
BitBLAS
BitBLAS is a library to support mixed-precision matrix multiplications, especially for quantized LLM deployment.
Stars: 502
BitBLAS is a library for mixed-precision BLAS operations on GPUs, for example, the $W_{wdtype}A_{adtype}$ mixed-precision matrix multiplication where $C_{cdtype}[M, N] = A_{adtype}[M, K] \times W_{wdtype}[N, K]$. BitBLAS aims to support efficient mixed-precision DNN model deployment, especially the $W_{wdtype}A_{adtype}$ quantization in large language models (LLMs), for example, the $W_{UINT4}A_{FP16}$ in GPTQ, the $W_{INT2}A_{FP16}$ in BitDistiller, the $W_{INT2}A_{INT8}$ in BitNet-b1.58. BitBLAS is based on techniques from our accepted submission at OSDI'24.
README:
BitBLAS is a library to support mixed-precision BLAS operations on GPUs, for example, the $W_{wdtype}A_{adtype}$ mixed-precision matrix multiplication where $C_{cdtype}[M, N] = A_{adtype}[M, K] \times W_{wdtype}[N, K]$. BitBLAS aims to support efficient mixed-precision DNN model deployment, especially the $W_{wdtype}A_{adtype}$ quantization in large language models (LLMs), for example, the $W_{UINT4}A_{FP16}$ in GPTQ, the $W_{INT2}A_{FP16}$ in BitDistiller, the $W_{INT2}A_{INT8}$ in BitNet-b1.58. BitBLAS is based on techniques from our paper "Ladder: Enabling Efficient Low-Precision Deep Learning Computing through Hardware-aware Tensor Transformation" at OSDI'24.
Some of the key features of BitBLAS include:
- High performance matrix multiplication for both GEMV (e.g., the single batch auto-regressive decode phase in LLM) and GEMM (e.g., the batched auto-regressive decode phase and the prefill phase in LLM):
- $W_{wdtype}A_{adtype}$ mixed-precision matrix multiplication including FP16xFP8/FP4/INT4/2/1, INT8xINT4/2/1, etc. Please checkout support matrix for detailed data types support.
- Matrix multiplication like FP16xFP16 and INT8xINT8.
- Auto-Tensorization for TensorCore-like hardware instructions.
- Implemented integration to PyTorch, GPTQModel, AutoGPTQ, vLLM and BitNet-b1.58 for LLM deployment. Please checkout benchmark summary for detailed end2end LLM inference performance.
- BitBLAS first implemented $W_{INT2}A_{INT8}$ GEMV/GEMM in BitNet-b1.58 with 8x/2x speedup over cuBLAS $W_{FP16}A_{FP16}$ on A100, please checkout op_benchmark_a100_int2_scaling for detailed benchmark results. Please checkout BitNet-b1.58 integration for the integration with the 3rdparty reproduced BitNet-b1.58 model.
- Support customizing mixed-precision DNN operations for your specific scenarios via the flexible DSL (TIR Script).
- 11/04/2024 🚀🚀: We've supported high performance A INT4 x W INT4/INT2 Matmul for BitNet a4.8.
- 10/02/2024 🚀🚀: We've added initial Flash Attention Ops and its implementation in Tilelang! Please refer to PythonAPI and QuickStart docs and PR #202.
- 08/12/2024 🚀🚀: We've improved performance for contiguous batching. To enable it, you'll need to set specific flags. For more details, please refer to PR #133.
- 07/11/2024 ✨: Ladder is published and presented in OSDI'24. Please find Ladder paper and presentation if you are interested in the technical details of BitBLAS.
- 06/25/2024 🚀🚀: BitBLAS has been integrated into GPTQModel! You can now use BitBLAS as a backend in GPTQ.
- 05/04/2024 🚀🚀: We’ve added integration examples for the 1.58-bit model! Check out the files under integration/BitNet.
- 04/30/2024 🚀🚀: BitBLAS now supports FP8 TensorCore ($W_{E5M2/E4M3}A_{E4M3/E5M2}$), providing more combinations beyond the three available in cuBLAS!
- 04/19/2024 ✨: We are excited to announce that BitBLAS, a high-performance library for mixed-precision DNN model deployment, is now open source and available to the public!
BitBLAS achieves exceptional performance across a variety of computational patterns. Below are selected results showcasing its capabilities:
-
End2End Integration with Quantize Inference Kernel for AutoGPTQ and vLLM.
-
Weight Only Matmul performance on A100
-
TensorCore FP16/INT8 GEMM Performance Vs. Vendor Library on A100 and RTX4090
For more detailed information on benchmark sets with other formats (NF4/FP4) and other devices (RTX 3090), please refer to the benchmark.
| A_dtype | W_dtype | Accum_dtype | Out_dtype | BitBLAS Support | Tested Platform |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BF16 | BF16 | FP32 | FP16 | √ | A100(SM_80)/A6000(SM_86) |
| BF16 | FP4_E2M1 | FP32 | FP16 | √ | A100(SM_80)/A6000(SM_86) |
| BF16 | FP8_E4M3 | FP32 | FP16 | √ | A100(SM_80)/A6000(SM_86) |
| BF16 | INT8 | FP32 | FP16 | √ | A100(SM_80)/A6000(SM_86) |
| BF16 | UINT4/INT4 | FP32 | FP16 | √ | A100(SM_80)/A6000(SM_86) |
| BF16 | UINT2/INT2 | FP32 | FP16 | √ | A100(SM_80)/A6000(SM_86) |
| BF16 | UINT1 | FP32 | FP16 | √ | A100(SM_80)/A6000(SM_86) |
| BF16 | NF4 | FP32 | FP16 | √ | A100(SM_80)/A6000(SM_86) |
| FP16 | FP16 | FP32/FP16 | FP16 | √ | V100(SM_70)/A100(SM_80)/A6000(SM_86)/RTX 4090(SM_89) |
| FP16 | FP4_E2M1 | FP32/FP16 | FP16 | √ | V100(SM_70)/A100(SM_80)/A6000(SM_86)/RTX 4090(SM_89) |
| FP16 | FP8_E4M3 | FP32/FP16 | FP16 | √ | V100(SM_70)/A100(SM_80)/A6000(SM_86)/RTX 4090(SM_89) |
| FP16 | INT8 | FP32/FP16 | FP16 | √ | V100(SM_70)/A100(SM_80)/A6000(SM_86)/RTX 4090(SM_89) |
| FP16 | UINT4/INT4 | FP32/FP16 | FP16 | √ | V100(SM_70)/A100(SM_80)/A6000(SM_86)/RTX 4090(SM_89) |
| FP16 | UINT2/INT2 | FP32/FP16 | FP16 | √ | V100(SM_70)/A100(SM_80)/A6000(SM_86)/RTX 4090(SM_89) |
| FP16 | UINT1 | FP32/FP16 | FP16 | √ | V100(SM_70)/A100(SM_80)/A6000(SM_86)/RTX 4090(SM_89) |
| FP16 | NF4 | FP32/FP16 | FP16 | √ | V100(SM_70)/A100(SM_80)/A6000(SM_86)/RTX 4090(SM_89) |
| INT8 | INT8 | INT32 | FP32/INT32/FP16/INT8 | √ | V100(SM_70)/A100(SM_80)/A6000(SM_86)/RTX 4090(SM_89) |
| INT8 | UINT4/INT4 | INT32 | FP32/INT32/FP16/INT8 | √ | V100(SM_70)/A100(SM_80)/A6000(SM_86)/RTX 4090(SM_89) |
| INT8 | UINT2/INT2 | INT32 | FP32/INT32/FP16/INT8 | √ | V100(SM_70)/A100(SM_80)/A6000(SM_86)/RTX 4090(SM_89) |
| INT8 | UINT1 | INT32 | FP32/INT32/FP16/INT8 | √ | V100(SM_70)/A100(SM_80)/A6000(SM_86)/RTX 4090(SM_89) |
| FP8_E4M3 | FP8_E4M3 | FP32 | FP32/FP16 | √ | RTX 4090(SM_89) |
| FP8_E5M2 | FP8_E5M2 | FP32 | FP32/FP16 | √ | RTX 4090(SM_89) |
| INT4 | INT4 | INT32 | FP32/FP16 | √ | RTX 4090(SM_89) |
| INT4 | INT4 | INT32 | FP32/FP16 | √ | RTX 4090(SM_89) |
We are continuously expanding the support matrix. If you have any specific requirements, please feel free to open an issue or PR.
Prerequisites for installation via wheel or PyPI
- Operating System: Ubuntu 20.04 or later
- Python Version: >= 3.8
- CUDA Version: >= 11.0
The easiest way to install BitBLAS is direcly from the PyPi using pip. To install the latest version, run the following command in your terminal.
pip install bitblasAlternatively, to install the latest version of BitBLAS from the github repository, you can run the following command:
pip install git+https://github.com/microsoft/BitBLAS.gitAfter installing BitBLAS, you can verify the installation by running:
python -c "import bitblas; print(bitblas.__version__)" Note: Currently, BitBLAS whl is only supported on Ubuntu 20.04 or later version as we build the whl files on this platform. Currently we only provide whl files for CUDA>=11.0 and with Python>=3.8. If you are using a different platform or environment, you may need to build BitBLAS from source. More installation methods can be found in the installation document.
BitBLAS provides two Python APIs to perform mixed-precision matrix multiplication:
-
bitblas.Matmulimplements the $W_{wdtype}A_{adtype}$ mixed-precision matrix multiplication of $C_{cdtype}[M, N] = A_{adtype}[M, K] \times W_{wdtype}[N, K]$ where $W_{wdtype}$ indicates the weight of $wtype$, A_{adtype} indicates the activation of $adtype$, and C_{cdtype} indicates the output of $cdtype$. -
bitblas.Linearis a PyTorchnn.Linear-like module to support a Linear of mixed-precision.
Here is an example for a $W_{INT4}A_{FP16}$ mixed-precision matrix multiplication: $out_{FP16}[M, N] = A_{FP16}[M, K] \times W_{INT4}[N, K]$, this example includes the creation of input matrices, quantization of weight matrices, and execution of the matrix multiplication with the bitblas.Matmul API. The result is then compared against a reference result obtained through conventional methods to ensure accuracy.
import bitblas
import torch
# uncomment to enable debug output
# bitblas.set_log_level("Debug")
matmul_config = bitblas.MatmulConfig(
M=1, # M dimension
N=2048, # N dimension
K=1024, # K dimension
A_dtype="float16", # activation A dtype
W_dtype="int4", # weight W dtype
accum_dtype="float16", # accumulation dtype
out_dtype="float16", # output dtype
layout="nt", # matrix layout, "nt" indicates the layout of A is non-transpose and the layout of W is transpose
with_bias=False, # bias
# configs for weight only quantization
group_size=None, # setting for grouped quantization
with_scaling=False, # setting for scaling factor
with_zeros=False, # setting for zeros
zeros_mode=None, # setting for how to calculating zeros
)
matmul = bitblas.Matmul(config=matmul_config)
# Create input matrices
input_tensor = torch.rand((1, 1024), dtype=torch.float16).cuda()
weight_tensor = torch.randint(0, 7, (2048, 1024), dtype=torch.int8).cuda()
# Transform weight tensor to int4 data type
weight_tensor_int4 = matmul.transform_weight(weight_tensor)
# Perform mixed-precision matrix multiplication
output_tensor = matmul(input_tensor, weight_tensor_int4)
# Reference result using PyTorch matmul for comparison
ref_result = torch.matmul(input_tensor, weight_tensor.t().to(torch.float16))
# Assert that the results are close within a specified tolerance, note that the int4 randint value is a little bigger than the float16 value, so we set the atol to 1.0
print("Ref output:", ref_result)
print("BitBLAS output:", output_tensor)
torch.testing.assert_close(output_tensor, ref_result, rtol=1e-2, atol=1e-0)Note: More examples can be found in the QuickStart document.
-
Installation: The installation document of BitBLAS. Make sure you already have the cuda toolkit (version >= 11.0) installed in the system.
- You can easily install from
pip install bitblasfrom PyPi. Currently we only provide whl files for CUDA>=11.0 and Ubuntu>=20.04 with Python>=3.8, if you are using a different version of CUDA or OS environment, you may need to build BitBLAS from source.
- You can easily install from
-
QuickStart: This document provides examples to use BitBLAS in your program with
bitblas.Matmulandbitblas.Linear. -
Python API: The Python API document of BitBLAS. BitBLAS provides two Python APIs to perform mixed-precision matrix multiplication:
-
bitblas.Matmulimplements the $W_{wdtype}A_{adtype}$ mixed-precision matrix multiplication of $C_{cdtype}[M, N] = A_{adtype}[M, K] \times W_{wdtype}[N, K]$. -
bitblas.Linearis a PyTorchnn.Linear-like module to support a Linear of mixed-precision.
-
-
Integration: Explore how BitBLAS seamlessly integrates with LLM deployment frameworks through our examples. Discover the ease of integrating BitBLAS with PyTorch, AutoGPTQ, and vLLM in the 3rd-party integration examples.
-
Customization: BitBLAS supports implementing customized mixed-precision DNN operations (e.g., Conv2D) rather than matrix multiplication with the flexible DSL (TIR Script).
Please cite BitBLAS/Ladder in your publications if it helps your research:
@inproceedings {ladder-osdi24,
author = {Lei Wang and Lingxiao Ma and Shijie Cao and Quanlu Zhang and Jilong Xue and Yining Shi and Ningxin Zheng and Ziming Miao and Fan Yang and Ting Cao and Yuqing Yang and Mao Yang},
title = {Ladder: Enabling Efficient Low-Precision Deep Learning Computing through Hardware-aware Tensor Transformation},
booktitle = {18th USENIX Symposium on Operating Systems Design and Implementation (OSDI 24)},
year = {2024},
isbn = {978-1-939133-40-3},
address = {Santa Clara, CA},
pages = {307--323},
url = {https://www.usenix.org/conference/osdi24/presentation/wang-lei},
publisher = {USENIX Association},
month = jul
}This project welcomes contributions and suggestions. Most contributions require you to agree to a Contributor License Agreement (CLA) declaring that you have the right to, and actually do, grant us the rights to use your contribution. For details, visit https://cla.opensource.microsoft.com.
When you submit a pull request, a CLA bot will automatically determine whether you need to provide a CLA and decorate the PR appropriately (e.g., status check, comment). Simply follow the instructions provided by the bot. You will only need to do this once across all repos using our CLA.
This project has adopted the Microsoft Open Source Code of Conduct. For more information see the Code of Conduct FAQ or contact [email protected] with any additional questions or comments.
This project may contain trademarks or logos for projects, products, or services. Authorized use of Microsoft trademarks or logos is subject to and must follow Microsoft's Trademark & Brand Guidelines. Use of Microsoft trademarks or logos in modified versions of this project must not cause confusion or imply Microsoft sponsorship. Any use of third-party trademarks or logos are subject to those third-party's policies.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for BitBLAS
Similar Open Source Tools

BitBLAS
BitBLAS is a library for mixed-precision BLAS operations on GPUs, for example, the $W_{wdtype}A_{adtype}$ mixed-precision matrix multiplication where $C_{cdtype}[M, N] = A_{adtype}[M, K] \times W_{wdtype}[N, K]$. BitBLAS aims to support efficient mixed-precision DNN model deployment, especially the $W_{wdtype}A_{adtype}$ quantization in large language models (LLMs), for example, the $W_{UINT4}A_{FP16}$ in GPTQ, the $W_{INT2}A_{FP16}$ in BitDistiller, the $W_{INT2}A_{INT8}$ in BitNet-b1.58. BitBLAS is based on techniques from our accepted submission at OSDI'24.

llm4ad
LLM4AD is an open-source Python-based platform leveraging Large Language Models (LLMs) for Automatic Algorithm Design (AD). It provides unified interfaces for methods, tasks, and LLMs, along with features like evaluation acceleration, secure evaluation, logs, GUI support, and more. The platform was originally developed for optimization tasks but is versatile enough to be used in other areas such as machine learning, science discovery, game theory, and engineering design. It offers various search methods and algorithm design tasks across different domains. LLM4AD supports remote LLM API, local HuggingFace LLM deployment, and custom LLM interfaces. The project is licensed under the MIT License and welcomes contributions, collaborations, and issue reports.
IDvs.MoRec
This repository contains the source code for the SIGIR 2023 paper 'Where to Go Next for Recommender Systems? ID- vs. Modality-based Recommender Models Revisited'. It provides resources for evaluating foundation, transferable, multi-modal, and LLM recommendation models, along with datasets, pre-trained models, and training strategies for IDRec and MoRec using in-batch debiased cross-entropy loss. The repository also offers large-scale datasets, code for SASRec with in-batch debias cross-entropy loss, and information on joining the lab for research opportunities.
qserve
QServe is a serving system designed for efficient and accurate Large Language Models (LLM) on GPUs with W4A8KV4 quantization. It achieves higher throughput compared to leading industry solutions, allowing users to achieve A100-level throughput on cheaper L40S GPUs. The system introduces the QoQ quantization algorithm with 4-bit weight, 8-bit activation, and 4-bit KV cache, addressing runtime overhead challenges. QServe improves serving throughput for various LLM models by implementing compute-aware weight reordering, register-level parallelism, and fused attention memory-bound techniques.

EasyEdit
EasyEdit is a Python package for edit Large Language Models (LLM) like `GPT-J`, `Llama`, `GPT-NEO`, `GPT2`, `T5`(support models from **1B** to **65B**), the objective of which is to alter the behavior of LLMs efficiently within a specific domain without negatively impacting performance across other inputs. It is designed to be easy to use and easy to extend.

deepfabric
DeepFabric is a CLI tool and SDK designed for researchers and developers to generate high-quality synthetic datasets at scale using large language models. It leverages a graph and tree-based architecture to create diverse and domain-specific datasets while minimizing redundancy. The tool supports generating Chain of Thought datasets for step-by-step reasoning tasks and offers multi-provider support for using different language models. DeepFabric also allows for automatic dataset upload to Hugging Face Hub and uses YAML configuration files for flexibility in dataset generation.
LLM4Decompile
LLM4Decompile is an open-source large language model dedicated to decompilation of Linux x86_64 binaries, supporting GCC's O0 to O3 optimization levels. It focuses on assessing re-executability of decompiled code through HumanEval-Decompile benchmark. The tool includes models with sizes ranging from 1.3 billion to 33 billion parameters, available on Hugging Face. Users can preprocess C code into binary and assembly instructions, then decompile assembly instructions into C using LLM4Decompile. Ongoing efforts aim to expand capabilities to support more architectures and configurations, integrate with decompilation tools like Ghidra and Rizin, and enhance performance with larger training datasets.
MiniCPM-V
MiniCPM-V is a series of end-side multimodal LLMs designed for vision-language understanding. The models take image and text inputs to provide high-quality text outputs. The series includes models like MiniCPM-Llama3-V 2.5 with 8B parameters surpassing proprietary models, and MiniCPM-V 2.0, a lighter model with 2B parameters. The models support over 30 languages, efficient deployment on end-side devices, and have strong OCR capabilities. They achieve state-of-the-art performance on various benchmarks and prevent hallucinations in text generation. The models can process high-resolution images efficiently and support multilingual capabilities.

langchain_dart
LangChain.dart is a Dart port of the popular LangChain Python framework created by Harrison Chase. LangChain provides a set of ready-to-use components for working with language models and a standard interface for chaining them together to formulate more advanced use cases (e.g. chatbots, Q&A with RAG, agents, summarization, extraction, etc.). The components can be grouped into a few core modules: * **Model I/O:** LangChain offers a unified API for interacting with various LLM providers (e.g. OpenAI, Google, Mistral, Ollama, etc.), allowing developers to switch between them with ease. Additionally, it provides tools for managing model inputs (prompt templates and example selectors) and parsing the resulting model outputs (output parsers). * **Retrieval:** assists in loading user data (via document loaders), transforming it (with text splitters), extracting its meaning (using embedding models), storing (in vector stores) and retrieving it (through retrievers) so that it can be used to ground the model's responses (i.e. Retrieval-Augmented Generation or RAG). * **Agents:** "bots" that leverage LLMs to make informed decisions about which available tools (such as web search, calculators, database lookup, etc.) to use to accomplish the designated task. The different components can be composed together using the LangChain Expression Language (LCEL).
Starmoon
Starmoon is an affordable, compact AI-enabled device that can understand and respond to your emotions with empathy. It offers supportive conversations and personalized learning assistance. The device is cost-effective, voice-enabled, open-source, compact, and aims to reduce screen time. Users can assemble the device themselves using off-the-shelf components and deploy it locally for data privacy. Starmoon integrates various APIs for AI language models, speech-to-text, text-to-speech, and emotion intelligence. The hardware setup involves components like ESP32S3, microphone, amplifier, speaker, LED light, and button, along with software setup instructions for developers. The project also includes a web app, backend API, and background task dashboard for monitoring and management.
airunner
AI Runner is a multi-modal AI interface that allows users to run open-source large language models and AI image generators on their own hardware. The tool provides features such as voice-based chatbot conversations, text-to-speech, speech-to-text, vision-to-text, text generation with large language models, image generation capabilities, image manipulation tools, utility functions, and more. It aims to provide a stable and user-friendly experience with security updates, a new UI, and a streamlined installation process. The application is designed to run offline on users' hardware without relying on a web server, offering a smooth and responsive user experience.
mindnlp
MindNLP is an open-source NLP library based on MindSpore. It provides a platform for solving natural language processing tasks, containing many common approaches in NLP. It can help researchers and developers to construct and train models more conveniently and rapidly. Key features of MindNLP include: * Comprehensive data processing: Several classical NLP datasets are packaged into a friendly module for easy use, such as Multi30k, SQuAD, CoNLL, etc. * Friendly NLP model toolset: MindNLP provides various configurable components. It is friendly to customize models using MindNLP. * Easy-to-use engine: MindNLP simplified complicated training process in MindSpore. It supports Trainer and Evaluator interfaces to train and evaluate models easily. MindNLP supports a wide range of NLP tasks, including: * Language modeling * Machine translation * Question answering * Sentiment analysis * Sequence labeling * Summarization MindNLP also supports industry-leading Large Language Models (LLMs), including Llama, GLM, RWKV, etc. For support related to large language models, including pre-training, fine-tuning, and inference demo examples, you can find them in the "llm" directory. To install MindNLP, you can either install it from Pypi, download the daily build wheel, or install it from source. The installation instructions are provided in the documentation. MindNLP is released under the Apache 2.0 license. If you find this project useful in your research, please consider citing the following paper: @misc{mindnlp2022, title={{MindNLP}: a MindSpore NLP library}, author={MindNLP Contributors}, howpublished = {\url{https://github.com/mindlab-ai/mindnlp}}, year={2022} }
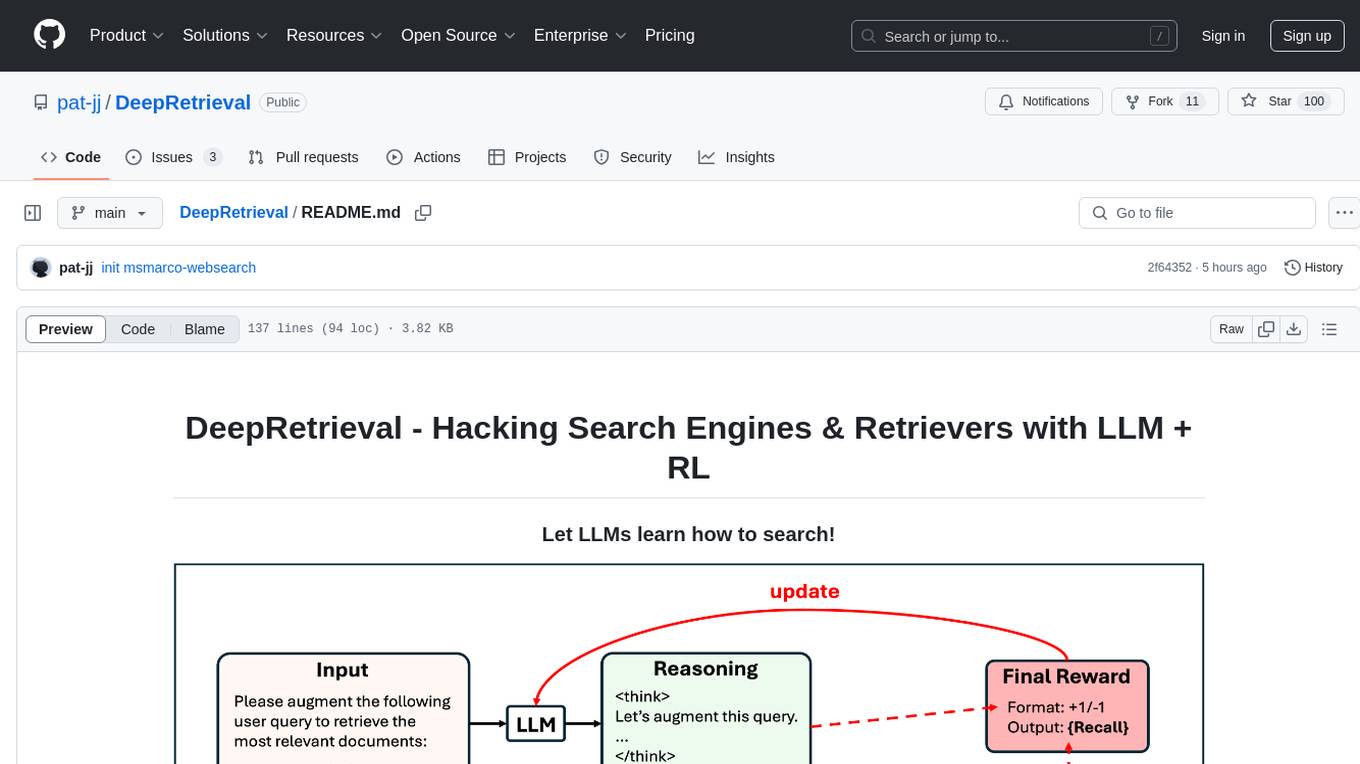
DeepRetrieval
DeepRetrieval is a tool designed to enhance search engines and retrievers using Large Language Models (LLMs) and Reinforcement Learning (RL). It allows LLMs to learn how to search effectively by integrating with search engine APIs and customizing reward functions. The tool provides functionalities for data preparation, training, evaluation, and monitoring search performance. DeepRetrieval aims to improve information retrieval tasks by leveraging advanced AI techniques.
KwaiAgents
KwaiAgents is a series of Agent-related works open-sourced by the [KwaiKEG](https://github.com/KwaiKEG) from [Kuaishou Technology](https://www.kuaishou.com/en). The open-sourced content includes: 1. **KAgentSys-Lite**: a lite version of the KAgentSys in the paper. While retaining some of the original system's functionality, KAgentSys-Lite has certain differences and limitations when compared to its full-featured counterpart, such as: (1) a more limited set of tools; (2) a lack of memory mechanisms; (3) slightly reduced performance capabilities; and (4) a different codebase, as it evolves from open-source projects like BabyAGI and Auto-GPT. Despite these modifications, KAgentSys-Lite still delivers comparable performance among numerous open-source Agent systems available. 2. **KAgentLMs**: a series of large language models with agent capabilities such as planning, reflection, and tool-use, acquired through the Meta-agent tuning proposed in the paper. 3. **KAgentInstruct**: over 200k Agent-related instructions finetuning data (partially human-edited) proposed in the paper. 4. **KAgentBench**: over 3,000 human-edited, automated evaluation data for testing Agent capabilities, with evaluation dimensions including planning, tool-use, reflection, concluding, and profiling.
optillm
optillm is an OpenAI API compatible optimizing inference proxy implementing state-of-the-art techniques to enhance accuracy and performance of LLMs, focusing on reasoning over coding, logical, and mathematical queries. By leveraging additional compute at inference time, it surpasses frontier models across diverse tasks.

ColossalAI
Colossal-AI is a deep learning system for large-scale parallel training. It provides a unified interface to scale sequential code of model training to distributed environments. Colossal-AI supports parallel training methods such as data, pipeline, tensor, and sequence parallelism and is integrated with heterogeneous training and zero redundancy optimizer.
For similar tasks

BitBLAS
BitBLAS is a library for mixed-precision BLAS operations on GPUs, for example, the $W_{wdtype}A_{adtype}$ mixed-precision matrix multiplication where $C_{cdtype}[M, N] = A_{adtype}[M, K] \times W_{wdtype}[N, K]$. BitBLAS aims to support efficient mixed-precision DNN model deployment, especially the $W_{wdtype}A_{adtype}$ quantization in large language models (LLMs), for example, the $W_{UINT4}A_{FP16}$ in GPTQ, the $W_{INT2}A_{FP16}$ in BitDistiller, the $W_{INT2}A_{INT8}$ in BitNet-b1.58. BitBLAS is based on techniques from our accepted submission at OSDI'24.
keras-llm-robot
The Keras-llm-robot Web UI project is an open-source tool designed for offline deployment and testing of various open-source models from the Hugging Face website. It allows users to combine multiple models through configuration to achieve functionalities like multimodal, RAG, Agent, and more. The project consists of three main interfaces: chat interface for language models, configuration interface for loading models, and tools & agent interface for auxiliary models. Users can interact with the language model through text, voice, and image inputs, and the tool supports features like model loading, quantization, fine-tuning, role-playing, code interpretation, speech recognition, image recognition, network search engine, and function calling.
VILA
VILA is a family of open Vision Language Models optimized for efficient video understanding and multi-image understanding. It includes models like NVILA, LongVILA, VILA-M3, VILA-U, and VILA-1.5, each offering specific features and capabilities. The project focuses on efficiency, accuracy, and performance in various tasks related to video, image, and language understanding and generation. VILA models are designed to be deployable on diverse NVIDIA GPUs and support long-context video understanding, medical applications, and multi-modal design.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

agentcloud
AgentCloud is an open-source platform that enables companies to build and deploy private LLM chat apps, empowering teams to securely interact with their data. It comprises three main components: Agent Backend, Webapp, and Vector Proxy. To run this project locally, clone the repository, install Docker, and start the services. The project is licensed under the GNU Affero General Public License, version 3 only. Contributions and feedback are welcome from the community.

oss-fuzz-gen
This framework generates fuzz targets for real-world `C`/`C++` projects with various Large Language Models (LLM) and benchmarks them via the `OSS-Fuzz` platform. It manages to successfully leverage LLMs to generate valid fuzz targets (which generate non-zero coverage increase) for 160 C/C++ projects. The maximum line coverage increase is 29% from the existing human-written targets.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement
The Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement repository provides packaged Industry Scenario DREAM Demos with ARM templates (Containing a demo web application, Power BI reports, Synapse resources, AML Notebooks etc.) that can be deployed in a customer’s subscription using the CAPE tool within a matter of few hours. Partners can also deploy DREAM Demos in their own subscriptions using DPoC.








