AReaL
Lightning-Fast RL for LLM Reasoning and Agents. Made Simple & Flexible.
Stars: 3573
AReaL (Ant Reasoning RL) is an open-source reinforcement learning system developed at the RL Lab, Ant Research. It is designed for training Large Reasoning Models (LRMs) in a fully open and inclusive manner. AReaL provides reproducible experiments for 1.5B and 7B LRMs, showcasing its scalability and performance across diverse computational budgets. The system follows an iterative training process to enhance model performance, with a focus on mathematical reasoning tasks. AReaL is equipped to adapt to different computational resource settings, enabling users to easily configure and launch training trials. Future plans include support for advanced models, optimizations for distributed training, and exploring research topics to enhance LRMs' reasoning capabilities.
README:
| Paper | Documentation | Ask DeepWiki | 🤗 Models & Data |
![]() WeChat (微信) Group |
WeChat (微信) Group |
AReaL is an open-source fully asynchronous reinforcement learning training system for large reasoning and agentic models, developed by members from Tsinghua IIIS and the AReaL Team at Ant Group. Built upon the open-source project ReaLHF, we are fully committed to open-source principles by providing the training details, data, and infrastructure required to reproduce our results, along with the models themselves. AReaL aims to help everyone build their own AI agents easily and affordably. Our team loves milk tea because it's delicious, customizable, and affordable—we hope you enjoy our project just as much as you'd enjoy real milk tea. Cheers!
AReaL Highlights
- ⚡ Flexibility: Seamless customization for multi-turn agentic rollout with other agentic frameworks.
- 📈 Scalability: Stable fully asynchronous RL training with industry-leading speed.
- ✨ Cutting-Edge Performance: State-of-the-art math, coding, search, and customer service agents.
[2026/02/06] We are delighted to introduce EigenData, a self-evolving data synthesis engine. Combined with RL training on AReaL, the 235B MoE model surpasses Gemini 3.0 Pro and GPT 5.2 on $\tau^2$-bench! Check out the paper, code, and announcement on X.
[2026/01/15] Congrats to our friends at CAMEL-AI for open-sourcing SETA, their terminal agent RL project trained with AReaL! Check out their training workflow and the announcement on X.
[2026/01/01] Happy New Year! Thanks to the outstanding contribution from
@HwVanICI, we are excited to officially announce stable support for AReaL training on
Ascend NPU devices! The code is actively maintained and continuously updated in the
ascend branch. Check out
our documentation
to get started, and feel free to report any issues!
📋 Previous Releases
[2025/08/30] Introducing ASearcher, a state-of-the-art search agent built with AReaL's end-to-end asynchronous RL training. Check out the paper and the open-source repository!
[2025/07/31] (AReaL-lite) We introduce AReaL-lite, a lightweight version of AReaL designed specifically for AI researchers and rapid prototyping. AReaL-lite features an algorithm-first API design that prioritizes ease of use and algorithm development, while natively supporting fully asynchronous agentic RL. With 80% fewer lines of code, AReaL-lite maintains 90% of AReaL's performance and core functionality. Check out our AReaL-lite design documentation and the quickstart guide to begin your journey with AReaL-lite!
[2025/06/03] (v0.3, boba²) We release boba² (double-boba) for fully asynchronous RL training, which achieves 2.77× speedup while delivering comparable or superior training performance compared to synchronous systems. Furthermore, asynchronous RL significantly simplifies multi-turn agentic RL training setup! Check out our v0.3 overview blog and the research paper.
[2025/03/31] (v0.2, boba) Introducing our milestone release—boba! Please call it A-ReaL-boba! This release features significantly faster training with SGLang support and state-of-the-art 7B and 32B models for mathematical reasoning. Check out our v0.2 technical blog.
[2025/02/24] (v0.1) Our initial release includes reproducible results for 1.5B and 7B Large Reasoning Models (LRMs). Check out our v0.1 technical blog.
First, install the package:
git clone https://github.com/inclusionAI/AReaL
cd AReaL
pip install uv
uv sync --extra cudaOur training scripts automatically download the required dataset (openai/gsm8k) and model (Qwen/Qwen2-1.5B-Instruct). To run on a single node:
python3 examples/math/gsm8k_rl.py --config examples/math/gsm8k_grpo.yaml scheduler.type=localTo run on a Ray cluster with 2 nodes and 8 GPUs per node (remember to update paths in the YAML file to point to your shared storage):
python3 examples/math/gsm8k_rl.py --config examples/math/gsm8k_grpo.yaml \
cluster.n_nodes=2 cluster.n_gpus_per_node=8 \
scheduler.type=rayFor comprehensive setup instructions, see our quickstart guide.
| Task | Description | Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Math | GSM8K math reasoning with GRPO, PPO, DAPO, REINFORCE, RLOO, LitePPO, DR-GRPO, GSPO, and more | - |
| Multi-Turn Math | Multi-turn math agent with reward discounting across turns | Training Curve |
| LoRA Math | Parameter-efficient math training with LoRA (SGLang/vLLM backends) | - |
| Countdown | Countdown numbers game with custom rewards | Training Curve |
| Task | Description | Performance |
|---|---|---|
| General Agent | General agentic training with any agentic frameworks | Guide |
| Tau2 Customer Service | Customer service agent on Tau2-Bench (retail, airline, telecom) | Paper |
| Search Agent | End-to-end search agent with Tongyi-DeepResearch workflow | Training Curve |
| Tool-Integrated Reasoning | Multi-turn tool calling during reasoning (Python executor, calculator) | Training Curve |
| OpenAI Agents Integration | Integration with OpenAI Agents SDK for agentic workflows | - |
| CAMEL-AI Integration | Integration with CAMEL-AI framework for agentic RL | - |
| Task | Description | Performance |
|---|---|---|
| VLM | Geometry3K and CLEVR Count 70K visual reasoning with GRPO | - |
| VLM on NPU | VLM training on Huawei NPU hardware | Benchmark Results |
| Task | Description | Performance |
|---|---|---|
| RLHF Reward Modeling | Bradley-Terry reward modeling on Anthropic HH-RLHF | Training Curve |
| SkyPilot Deployment | Cloud deployment with SkyPilot (GCP, AWS, Kubernetes) | Screenshots |
All RL algorithms support both asynchronous and synchronous versions by setting
max_head_offpolicyness=0. See Asynchronous RL Guide.
| Algorithm | Documentation | Paper | Configuration |
|---|---|---|---|
| GRPO | 📖 Docs | 📄 Paper | 🔗 GSM8K Example |
| GSPO | 📖 Docs | 📄 Paper | 🔗 GSM8K Example |
| PPO | 📖 Docs | 📄 Paper | 🔗 GSM8K Example |
| DAPO | 📖 Docs | 📄 Paper | 🔗 GSM8K Example |
| LitePPO | 📖 Docs | 📄 Paper | 🔗 GSM8K Example |
| Dr.GRPO | 📖 Docs | 📄 Paper | 🔗 GSM8K Example |
| REINFORCE++ | - | 📄 Paper | 🔗 GSM8K Example |
| RLOO | 📖 Docs | 📄 Paper | 🔗 GSM8K Example |
| SAPO | 📖 Docs | 📄 Paper | 🔗 GSM8K Example |
| M2PO | 📖 Docs | 📄 Paper | 🔗 GSM8K Example |
| RLHF Reward Modeling | - | - | 🔗 RLHF Example |
| SFT | - | - | 🔗 GSM8K Example |
| Model Family | Megatron | PyTorch FSDP | PyTorch Archon | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qwen2/3 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | - |
| Qwen3-MoE | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | - |
| Qwen2.5-VL | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | Vision-language model |
| Qwen3-VL | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | Vision-language model |
| Gemma 3 | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | Vision-language model |
| Other Hugging Face LLM | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | Compatibility depending on the version of transformers
|
Check the AI Coding Assistant Guide and Archon Reference for how to integrate new models into AReaL.
| Backend | DP | Tensor Parallel | Sequence Parallel within TP | Context Parallel | Pipeline Parallel | Expert Parallel | 1D Sequence Packing | LoRA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Megatron | ✅ (ZeRO-1) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
| PyTorch FSDP | ✅ (FSDP2) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ |
| PyTorch Archon | ✅ (FSDP2) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
| Backend | Tensor Parallel | Context Parallel | Pipeline Parallel | Data Parallel Attention | Expert Parallel |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| vLLM | ✅ | ❓ | ✅ | ❓ | ❓ |
| SGLang | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ |
- Improving Algorithm Performance
- Agent Workflow Best Practices
- Debugging
- Handling OOM Issues
- Performance Profiling
- CLI Configurations
- Checkpointing
- Metrics Tracking
- Allocation Mode
- Rollout Workflow
- Agent Workflow
- AI-Assisted Development
We warmly welcome contributions from the community! Whether you're fixing bugs, adding features, improving documentation, or helping others, your contribution is valued. Please check our Contributing Guide for detailed information.
# Fork and clone the repository
git clone https://github.com/YOUR-USERNAME/AReaL
cd AReaL
# Install uv and sync dependencies
pip install uv
# Use `--extra cuda` on Linux with CUDA for full functionality
uv sync --extra cuda --group dev
# Or without CUDA support
# uv sync --group dev
# Set up pre-commit hooks for automatic formatting
pre-commit install
# Make changes
git checkout -b feat/gpt-o5
git add .
# `git commit` will automatically format your file
git commit -m "Implement gpt-o5 training loop"
git pushAReaL is under active development with planned minor releases weekly and major releases monthly. We warmly welcome community engagement and contributions. We are also actively hiring interns and full-time employees with open positions in both the US and China.
We gratefully acknowledge that major contributors are from the AReaL Team at the Institute for Interdisciplinary Information Sciences (IIIS), Tsinghua University and Ant Group.
We have also received invaluable assistance from the following groups (listed alphabetically):
-
The Data Intelligence Lab at Ant Research for their data support
-
@HwVanICI for support on vLLM, LoRA, NPU integration, and more
-
The Relaxed System Lab at HKUST for seamless collaboration on numerous system-related aspects
-
The SGLang team for supporting custom weight update features and their contributions during AReaL-lite development
-
The Super Computing Technology (SCT) team at Ant Group for their expertise in large-scale cluster operations and maintenance
-
Special thanks to @Lyken17 for providing valuable suggestions throughout the API design process
We also deeply appreciate all pioneering work from the community, particularly the ReaLHF project from OpenPsi Inc. and other outstanding projects, including but not limited to DeepScaleR, Open-Reasoner-Zero, OpenRLHF, VeRL, SGLang, QwQ, Light-R1, and DAPO.
@inproceedings{mei2025real,
author = {Mei, Zhiyu and Fu, Wei and Li, Kaiwei and Wang, Guangju and Zhang, Huanchen and Wu, Yi},
title = {ReaL: Efficient RLHF Training of Large Language Models with Parameter Reallocation},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the Eighth Conference on Machine Learning and Systems,
MLSys 2025, Santa Clara, CA, USA, May 12-15, 2025},
publisher = {mlsys.org},
year = {2025},
}@misc{fu2025areal,
title={AReaL: A Large-Scale Asynchronous Reinforcement Learning System for Language Reasoning},
author={Wei Fu and Jiaxuan Gao and Xujie Shen and Chen Zhu and Zhiyu Mei and Chuyi He and Shusheng Xu and Guo Wei and Jun Mei and Jiashu Wang and Tongkai Yang and Binhang Yuan and Yi Wu},
year={2025},
eprint={2505.24298},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.LG},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2505.24298},
}For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for AReaL
Similar Open Source Tools

AReaL
AReaL (Ant Reasoning RL) is an open-source reinforcement learning system developed at the RL Lab, Ant Research. It is designed for training Large Reasoning Models (LRMs) in a fully open and inclusive manner. AReaL provides reproducible experiments for 1.5B and 7B LRMs, showcasing its scalability and performance across diverse computational budgets. The system follows an iterative training process to enhance model performance, with a focus on mathematical reasoning tasks. AReaL is equipped to adapt to different computational resource settings, enabling users to easily configure and launch training trials. Future plans include support for advanced models, optimizations for distributed training, and exploring research topics to enhance LRMs' reasoning capabilities.
pai-opencode
PAI-OpenCode is a complete port of Daniel Miessler's Personal AI Infrastructure (PAI) to OpenCode, an open-source, provider-agnostic AI coding assistant. It brings modular capabilities, dynamic multi-agent orchestration, session history, and lifecycle automation to personalize AI assistants for users. With support for 75+ AI providers, PAI-OpenCode offers dynamic per-task model routing, full PAI infrastructure, real-time session sharing, and multiple client options. The tool optimizes cost and quality with a 3-tier model strategy and a 3-tier research system, allowing users to switch presets for different routing strategies. PAI-OpenCode's architecture preserves PAI's design while adapting to OpenCode, documented through Architecture Decision Records (ADRs).

motia
Motia is an AI agent framework designed for software engineers to create, test, and deploy production-ready AI agents quickly. It provides a code-first approach, allowing developers to write agent logic in familiar languages and visualize execution in real-time. With Motia, developers can focus on business logic rather than infrastructure, offering zero infrastructure headaches, multi-language support, composable steps, built-in observability, instant APIs, and full control over AI logic. Ideal for building sophisticated agents and intelligent automations, Motia's event-driven architecture and modular steps enable the creation of GenAI-powered workflows, decision-making systems, and data processing pipelines.
sktime
sktime is a Python library for time series analysis that provides a unified interface for various time series learning tasks such as classification, regression, clustering, annotation, and forecasting. It offers time series algorithms and tools compatible with scikit-learn for building, tuning, and validating time series models. sktime aims to enhance the interoperability and usability of the time series analysis ecosystem by empowering users to apply algorithms across different tasks and providing interfaces to related libraries like scikit-learn, statsmodels, tsfresh, PyOD, and fbprophet.

Athena-Public
Project Athena is a Linux OS designed for AI Agents, providing memory, persistence, scheduling, and governance for AI models. It offers a comprehensive memory layer that survives across sessions, models, and IDEs, allowing users to own their data and port it anywhere. The system is built bottom-up through 1,079+ sessions, focusing on depth and compounding knowledge. Athena features a trilateral feedback loop for cross-model validation, a Model Context Protocol server with 9 tools, and a robust security model with data residency options. The repository structure includes an SDK package, examples for quickstart, scripts, protocols, workflows, and deep documentation. Key concepts cover architecture, knowledge graph, semantic memory, and adaptive latency. Workflows include booting, reasoning modes, planning, research, and iteration. The project has seen significant content expansion, viral validation, and metrics improvements.
UniCoT
Uni-CoT is a unified reasoning framework that extends Chain-of-Thought (CoT) principles to the multimodal domain, enabling Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) to perform interpretable, step-by-step reasoning across both text and vision. It decomposes complex multimodal tasks into structured, manageable steps that can be executed sequentially or in parallel, allowing for more scalable and systematic reasoning.
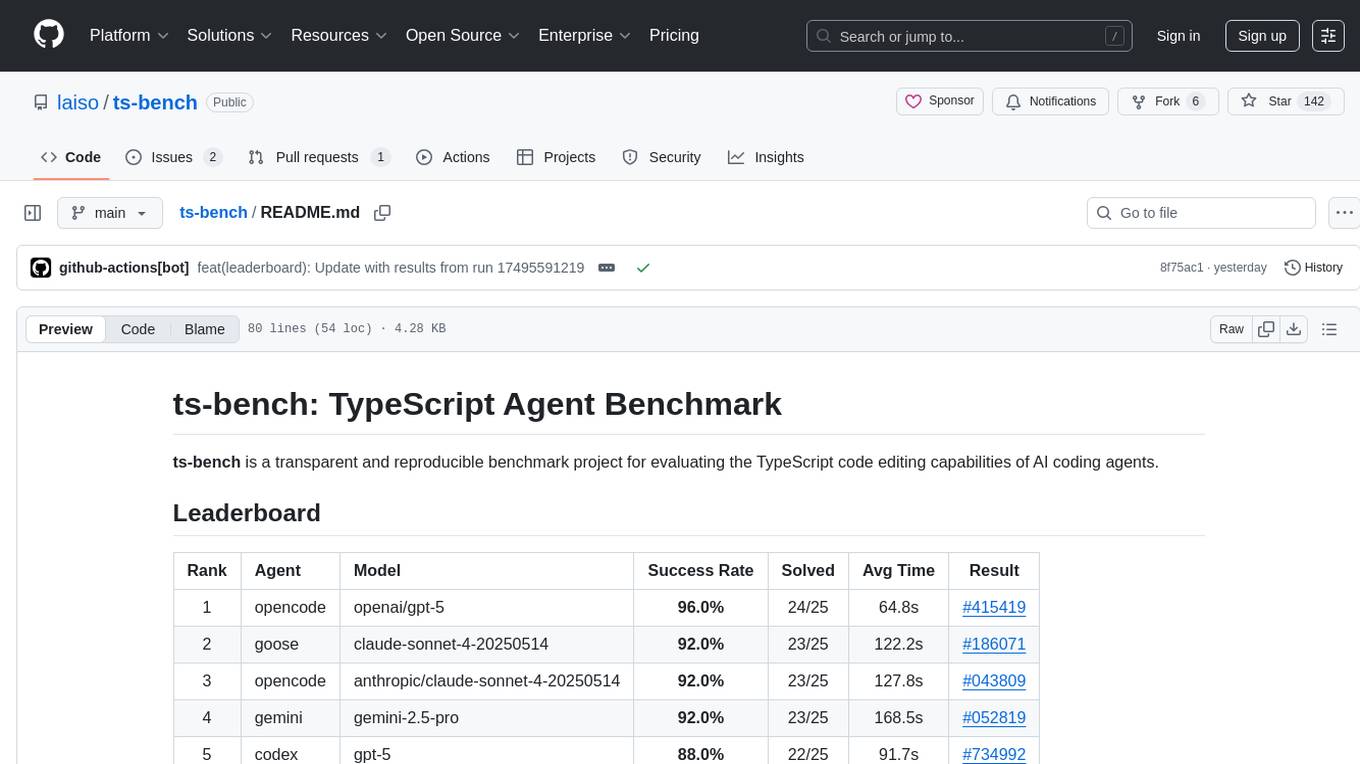
ts-bench
TS-Bench is a performance benchmarking tool for TypeScript projects. It provides detailed insights into the performance of TypeScript code, helping developers optimize their projects. With TS-Bench, users can measure and compare the execution time of different code snippets, functions, or modules. The tool offers a user-friendly interface for running benchmarks and analyzing the results. TS-Bench is a valuable asset for developers looking to enhance the performance of their TypeScript applications.

EasyEdit
EasyEdit is a Python package for edit Large Language Models (LLM) like `GPT-J`, `Llama`, `GPT-NEO`, `GPT2`, `T5`(support models from **1B** to **65B**), the objective of which is to alter the behavior of LLMs efficiently within a specific domain without negatively impacting performance across other inputs. It is designed to be easy to use and easy to extend.
spark-nlp
Spark NLP is a state-of-the-art Natural Language Processing library built on top of Apache Spark. It provides simple, performant, and accurate NLP annotations for machine learning pipelines that scale easily in a distributed environment. Spark NLP comes with 36000+ pretrained pipelines and models in more than 200+ languages. It offers tasks such as Tokenization, Word Segmentation, Part-of-Speech Tagging, Named Entity Recognition, Dependency Parsing, Spell Checking, Text Classification, Sentiment Analysis, Token Classification, Machine Translation, Summarization, Question Answering, Table Question Answering, Text Generation, Image Classification, Image to Text (captioning), Automatic Speech Recognition, Zero-Shot Learning, and many more NLP tasks. Spark NLP is the only open-source NLP library in production that offers state-of-the-art transformers such as BERT, CamemBERT, ALBERT, ELECTRA, XLNet, DistilBERT, RoBERTa, DeBERTa, XLM-RoBERTa, Longformer, ELMO, Universal Sentence Encoder, Llama-2, M2M100, BART, Instructor, E5, Google T5, MarianMT, OpenAI GPT2, Vision Transformers (ViT), OpenAI Whisper, and many more not only to Python and R, but also to JVM ecosystem (Java, Scala, and Kotlin) at scale by extending Apache Spark natively.
HuatuoGPT-II
HuatuoGPT2 is an innovative domain-adapted medical large language model that excels in medical knowledge and dialogue proficiency. It showcases state-of-the-art performance in various medical benchmarks, surpassing GPT-4 in expert evaluations and fresh medical licensing exams. The open-source release includes HuatuoGPT2 models in 7B, 13B, and 34B versions, training code for one-stage adaptation, partial pre-training and fine-tuning instructions, and evaluation methods for medical response capabilities and professional pharmacist exams. The tool aims to enhance LLM capabilities in the Chinese medical field through open-source principles.
microgpt-c
MicroGPT-C is a project that focuses on tiny specialist models working together to outperform monoliths on specific tasks. It is a C port of a Python GPT model, rewritten in pure C99 with zero dependencies. The project explores the concept of coordinated intelligence through 'organelles' that differentiate based on training data, resulting in improved performance across logic games and real-world data experiments.

deepfabric
DeepFabric is a CLI tool and SDK designed for researchers and developers to generate high-quality synthetic datasets at scale using large language models. It leverages a graph and tree-based architecture to create diverse and domain-specific datasets while minimizing redundancy. The tool supports generating Chain of Thought datasets for step-by-step reasoning tasks and offers multi-provider support for using different language models. DeepFabric also allows for automatic dataset upload to Hugging Face Hub and uses YAML configuration files for flexibility in dataset generation.
IDvs.MoRec
This repository contains the source code for the SIGIR 2023 paper 'Where to Go Next for Recommender Systems? ID- vs. Modality-based Recommender Models Revisited'. It provides resources for evaluating foundation, transferable, multi-modal, and LLM recommendation models, along with datasets, pre-trained models, and training strategies for IDRec and MoRec using in-batch debiased cross-entropy loss. The repository also offers large-scale datasets, code for SASRec with in-batch debias cross-entropy loss, and information on joining the lab for research opportunities.
qserve
QServe is a serving system designed for efficient and accurate Large Language Models (LLM) on GPUs with W4A8KV4 quantization. It achieves higher throughput compared to leading industry solutions, allowing users to achieve A100-level throughput on cheaper L40S GPUs. The system introduces the QoQ quantization algorithm with 4-bit weight, 8-bit activation, and 4-bit KV cache, addressing runtime overhead challenges. QServe improves serving throughput for various LLM models by implementing compute-aware weight reordering, register-level parallelism, and fused attention memory-bound techniques.
axonhub
AxonHub is an all-in-one AI development platform that serves as an AI gateway allowing users to switch between model providers without changing any code. It provides features like vendor lock-in prevention, integration simplification, observability enhancement, and cost control. Users can access any model using any SDK with zero code changes. The platform offers full request tracing, enterprise RBAC, smart load balancing, and real-time cost tracking. AxonHub supports multiple databases, provides a unified API gateway, and offers flexible model management and API key creation for authentication. It also integrates with various AI coding tools and SDKs for seamless usage.
For similar tasks

AReaL
AReaL (Ant Reasoning RL) is an open-source reinforcement learning system developed at the RL Lab, Ant Research. It is designed for training Large Reasoning Models (LRMs) in a fully open and inclusive manner. AReaL provides reproducible experiments for 1.5B and 7B LRMs, showcasing its scalability and performance across diverse computational budgets. The system follows an iterative training process to enhance model performance, with a focus on mathematical reasoning tasks. AReaL is equipped to adapt to different computational resource settings, enabling users to easily configure and launch training trials. Future plans include support for advanced models, optimizations for distributed training, and exploring research topics to enhance LRMs' reasoning capabilities.
lighteval
LightEval is a lightweight LLM evaluation suite that Hugging Face has been using internally with the recently released LLM data processing library datatrove and LLM training library nanotron. We're releasing it with the community in the spirit of building in the open. Note that it is still very much early so don't expect 100% stability ^^' In case of problems or question, feel free to open an issue!
Firefly
Firefly is an open-source large model training project that supports pre-training, fine-tuning, and DPO of mainstream large models. It includes models like Llama3, Gemma, Qwen1.5, MiniCPM, Llama, InternLM, Baichuan, ChatGLM, Yi, Deepseek, Qwen, Orion, Ziya, Xverse, Mistral, Mixtral-8x7B, Zephyr, Vicuna, Bloom, etc. The project supports full-parameter training, LoRA, QLoRA efficient training, and various tasks such as pre-training, SFT, and DPO. Suitable for users with limited training resources, QLoRA is recommended for fine-tuning instructions. The project has achieved good results on the Open LLM Leaderboard with QLoRA training process validation. The latest version has significant updates and adaptations for different chat model templates.
Awesome-Text2SQL
Awesome Text2SQL is a curated repository containing tutorials and resources for Large Language Models, Text2SQL, Text2DSL, Text2API, Text2Vis, and more. It provides guidelines on converting natural language questions into structured SQL queries, with a focus on NL2SQL. The repository includes information on various models, datasets, evaluation metrics, fine-tuning methods, libraries, and practice projects related to Text2SQL. It serves as a comprehensive resource for individuals interested in working with Text2SQL and related technologies.
create-million-parameter-llm-from-scratch
The 'create-million-parameter-llm-from-scratch' repository provides a detailed guide on creating a Large Language Model (LLM) with 2.3 million parameters from scratch. The blog replicates the LLaMA approach, incorporating concepts like RMSNorm for pre-normalization, SwiGLU activation function, and Rotary Embeddings. The model is trained on a basic dataset to demonstrate the ease of creating a million-parameter LLM without the need for a high-end GPU.
StableToolBench
StableToolBench is a new benchmark developed to address the instability of Tool Learning benchmarks. It aims to balance stability and reality by introducing features such as a Virtual API System with caching and API simulators, a new set of solvable queries determined by LLMs, and a Stable Evaluation System using GPT-4. The Virtual API Server can be set up either by building from source or using a prebuilt Docker image. Users can test the server using provided scripts and evaluate models with Solvable Pass Rate and Solvable Win Rate metrics. The tool also includes model experiments results comparing different models' performance.
BetaML.jl
The Beta Machine Learning Toolkit is a package containing various algorithms and utilities for implementing machine learning workflows in multiple languages, including Julia, Python, and R. It offers a range of supervised and unsupervised models, data transformers, and assessment tools. The models are implemented entirely in Julia and are not wrappers for third-party models. Users can easily contribute new models or request implementations. The focus is on user-friendliness rather than computational efficiency, making it suitable for educational and research purposes.
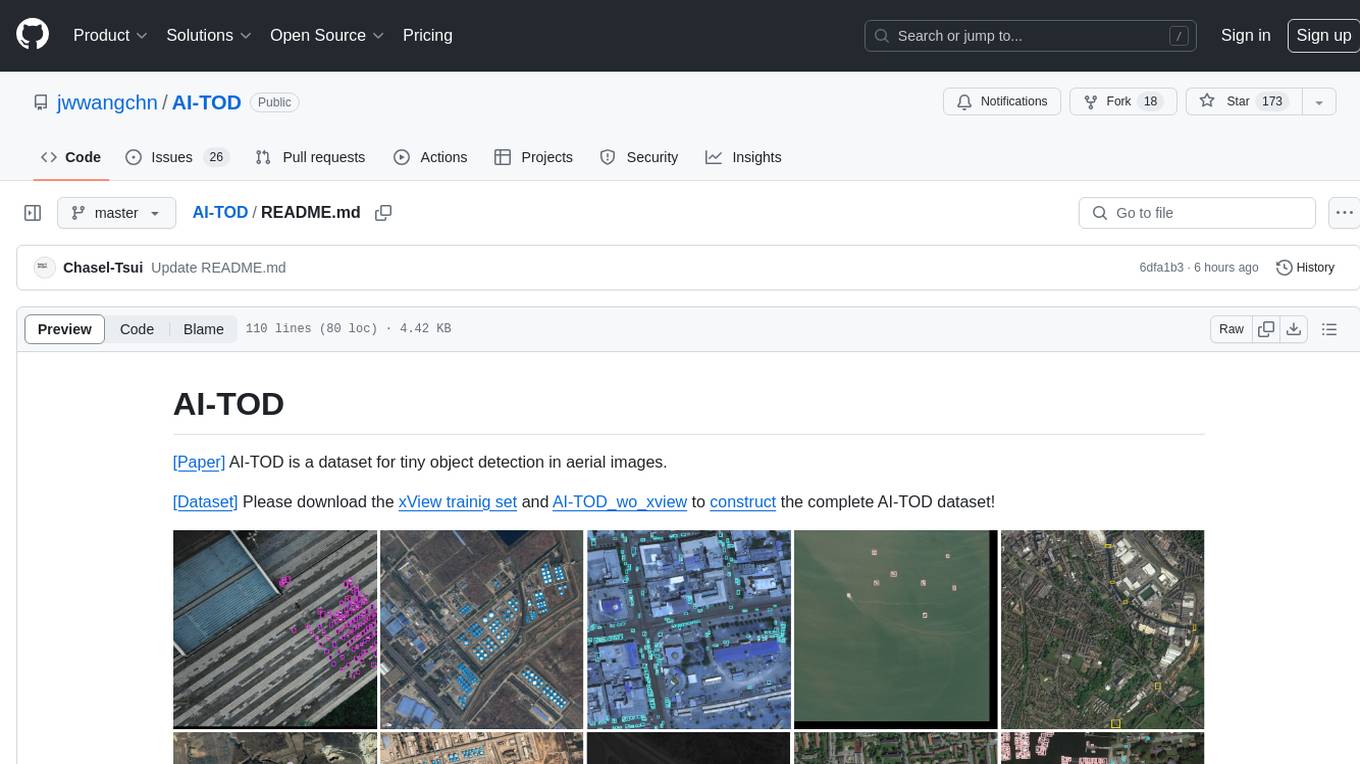
AI-TOD
AI-TOD is a dataset for tiny object detection in aerial images, containing 700,621 object instances across 28,036 images. Objects in AI-TOD are smaller with a mean size of 12.8 pixels compared to other aerial image datasets. To use AI-TOD, download xView training set and AI-TOD_wo_xview, then generate the complete dataset using the provided synthesis tool. The dataset is publicly available for academic and research purposes under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.