py-vectara-agentic
A python library for creating AI assistants with Vectara, using Agentic RAG
Stars: 98
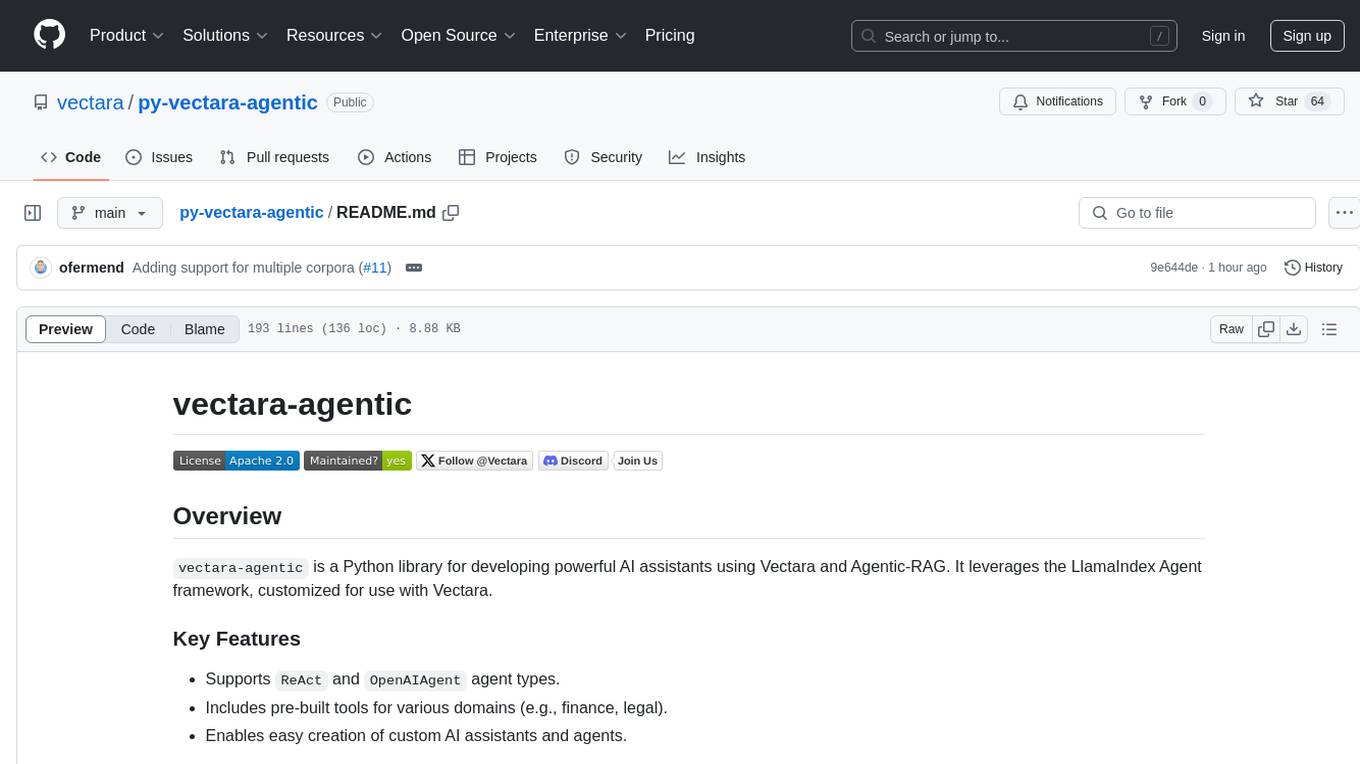
The `vectara-agentic` Python library is designed for developing powerful AI assistants using Vectara and Agentic-RAG. It supports various agent types, includes pre-built tools for domains like finance and legal, and enables easy creation of custom AI assistants and agents. The library provides tools for summarizing text, rephrasing text, legal tasks like summarizing legal text and critiquing as a judge, financial tasks like analyzing balance sheets and income statements, and database tools for inspecting and querying databases. It also supports observability via LlamaIndex and Arize Phoenix integration.
README:
Documentation · Examples · Discord
vectara-agentic is a Python library for developing powerful AI assistants and agents using Vectara and Agentic-RAG. It leverages the LlamaIndex Agent framework and provides helper functions to quickly create tools that connect to Vectara corpora.
-
Rapid Tool Creation:
Build Vectara RAG tools or search tools with a single line of code. -
Agent Flexibility:
Supports multiple agent types includingReAct,OpenAIAgent,LATS, andLLMCompiler. -
Pre-Built Domain Tools:
Tools tailored for finance, legal, and other verticals. -
Multi-LLM Integration:
Seamless integration with OpenAI, Anthropic, Gemini, GROQ, Together.AI, Cohere, Bedrock, and Fireworks. -
Observability:
Built-in support with Arize Phoenix for monitoring and feedback. -
Workflow Support:
Extend your agent’s capabilities by defining custom workflows using therun()method.
Check out our example AI assistants:
- Vectara account
- A Vectara corpus with an API key
- Python 3.10 or higher
- OpenAI API key (or API keys for Anthropic, TOGETHER.AI, Fireworks AI, Bedrock, Cohere, GEMINI or GROQ, if you choose to use them)
pip install vectara-agenticimport os
from vectara_agentic.tools import VectaraToolFactory
vec_factory = VectaraToolFactory(
vectara_api_key=os.environ['VECTARA_API_KEY'],
vectara_customer_id=os.environ['VECTARA_CUSTOMER_ID'],
vectara_corpus_key=os.environ['VECTARA_CORPUS_KEY']
)A RAG tool calls the full Vectara RAG pipeline to provide summarized responses to queries grounded in data.
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
years = list(range(2020, 2024))
tickers = {
"AAPL": "Apple Computer",
"GOOG": "Google",
"AMZN": "Amazon",
"SNOW": "Snowflake",
}
class QueryFinancialReportsArgs(BaseModel):
query: str = Field(..., description="The user query.")
year: int | str = Field(..., description=f"The year this query relates to. An integer between {min(years)} and {max(years)} or a string specifying a condition on the year (example: '>2020').")
ticker: str = Field(..., description=f"The company ticker. Must be a valid ticket symbol from the list {tickers.keys()}.")
query_financial_reports_tool = vec_factory.create_rag_tool(
tool_name="query_financial_reports",
tool_description="Query financial reports for a company and year",
tool_args_schema=QueryFinancialReportsArgs,
lambda_val=0.005,
summary_num_results=7,
# Additional arguments
)See the docs for additional arguments to customize your Vectara RAG tool.
In addition to RAG tools, you can generate a lot of other types of tools the agent can use. These could be mathematical tools, tools that call other APIs to get more information, or any other type of tool.
See Agent Tools for more information.
from vectara_agentic import Agent
agent = Agent(
tools=[query_financial_reports_tool],
topic="10-K financial reports",
custom_instructions="""
- You are a helpful financial assistant in conversation with a user. Use your financial expertise when crafting a query to the tool, to ensure you get the most accurate information.
- You can answer questions, provide insights, or summarize any information from financial reports.
- A user may refer to a company's ticker instead of its full name - consider those the same when a user is asking about a company.
- When calculating a financial metric, make sure you have all the information from tools to complete the calculation.
- In many cases you may need to query tools on each sub-metric separately before computing the final metric.
- When using a tool to obtain financial data, consider the fact that information for a certain year may be reported in the following year's report.
- Report financial data in a consistent manner. For example if you report revenue in thousands, always report revenue in thousands.
"""
)See the docs for additional arguments, including agent_progress_callback and query_logging_callback.
res = agent.chat("What was the revenue for Apple in 2021?")
print(res.response)Note that:
-
vectara-agenticalso supportsachat()and two streaming variantsstream_chat()andastream_chat(). - The response types from
chat()andachat()are of typeAgentResponse. If you just need the actual string response it's available as theresponsevariable, or just usestr(). For advanced use-cases you can look at otherAgentResponsevariables such assources.
In addition to standard chat interactions, vectara-agentic supports custom workflows via the run() method.
Workflows allow you to structure multi-step interactions where inputs and outputs are validated using Pydantic models.
To learn more about workflows read the documentation
Create a workflow by subclassing llama_index.core.workflow.Workflow and defining the input/output models:
from pydantic import BaseModel
from llama_index.core.workflow import (
StartEvent,StopEvent, Workflow, step,
)
class MyWorkflow(Workflow):
class InputsModel(BaseModel):
query: str
class OutputsModel(BaseModel):
answer: str
@step
async def my_step(self, ev: StartEvent) -> StopEvent:
# do something here
return StopEvent(result="Hello, world!")When the run() method in vectara-agentic is invoked, it calls the workflow with the following variables in the StartEvent:
-
agent: the agent object used to callrun()(self) -
tools: the tools provided to the agent. Those can be used as needed in the flow. -
llm: a pointer to a LlamaIndex llm, so it can be used in the workflow. For example, one of the steps may callllm.acomplete(prompt) -
verbose: controls whether extra debug information is displayed -
inputs: this is the actual inputs to the workflow provided by the call torun()and must be of typeInputsModel
When initializing your agent, pass the workflow class using the workflow_cls parameter:
agent = Agent(
tools=[query_financial_reports_tool],
topic="10-K financial reports",
custom_instructions="You are a helpful financial assistant.",
workflow_cls=MyWorkflow, # Provide your custom workflow here
workflow_timeout=120 # Optional: Set a timeout (default is 120 seconds)
)Prepare the inputs using your workflow’s InputsModel and execute the workflow using run():
# Create an instance of the workflow's input model
inputs = MyWorkflow.InputsModel(query="What is Vectara?", extra_param=42)
# Run the workflow (ensure you're in an async context or use asyncio.run)
workflow_result = asyncio.run(agent.run(inputs))
# Access the output from the workflow's OutputsModel
print(workflow_result.answer)vectara-agentic already includes one useful workflow you can use right away (it is also useful as an advanced example)
This workflow is called SubQuestionQueryWorkflow and it works by breaking a complex query into sub-queries and then
executing each sub-query with the agent until it reaches a good response.
vectara-agentic provides two helper functions to connect with Vectara RAG
-
create_rag_tool()to create an agent tool that connects with a Vectara corpus for querying. -
create_search_tool()to create a tool to search a Vectara corpus and return a list of matching documents.
See the documentation for the full list of arguments for create_rag_tool() and create_search_tool(),
to understand how to configure Vectara query performed by those tools.
A Vectara RAG tool is often the main workhorse for any Agentic RAG application, and enables the agent to query one or more Vectara RAG corpora.
The tool generated always includes the query argument, followed by 1 or more optional arguments used for
metadata filtering, defined by tool_args_schema.
For example, in the quickstart example the schema is:
class QueryFinancialReportsArgs(BaseModel):
query: str = Field(..., description="The user query.")
year: int | str = Field(..., description=f"The year this query relates to. An integer between {min(years)} and {max(years)} or a string specifying a condition on the year (example: '>2020').")
ticker: str = Field(..., description=f"The company ticker. Must be a valid ticket symbol from the list {tickers.keys()}.")
The query is required and is always the query string.
The other arguments are optional and will be interpreted as Vectara metadata filters.
For example, in the example above, the agent may call the query_financial_reports_tool tool with
query='what is the revenue?', year=2022 and ticker='AAPL'. Subsequently the RAG tool will issue
a Vectara RAG query with the same query, but with metadata filtering (doc.year=2022 and doc.ticker='AAPL').
There are also additional cool features supported here:
- An argument can be a condition, for example year='>2022' translates to the correct metadata filtering condition doc.year>2022
- if
fixed_filteris defined in the RAG tool, it provides a constant metadata filtering that is always applied. For example, if fixed_filter=doc.filing_type='10K'then a query with query='what is the reveue', year=2022 and ticker='AAPL' would translate into query='what is the revenue' with metadata filtering condition of "doc.year=2022 AND doc.ticker='AAPL' and doc.filing_type='10K'"
Note that tool_args_type is an optional dictionary that indicates the level at which metadata filtering
is applied for each argument (doc or part)
The Vectara search tool allows the agent to list documents that match a query. This can be helpful to the agent to answer queries like "how many documents discuss the iPhone?" or other similar queries that require a response in terms of a list of matching documents.
vectara-agentic provides a few tools out of the box (see ToolsCatalog for details):
- Standard tools:
-
summarize_text: a tool to summarize a long text into a shorter summary (uses LLM) -
rephrase_text: a tool to rephrase a given text, given a set of rephrase instructions (uses LLM) These tools use an LLM and so would use theToolsLLM specified in yourAgentConfig. To instantiate them:
from vectara_agentic.tools_catalog import ToolsCatalog
summarize_text = ToolsCatalog(agent_config).summarize_textThis ensures the summarize_text tool is configured with the proper LLM provider and model as specified in the Agent configuration.
- Legal tools: a set of tools for the legal vertical, such as:
-
summarize_legal_text: summarize legal text with a certain point of view -
critique_as_judge: critique a legal text as a judge, providing their perspective
- Financial tools: based on tools from Yahoo! Finance:
- tools to understand the financials of a public company like:
balance_sheet,income_statement,cash_flow -
stock_news: provides news about a company -
stock_analyst_recommendations: provides stock analyst recommendations for a company.
- Database tools: providing tools to inspect and query a database
-
list_tables: list all tables in the database -
describe_tables: describe the schema of tables in the database -
load_data: returns data based on a SQL query -
load_sample_data: returns the first 25 rows of a table -
load_unique_values: returns the top unique values for a given column
In addition, we include various other tools from LlamaIndex ToolSpecs:
- Tavily search and EXA.AI
- arxiv
- neo4j & Kuzu for Graph DB integration
- Google tools (including gmail, calendar, and search)
- Slack
Note that some of these tools may require API keys as environment variables
You can create your own tool directly from a Python function using the create_tool() method of the ToolsFactory class:
def mult_func(x, y):
return x * y
mult_tool = ToolsFactory().create_tool(mult_func)Note: When you define your own Python functions as tools, implement them at the top module level, and not as nested functions. Nested functions are not supported if you use serialization (dumps/loads or from_dict/to_dict).
The main way to control the behavior of vectara-agentic is by passing an AgentConfig object to your Agent when creating it.
For example:
agent_config = AgentConfig(
agent_type = AgentType.REACT,
main_llm_provider = ModelProvider.ANTHROPIC,
main_llm_model_name = 'claude-3-5-sonnet-20241022',
tool_llm_provider = ModelProvider.TOGETHER,
tool_llm_model_name = 'meta-llama/Llama-3.3-70B-Instruct-Turbo'
)
agent = Agent(
tools=[query_financial_reports_tool],
topic="10-K financial reports",
custom_instructions="You are a helpful financial assistant in conversation with a user.",
agent_config=agent_config
)The AgentConfig object may include the following items:
-
agent_type: the agent type. Valid values areREACT,LLMCOMPILER,LATSorOPENAI(default:OPENAI). -
main_llm_providerandtool_llm_provider: the LLM provider for main agent and for the tools. Valid values areOPENAI,ANTHROPIC,TOGETHER,GROQ,COHERE,BEDROCK,GEMINIorFIREWORKS(default:OPENAI). -
main_llm_model_nameandtool_llm_model_name: agent model name for agent and tools (default depends on provider). -
observer: the observer type; should beARIZE_PHOENIXor if undefined no observation framework will be used. -
endpoint_api_key: a secret key if using the API endpoint option (defaults todev-api-key) -
max_reasoning_steps: the maximum number of reasoning steps (iterations for React and function calls for OpenAI agent, respectively). Defaults to 50.
If any of these are not provided, AgentConfig first tries to read the values from the OS environment.
When creating a VectaraToolFactory, you can pass in a vectara_api_key, and vectara_corpus_key to the factory.
If not passed in, it will be taken from the environment variables (VECTARA_API_KEY and VECTARA_CORPUS_KEY). Note that VECTARA_CORPUS_KEY can be a single KEY or a comma-separated list of KEYs (if you want to query multiple corpora).
These values will be used as credentials when creating Vectara tools - in create_rag_tool() and create_search_tool().
If you want to setup vectara-agentic to use your own self-hosted LLM endpoint, follow the example below
config = AgentConfig(
agent_type=AgentType.REACT,
main_llm_provider=ModelProvider.PRIVATE,
main_llm_model_name="meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct",
private_llm_api_base="http://vllm-server.company.com/v1",
private_llm_api_key="TEST_API_KEY",
)
agent = Agent(agent_config=config, tools=tools, topic=topic,
custom_instructions=custom_instructions)In this case we specify the Main LLM provider to be privately hosted with Llama-3.1-8B as the model.
- The
ModelProvider.PRIVATEspecifies a privately hosted LLM. - The
private_llm_api_basespecifies the api endpoint to use, and theprivate_llm_api_keyspecifies the private API key requires to use this service.
The custom instructions you provide to the agent guide its behavior. Here are some guidelines when creating your instructions:
- Write precise and clear instructions, without overcomplicating.
- Consider edge cases and unusual or atypical scenarios.
- Be cautious to not over-specify behavior based on your primary use-case, as it may limit the agent's ability to behave properly in others.
The Agent class defines a few helpful methods to help you understand the internals of your application.
- The
report()method prints out the agent object’s type, the tools, and the LLMs used for the main agent and tool calling. - The
token_counts()method tells you how many tokens you have used in the current session for both the main agent and tool calling LLMs. This can be helpful if you want to track spend by token.
The Agent class supports serialization. Use the dumps() to serialize and loads() to read back from a serialized stream.
Note: due to cloudpickle limitations, if a tool contains Python weakref objects, serialization won't work and an exception will be raised.
vectara-agentic supports observability via the existing integration of LlamaIndex and Arize Phoenix.
First, set VECTARA_AGENTIC_OBSERVER_TYPE to ARIZE_PHOENIX in AgentConfig (or env variable).
Then you can use Arize Phoenix in three ways:
-
Locally.
- If you have a local phoenix server that you've run using e.g.
python -m phoenix.server.main serve, vectara-agentic will send all traces to it. - If not, vectara-agentic will run a local instance during the agent's lifecycle, and will close it when finished.
- In both cases, traces will be sent to the local instance, and you can see the dashboard at
http://localhost:6006
- If you have a local phoenix server that you've run using e.g.
-
Hosted Instance. In this case the traces are sent to the Phoenix instances hosted on Arize.
- Go to
https://app.phoenix.arize.com, setup an account if you don't have one. - create an API key and put it in the
PHOENIX_API_KEYenvironment variable - this indicates you want to use the hosted version. - To view the traces go to
https://app.phoenix.arize.com.
- Go to
Now when you run your agent, all call traces are sent to Phoenix and recorded.
In addition, vectara-agentic also records FCS (factual consistency score, aka HHEM) values into Arize for every Vectara RAG call. You can see those results in the Feedback column of the arize UI.
vectara-agentic can be easily hosted locally or on a remote machine behind an API endpoint, by following theses steps:
Ensure that you have your API key set up as an environment variable:
export VECTARA_AGENTIC_API_KEY=<YOUR-ENDPOINT-API-KEY>
if you don't specify an Endpoint API key it uses the default "dev-api-key".
Initialize the agent and start the FastAPI server by following this example:
from vectara_agentic.agent import Agent
from vectara_agentic.agent_endpoint import start_app
agent = Agent(...) # Initialize your agent with appropriate parameters
start_app(agent)
You can customize the host and port by passing them as arguments to start_app():
- Default: host="0.0.0.0" and port=8000. For example:
start_app(agent, host="0.0.0.0", port=8000)
Once the server is running, you can interact with it using curl or any HTTP client. For example:
curl -G "http://<remote-server-ip>:8000/chat" \
--data-urlencode "message=What is Vectara?" \
-H "X-API-Key: <YOUR-ENDPOINT-API-KEY>"
We welcome contributions! Please see our contributing guide for more information.
This project is licensed under the Apache 2.0 License. See the LICENSE file for details.
- Website: vectara.com
- Twitter: @vectara
- GitHub: @vectara
- LinkedIn: @vectara
- Discord: Join our community
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for py-vectara-agentic
Similar Open Source Tools

py-vectara-agentic
The `vectara-agentic` Python library is designed for developing powerful AI assistants using Vectara and Agentic-RAG. It supports various agent types, includes pre-built tools for domains like finance and legal, and enables easy creation of custom AI assistants and agents. The library provides tools for summarizing text, rephrasing text, legal tasks like summarizing legal text and critiquing as a judge, financial tasks like analyzing balance sheets and income statements, and database tools for inspecting and querying databases. It also supports observability via LlamaIndex and Arize Phoenix integration.
Hurley-AI
Hurley AI is a next-gen framework for developing intelligent agents through Retrieval-Augmented Generation. It enables easy creation of custom AI assistants and agents, supports various agent types, and includes pre-built tools for domains like finance and legal. Hurley AI integrates with LLM inference services and provides observability with Arize Phoenix. Users can create Hurley RAG tools with a single line of code and customize agents with specific instructions. The tool also offers various helper functions to connect with Hurley RAG and search tools, along with pre-built tools for tasks like summarizing text, rephrasing text, understanding memecoins, and querying databases.
paper-qa
PaperQA is a minimal package for question and answering from PDFs or text files, providing very good answers with in-text citations. It uses OpenAI Embeddings to embed and search documents, and includes a process of embedding docs, queries, searching for top passages, creating summaries, using an LLM to re-score and select relevant summaries, putting summaries into prompt, and generating answers. The tool can be used to answer specific questions related to scientific research by leveraging citations and relevant passages from documents.
fabrice-ai
A lightweight, functional, and composable framework for building AI agents that work together to solve complex tasks. Built with TypeScript and designed to be serverless-ready. Fabrice embraces functional programming principles, remains stateless, and stays focused on composability. It provides core concepts like easy teamwork creation, infrastructure-agnosticism, statelessness, and includes all tools and features needed to build AI teams. Agents are specialized workers with specific roles and capabilities, able to call tools and complete tasks. Workflows define how agents collaborate to achieve a goal, with workflow states representing the current state of the workflow. Providers handle requests to the LLM and responses. Tools extend agent capabilities by providing concrete actions they can perform. Execution involves running the workflow to completion, with options for custom execution and BDD testing.
ai2-scholarqa-lib
Ai2 Scholar QA is a system for answering scientific queries and literature review by gathering evidence from multiple documents across a corpus and synthesizing an organized report with evidence for each claim. It consists of a retrieval component and a three-step generator pipeline. The retrieval component fetches relevant evidence passages using the Semantic Scholar public API and reranks them. The generator pipeline includes quote extraction, planning and clustering, and summary generation. The system is powered by the ScholarQA class, which includes components like PaperFinder and MultiStepQAPipeline. It requires environment variables for Semantic Scholar API and LLMs, and can be run as local docker containers or embedded into another application as a Python package.
garak
Garak is a free tool that checks if a Large Language Model (LLM) can be made to fail in a way that is undesirable. It probes for hallucination, data leakage, prompt injection, misinformation, toxicity generation, jailbreaks, and many other weaknesses. Garak's a free tool. We love developing it and are always interested in adding functionality to support applications.
debug-gym
debug-gym is a text-based interactive debugging framework designed for debugging Python programs. It provides an environment where agents can interact with code repositories, use various tools like pdb and grep to investigate and fix bugs, and propose code patches. The framework supports different LLM backends such as OpenAI, Azure OpenAI, and Anthropic. Users can customize tools, manage environment states, and run agents to debug code effectively. debug-gym is modular, extensible, and suitable for interactive debugging tasks in a text-based environment.
mentals-ai
Mentals AI is a tool designed for creating and operating agents that feature loops, memory, and various tools, all through straightforward markdown syntax. This tool enables you to concentrate solely on the agent’s logic, eliminating the necessity to compose underlying code in Python or any other language. It redefines the foundational frameworks for future AI applications by allowing the creation of agents with recursive decision-making processes, integration of reasoning frameworks, and control flow expressed in natural language. Key concepts include instructions with prompts and references, working memory for context, short-term memory for storing intermediate results, and control flow from strings to algorithms. The tool provides a set of native tools for message output, user input, file handling, Python interpreter, Bash commands, and short-term memory. The roadmap includes features like a web UI, vector database tools, agent's experience, and tools for image generation and browsing. The idea behind Mentals AI originated from studies on psychoanalysis executive functions and aims to integrate 'System 1' (cognitive executor) with 'System 2' (central executive) to create more sophisticated agents.
MiniAgents
MiniAgents is an open-source Python framework designed to simplify the creation of multi-agent AI systems. It offers a parallelism and async-first design, allowing users to focus on building intelligent agents while handling concurrency challenges. The framework, built on asyncio, supports LLM-based applications with immutable messages and seamless asynchronous token and message streaming between agents.
garak
Garak is a vulnerability scanner designed for LLMs (Large Language Models) that checks for various weaknesses such as hallucination, data leakage, prompt injection, misinformation, toxicity generation, and jailbreaks. It combines static, dynamic, and adaptive probes to explore vulnerabilities in LLMs. Garak is a free tool developed for red-teaming and assessment purposes, focusing on making LLMs or dialog systems fail. It supports various LLM models and can be used to assess their security and robustness.
vectorflow
VectorFlow is an open source, high throughput, fault tolerant vector embedding pipeline. It provides a simple API endpoint for ingesting large volumes of raw data, processing, and storing or returning the vectors quickly and reliably. The tool supports text-based files like TXT, PDF, HTML, and DOCX, and can be run locally with Kubernetes in production. VectorFlow offers functionalities like embedding documents, running chunking schemas, custom chunking, and integrating with vector databases like Pinecone, Qdrant, and Weaviate. It enforces a standardized schema for uploading data to a vector store and supports features like raw embeddings webhook, chunk validation webhook, S3 endpoint, and telemetry. The tool can be used with the Python client and provides detailed instructions for running and testing the functionalities.
LayerSkip
LayerSkip is an implementation enabling early exit inference and self-speculative decoding. It provides a code base for running models trained using the LayerSkip recipe, offering speedup through self-speculative decoding. The tool integrates with Hugging Face transformers and provides checkpoints for various LLMs. Users can generate tokens, benchmark on datasets, evaluate tasks, and sweep over hyperparameters to optimize inference speed. The tool also includes correctness verification scripts and Docker setup instructions. Additionally, other implementations like gpt-fast and Native HuggingFace are available. Training implementation is a work-in-progress, and contributions are welcome under the CC BY-NC license.
paper-qa
PaperQA is a minimal package for question and answering from PDFs or text files, providing very good answers with in-text citations. It uses OpenAI Embeddings to embed and search documents, and follows a process of embedding docs and queries, searching for top passages, creating summaries, scoring and selecting relevant summaries, putting summaries into prompt, and generating answers. Users can customize prompts and use various models for embeddings and LLMs. The tool can be used asynchronously and supports adding documents from paths, files, or URLs.
safety-tooling
This repository, safety-tooling, is designed to be shared across various AI Safety projects. It provides an LLM API with a common interface for OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google models. The aim is to facilitate collaboration among AI Safety researchers, especially those with limited software engineering backgrounds, by offering a platform for contributing to a larger codebase. The repo can be used as a git submodule for easy collaboration and updates. It also supports pip installation for convenience. The repository includes features for installation, secrets management, linting, formatting, Redis configuration, testing, dependency management, inference, finetuning, API usage tracking, and various utilities for data processing and experimentation.
invariant
Invariant Analyzer is an open-source scanner designed for LLM-based AI agents to find bugs, vulnerabilities, and security threats. It scans agent execution traces to identify issues like looping behavior, data leaks, prompt injections, and unsafe code execution. The tool offers a library of built-in checkers, an expressive policy language, data flow analysis, real-time monitoring, and extensible architecture for custom checkers. It helps developers debug AI agents, scan for security violations, and prevent security issues and data breaches during runtime. The analyzer leverages deep contextual understanding and a purpose-built rule matching engine for security policy enforcement.

ash_ai
Ash AI is a tool that provides a Model Context Protocol (MCP) server for exposing tool definitions to an MCP client. It allows for the installation of dev and production MCP servers, and supports features like OAuth2 flow with AshAuthentication, tool data access, tool execution callbacks, prompt-backed actions, and vectorization strategies. Users can also generate a chat feature for their Ash & Phoenix application using `ash_oban` and `ash_postgres`, and specify LLM API keys for OpenAI. The tool is designed to help developers experiment with tools and actions, monitor tool execution, and expose actions as tool calls.
For similar tasks

py-vectara-agentic
The `vectara-agentic` Python library is designed for developing powerful AI assistants using Vectara and Agentic-RAG. It supports various agent types, includes pre-built tools for domains like finance and legal, and enables easy creation of custom AI assistants and agents. The library provides tools for summarizing text, rephrasing text, legal tasks like summarizing legal text and critiquing as a judge, financial tasks like analyzing balance sheets and income statements, and database tools for inspecting and querying databases. It also supports observability via LlamaIndex and Arize Phoenix integration.
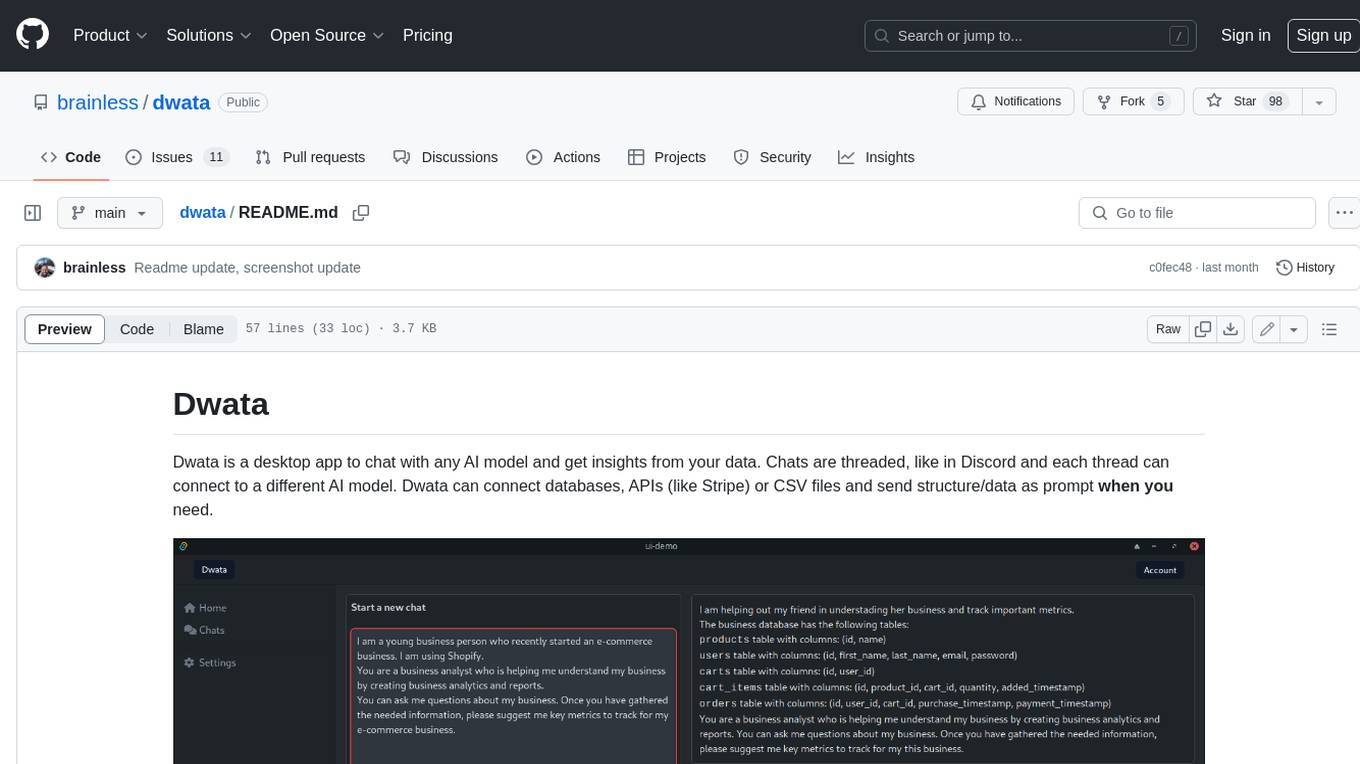
dwata
Dwata is a desktop application that allows users to chat with any AI model and gain insights from their data. Chats are organized into threads, similar to Discord, with each thread connecting to a different AI model. Dwata can connect to databases, APIs (such as Stripe), or CSV files and send structured data as prompts when needed. The AI's response will often include SQL or Python code, which can be used to extract the desired insights. Dwata can validate AI-generated SQL to ensure that the tables and columns referenced are correct and can execute queries against the database from within the application. Python code (typically using Pandas) can also be executed from within Dwata, although this feature is still in development. Dwata supports a range of AI models, including OpenAI's GPT-4, GPT-4 Turbo, and GPT-3.5 Turbo; Groq's LLaMA2-70b and Mixtral-8x7b; Phind's Phind-34B and Phind-70B; Anthropic's Claude; and Ollama's Llama 2, Mistral, and Phi-2 Gemma. Dwata can compare chats from different models, allowing users to see the responses of multiple models to the same prompts. Dwata can connect to various data sources, including databases (PostgreSQL, MySQL, MongoDB), SaaS products (Stripe, Shopify), CSV files/folders, and email (IMAP). The desktop application does not collect any private or business data without the user's explicit consent.
aiosqlite
aiosqlite is a Python library that provides a friendly, async interface to SQLite databases. It replicates the standard sqlite3 module but with async versions of all the standard connection and cursor methods, along with context managers for automatically closing connections and cursors. It allows interaction with SQLite databases on the main AsyncIO event loop without blocking execution of other coroutines while waiting for queries or data fetches. The library also replicates most of the advanced features of sqlite3, such as row factories and total changes tracking.
sqlcoder
Defog's SQLCoder is a family of state-of-the-art large language models (LLMs) designed for converting natural language questions into SQL queries. It outperforms popular open-source models like gpt-4 and gpt-4-turbo on SQL generation tasks. SQLCoder has been trained on more than 20,000 human-curated questions based on 10 different schemas, and the model weights are licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0. Users can interact with SQLCoder through the 'transformers' library and run queries using the 'sqlcoder launch' command in the terminal. The tool has been tested on NVIDIA GPUs with more than 16GB VRAM and Apple Silicon devices with some limitations. SQLCoder offers a demo on their website and supports quantized versions of the model for consumer GPUs with sufficient memory.
app
WebDB is a comprehensive and free database Integrated Development Environment (IDE) designed to maximize efficiency in database development and management. It simplifies and enhances database operations with features like DBMS discovery, query editor, time machine, NoSQL structure inferring, modern ERD visualization, and intelligent data generator. Developed with robust web technologies, WebDB is suitable for both novice and experienced database professionals.
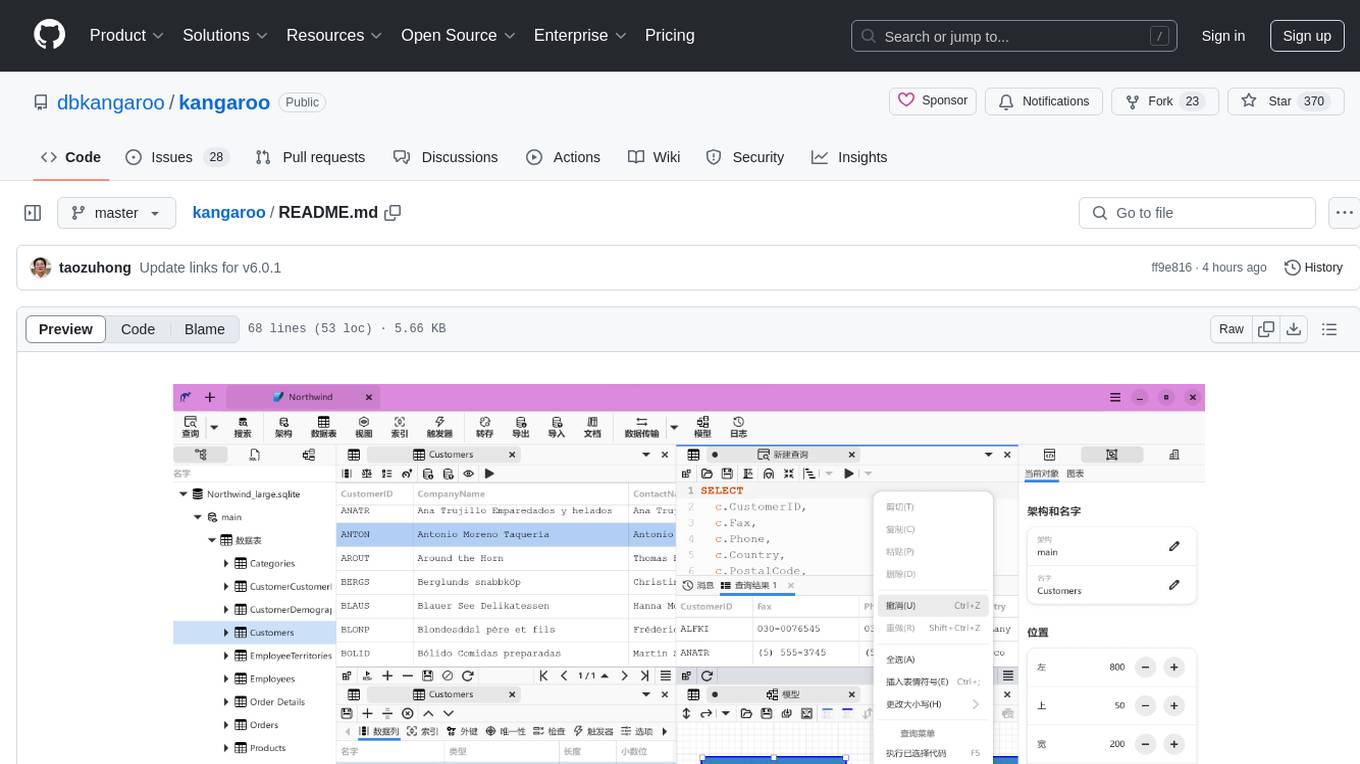
kangaroo
Kangaroo is an AI-powered SQL client and admin tool for popular databases like SQLite, MySQL, PostgreSQL, etc. It supports various functionalities such as table design, query, model, sync, export/import, and more. The tool is designed to be comfortable, fun, and developer-friendly, with features like code intellisense and autocomplete. Kangaroo aims to provide a seamless experience for database management across different operating systems.
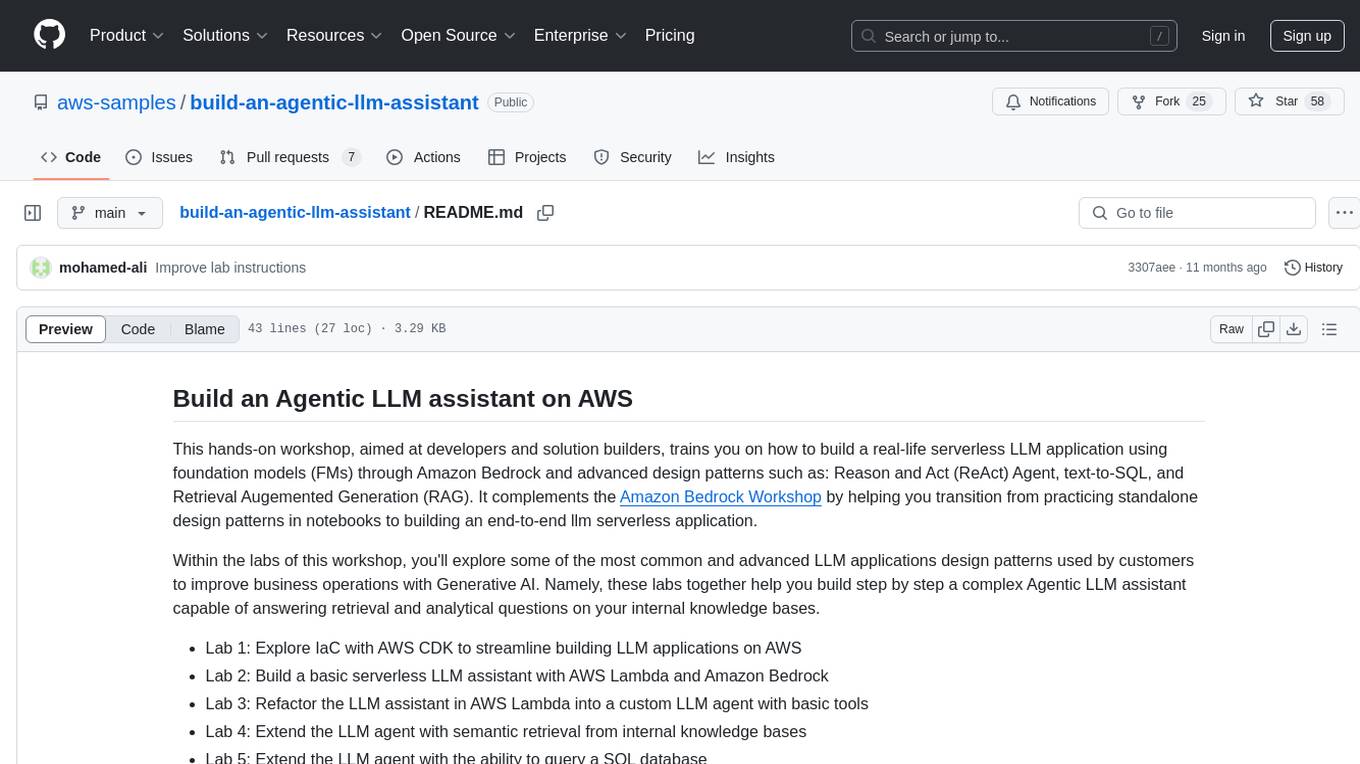
build-an-agentic-llm-assistant
This repository provides a hands-on workshop for developers and solution builders to build a real-life serverless LLM application using foundation models (FMs) through Amazon Bedrock and advanced design patterns such as Reason and Act (ReAct) Agent, text-to-SQL, and Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG). It guides users through labs to explore common and advanced LLM application design patterns, helping them build a complex Agentic LLM assistant capable of answering retrieval and analytical questions on internal knowledge bases. The repository includes labs on IaC with AWS CDK, building serverless LLM assistants with AWS Lambda and Amazon Bedrock, refactoring LLM assistants into custom agents, extending agents with semantic retrieval, and querying SQL databases. Users need to set up AWS Cloud9, configure model access on Amazon Bedrock, and use Amazon SageMaker Studio environment to run data-pipelines notebooks.
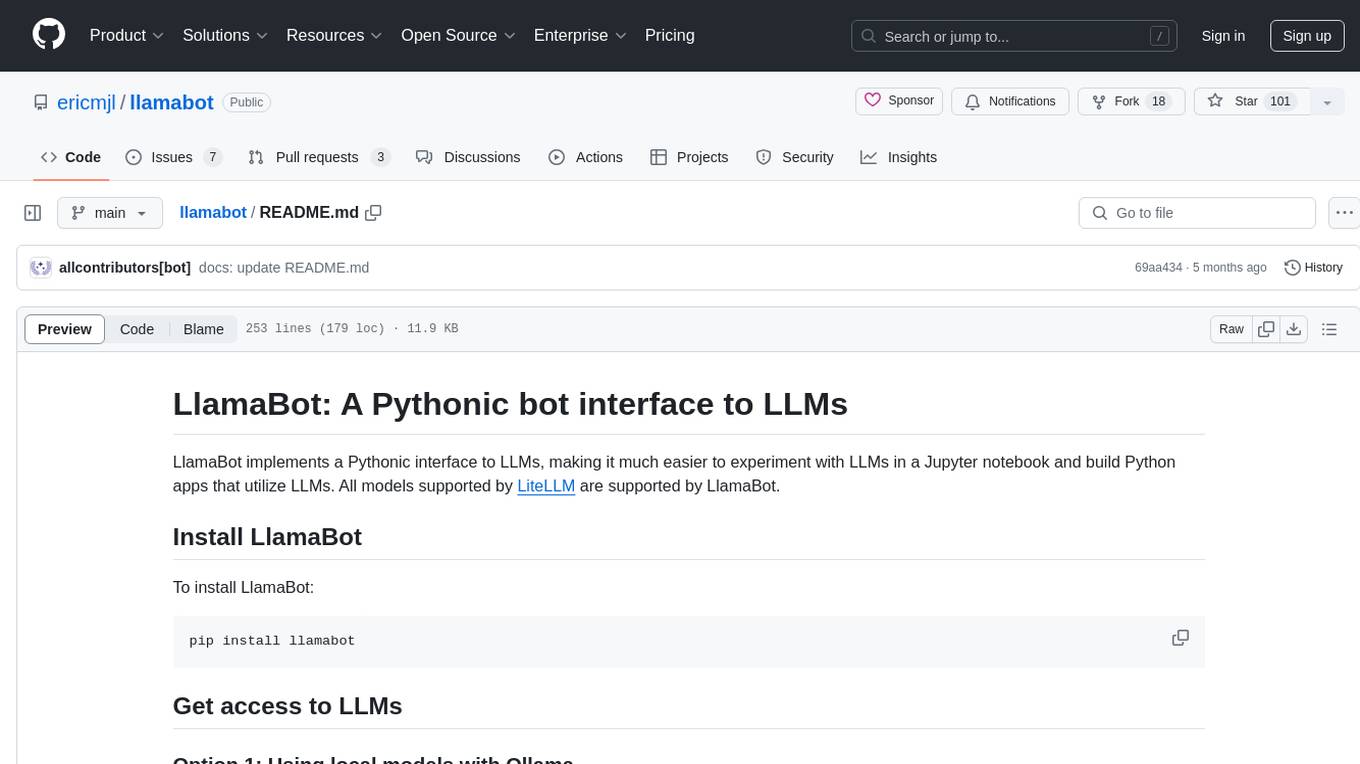
llamabot
LlamaBot is a Pythonic bot interface to Large Language Models (LLMs), providing an easy way to experiment with LLMs in Jupyter notebooks and build Python apps utilizing LLMs. It supports all models available in LiteLLM. Users can access LLMs either through local models with Ollama or by using API providers like OpenAI and Mistral. LlamaBot offers different bot interfaces like SimpleBot, ChatBot, QueryBot, and ImageBot for various tasks such as rephrasing text, maintaining chat history, querying documents, and generating images. The tool also includes CLI demos showcasing its capabilities and supports contributions for new features and bug reports from the community.
For similar jobs

promptflow
**Prompt flow** is a suite of development tools designed to streamline the end-to-end development cycle of LLM-based AI applications, from ideation, prototyping, testing, evaluation to production deployment and monitoring. It makes prompt engineering much easier and enables you to build LLM apps with production quality.

deepeval
DeepEval is a simple-to-use, open-source LLM evaluation framework specialized for unit testing LLM outputs. It incorporates various metrics such as G-Eval, hallucination, answer relevancy, RAGAS, etc., and runs locally on your machine for evaluation. It provides a wide range of ready-to-use evaluation metrics, allows for creating custom metrics, integrates with any CI/CD environment, and enables benchmarking LLMs on popular benchmarks. DeepEval is designed for evaluating RAG and fine-tuning applications, helping users optimize hyperparameters, prevent prompt drifting, and transition from OpenAI to hosting their own Llama2 with confidence.

MegaDetector
MegaDetector is an AI model that identifies animals, people, and vehicles in camera trap images (which also makes it useful for eliminating blank images). This model is trained on several million images from a variety of ecosystems. MegaDetector is just one of many tools that aims to make conservation biologists more efficient with AI. If you want to learn about other ways to use AI to accelerate camera trap workflows, check out our of the field, affectionately titled "Everything I know about machine learning and camera traps".

leapfrogai
LeapfrogAI is a self-hosted AI platform designed to be deployed in air-gapped resource-constrained environments. It brings sophisticated AI solutions to these environments by hosting all the necessary components of an AI stack, including vector databases, model backends, API, and UI. LeapfrogAI's API closely matches that of OpenAI, allowing tools built for OpenAI/ChatGPT to function seamlessly with a LeapfrogAI backend. It provides several backends for various use cases, including llama-cpp-python, whisper, text-embeddings, and vllm. LeapfrogAI leverages Chainguard's apko to harden base python images, ensuring the latest supported Python versions are used by the other components of the stack. The LeapfrogAI SDK provides a standard set of protobuffs and python utilities for implementing backends and gRPC. LeapfrogAI offers UI options for common use-cases like chat, summarization, and transcription. It can be deployed and run locally via UDS and Kubernetes, built out using Zarf packages. LeapfrogAI is supported by a community of users and contributors, including Defense Unicorns, Beast Code, Chainguard, Exovera, Hypergiant, Pulze, SOSi, United States Navy, United States Air Force, and United States Space Force.

llava-docker
This Docker image for LLaVA (Large Language and Vision Assistant) provides a convenient way to run LLaVA locally or on RunPod. LLaVA is a powerful AI tool that combines natural language processing and computer vision capabilities. With this Docker image, you can easily access LLaVA's functionalities for various tasks, including image captioning, visual question answering, text summarization, and more. The image comes pre-installed with LLaVA v1.2.0, Torch 2.1.2, xformers 0.0.23.post1, and other necessary dependencies. You can customize the model used by setting the MODEL environment variable. The image also includes a Jupyter Lab environment for interactive development and exploration. Overall, this Docker image offers a comprehensive and user-friendly platform for leveraging LLaVA's capabilities.

carrot
The 'carrot' repository on GitHub provides a list of free and user-friendly ChatGPT mirror sites for easy access. The repository includes sponsored sites offering various GPT models and services. Users can find and share sites, report errors, and access stable and recommended sites for ChatGPT usage. The repository also includes a detailed list of ChatGPT sites, their features, and accessibility options, making it a valuable resource for ChatGPT users seeking free and unlimited GPT services.

TrustLLM
TrustLLM is a comprehensive study of trustworthiness in LLMs, including principles for different dimensions of trustworthiness, established benchmark, evaluation, and analysis of trustworthiness for mainstream LLMs, and discussion of open challenges and future directions. Specifically, we first propose a set of principles for trustworthy LLMs that span eight different dimensions. Based on these principles, we further establish a benchmark across six dimensions including truthfulness, safety, fairness, robustness, privacy, and machine ethics. We then present a study evaluating 16 mainstream LLMs in TrustLLM, consisting of over 30 datasets. The document explains how to use the trustllm python package to help you assess the performance of your LLM in trustworthiness more quickly. For more details about TrustLLM, please refer to project website.

AI-YinMei
AI-YinMei is an AI virtual anchor Vtuber development tool (N card version). It supports fastgpt knowledge base chat dialogue, a complete set of solutions for LLM large language models: [fastgpt] + [one-api] + [Xinference], supports docking bilibili live broadcast barrage reply and entering live broadcast welcome speech, supports Microsoft edge-tts speech synthesis, supports Bert-VITS2 speech synthesis, supports GPT-SoVITS speech synthesis, supports expression control Vtuber Studio, supports painting stable-diffusion-webui output OBS live broadcast room, supports painting picture pornography public-NSFW-y-distinguish, supports search and image search service duckduckgo (requires magic Internet access), supports image search service Baidu image search (no magic Internet access), supports AI reply chat box [html plug-in], supports AI singing Auto-Convert-Music, supports playlist [html plug-in], supports dancing function, supports expression video playback, supports head touching action, supports gift smashing action, supports singing automatic start dancing function, chat and singing automatic cycle swing action, supports multi scene switching, background music switching, day and night automatic switching scene, supports open singing and painting, let AI automatically judge the content.