
Step-DPO
Implementation for "Step-DPO: Step-wise Preference Optimization for Long-chain Reasoning of LLMs"
Stars: 155
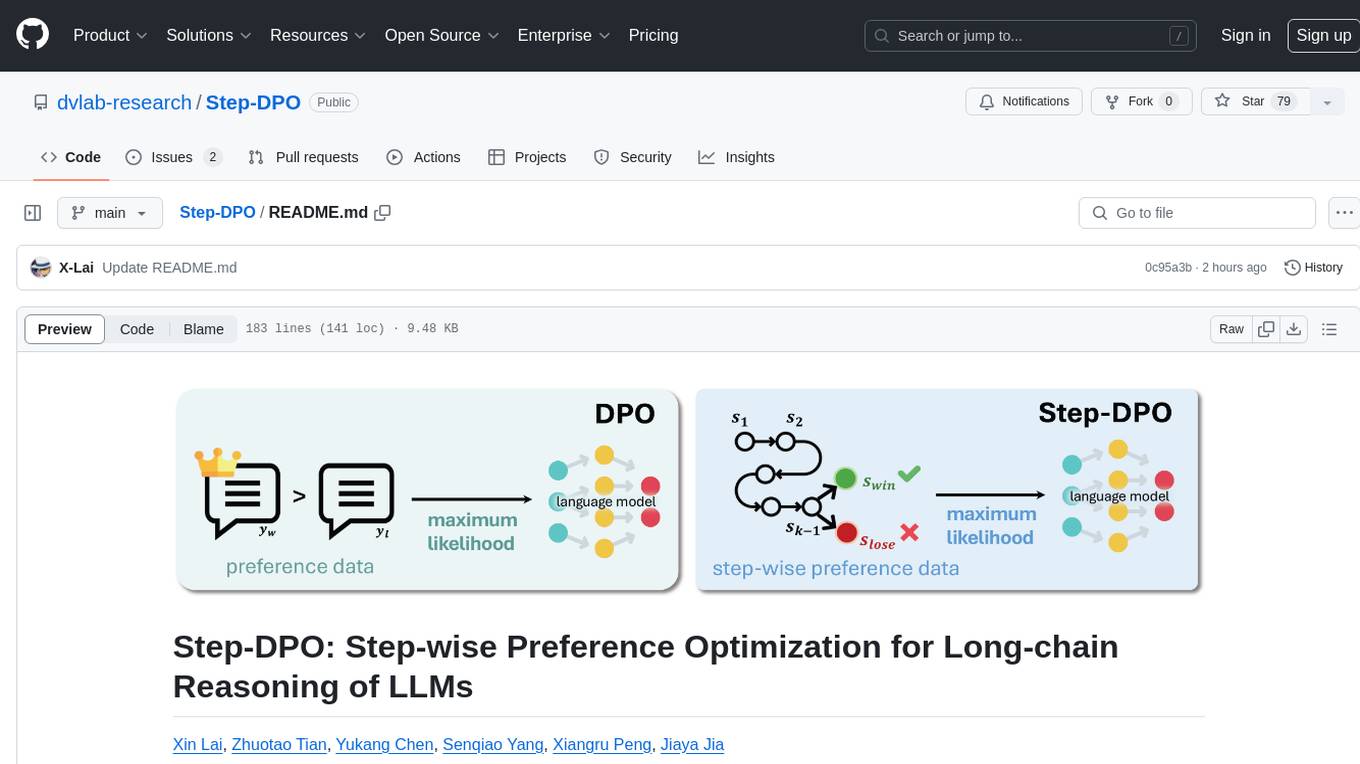
Step-DPO is a method for enhancing long-chain reasoning ability of LLMs with a data construction pipeline creating a high-quality dataset. It significantly improves performance on math and GSM8K tasks with minimal data and training steps. The tool fine-tunes pre-trained models like Qwen2-7B-Instruct with Step-DPO, achieving superior results compared to other models. It provides scripts for training, evaluation, and deployment, along with examples and acknowledgements.
README:
Xin Lai, Zhuotao Tian, Yukang Chen, Senqiao Yang, Xiangru Peng, Jiaya Jia
This repo provides the implementation of Step-DPO, a simple, effective, and data-efficient method for boosting the long-chain reasoning ability of LLMs, with a data construction pipeline that yields a high-quality dataset containing 10K step-wise preference pairs.
Notably, Step-DPO boosts the performance of Qwen2-7B-Instruct from 53.0% to 58.6% on MATH, and 85.5% to 87.9% on GSM8K, with as few as 10K data and hundreds of training steps!
Moreover, Step-DPO, when applied to Qwen2-72B-Instruct, achieves scores of 70.8% and 94.0% on the test sets of MATH and GSM8K, respectively, surpassing a series of closed-source models without bells and wistles, including GPT-4-1106, Claude-3-Opus, and Gemini-1.5-Pro.
- News
- Datasets
- Models
- Installation
- Training
- Evaluation
- Data Construction Pipeline
- Deployment
- Examples
- Acknowledgement
- Citation
- [x] [2024.7.7] We release the scripts for Data Construction Pipeline! You can construct dataset on your own with these scripts!
- [x] [2024.7.1] We release the demo of the model Qwen2-7B-Instruct-Step-DPO. Welcome to try it on Demo!
- [x] [2024.6.28] We release the pre-print of Step-DPO and this GitHub repo, including training/evaluation scripts, pre-trained models and data.
We build a 10K math preference datasets for Step-DPO, which can be downloaded from the following link.
| Dataset | Size | Link |
|---|---|---|
| xinlai/Math-Step-DPO-10K | 10,795 | 🤗 Hugging Face |
It is notable that the model Qwen2-72B-Instruct + Step-DPO could achieve 70.8% and 94.0% on MATH and GSM8K test sets. Step-DPO also brings considerable improvement over various models as follows. Welcome to download and use.
| Models | Size | MATH | GSM8K | Odyssey-MATH | Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qwen2-7B-Instruct | 7B | 53.0 | 85.5 | - | - |
| Qwen2-7B-Instruct + Step-DPO | 7B | 58.6 (+5.6) | 87.9 (+2.4) | - | 🤗 HF |
| DeepSeekMath-RL | 7B | 51.7 | 88.2 | - | - |
| DeepSeekMath-RL + Step-DPO | 7B | 53.2 (+1.5) | 88.7 (+0.5) | - | 🤗 HF |
| Qwen2-7B-SFT | 7B | 54.8 | 88.2 | - | 🤗 HF |
| Qwen2-7B-SFT + Step-DPO | 7B | 55.8 (+1.0) | 88.5 (+0.3) | - | 🤗 HF |
| Qwen1.5-32B-SFT | 32B | 54.9 | 90.0 | - | 🤗 HF |
| Qwen1.5-32B-SFT + Step-DPO | 32B | 56.9 (+2.0) | 90.9 (+0.9) | - | 🤗 HF |
| Qwen2-57B-A14B-SFT | 57B | 54.6 | 89.8 | - | 🤗 HF |
| Qwen2-57B-A14B-SFT + Step-DPO | 57B | 56.5 (+1.9) | 90.0 (+0.2) | - | 🤗 HF |
| Llama-3-70B-SFT | 70B | 56.9 | 92.2 | - | 🤗 HF |
| Llama-3-70B-SFT + Step-DPO | 70B | 59.5 (+2.6) | 93.3 (+1.1) | - | 🤗 HF |
| Qwen2-72B-SFT | 72B | 61.7 | 92.9 | 44.2 | 🤗 HF |
| Qwen2-72B-SFT + Step-DPO | 72B | 64.7 (+3.0) | 93.9 (+1.0) | 47.0 (+2.8) | 🤗 HF |
| Qwen2-72B-Instruct | 72B | 69.4 | 92.4 | 47.0 | - |
| Qwen2-72B-Instruct + Step-DPO | 72B | 70.8 (+1.4) | 94.0 (+1.6) | 50.1 (+3.1) | 🤗 HF |
Note: Odyssey-MATH contains competition-level math problems.
conda create -n step_dpo python=3.10
conda activate step_dpo
pip install -r requirements.txt
We use Qwen2, Qwen1.5, Llama-3, and DeepSeekMath models as the pre-trained weights and fine-tune them with Step-DPO. Download based on your choices.
Note: models with '-SFT' are supervised fine-tuned by our 299K SFT data based on open-source base models. You could perform Step-DPO on either our SFT models or existing open-source instruct models.
Here is a script example to perform Step-DPO on Qwen/Qwen2-72B-Instruct:
ACCELERATE_LOG_LEVEL=info accelerate launch --config_file accelerate_configs/deepspeed_zero3_cpu.yaml --mixed_precision bf16 \
--num_processes 8 \
train.py configs/config_full.yaml \
--model_name_or_path="Qwen/Qwen2-72B-Instruct" \
--data_path="xinlai/Math-Step-DPO-10K" \
--per_device_train_batch_size=2 \
--gradient_accumulation_steps=8 \
--torch_dtype=bfloat16 \
--bf16=True \
--beta=0.4 \
--num_train_epochs=4 \
--save_strategy='steps' \
--save_steps=200 \
--save_total_limit=1 \
--output_dir=outputs/qwen2-72b-instruct-step-dpo \
--hub_model_id=qwen2-72b-instruct-step-dpo \
--prompt=qwen2-boxedHere are script examples to evaluate fine-tuned models on both GSM8K and MATH test sets:
python eval_math.py \
--model outputs/qwen2-72b-instruct-step-dpo \
--data_file ./data/test/GSM8K_test_data.jsonl \
--save_path 'eval_results/gsm8k/qwen2-72b-instruct-step-dpo.json' \
--prompt 'qwen2-boxed' \
--tensor_parallel_size 8
python eval_math.py \
--model outputs/qwen2-72b-instruct-step-dpo \
--data_file ./data/test/MATH_test_data.jsonl \
--save_path 'eval_results/math/qwen2-72b-instruct-step-dpo.json' \
--prompt 'qwen2-boxed' \
--tensor_parallel_size 8
We release the scripts to construct the Step-DPO data, as shown in the data_pipeline/ directory. Please follow the instructions below.
cd Step-DPO
# Step 1: Error Collection
# Before executing, please set the MODEL_PATH, PRED_PATH, EVAL_PROMPT
bash data_pipeline/step1.sh
# Step 2: Locate Erroneous Step by GPT-4o
# Before executing, please set the OPENAI_BASE_URL, OPENAI_API_KEY
bash data_pipeline/step2.sh
# Step 3: Rectify by the model itself
# Before executing, please set the MODEL_PATH, EVAL_PROMPT, JSON_FILE, PRED_PATH, SAVE_PATH
bash data_pipeline/step3.sh
# Finally, Get the resulting dataset
# Before executing, please set the EVAL_PROMPT, JSON_FILE, PRED_PATH, SAVE_PATH
bash data_pipeline/merge.sh
For deployment, please directly use the following command:
python3 app.py --model_path_or_name xinlai/Qwen2-7B-Instruct-Step-DPO
This repository is based on alignment-handbook, DeepSeekMath, and MetaMath.
Many thanks for their efforts!
If you find this project useful in your research, please consider citing us:
@article{lai2024stepdpo,
title={Step-DPO: Step-wise Preference Optimization for Long-chain Reasoning of LLMs},
author={Xin Lai and Zhuotao Tian and Yukang Chen and Senqiao Yang and Xiangru Peng and Jiaya Jia},
journal={arXiv:2406.18629},
year={2024}
}
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for Step-DPO
Similar Open Source Tools

Step-DPO
Step-DPO is a method for enhancing long-chain reasoning ability of LLMs with a data construction pipeline creating a high-quality dataset. It significantly improves performance on math and GSM8K tasks with minimal data and training steps. The tool fine-tunes pre-trained models like Qwen2-7B-Instruct with Step-DPO, achieving superior results compared to other models. It provides scripts for training, evaluation, and deployment, along with examples and acknowledgements.
speechless
Speechless.AI is committed to integrating the superior language processing and deep reasoning capabilities of large language models into practical business applications. By enhancing the model's language understanding, knowledge accumulation, and text creation abilities, and introducing long-term memory, external tool integration, and local deployment, our aim is to establish an intelligent collaborative partner that can independently interact, continuously evolve, and closely align with various business scenarios.

Xwin-LM
Xwin-LM is a powerful and stable open-source tool for aligning large language models, offering various alignment technologies like supervised fine-tuning, reward models, reject sampling, and reinforcement learning from human feedback. It has achieved top rankings in benchmarks like AlpacaEval and surpassed GPT-4. The tool is continuously updated with new models and features.
DataFlow
DataFlow is a data preparation and training system designed to parse, generate, process, and evaluate high-quality data from noisy sources, improving the performance of large language models in specific domains. It constructs diverse operators and pipelines, validated to enhance domain-oriented LLM's performance in fields like healthcare, finance, and law. DataFlow also features an intelligent DataFlow-agent capable of dynamically assembling new pipelines by recombining existing operators on demand.
Open-dLLM
Open-dLLM is the most open release of a diffusion-based large language model, providing pretraining, evaluation, inference, and checkpoints. It introduces Open-dCoder, the code-generation variant of Open-dLLM. The repo offers a complete stack for diffusion LLMs, enabling users to go from raw data to training, checkpoints, evaluation, and inference in one place. It includes pretraining pipeline with open datasets, inference scripts for easy sampling and generation, evaluation suite with various metrics, weights and checkpoints on Hugging Face, and transparent configs for full reproducibility.

MOSS-TTS
MOSS-TTS Family is an open-source speech and sound generation model family designed for high-fidelity, high-expressiveness, and complex real-world scenarios. It includes five production-ready models: MOSS-TTS, MOSS-TTSD, MOSS-VoiceGenerator, MOSS-TTS-Realtime, and MOSS-SoundEffect, each serving specific purposes in speech generation, dialogue, voice design, real-time interactions, and sound effect generation. The models offer features like long-speech generation, fine-grained control over phonemes and duration, multilingual synthesis, voice cloning, and real-time voice agents.
LlamaV-o1
LlamaV-o1 is a Large Multimodal Model designed for spontaneous reasoning tasks. It outperforms various existing models on multimodal reasoning benchmarks. The project includes a Step-by-Step Visual Reasoning Benchmark, a novel evaluation metric, and a combined Multi-Step Curriculum Learning and Beam Search Approach. The model achieves superior performance in complex multi-step visual reasoning tasks in terms of accuracy and efficiency.
Native-LLM-for-Android
This repository provides a demonstration of running a native Large Language Model (LLM) on Android devices. It supports various models such as Qwen2.5-Instruct, MiniCPM-DPO/SFT, Yuan2.0, Gemma2-it, StableLM2-Chat/Zephyr, and Phi3.5-mini-instruct. The demo models are optimized for extreme execution speed after being converted from HuggingFace or ModelScope. Users can download the demo models from the provided drive link, place them in the assets folder, and follow specific instructions for decompression and model export. The repository also includes information on quantization methods and performance benchmarks for different models on various devices.
InternLM
InternLM is a powerful language model series with features such as 200K context window for long-context tasks, outstanding comprehensive performance in reasoning, math, code, chat experience, instruction following, and creative writing, code interpreter & data analysis capabilities, and stronger tool utilization capabilities. It offers models in sizes of 7B and 20B, suitable for research and complex scenarios. The models are recommended for various applications and exhibit better performance than previous generations. InternLM models may match or surpass other open-source models like ChatGPT. The tool has been evaluated on various datasets and has shown superior performance in multiple tasks. It requires Python >= 3.8, PyTorch >= 1.12.0, and Transformers >= 4.34 for usage. InternLM can be used for tasks like chat, agent applications, fine-tuning, deployment, and long-context inference.
END-TO-END-GENERATIVE-AI-PROJECTS
The 'END TO END GENERATIVE AI PROJECTS' repository is a collection of awesome industry projects utilizing Large Language Models (LLM) for various tasks such as chat applications with PDFs, image to speech generation, video transcribing and summarizing, resume tracking, text to SQL conversion, invoice extraction, medical chatbot, financial stock analysis, and more. The projects showcase the deployment of LLM models like Google Gemini Pro, HuggingFace Models, OpenAI GPT, and technologies such as Langchain, Streamlit, LLaMA2, LLaMAindex, and more. The repository aims to provide end-to-end solutions for different AI applications.
EVE
EVE is an official PyTorch implementation of Unveiling Encoder-Free Vision-Language Models. The project aims to explore the removal of vision encoders from Vision-Language Models (VLMs) and transfer LLMs to encoder-free VLMs efficiently. It also focuses on bridging the performance gap between encoder-free and encoder-based VLMs. EVE offers a superior capability with arbitrary image aspect ratio, data efficiency by utilizing publicly available data for pre-training, and training efficiency with a transparent and practical strategy for developing a pure decoder-only architecture across modalities.
RLinf
RLinf is a flexible and scalable open-source infrastructure designed for post-training foundation models via reinforcement learning. It provides a robust backbone for next-generation training, supporting open-ended learning, continuous generalization, and limitless possibilities in intelligence development. The tool offers unique features like Macro-to-Micro Flow, flexible execution modes, auto-scheduling strategy, embodied agent support, and fast adaptation for mainstream VLA models. RLinf is fast with hybrid mode and automatic online scaling strategy, achieving significant throughput improvement and efficiency. It is also flexible and easy to use with multiple backend integrations, adaptive communication, and built-in support for popular RL methods. The roadmap includes system-level enhancements and application-level extensions to support various training scenarios and models. Users can get started with complete documentation, quickstart guides, key design principles, example gallery, advanced features, and guidelines for extending the framework. Contributions are welcome, and users are encouraged to cite the GitHub repository and acknowledge the broader open-source community.
awesome-ai-efficiency
Awesome AI Efficiency is a curated list of resources dedicated to enhancing efficiency in AI systems. The repository covers various topics essential for optimizing AI models and processes, aiming to make AI faster, cheaper, smaller, and greener. It includes topics like quantization, pruning, caching, distillation, factorization, compilation, parameter-efficient fine-tuning, speculative decoding, hardware optimization, training techniques, inference optimization, sustainability strategies, and scalability approaches.
Video-ChatGPT
Video-ChatGPT is a video conversation model that aims to generate meaningful conversations about videos by combining large language models with a pretrained visual encoder adapted for spatiotemporal video representation. It introduces high-quality video-instruction pairs, a quantitative evaluation framework for video conversation models, and a unique multimodal capability for video understanding and language generation. The tool is designed to excel in tasks related to video reasoning, creativity, spatial and temporal understanding, and action recognition.
MMOS
MMOS (Mix of Minimal Optimal Sets) is a dataset designed for math reasoning tasks, offering higher performance and lower construction costs. It includes various models and data subsets for tasks like arithmetic reasoning and math word problem solving. The dataset is used to identify minimal optimal sets through reasoning paths and statistical analysis, with a focus on QA-pairs generated from open-source datasets. MMOS also provides an auto problem generator for testing model robustness and scripts for training and inference.
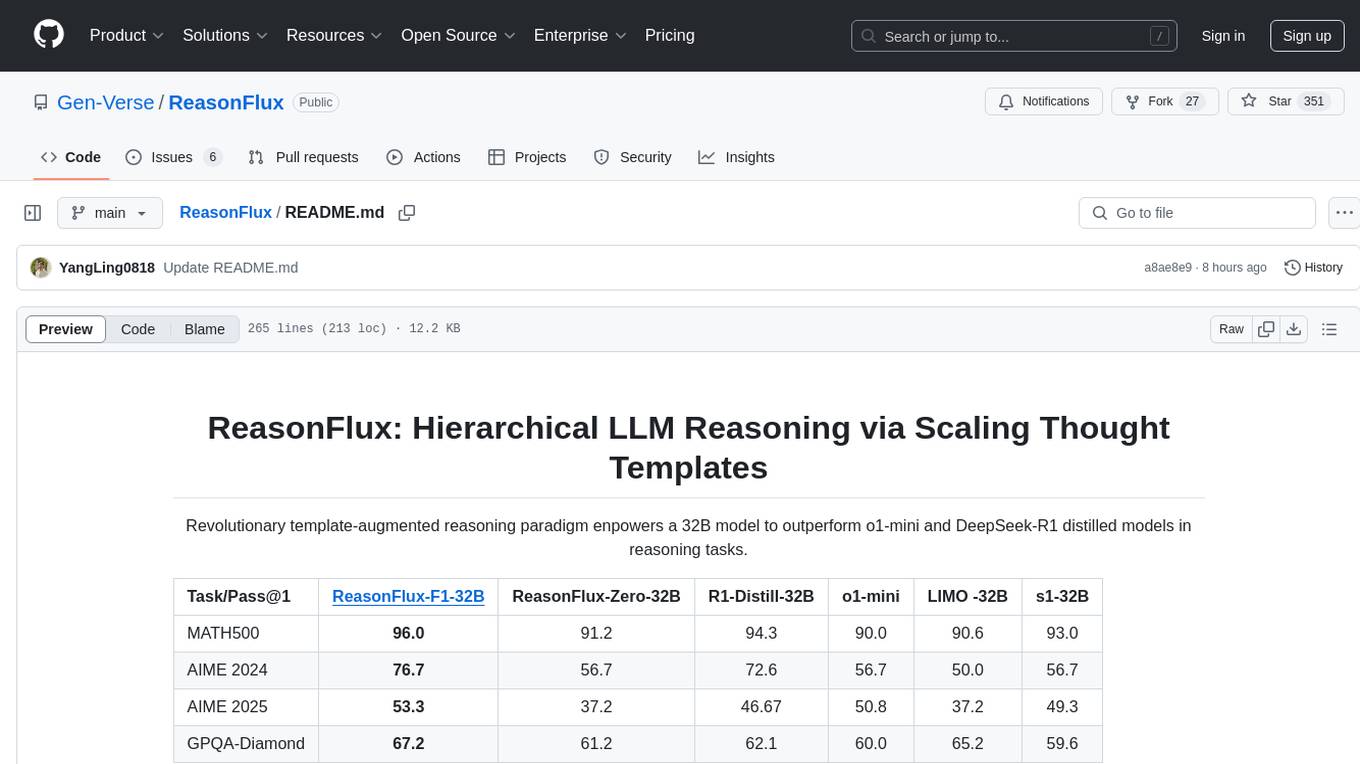
ReasonFlux
ReasonFlux is a revolutionary template-augmented reasoning paradigm that empowers a 32B model to outperform other models in reasoning tasks. The repository provides official resources for the paper 'ReasonFlux: Hierarchical LLM Reasoning via Scaling Thought Templates', including the latest released model ReasonFlux-F1-32B. It includes updates, dataset links, model zoo, getting started guide, training instructions, evaluation details, inference examples, performance comparisons, reasoning examples, preliminary work references, and citation information.
For similar tasks
hume-python-sdk
The Hume AI Python SDK allows users to integrate Hume APIs directly into their Python applications. Users can access complete documentation, quickstart guides, and example notebooks to get started. The SDK is designed to provide support for Hume's expressive communication platform built on scientific research. Users are encouraged to create an account at beta.hume.ai and stay updated on changes through Discord. The SDK may undergo breaking changes to improve tooling and ensure reliable releases in the future.

Step-DPO
Step-DPO is a method for enhancing long-chain reasoning ability of LLMs with a data construction pipeline creating a high-quality dataset. It significantly improves performance on math and GSM8K tasks with minimal data and training steps. The tool fine-tunes pre-trained models like Qwen2-7B-Instruct with Step-DPO, achieving superior results compared to other models. It provides scripts for training, evaluation, and deployment, along with examples and acknowledgements.
mimir
MIMIR is a Python package designed for measuring memorization in Large Language Models (LLMs). It provides functionalities for conducting experiments related to membership inference attacks on LLMs. The package includes implementations of various attacks such as Likelihood, Reference-based, Zlib Entropy, Neighborhood, Min-K% Prob, Min-K%++, Gradient Norm, and allows users to extend it by adding their own datasets and attacks.
TriForce
TriForce is a training-free tool designed to accelerate long sequence generation. It supports long-context Llama models and offers both on-chip and offloading capabilities. Users can achieve a 2.2x speedup on a single A100 GPU. TriForce also provides options for offloading with tensor parallelism or without it, catering to different hardware configurations. The tool includes a baseline for comparison and is optimized for performance on RTX 4090 GPUs. Users can cite the associated paper if they find TriForce useful for their projects.
agentdojo
AgentDojo is a dynamic environment designed to evaluate prompt injection attacks and defenses for large language models (LLM) agents. It provides a benchmark script to run different suites and tasks with specified LLM models, defenses, and attacks. The tool is under active development, and users can inspect the results through dedicated documentation pages and the Invariant Benchmark Registry.

ai-on-gke
This repository contains assets related to AI/ML workloads on Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE). Run optimized AI/ML workloads with Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) platform orchestration capabilities. A robust AI/ML platform considers the following layers: Infrastructure orchestration that support GPUs and TPUs for training and serving workloads at scale Flexible integration with distributed computing and data processing frameworks Support for multiple teams on the same infrastructure to maximize utilization of resources

ray
Ray is a unified framework for scaling AI and Python applications. It consists of a core distributed runtime and a set of AI libraries for simplifying ML compute, including Data, Train, Tune, RLlib, and Serve. Ray runs on any machine, cluster, cloud provider, and Kubernetes, and features a growing ecosystem of community integrations. With Ray, you can seamlessly scale the same code from a laptop to a cluster, making it easy to meet the compute-intensive demands of modern ML workloads.

labelbox-python
Labelbox is a data-centric AI platform for enterprises to develop, optimize, and use AI to solve problems and power new products and services. Enterprises use Labelbox to curate data, generate high-quality human feedback data for computer vision and LLMs, evaluate model performance, and automate tasks by combining AI and human-centric workflows. The academic & research community uses Labelbox for cutting-edge AI research.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.












