
llm4ad
LLM4AD: A Platform for Algorithm Design with Large Language Model
Stars: 294

LLM4AD is an open-source Python-based platform leveraging Large Language Models (LLMs) for Automatic Algorithm Design (AD). It provides unified interfaces for methods, tasks, and LLMs, along with features like evaluation acceleration, secure evaluation, logs, GUI support, and more. The platform was originally developed for optimization tasks but is versatile enough to be used in other areas such as machine learning, science discovery, game theory, and engineering design. It offers various search methods and algorithm design tasks across different domains. LLM4AD supports remote LLM API, local HuggingFace LLM deployment, and custom LLM interfaces. The project is licensed under the MIT License and welcomes contributions, collaborations, and issue reports.
README:
LLM4AD is an open-source Python-based Platform leveraging Large Language Models (LLMs) for Automatic Algorithm Design (AD). Please refer to the paper [LLM4AD] for detailed information, including the overview, methodology, and benchmark results.
LLM4AD is accomplished with Documents and Examples materials to support users and developers to easily test, build and deploy their own LLM4AD applications and conduct research.
LLM4AD was originally developed for optimisation tasks. The framework is versatile enough to be used in other areas, including machine learning, science discovery, game theory and engineering design.
For more information, see the contact list
-
2024.12 🎉🎉 LLM4AD paper Released “LLM4AD: A Platform for Algorithm Design with Large Language Model" !
-
2024.11 🎉🎉 LLM4AD v1.0 Released !
-
2024.10 🎉🎉 Survey Paper “A Systematic Survey on Large Language Models for Algorithm Design” is online !
| Feature | Support / To be supported |
|---|---|
| Unified Interfaces for methods | 🔥Support |
| Unified Interfaces for tasks | 🔥Support |
| Unified Interfaces for LLMs | 🔥Support |
| Evaluation acceleration: multiprocessing evaluation | 🔥Support |
| Secure Evaluation: main process protection, timeout interruption | 🔥Support |
| Logs: local logs, Wandb and Tensorboard support | 🔥Support |
| GUI: methods selection, tasks selection, convergence, best algorithm, ... | 🔥Support |
| Resume run | 🔥Support |
| Support other programming languages | 🚀Coming soon |
| More search methods | 🚀Coming soon |
| More task examples | 🚀Coming soon |
[!Important] The Python version must be larger or equal to Python 3.9, and less than Python 3.13.
[!Important] If you are testing machine learning tasks or using GUI, please install gym via
pip install gym. Please note that the gym version may be conflict with your own Python environment, please refer to gym's docs to obtain appropriate version.
[!Important] If you are testing machine learning tasks or using GUI, please install gym via
pip install gym. Please note that the gym version may be conflict with your own Python environment, please refer to gym's docs to obtain appropriate version.
-
refer to requirements.txt
-
Numba (if you want to use Numba accelerate)
-
Tensorboard (if you want to use a Tensorboard logger)
-
wandb (if you want to use wandb logger)
-
gym (if you want to try GUI, and Machine Learning tasks)
-
pandas (if you want to try Science Discovery tasks)
-
all required packages in requirements.txt (if you want to use GUI)
We suggest to install and run LLM4AD in conda env with python>=3.9, <3.13
cd LLM4AD pip install .
We suggest to install and run LLM4AD in conda env with python>=3.9, <3.13
pip install llm4ad
[!Note] Configure your LLM api before running the script. For example:
- Set
host: 'api.deepseek.com'- Set
key: 'your api key'- Set
model`deepseek-chat'
from llm4ad.task.optimization.online_bin_packing import OBPEvaluation
from llm4ad.tools.llm.llm_api_https import HttpsApi
from llm4ad.method.eoh import EoH, EoHProfiler
def main():
llm = HttpsApi(host="xxx", # your host endpoint, e.g., api.openai.com, api.deepseek.com
key="sk-xxx", # your key, e.g., sk-xxxxxxxxxx
model="xxx", # your llm, e.g., gpt-3.5-turbo, deepseek-chat
timeout=20)
task = OBPEvaluation()
method = EoH(llm=llm,
profiler=EoHProfiler(log_dir='logs/eoh', log_style='simple'),
evaluation=task,
max_sample_nums=20,
max_generations=10,
pop_size=4,
num_samplers=1,
num_evaluators=1,
debug_mode=False)
method.run()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()Check Documents for more tasks and examples
[!Important] Install all required packages in requirements.txt for GUI usage
$ cd GUI
$ python run_gui.pyCheck GUI Introduction for more information
| Methods | Paper title |
|---|---|
| EoH |
Evolution of Heuristics: Towards Efficient Automatic Algorithm Design Using Large Language Model (ICML 2024) Algorithm Evolution using Large Language Model (Arxiv 2023, AEL, the early version of EoH) |
| MEoH | Multi-objective Evolution of Heuristic Using Large Language Model (AAAI 25) |
| FunSearch | Mathematical Discoveries from Program Search with Large Language Models (Nature 2024) |
|
(1+1)-EPS (HillClimbing) |
Understanding the Importance of Evolutionary Search in Automated Heuristic Design with Large Language Models (PPSN 2024) |
| RandomSampling | ---- |
| Neighborhood search methods | Coming soon |
| Multi-objective search methods | Coming soon |
| Others | Coming soon |
| Area | Algorithm Task | Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Optimization | [Online Bin Packing, Constructive heuristic] | paper |
| Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP), Construct heuristic | paper | |
| Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP), Guided local search | paper | |
| 1-dimensional Bin Packing (BP1D), Construct heuristic | paper | |
| 2-dimensional Bin Packing (BP2D), Construct heuristic | paper | |
| Capacitated Facility Location Problem (CFLP), Construct heuristic | paper | |
| Knapsack Problem (KP), Construct heuristic | paper | |
| Quadratic Assignment Problem (QAP), Construct heuristic | paper | |
| Set Cover Problem (SCP), Construct heuristic | paper | |
| Flow Shop Scheduling Problem (FSSP), Construct heuristic | paper | |
| Flow Shop Scheduling Problem (FSSP), Guided local search | paper | |
| Bayesian Optimization, Cost-aware Acquisition Function Design | paper | |
| Machine Learning | Adversarial Attack, Attack strategy | paper |
| Acrobot, Heuristic (Agent) | ||
| Cart Pole, Heuristic (Agent) | ||
| Mountain Car, Heuristic (Agent) | ||
| Science Discovery | Computational fluid dynamics, Turbulence model design | paper |
| Bacteria Growth, Function | ||
| Oscillator, Equation | ||
| Stress & Strain, Equation | ||
| Math | Admissible Sets | paper |
| coming soon ... |
There are three approaches on LLM interface implementation, check Tutorial on LLM interface implementation for more information.
- Remote LLM API (e.g., GPT4o, GPT3.5, Gemini Pro, Deepseek ...) (<Recommended !!!>)
- Local HuggingFace LLM Deployment (e.g., Llamacode, Llama, Gemma, Deepseek, ...)
- Your Implementation If you want to use your own GPT API or local LLMs deployment, please create and add your interface in LLM
A Step-by-step Tutorial on using LLM4AD to solve your algorithm design task is provided here
This project is licensed under the MIT License - see the LICENSE file for details. Parts of this project use code licensed under the Apache License 2.0.
If you find LLM4AD helpful please cite:
@article{liu2024llm4ad,
title = {LLM4AD: A Platform for Algorithm Design with Large Language Model},
author = {Fei Liu and Rui Zhang and Zhuoliang Xie and Rui Sun and Kai Li and Xi Lin and Zhenkun Wang and Zhichao Lu and Qingfu Zhang},
year = {2024},
eprint = {2412.17287},
archivePrefix = {arXiv},
primaryClass = {cs.AI},
url = {https://arxiv.org/abs/2412.17287},
}This platform is developed and maintained by LLM4AD developer group from the City University of Hong Kong (CityUHK) and the Southern University of Science and Technology (SUSTech). We develop LLM4AD platform for research purposes and hope to contribute to the research area by delivering tools for LLM-based algorithm design methods.
- Contribution: We are more than welcome to contribute (see our 📖 contribution guide) including developing code and ideas to improve our platform.
- Collaborations: If you like our platform, and you would like to use it for profit-making purposes? We are always searching for industrial collaborations because they help direct research to meet the industry’s needs.
- Issue: If you find a bug or you have any kind of concern regarding the correctness, please report us an issue.
- Profit Purpose: If you intend to use LLM4AD for any profit-making purposes, please contact us.
If you are interested in LLM4AD or if you encounter any difficulty using the platform, you can:
-
Visit our website LLM4AD Web
-
Visit our collection a collection of resources and research papers on LLM4AD
-
Visit Discussions to connect with other members of our community
-
Join our QQ Group

-
Contact us through email [email protected]
-
Submit an issue
Any new ideas, features, and improvements are welcomed!
You can contribute to LLM4AD follow our 📖 Contribution Guide.
Thank you for contributing to LLM4AD and welcome to being part of the LLM4AD community! ✨
Fei Liu |
 Kai Li |
Rui Sun |
Julian XIE |
Shunyu Yao |
Rui Zhang |
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for llm4ad
Similar Open Source Tools

llm4ad
LLM4AD is an open-source Python-based platform leveraging Large Language Models (LLMs) for Automatic Algorithm Design (AD). It provides unified interfaces for methods, tasks, and LLMs, along with features like evaluation acceleration, secure evaluation, logs, GUI support, and more. The platform was originally developed for optimization tasks but is versatile enough to be used in other areas such as machine learning, science discovery, game theory, and engineering design. It offers various search methods and algorithm design tasks across different domains. LLM4AD supports remote LLM API, local HuggingFace LLM deployment, and custom LLM interfaces. The project is licensed under the MIT License and welcomes contributions, collaborations, and issue reports.
beeai-framework
BeeAI Framework is a versatile tool for building production-ready multi-agent systems. It offers flexibility in orchestrating agents, seamless integration with various models and tools, and production-grade controls for scaling. The framework supports Python and TypeScript libraries, enabling users to implement simple to complex multi-agent patterns, connect with AI services, and optimize token usage and resource management.
BitBLAS
BitBLAS is a library for mixed-precision BLAS operations on GPUs, for example, the $W_{wdtype}A_{adtype}$ mixed-precision matrix multiplication where $C_{cdtype}[M, N] = A_{adtype}[M, K] \times W_{wdtype}[N, K]$. BitBLAS aims to support efficient mixed-precision DNN model deployment, especially the $W_{wdtype}A_{adtype}$ quantization in large language models (LLMs), for example, the $W_{UINT4}A_{FP16}$ in GPTQ, the $W_{INT2}A_{FP16}$ in BitDistiller, the $W_{INT2}A_{INT8}$ in BitNet-b1.58. BitBLAS is based on techniques from our accepted submission at OSDI'24.
camel
CAMEL is an open-source library designed for the study of autonomous and communicative agents. We believe that studying these agents on a large scale offers valuable insights into their behaviors, capabilities, and potential risks. To facilitate research in this field, we implement and support various types of agents, tasks, prompts, models, and simulated environments.
superduperdb
SuperDuperDB is a Python framework for integrating AI models, APIs, and vector search engines directly with your existing databases, including hosting of your own models, streaming inference and scalable model training/fine-tuning. Build, deploy and manage any AI application without the need for complex pipelines, infrastructure as well as specialized vector databases, and moving our data there, by integrating AI at your data's source: - Generative AI, LLMs, RAG, vector search - Standard machine learning use-cases (classification, segmentation, regression, forecasting recommendation etc.) - Custom AI use-cases involving specialized models - Even the most complex applications/workflows in which different models work together SuperDuperDB is **not** a database. Think `db = superduper(db)`: SuperDuperDB transforms your databases into an intelligent platform that allows you to leverage the full AI and Python ecosystem. A single development and deployment environment for all your AI applications in one place, fully scalable and easy to manage.
Evaluator
NeMo Evaluator SDK is an open-source platform for robust, reproducible, and scalable evaluation of Large Language Models. It enables running hundreds of benchmarks across popular evaluation harnesses against any OpenAI-compatible model API. The platform ensures auditable and trustworthy results by executing evaluations in open-source Docker containers. NeMo Evaluator SDK is built on four core principles: Reproducibility by Default, Scale Anywhere, State-of-the-Art Benchmarking, and Extensible and Customizable.

mage-ai
Mage is an open-source data pipeline tool for transforming and integrating data. It offers an easy developer experience, engineering best practices built-in, and data as a first-class citizen. Mage makes it easy to build, preview, and launch data pipelines, and provides observability and scaling capabilities. It supports data integrations, streaming pipelines, and dbt integration.
FlagEmbedding
FlagEmbedding focuses on retrieval-augmented LLMs, consisting of the following projects currently: * **Long-Context LLM** : Activation Beacon * **Fine-tuning of LM** : LM-Cocktail * **Embedding Model** : Visualized-BGE, BGE-M3, LLM Embedder, BGE Embedding * **Reranker Model** : llm rerankers, BGE Reranker * **Benchmark** : C-MTEB

openrl
OpenRL is an open-source general reinforcement learning research framework that supports training for various tasks such as single-agent, multi-agent, offline RL, self-play, and natural language. Developed based on PyTorch, the goal of OpenRL is to provide a simple-to-use, flexible, efficient and sustainable platform for the reinforcement learning research community. It supports a universal interface for all tasks/environments, single-agent and multi-agent tasks, offline RL training with expert dataset, self-play training, reinforcement learning training for natural language tasks, DeepSpeed, Arena for evaluation, importing models and datasets from Hugging Face, user-defined environments, models, and datasets, gymnasium environments, callbacks, visualization tools, unit testing, and code coverage testing. It also supports various algorithms like PPO, DQN, SAC, and environments like Gymnasium, MuJoCo, Atari, and more.
Cherry_LLM
Cherry Data Selection project introduces a self-guided methodology for LLMs to autonomously discern and select cherry samples from open-source datasets, minimizing manual curation and cost for instruction tuning. The project focuses on selecting impactful training samples ('cherry data') to enhance LLM instruction tuning by estimating instruction-following difficulty. The method involves phases like 'Learning from Brief Experience', 'Evaluating Based on Experience', and 'Retraining from Self-Guided Experience' to improve LLM performance.
agentsys
AgentSys is a modular runtime and orchestration system for AI agents, with 13 plugins, 42 agents, and 28 skills that compose into structured pipelines for software development. It handles task selection, branch management, code review, artifact cleanup, CI, PR comments, and deployment. The system runs on Claude Code, OpenCode, and Codex CLI, providing a functional software suite and runtime for AI agent orchestration.
SciCode
SciCode is a challenging benchmark designed to evaluate the capabilities of language models (LMs) in generating code for solving realistic scientific research problems. It contains 338 subproblems decomposed from 80 challenging main problems across 16 subdomains from 6 domains. The benchmark offers optional descriptions specifying useful scientific background information and scientist-annotated gold-standard solutions and test cases for evaluation. SciCode demonstrates a realistic workflow of identifying critical science concepts and facts and transforming them into computation and simulation code, aiming to help showcase LLMs' progress towards assisting scientists and contribute to the future building and evaluation of scientific AI.
inference
Xorbits Inference (Xinference) is a powerful and versatile library designed to serve language, speech recognition, and multimodal models. With Xorbits Inference, you can effortlessly deploy and serve your or state-of-the-art built-in models using just a single command. Whether you are a researcher, developer, or data scientist, Xorbits Inference empowers you to unleash the full potential of cutting-edge AI models.
BharatMLStack
BharatMLStack is a comprehensive, production-ready machine learning infrastructure platform designed to democratize ML capabilities across India and beyond. It provides a robust, scalable, and accessible ML stack empowering organizations to build, deploy, and manage machine learning solutions at massive scale. It includes core components like Horizon, Trufflebox UI, Online Feature Store, Go SDK, Python SDK, and Numerix, offering features such as control plane, ML management console, real-time features, mathematical compute engine, and more. The platform is production-ready, cloud agnostic, and offers observability through built-in monitoring and logging.
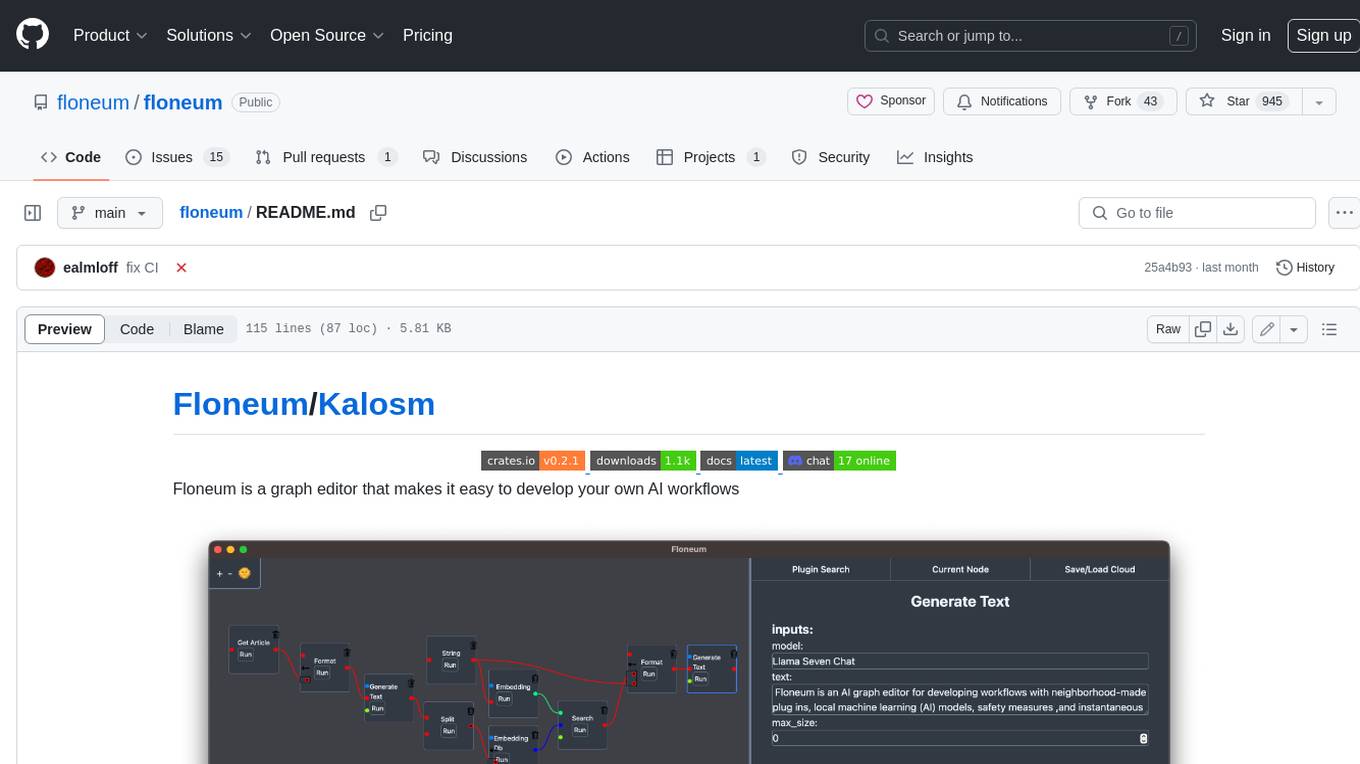
floneum
Floneum is a graph editor that makes it easy to develop your own AI workflows. It uses large language models (LLMs) to run AI models locally, without any external dependencies or even a GPU. This makes it easy to use LLMs with your own data, without worrying about privacy. Floneum also has a plugin system that allows you to improve the performance of LLMs and make them work better for your specific use case. Plugins can be used in any language that supports web assembly, and they can control the output of LLMs with a process similar to JSONformer or guidance.

nuitrack-sdk
Nuitrack™ is an ultimate 3D body tracking solution developed by 3DiVi Inc. It enables body motion analytics applications for virtually any widespread depth sensors and hardware platforms, supporting a wide range of applications from real-time gesture recognition on embedded platforms to large-scale multisensor analytical systems. Nuitrack provides highly-sophisticated 3D skeletal tracking, basic facial analysis, hand tracking, and gesture recognition APIs for UI control. It offers two skeletal tracking engines: classical for embedded hardware and AI for complex poses, providing a human-centric spatial understanding tool for natural and intelligent user engagement.
For similar tasks

llm4ad
LLM4AD is an open-source Python-based platform leveraging Large Language Models (LLMs) for Automatic Algorithm Design (AD). It provides unified interfaces for methods, tasks, and LLMs, along with features like evaluation acceleration, secure evaluation, logs, GUI support, and more. The platform was originally developed for optimization tasks but is versatile enough to be used in other areas such as machine learning, science discovery, game theory, and engineering design. It offers various search methods and algorithm design tasks across different domains. LLM4AD supports remote LLM API, local HuggingFace LLM deployment, and custom LLM interfaces. The project is licensed under the MIT License and welcomes contributions, collaborations, and issue reports.
LLM-as-HH
LLM-as-HH is a codebase that accompanies the paper ReEvo: Large Language Models as Hyper-Heuristics with Reflective Evolution. It introduces Language Hyper-Heuristics (LHHs) that leverage LLMs for heuristic generation with minimal manual intervention and open-ended heuristic spaces. Reflective Evolution (ReEvo) is presented as a searching framework that emulates the reflective design approach of human experts while surpassing human capabilities with scalable LLM inference, Internet-scale domain knowledge, and powerful evolutionary search. The tool can improve various algorithms on problems like Traveling Salesman Problem, Capacitated Vehicle Routing Problem, Orienteering Problem, Multiple Knapsack Problems, Bin Packing Problem, and Decap Placement Problem in both black-box and white-box settings.
For similar jobs
Interview-for-Algorithm-Engineer
This repository provides a collection of interview questions and answers for algorithm engineers. The questions are organized by topic, and each question includes a detailed explanation of the answer. This repository is a valuable resource for anyone preparing for an algorithm engineering interview.

LLM-as-HH
LLM-as-HH is a codebase that accompanies the paper ReEvo: Large Language Models as Hyper-Heuristics with Reflective Evolution. It introduces Language Hyper-Heuristics (LHHs) that leverage LLMs for heuristic generation with minimal manual intervention and open-ended heuristic spaces. Reflective Evolution (ReEvo) is presented as a searching framework that emulates the reflective design approach of human experts while surpassing human capabilities with scalable LLM inference, Internet-scale domain knowledge, and powerful evolutionary search. The tool can improve various algorithms on problems like Traveling Salesman Problem, Capacitated Vehicle Routing Problem, Orienteering Problem, Multiple Knapsack Problems, Bin Packing Problem, and Decap Placement Problem in both black-box and white-box settings.

universal
The Universal Numbers Library is a header-only C++ template library designed for universal number arithmetic, offering alternatives to native integer and floating-point for mixed-precision algorithm development and optimization. It tailors arithmetic types to the application's precision and dynamic range, enabling improved application performance and energy efficiency. The library provides fast implementations of special IEEE-754 formats like quarter precision, half-precision, and quad precision, as well as vendor-specific extensions. It supports static and elastic integers, decimals, fixed-points, rationals, linear floats, tapered floats, logarithmic, interval, and adaptive-precision integers, rationals, and floats. The library is suitable for AI, DSP, HPC, and HFT algorithms.
UmaAi
UmaAi is a tool designed for algorithm learning purposes, specifically focused on analyzing scenario mechanics in a game. It provides functionalities such as simulating scenarios, searching, handwritten-logic, and OCR integration. The tool allows users to modify settings in config.h for evaluating cardset strength, simulating games, and understanding game mechanisms through the source code. It emphasizes that it should not be used for illegal purposes and is intended for educational use only.
KuiperLLama
KuiperLLama is a custom large model inference framework that guides users in building a LLama-supported inference framework with Cuda acceleration from scratch. The framework includes modules for architecture design, LLama2 model support, model quantization, Cuda basics, operator implementation, and fun tasks like text generation and storytelling. It also covers learning other commercial inference frameworks for comprehensive understanding. The project provides detailed tutorials and resources for developing and optimizing large models for efficient inference.
Awesome-RoadMaps-and-Interviews
Awesome RoadMaps and Interviews is a comprehensive repository that aims to provide guidance for technical interviews and career development in the ITCS field. It covers a wide range of topics including interview strategies, technical knowledge, and practical insights gained from years of interviewing experience. The repository emphasizes the importance of combining theoretical knowledge with practical application, and encourages users to expand their interview preparation beyond just algorithms. It also offers resources for enhancing knowledge breadth, depth, and programming skills through curated roadmaps, mind maps, cheat sheets, and coding snippets. The content is structured to help individuals navigate various technical roles and technologies, fostering continuous learning and professional growth.
ai_igu
AI-IGU is a GitHub repository focused on Artificial Intelligence (AI) concepts, technology, software development, and algorithm improvement for all ages and professions. It emphasizes the importance of future software for future scientists and the increasing need for software developers in the industry. The repository covers various topics related to AI, including machine learning, deep learning, data mining, data science, big data, and more. It provides educational materials, practical examples, and hands-on projects to enhance software development skills and create awareness in the field of AI.

llm4ad
LLM4AD is an open-source Python-based platform leveraging Large Language Models (LLMs) for Automatic Algorithm Design (AD). It provides unified interfaces for methods, tasks, and LLMs, along with features like evaluation acceleration, secure evaluation, logs, GUI support, and more. The platform was originally developed for optimization tasks but is versatile enough to be used in other areas such as machine learning, science discovery, game theory, and engineering design. It offers various search methods and algorithm design tasks across different domains. LLM4AD supports remote LLM API, local HuggingFace LLM deployment, and custom LLM interfaces. The project is licensed under the MIT License and welcomes contributions, collaborations, and issue reports.







