desktop
The desktop app for ComfyUI.
Stars: 1252
ComfyUI Desktop is a packaged desktop application that allows users to easily use ComfyUI with bundled features like ComfyUI source code, ComfyUI-Manager, and uv. It automatically installs necessary Python dependencies and updates with stable releases. The app comes with Electron, Chromium binaries, and node modules. Users can store ComfyUI files in a specified location and manage model paths. The tool requires Python 3.12+ and Visual Studio with Desktop C++ workload for Windows. It uses nvm to manage node versions and yarn as the package manager. Users can install ComfyUI and dependencies using comfy-cli, download uv, and build/launch the code. Troubleshooting steps include rebuilding modules and installing missing libraries. The tool supports debugging in VSCode and provides utility scripts for cleanup. Crash reports can be sent to help debug issues, but no personal data is included.
README:
Please read this https://comfyorg.notion.site
Windows (NVIDIA) NSIS x64: Download
macOS ARM: Download
This desktop app is a packaged way to use ComfyUI and comes bundled with a few things:
- Stable version of ComfyUI from releases
- ComfyUI_frontend
- ComfyUI-Manager
- uv
On startup, it will install all the necessary python dependencies with uv and start the ComfyUI server. The app will automatically update with stable releases of ComfyUI, ComfyUI-Manager, and the uv executable as well as some desktop specific features.
Developers, read on.
The desktop application comes bundled with:
- ComfyUI source code
- ComfyUI-Manager
- Electron, Chromium binaries, and node modules
Windows
We use the NSIS installer for Windows and it will install files in these locations:
Bundled Resources: %APPDATA%\Local\Programs\comfyui-electron
User files are stored here: %APPDATA%\ComfyUI
Automatic Updates: %APPDATA%\Local\comfyui-electron-updater
macOS
The macOS application is distributed as a DMG and will install files in:
~/Library/Application Support/ComfyUI
The application will be dragged into /Applications
Linux
~/.config/ComfyUI
You will also be asked to select a location to store ComfyUI files like models, inputs, outputs, custom_nodes and saved workflows. This directory is stored in the basePath key of config.json.
On Windows: %APPDATA%\ComfyUI\config.json
On macOS: ~/Library/Application Support/ComfyUI/config.json
On Linux: ~/.config/ComfyUI/config.json
This directory is also written as the base_path in extra_model_config.yaml. The Desktop app will look for model checkpoints here by default, but you can add additional models to the search path by editing this file.
On Windows: %APPDATA%\ComfyUI\extra_model_config.yaml
On macOS: ~/Library/Application Support/ComfyUI/extra_model_config.yaml
On Linux: ~/.config/ComfyUI/extra_model_config.yaml
We use electron-log to log everything. Electron main process logs are in main.log, and ComfyUI server logs are in comfyui_<date>.log.
on Linux: ~/.config/{app name}/logs
on macOS: ~/Library/Logs/{app name}
on Windows: %AppData%\{app name}\logs
Make sure you have python 3.12+ installed. It is recommended to setup a virtual environment.
Linux/MacOS:
python -m venv venv
source venv/bin/activateWindows:
py -3.12 -m venv venv
.\venv\Scripts\Activate.ps1Visual studio 2019 or later with the Desktop C++ workload is required for node-gyp. See the node-gyp windows installation notes. Also requires the spectre-mitigated libraries, found in the individual components section of the VS installer.
Confirmed working:
- Visual Studio Community 2022 - 17.12.1
- Desktop development with C++ workload
- MSVC v143 x64 spectre-mitigated libraries (Latest / v14.42-17.12)
Look for "MSVC v143 - VS 2022 C++ x64/x86 Spectre-mitigated libs" If you're using other toolsets, you may need their corresponding Spectre-mitigated libraries as well
We recommend using nvm to manage node versions. This project uses node v20.x.
Microsoft recommends nvm-windows on their Node.js on Windows page.
nvm install 20
nvm use 20This project uses yarn as its package manager. If you do not already have a yarn binary available on your PATH, run:
# corepack is a set of utilities included with all recent distributions of node
corepack enable
yarn set version 4.5.0 # Look at the packageManager key in package.json for the exact version.This will install a usable yarn binary. Then, in the root directory of this repo (ie adjacent to the top-level package.json file), run:
yarn installBefore you can start the electron application, you need to download the ComfyUI source code and other things that are usually bundled with the application.
First, initialize the application resources by running yarn make:assets:
This command will install ComfyUI and ComfyUI-Manager under assets/. The exact versions of each package is defined in package.json.
You can then run start to build and launch the app. A watcher will also be started; it will automatically rebuild the app when a source file is changed:
deactivate # Deactivate your existing python env to avoid influencing the
yarn startYou can also build the package and/or distributables using the make command:
# build the platform-dependent package and any distributables
yarn make
# build cross-platform, e.g. windows from linux
yarn make --windowsThe requirements.compiled file is a pre-compiled requirements file that is used to install the dependencies for the application. It is generated by the comfy-cli.
You can generate the compiled requirements files by running the following commands from the project root directory:
## Nvidia Cuda requirements
uv pip compile assets\ComfyUI\requirements.txt assets\ComfyUI\custom_nodes\ComfyUI-Manager\requirements.txt --emit-index-annotation --emit-index-url --index-strategy unsafe-best-match -o assets\requirements\windows_nvidia.compiled --override assets\override.txt `
--index-url https://pypi.org/simple `
--extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu126
## CPU requirements
uv pip compile assets\ComfyUI\requirements.txt assets\ComfyUI\custom_nodes\ComfyUI-Manager\requirements.txt --emit-index-annotation --emit-index-url --index-strategy unsafe-best-match -o assets\requirements\windows_cpu.compiled `
--index-url https://pypi.org/simple## macOS requirements
uv pip compile assets/ComfyUI/requirements.txt assets/ComfyUI/custom_nodes/ComfyUI-Manager/requirements.txt --emit-index-annotation --emit-index-url --index-strategy unsafe-best-match -o assets/requirements/macos.compiled --override assets/override.txt \
--index-url https://pypi.org/simpleIf you get an error similar to:
The module '/electron/node_modules/node-pty/build/Release/pty.node' was compiled against a different Node.js version using NODE_MODULE_VERSION 115. This version of Node.js requires NODE_MODULE_VERSION 125. Please try re-compiling or re-installing the module (for instance, using `npm rebuild` or `npm install`).
You will need to rebuild the node-pty using electron-rebuild, for example:
npx electron-rebuild
or if that fails
yarn add -D @electron/rebuild
rm -rf node_modules
rm yarn.lock
yarn install
npx electron-rebuild
You may get errors reporting that the build is unable to find e.g. libnss3.so if electron prerequisites are not included in your distro. Find the correct package for your distro and install.
apt example:
apt-get install libnss3
There are helpful debug launch scripts for VSCode / Cursor under .vscode/launch.json. The default launch script runs the Electron launcher in the project root and attaches the debugger. By default, the app is not built when this is used.
The default launch script can be run by pressing F5 in VSCode or VSCode derivative. Ctrl + Shift + F5 restarts the app with the debugger attached. Shift + F5 terminates the debugger and the process tree it is attached to.
To keep the app built and up to date as you make changes, run the Start Vite Build Watchers build task defined in .vscode/tasks.json. This spawns two watcher tasks - one for the main app, and one for the preload script. These watchers will automatically rebuild the app when a source file is changed.
The launch environment can be customised, e.g. add a "linux" section to source your ~/.profile (and other interactive config) when debugging in linux:
{
"version": "2.0.0",
"tasks": [
{
"linux": { "options": { "shell": { "args": ["-ci"] } } }
}
]
}When the app has been packaged for use as a production app, it ignores environment variables used to configure development settings. To force the app to read env vars when packaged, use the --dev-mode command line argument to launch the app.
We use Todesktop to build and codesign our distributables. To make a new release:
- Create a PR that updates package.json to the next version.
- Create a Github Release with semantic version tag eg. "v1.0.0"
- Make sure it is a pre-release.
- Check the Github action "Publish All" runs. It should update the release body with Download links when it is finished.
- Test the build, and if it looks good release it on ToDesktop. Also mark the release as "Latest".
If a build fails for some reason, you can manually retry by running the "Publish All" GH action with a release tag as input.
Follow the above steps for local development setup first.
# Authentication will be required.
yarn publishA number of utility scripts are defined under the "scripts" field of package.json. For example, to clean up the build artifacts you can run:
yarn clean
# Remove files created by yarn make:assets
yarn clean:assets
# clean:slate also removes node_modules
yarn clean:slateAt the onboarding step, you can opt-in to send us usage metrics. This really helps us prioritize issues and focus our limited engineering time. Read our privacy policy here.
You can opt-out at anytime from the settings menu and nothing will ever be sent.
In either case, no personal data, workflows or logs will be sent.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for desktop
Similar Open Source Tools

desktop
ComfyUI Desktop is a packaged desktop application that allows users to easily use ComfyUI with bundled features like ComfyUI source code, ComfyUI-Manager, and uv. It automatically installs necessary Python dependencies and updates with stable releases. The app comes with Electron, Chromium binaries, and node modules. Users can store ComfyUI files in a specified location and manage model paths. The tool requires Python 3.12+ and Visual Studio with Desktop C++ workload for Windows. It uses nvm to manage node versions and yarn as the package manager. Users can install ComfyUI and dependencies using comfy-cli, download uv, and build/launch the code. Troubleshooting steps include rebuilding modules and installing missing libraries. The tool supports debugging in VSCode and provides utility scripts for cleanup. Crash reports can be sent to help debug issues, but no personal data is included.
frontend
Nuclia frontend apps and libraries repository contains various frontend applications and libraries for the Nuclia platform. It includes components such as Dashboard, Widget, SDK, Sistema (design system), NucliaDB admin, CI/CD Deployment, and Maintenance page. The repository provides detailed instructions on installation, dependencies, and usage of these components for both Nuclia employees and external developers. It also covers deployment processes for different components and tools like ArgoCD for monitoring deployments and logs. The repository aims to facilitate the development, testing, and deployment of frontend applications within the Nuclia ecosystem.
moly
Moly is an AI LLM client written in Rust, showcasing the capabilities of the Makepad UI toolkit and Project Robius, a framework for multi-platform application development in Rust. It is currently in beta, allowing users to build and run Moly on macOS, Linux, and Windows. The tool provides packaging support for different platforms, such as `.app`, `.dmg`, `.deb`, AppImage, pacman, and `.exe` (NSIS). Users can easily set up WasmEdge using `moly-runner` and leverage `cargo` commands to build and run Moly. Additionally, Moly offers pre-built releases for download and supports packaging for distribution on Linux, Windows, and macOS.
ai-starter-kit
SambaNova AI Starter Kits is a collection of open-source examples and guides designed to facilitate the deployment of AI-driven use cases for developers and enterprises. The kits cover various categories such as Data Ingestion & Preparation, Model Development & Optimization, Intelligent Information Retrieval, and Advanced AI Capabilities. Users can obtain a free API key using SambaNova Cloud or deploy models using SambaStudio. Most examples are written in Python but can be applied to any programming language. The kits provide resources for tasks like text extraction, fine-tuning embeddings, prompt engineering, question-answering, image search, post-call analysis, and more.
tiledesk-dashboard
Tiledesk is an open-source live chat platform with integrated chatbots written in Node.js and Express. It is designed to be a multi-channel platform for web, Android, and iOS, and it can be used to increase sales or provide post-sales customer service. Tiledesk's chatbot technology allows for automation of conversations, and it also provides APIs and webhooks for connecting external applications. Additionally, it offers a marketplace for apps and features such as CRM, ticketing, and data export.
llm-ollama
LLM-ollama is a plugin that provides access to models running on an Ollama server. It allows users to query the Ollama server for a list of models, register them with LLM, and use them for prompting, chatting, and embedding. The plugin supports image attachments, embeddings, JSON schemas, async models, model aliases, and model options. Users can interact with Ollama models through the plugin in a seamless and efficient manner.
WindowsAgentArena
Windows Agent Arena (WAA) is a scalable Windows AI agent platform designed for testing and benchmarking multi-modal, desktop AI agents. It provides researchers and developers with a reproducible and realistic Windows OS environment for AI research, enabling testing of agentic AI workflows across various tasks. WAA supports deploying agents at scale using Azure ML cloud infrastructure, allowing parallel running of multiple agents and delivering quick benchmark results for hundreds of tasks in minutes.
hordelib
horde-engine is a wrapper around ComfyUI designed to run inference pipelines visually designed in the ComfyUI GUI. It enables users to design inference pipelines in ComfyUI and then call them programmatically, maintaining compatibility with the existing horde implementation. The library provides features for processing Horde payloads, initializing the library, downloading and validating models, and generating images based on input data. It also includes custom nodes for preprocessing and tasks such as face restoration and QR code generation. The project depends on various open source projects and bundles some dependencies within the library itself. Users can design ComfyUI pipelines, convert them to the backend format, and run them using the run_image_pipeline() method in hordelib.comfy.Comfy(). The project is actively developed and tested using git, tox, and a specific model directory structure.

telemetry-airflow
This repository codifies the Airflow cluster that is deployed at workflow.telemetry.mozilla.org (behind SSO) and commonly referred to as "WTMO" or simply "Airflow". Some links relevant to users and developers of WTMO: * The `dags` directory in this repository contains some custom DAG definitions * Many of the DAGs registered with WTMO don't live in this repository, but are instead generated from ETL task definitions in bigquery-etl * The Data SRE team maintains a WTMO Developer Guide (behind SSO)
screeps-starter-rust
screeps-starter-rust is a Rust AI starter kit for Screeps: World, a JavaScript-based MMO game. It utilizes the screeps-game-api bindings from the rustyscreeps organization and wasm-pack for building Rust code to WebAssembly. The example includes Rollup for bundling javascript, Babel for transpiling code, and screeps-api Node.js package for deployment. Users can refer to the Rust version of game APIs documentation at https://docs.rs/screeps-game-api/. The tool supports most crates on crates.io, except those interacting with OS APIs.
sandbox
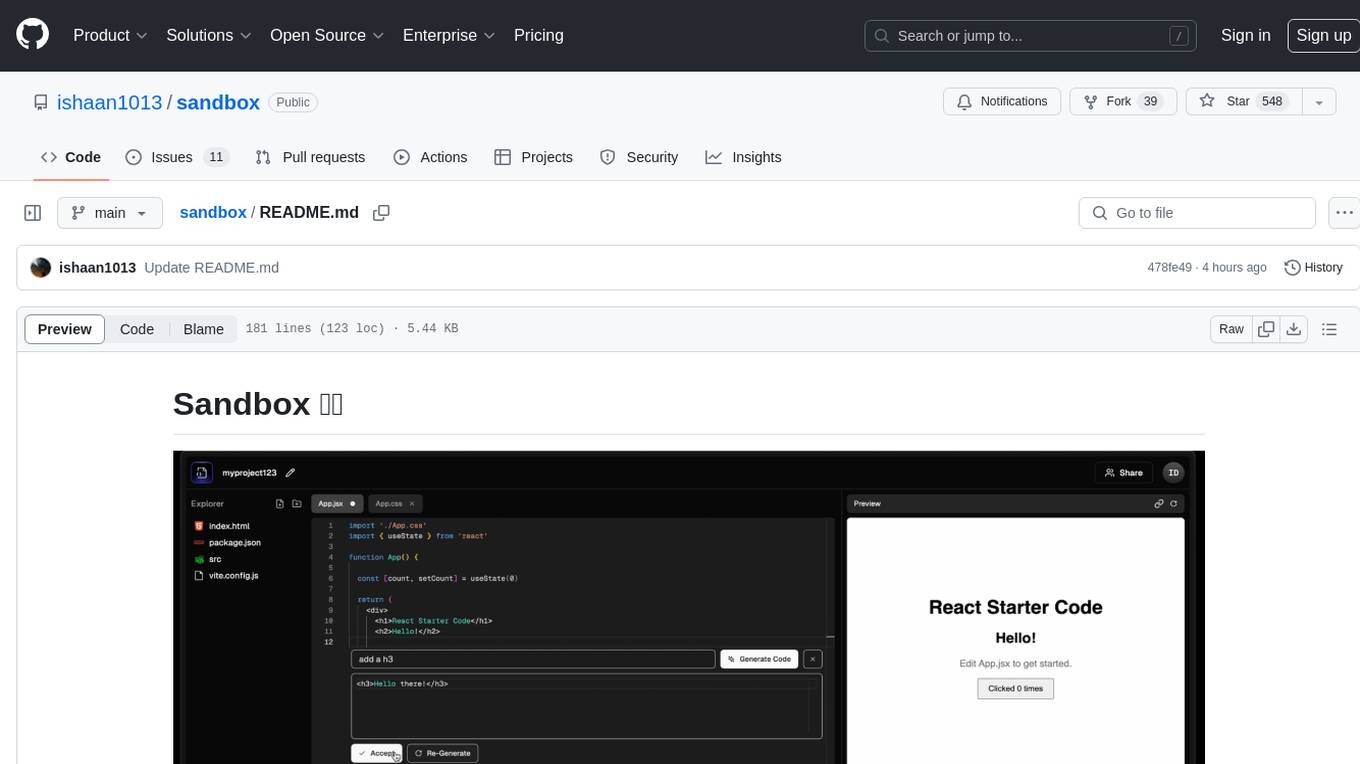
Sandbox is an open-source cloud-based code editing environment with custom AI code autocompletion and real-time collaboration. It consists of a frontend built with Next.js, TailwindCSS, Shadcn UI, Clerk, Monaco, and Liveblocks, and a backend with Express, Socket.io, Cloudflare Workers, D1 database, R2 storage, Workers AI, and Drizzle ORM. The backend includes microservices for database, storage, and AI functionalities. Users can run the project locally by setting up environment variables and deploying the containers. Contributions are welcome following the commit convention and structure provided in the repository.
LLM-Engineers-Handbook
The LLM Engineer's Handbook is an official repository containing a comprehensive guide on creating an end-to-end LLM-based system using best practices. It covers data collection & generation, LLM training pipeline, a simple RAG system, production-ready AWS deployment, comprehensive monitoring, and testing and evaluation framework. The repository includes detailed instructions on setting up local and cloud dependencies, project structure, installation steps, infrastructure setup, pipelines for data processing, training, and inference, as well as QA, tests, and running the project end-to-end.
opencharacter
OpenCharacter is an open-source tool that allows users to create and run characters locally with local models or use the hosted version. The stack includes Next.js for frontend, TailwindCSS for styling, Drizzle ORM for database access, NextAuth for authentication, Cloudflare D1 for serverless databases, Cloudflare Pages for hosting, and ShadcnUI as the component library. Users can integrate OpenCharacter with OpenRouter by configuring the OpenRouter API key. The tool is fully scalable, composable, and cost-effective, with powerful tools like Wrangler for database management and migrations. No environment variables are needed, making it easy to use and deploy.
shinkai-node
Shinkai Node is a tool that enables users to create AI agents without coding. Users can define tasks, schedule actions, and let Shinkai generate custom code. The tool also provides native crypto support. It has a companion repo called Shinkai Apps for the frontend. The tool offers easy local compilation and OpenAPI support for generating schemas and Swagger UI. Users can run tests and dockerized tests for the tool. It also provides guidance on releasing a new version.
vim-ollama
The 'vim-ollama' plugin for Vim adds Copilot-like code completion support using Ollama as a backend, enabling intelligent AI-based code completion and integrated chat support for code reviews. It does not rely on cloud services, preserving user privacy. The plugin communicates with Ollama via Python scripts for code completion and interactive chat, supporting Vim only. Users can configure LLM models for code completion tasks and interactive conversations, with detailed installation and usage instructions provided in the README.
For similar tasks

desktop
ComfyUI Desktop is a packaged desktop application that allows users to easily use ComfyUI with bundled features like ComfyUI source code, ComfyUI-Manager, and uv. It automatically installs necessary Python dependencies and updates with stable releases. The app comes with Electron, Chromium binaries, and node modules. Users can store ComfyUI files in a specified location and manage model paths. The tool requires Python 3.12+ and Visual Studio with Desktop C++ workload for Windows. It uses nvm to manage node versions and yarn as the package manager. Users can install ComfyUI and dependencies using comfy-cli, download uv, and build/launch the code. Troubleshooting steps include rebuilding modules and installing missing libraries. The tool supports debugging in VSCode and provides utility scripts for cleanup. Crash reports can be sent to help debug issues, but no personal data is included.
comfy-cli
comfy-cli is a command line tool designed to simplify the installation and management of ComfyUI, an open-source machine learning framework. It allows users to easily set up ComfyUI, install packages, manage custom nodes, download checkpoints, and ensure cross-platform compatibility. The tool provides comprehensive documentation and examples to aid users in utilizing ComfyUI efficiently.
comfy-cli
Comfy-cli is a command line tool designed to facilitate the installation and management of ComfyUI, an open-source machine learning framework. Users can easily set up ComfyUI, install packages, and manage custom nodes directly from the terminal. The tool offers features such as easy installation, seamless package management, custom node management, checkpoint downloads, cross-platform compatibility, and comprehensive documentation. Comfy-cli simplifies the process of working with ComfyUI, making it convenient for users to handle various tasks related to the framework.
openllmetry-js
OpenLLMetry-JS is a set of extensions built on top of OpenTelemetry that gives you complete observability over your LLM application. Because it uses OpenTelemetry under the hood, it can be connected to your existing observability solutions - Datadog, Honeycomb, and others. It's built and maintained by Traceloop under the Apache 2.0 license. The repo contains standard OpenTelemetry instrumentations for LLM providers and Vector DBs, as well as a Traceloop SDK that makes it easy to get started with OpenLLMetry-JS, while still outputting standard OpenTelemetry data that can be connected to your observability stack. If you already have OpenTelemetry instrumented, you can just add any of our instrumentations directly.
Awesome-ChatTTS
Awesome-ChatTTS is an official recommended guide for ChatTTS beginners, compiling common questions and related resources. It provides a comprehensive overview of the project, including official introduction, quick experience options, popular branches, parameter explanations, voice seed details, installation guides, FAQs, and error troubleshooting. The repository also includes video tutorials, discussion community links, and project trends analysis. Users can explore various branches for different functionalities and enhancements related to ChatTTS.
ClaudeSync
ClaudeSync is a powerful tool designed to seamlessly synchronize local files with Claude.ai projects. It bridges the gap between local development environment and Claude.ai's knowledge base, offering real-time synchronization, CLI for easy management, support for multiple organizations and projects, intelligent file filtering, configurable sync interval, two-way synchronization, and more. It ensures data privacy, open source transparency, and comes with disclaimers for use at own risk. Users can quickly start syncing by installing, logging in, selecting organization and project, and running sync. Advanced features include API, organization, project, file, chat management, configuration, synchronization modes, scheduled sync, providers, custom ignore file, and troubleshooting. Contributions are welcome, and communication channels include GitHub Issues and Discord. Licensed under MIT License.
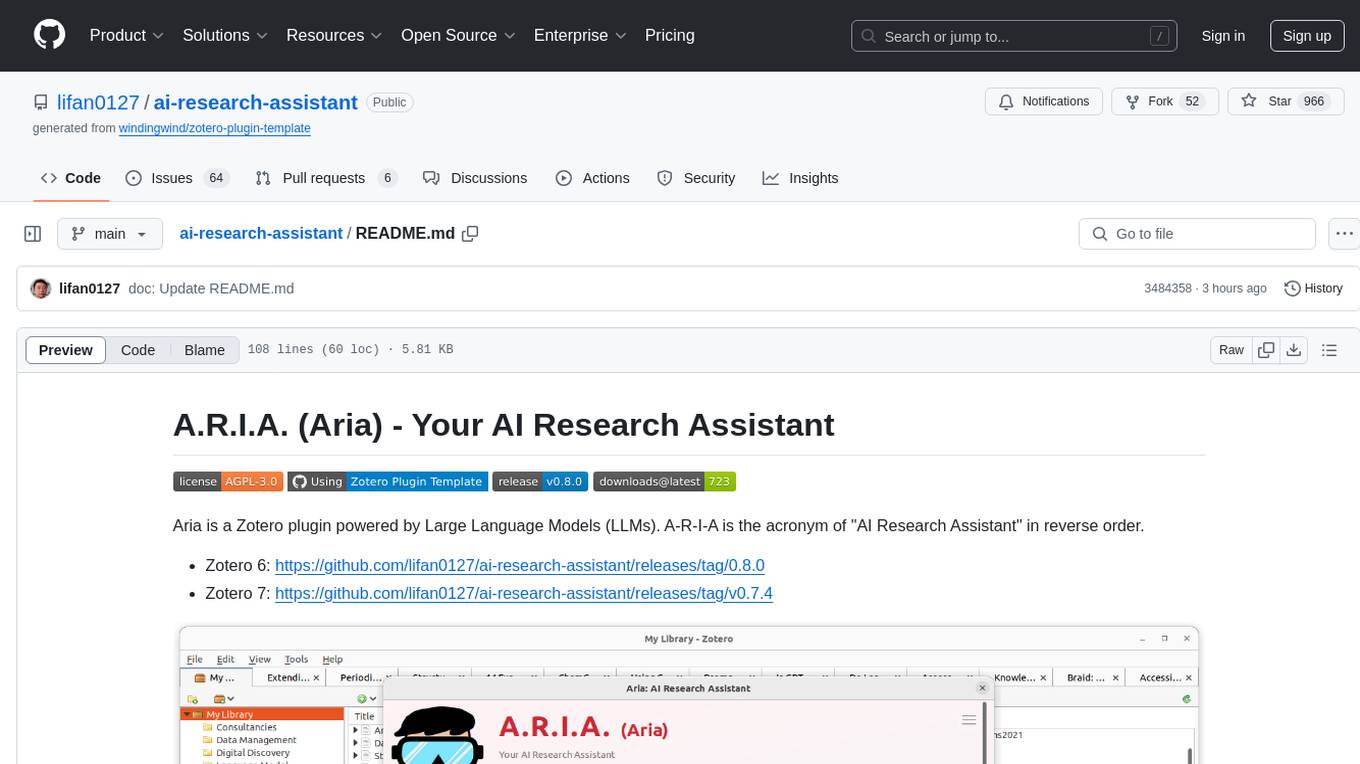
ai-research-assistant
Aria is a Zotero plugin that serves as an AI Research Assistant powered by Large Language Models (LLMs). It offers features like drag-and-drop referencing, autocompletion for creators and tags, visual analysis using GPT-4 Vision, and saving chats as notes and annotations. Aria requires the OpenAI GPT-4 model family and provides a configurable interface through preferences. Users can install Aria by downloading the latest release from GitHub and activating it in Zotero. The tool allows users to interact with Zotero library through conversational AI and probabilistic models, with the ability to troubleshoot errors and provide feedback for improvement.

chat-mcp
A Cross-Platform Interface for Large Language Models (LLMs) utilizing the Model Context Protocol (MCP) to connect and interact with various LLMs. The desktop app, built on Electron, ensures compatibility across Linux, macOS, and Windows. It simplifies understanding MCP principles, facilitates testing of multiple servers and LLMs, and supports dynamic LLM configuration and multi-client management. The UI can be extracted for web use, ensuring consistency across web and desktop versions.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

agentcloud
AgentCloud is an open-source platform that enables companies to build and deploy private LLM chat apps, empowering teams to securely interact with their data. It comprises three main components: Agent Backend, Webapp, and Vector Proxy. To run this project locally, clone the repository, install Docker, and start the services. The project is licensed under the GNU Affero General Public License, version 3 only. Contributions and feedback are welcome from the community.

oss-fuzz-gen
This framework generates fuzz targets for real-world `C`/`C++` projects with various Large Language Models (LLM) and benchmarks them via the `OSS-Fuzz` platform. It manages to successfully leverage LLMs to generate valid fuzz targets (which generate non-zero coverage increase) for 160 C/C++ projects. The maximum line coverage increase is 29% from the existing human-written targets.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement
The Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement repository provides packaged Industry Scenario DREAM Demos with ARM templates (Containing a demo web application, Power BI reports, Synapse resources, AML Notebooks etc.) that can be deployed in a customer’s subscription using the CAPE tool within a matter of few hours. Partners can also deploy DREAM Demos in their own subscriptions using DPoC.