI model through the 'LlamaCpp' library to respond coherently. The chatbot offers features like local AI/Runpod deployment support, cybersecurity chat assistance, interactive interface, clear output presentation, static code analysis, and vulnerability analysis. Users can interact with HackBot through a command-line interface and utilize it for various cybersecurity tasks.
tribe
Tribe AI is a low code tool designed to rapidly build and coordinate multi-agent teams. It leverages the langgraph framework to customize and coordinate teams of agents, allowing tasks to be split among agents with different strengths for faster and better problem-solving. The tool supports persistent conversations, observability, tool calling, human-in-the-loop functionality, easy deployment with Docker, and multi-tenancy for managing multiple users and teams.
Customer-Service-Conversational-Insights-with-Azure-OpenAI-Services
This solution accelerator is built on Azure Cognitive Search Service and Azure OpenAI Service to synthesize post-contact center transcripts for intelligent contact center scenarios. It converts raw transcripts into customer call summaries to extract insights around product and service performance. Key features include conversation summarization, key phrase extraction, speech-to-text transcription, sensitive information extraction, sentiment analysis, and opinion mining. The tool enables data professionals to quickly analyze call logs for improvement in contact center operations.
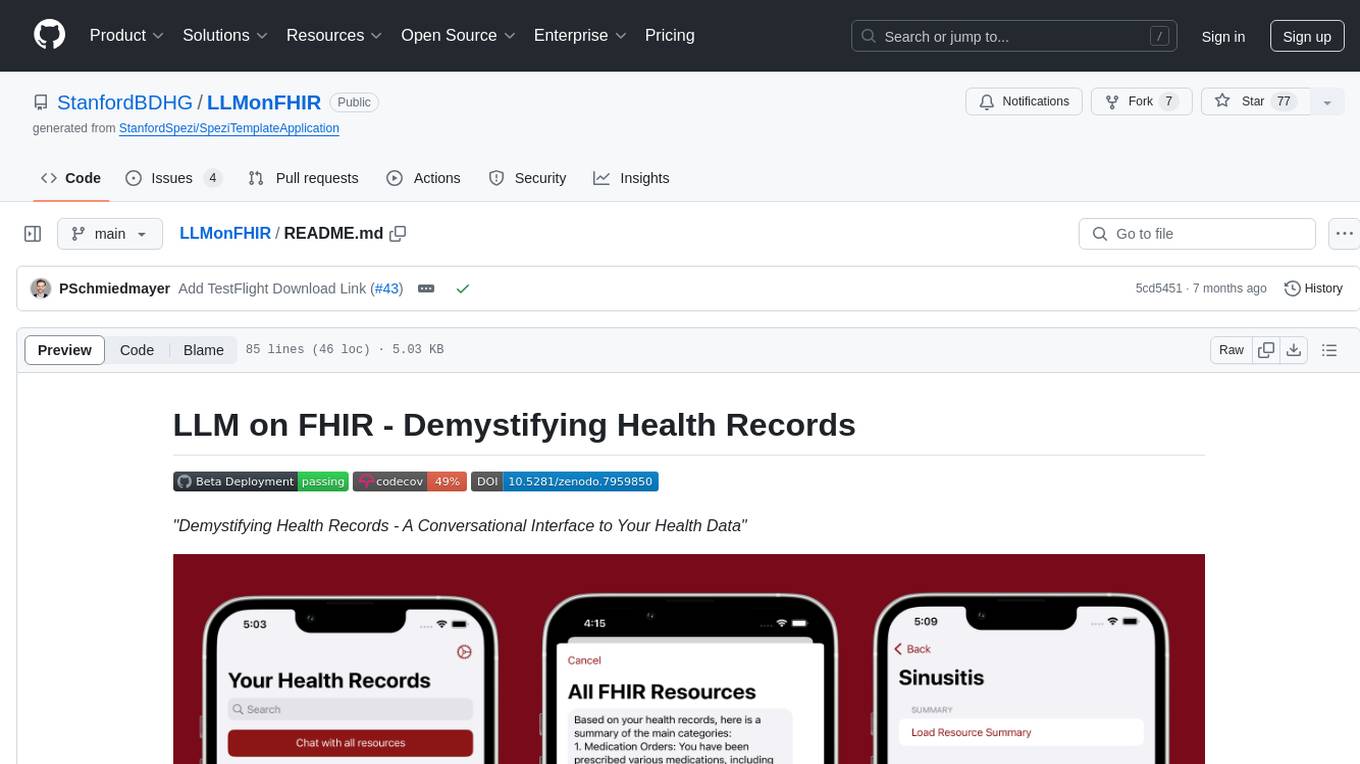
LLMonFHIR
LLMonFHIR is an iOS application that utilizes large language models (LLMs) to interpret and provide context around patient data in the Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR) format. It connects to the OpenAI GPT API to analyze FHIR resources, supports multiple languages, and allows users to interact with their health data stored in the Apple Health app. The app aims to simplify complex health records, provide insights, and facilitate deeper understanding through a conversational interface. However, it is an experimental app for informational purposes only and should not be used as a substitute for professional medical advice. Users are advised to verify information provided by AI models and consult healthcare professionals for personalized advice.

onnx
Open Neural Network Exchange (ONNX) is an open ecosystem that empowers AI developers to choose the right tools as their project evolves. ONNX provides an open source format for AI models, both deep learning and traditional ML. It defines an extensible computation graph model, as well as definitions of built-in operators and standard data types. Currently, we focus on the capabilities needed for inferencing (scoring). ONNX is widely supported and can be found in many frameworks, tools, and hardware, enabling interoperability between different frameworks and streamlining the path from research to production to increase the speed of innovation in the AI community. Join us to further evolve ONNX.
council
Council is an open-source platform designed for the rapid development and deployment of customized generative AI applications using teams of agents. It extends the LLM tool ecosystem by providing advanced control flow and scalable oversight for AI agents. Users can create sophisticated agents with predictable behavior by leveraging Council's powerful approach to control flow using Controllers, Filters, Evaluators, and Budgets. The framework allows for automated routing between agents, comparing, evaluating, and selecting the best results for a task. Council aims to facilitate packaging and deploying agents at scale on multiple platforms while enabling enterprise-grade monitoring and quality control.
For similar tasks

aiid
The Artificial Intelligence Incident Database (AIID) is a collection of incidents involving the development and use of artificial intelligence (AI). The database is designed to help researchers, policymakers, and the public understand the potential risks and benefits of AI, and to inform the development of policies and practices to mitigate the risks and promote the benefits of AI. The AIID is a collaborative project involving researchers from the University of California, Berkeley, the University of Washington, and the University of Toronto.
For similar jobs
AirCasting
AirCasting is a platform for gathering, visualizing, and sharing environmental data. It aims to provide a central hub for environmental data, making it easier for people to access and use this information to make informed decisions about their environment.

aiid
The Artificial Intelligence Incident Database (AIID) is a collection of incidents involving the development and use of artificial intelligence (AI). The database is designed to help researchers, policymakers, and the public understand the potential risks and benefits of AI, and to inform the development of policies and practices to mitigate the risks and promote the benefits of AI. The AIID is a collaborative project involving researchers from the University of California, Berkeley, the University of Washington, and the University of Toronto.
open-webui
Open WebUI is an extensible, feature-rich, and user-friendly self-hosted WebUI designed to operate entirely offline. It supports various LLM runners, including Ollama and OpenAI-compatible APIs. For more information, be sure to check out our Open WebUI Documentation.

glide
Glide is a cloud-native LLM gateway that provides a unified REST API for accessing various large language models (LLMs) from different providers. It handles LLMOps tasks such as model failover, caching, key management, and more, making it easy to integrate LLMs into applications. Glide supports popular LLM providers like OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI, AWS Bedrock (Titan), Cohere, Google Gemini, OctoML, and Ollama. It offers high availability, performance, and observability, and provides SDKs for Python and NodeJS to simplify integration.
litgpt
LitGPT is a command-line tool designed to easily finetune, pretrain, evaluate, and deploy 20+ LLMs **on your own data**. It features highly-optimized training recipes for the world's most powerful open-source large-language-models (LLMs).

khoj
Khoj is an open-source, personal AI assistant that extends your capabilities by creating always-available AI agents. You can share your notes and documents to extend your digital brain, and your AI agents have access to the internet, allowing you to incorporate real-time information. Khoj is accessible on Desktop, Emacs, Obsidian, Web, and Whatsapp, and you can share PDF, markdown, org-mode, notion files, and GitHub repositories. You'll get fast, accurate semantic search on top of your docs, and your agents can create deeply personal images and understand your speech. Khoj is self-hostable and always will be.
firecrawl
Firecrawl is an API service that takes a URL, crawls it, and converts it into clean markdown. It crawls all accessible subpages and provides clean markdown for each, without requiring a sitemap. The API is easy to use and can be self-hosted. It also integrates with Langchain and Llama Index. The Python SDK makes it easy to crawl and scrape websites in Python code.
NeMo
NeMo Framework is a generative AI framework built for researchers and pytorch developers working on large language models (LLMs), multimodal models (MM), automatic speech recognition (ASR), and text-to-speech synthesis (TTS). The primary objective of NeMo is to provide a scalable framework for researchers and developers from industry and academia to more easily implement and design new generative AI models by being able to leverage existing code and pretrained models.