ai_igu
AI Applications for TURKIYE
Stars: 74
AI-IGU is a GitHub repository focused on Artificial Intelligence (AI) concepts, technology, software development, and algorithm improvement for all ages and professions. It emphasizes the importance of future software for future scientists and the increasing need for software developers in the industry. The repository covers various topics related to AI, including machine learning, deep learning, data mining, data science, big data, and more. It provides educational materials, practical examples, and hands-on projects to enhance software development skills and create awareness in the field of AI.
README:
Teknoloji, Yazılım ve Algoritma Geliştirmeyi Her Yaşa ve Her Mesleğe Hitaben Öğretmemiz Lazım !!!!!!!
Sanayinin ihtiyacı olan yazılımcı sınıtısı giderek artacak... Peki Çözüm Ne olacak ?? Çözüm Ne olmalı ??
Öğrencilik günümüzde ikiye ayrıldı. Günümüz mezunları ile geçmiş mezuniyetler arasında çok fark olacak ... Bu işin bir noktasından Başlanılmalı ...
Akademik hayatının birinci önceliği diploma verme kurumu olmadığı sektör ile öğrencilerimiz arasında köprü olmasının önemini vurgulanmalıdır.
Bu köprü sürecinde eğerki temellerinizi veri yapısı - algoritma - yazılım - programlama - uygulama ile destekleyenler etkili bir süreç geliştirebilecektir.
Bu platformu kendi algoritmaları ile destekleyenler yeni meslekler ortaya çıktıkca adapte olabileceklerdir.
- Yaşamınızın merkezinde algoritma geliştirmeyi almak önemlidir,
- Sisteme entegre edilebilecek şekilde algoritma geliştirilmesi önemlidir,
- Fikri Mülkiyet Haklarınızı (TPMK Fikri ve Sınai Mülkiyet Hakları) almak ve korumak önemlidir.
Bu eğitimler ile birinci hedef: Yazılım Geliştirme alanında bir farkındalık oluşturarak sizlerin sıfırdan ileri seviyeye veya teorik olarak öğrenip ilerletemediğiniz yazılım geliştirme becerinizi arttırmaktır.
Bu eğitimler ile ikinci hedef: Klasik konu algısından sıyrılarak uygulamalar için yazılım tabanlı algoritma geliştirmektir.
Belki başka bir zamanda başka bir konumda bu algoritmalar noktasında uygulama geliştirmek için zamanınız olmamış olabilir --> Bir yerden başlamanız lazım. Eğerki şuan buradaysak ve bu eğitim alanında deneyim kazanmaya başlamak istiyorsak doğru bir konumdasınız :D Önemli olan başlamak - devamdır...
Eğitimin Amacı: Yapay Zeka (YZ)'yi kavram halinden çıkarıp uygulama + teorik şeklinde bütünleştirilerek tümleşik bir sistemin ortaya çıkarılmasıdır.
- Yapay Zeka (YZ) çalışmalarında Türkçe literatürün önemi
- YZ çalışmalarında Türkçe verilerin işleyebilmenin önemli
- YZ ile bütünleşen gerçek verilerin işlerken karşılaşılan sorunlara çözümler üretebilme
- Oluşan çözümlerin gerçek hayat verileri olarak nasıl kullanılabileceği
- YZ algoritması geliştirilmesinde bilinç ve farkındalık oluşturabilmek
- Yaşadığımız şehrin, ilçenin, evinizin verilerine YZ ile ortak çözümler geliştirebilmek - üretebilmek
- YZ Türkçe Açık Kaynak Geliştiriciliğin önemi
- Kurumlarımızın verilerine akademinin işbirliği - aracılığı ile çözümlerin ortaya koyabilmesi
- Ülkemizin Açık Kaynak Veri Paylasımı noktasındaki çalışmaları dünyaya tanıtma ve duyurma
- Açık kaynak verinin işlenmesinde işlem aşamaları
- Etkileşimli çalışma ile YZ algoritmalarının sistemsel bütünlüğünü öğrenme
- YZ alanında sürdürülebilirlik sağlanması
- YZ çalışmalarında gelişimin öğrenerek sağlanabilmesi
Tablo 1. Yazılım, Algoritma, Programlama noktasında dünya üzerinde önemli teknoloji gelişimleri (Tablo oluşumunda kullanılan referans listesi aşağıdadır.)
El-Harezmi -> Harzemli algoritmaların geliştirimesi üzerindeki çalışmaları nedeniyle bilimde algoritmaların mucidi olarak geçmektedir. Algoritma ismi Harzemlinin isminden türetilmiştir. Matematik üzerinede önemli katkıları olan Harzemli cebirinde kurucusudur. Cebir kitabında denklem kurulması ve kareköklü ifadelerin çözümünü ve algoritmasını ele almıştır.
DERS 1 -> Yapay Zeka Uygulama ve Proje Geliştirme İşlem Alanları
DERS 2 -> YZ Uygulamalarında Google Drive + Google Colab + Github Ayarları, Python Programlama Dili Kütüphaneleri 1 - Pandas, Numpy, Matplotlib, BeautifulSoup ve OpenCV Kütüphanelerinin Uygulamaları
DERS 10 -> Python Programlama Dili ile Derin Öğrenme Tabanlı Araç Veri Seti üzerinden YZ Fiyat Tahmini Uygulamasının Gerçekleştirilmesi
DERS 11 -> Python Programlama Dili ile Derin Öğrenme Tabanlı NLP Veri Seti üzerinden YZ Metin Analizi Uygulamasının Gerçekleştirilmesi
DERS 0 -> Yapay Zeka (YZ) Kavramı ve Tarihsel Gelişim Süreci, YZ Alt Dalları (Uzman Sistemler, Bulanık Mantık, Yapay Sinir Ağı, Genetik Algoritma, Makine Öğrenmesi, Derin Öğrenme), Veri Madenciliği, Veri Bilimi, Büyük Veri, Veri Seti Kavramları ve Google Drive, Google Colab, Linkedin, Github ve Portfolyonun Önemi
IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) Yaklaşık 140 yıllık bilgi paylaşımı için aktif kullanılan bir platformdur.
IEEE Moddosu: Advancing technology for humanity -> Erişim adresi: https://www.ieee.org/
C++; if / if-else / switch-case
C#; if/ if-else / swictch-case
Python; if / if-elif-else / switch-case
Java; if / if-else / switch-case
C ve C++; while, do while ve for
C#; while, do-while, for ve foreach
Python; While, for, range, len ve in
Java; while, do-while ve for
- Github: Günümüz yazılım geliştirme sektörünün önemli bir platformdur. Erişim Adresi -> https://github.com/
- LinkedIn: Günümüz iş dünyasının aktif kullandığı profesyonel iş ağı platformudur. Erişim Adresi -> https://www.linkedin.com/
- Google Drive: https://drive.google.com/
- Google Colab: https://colab.research.google.com/
- Kaggle: https://www.kaggle.com/
- Google Scholar: https://scholar.google.com/
- Dergipark: https://dergipark.org.tr/tr/
- IEEE Makale Yayınları: https://www.ieee.org/
- YÖK Tez Yayınları: https://tez.yok.gov.tr/UlusalTezMerkezi/
- Kongre Bildiri Yayınları
# Github ve Linkedin için bir mail adresiniz üzerinden istenilen üyelikleri oluşturup işlemi tamamlıyorsunuz.
Google Colab ve Drive için bir google mail adresi üzerinde aşağıdaki aşamaları tek tek gerçekleştirilmesi ve önemli noktaları yazarak not almanız gerekmektedir. Bu bağlamda hangi aşamada hata alırsanız o kısımda durmanız ve bir adım geriye giderek süreci kontrol etmeniz gerekmektedir!
-
Uygulama -> İBB Açık Veri Portalı, Atıktan Geri Kazanım Miktarları (IBB ACIK VERI PORTALI; Version V2) [Veri seti]. İstanbul Büyük Şehir Belediyesi İBB Açık Veri Portalı. https://data.ibb.gov.tr/dataset/atiktan-geri-kazanim-miktarlari
-
Uygulama -> İBB Açık Veri Portalı, İlçe Bazında Su Tüketim Miktarı, Veri Seti Linki-->> https://data.ibb.gov.tr/dataset/ilce-bazinda-su-tuketim-miktari
-
Çevre, Şehircilik ve İklim Değişikliği Bakanlığı - Ulusal Akıllı Şehir Açık Veri Platformu -> https://ulasav.csb.gov.tr/
-
Ankara Büyükşehir Belediyesi Açık Veri Portalı -> https://seffaf.ankara.bel.tr/
-
İstanbul Büyükşehir Belediyesi Açık Veri Portalı -> https://data.ibb.gov.tr
-
İzmir Büyükşehir Belediyesi Açık Veri Portalı Büyükşehir Belediyesi -> https://acikveri.bizizmir.com/
-
Kocaeli Büyükşehir Belediyesi Açık Veri Portalı -> https://veri.kocaeli.bel.tr/
-
Ordu Büyükşehir Belediyesi Açık Veri Platformu -> https://acikveri.ordu.bel.tr/
-
Kaggle - Datasets -> https://www.kaggle.com/datasets
1.1. Yapay Zeka Uygulama Alanları
Siber Güvenlik -> Yüz Tanıma Sistemi, Siber Tehdit Analizi ve Tespiti
Sağlık -> Hastalık Teşhisi
Eğitim -> Kişiselleştirilmiş Öğrenme, Yabancı Dil Öğrenimi
Finans ve Bankacılık -> Kredi Skorlama, Dolandırıcılık Tespiti
E-Ticaret -> Öneri Sistemi, Sohbet Botları, Stok Takip Sistemi
Otomotiv -> Otonom Arabalar Görüntü İşleme ile Hareket Sistemi Planlaması
Robotik -> Robotik Cerrahi
Gıda -> Tedarik Zincirinde Verimlilik Analizi, Tarla Sulama Sistemi, Meyve Teşhiş Sistemi
İnsan Kaynakları -> Özgeçmiş Analiz Sistemi, Çalışan Performans Analizi
Enerji ve Çevre -> Aklıllı Enerji Sistemi, Yenilenebilir Enerji Sistemi
Müzik ve Sanat -> Müzik besteleme, Görüntü oluşturma ile eser oluşturma
1.2. Yapay Zeka İşlem Sürecinde Proje Oluşturma İşlem Adımları
- Programın Başlangıcı
- Veri Yapıları ve Algoritma Bilgisi
- Programlama Bilgisi
- Veri Toplama (Veri Seti veya Veri Takibi)
- Veriyi Hazırlama
- Model Oluşturma
- Eğitimi Başlatma
- Eğitim Sonrasında Modelin Hatasının ve Doğruluğunun Tespiti
- Eğitim Sonrasında Modelin Sonuçlarının Değerlendirilmesi
- Eğitim Sürecinde Modelin Başarı ve Hata Grafiğinin Oluşturulması
- Gerçek ve Tahmin Edilen Değerler Arasındaki Farkı Bulma
- Sistemin Yüzdelik Hata Payının Bulunması
- Programın Bitirilmesi
DERS 2 -> YZ Uygulamalarında Google Drive + Google Colab + Github Ayarları, Python Programlama Dili Kütüphaneleri 1 - Pandas, Numpy, Matplotlib, BeautifulSoup ve OpenCV Kütüphanelerinin Uygulamaları
Github Ayarları ve Github Paylaşımları - Yeni Paylaşım Ortamının Oluşturulması (Repositories - > New)
2.1. Bilgisayarınız üzerinde kullanıdğınız tarayıcıda google hesabınız aktif ederek, drive alanına bağlantı sağlayan.
2.2. Aşama -> Google Drive Sistemini Aktif Edin ve Drive alanınızı açın.
Daha sonra drive içerisinde "YAPAYZEKA_PYTHON" ismiyle vereceğiniz yeni klasöre yüklemesini - kaydedilmesi işlemlerini gerçekleştiriniz.
2.3. Aşama -> Google Drive Alanında "YAPAYZEKA_PYTHON" ismiyle yeni klasör oluşturun.
2.4. Aşama -> Google Drive Alanında "YAPAYZEKA_PYTHON" ismiyle yeni klasör içerisine giriş yapın...
2.5. Aşama -> GOOGLE COLAB ve GOOGLE DRIVE YAPILANDIRMASI
2.6. Colaboratory -->
2.7. Colaboratory -->
2.8. Google Drive'da Google Colab Kod Alanı Oluşturulması
2.9. Google Colab Üzerinde Oluşturulan Boş Kod Ekranı
2.10. Google Colab çalışma dosyasının "Untitled0.ipynb" ismini "D1_Python_ilk_ayarlar.ipynb" ile değiştiriyoruz.
2.11. Drive Alanınız içerisinde çalışma alanımız olacak "YAPAYZEKA_PYTHON" klasörü içerisinde "D1_Python_ilk_ayarlar.ipynb" olduğunu teyit ediyoruz...
2.12. Drive alanınızda birden fazla çalışma ortamı oluşturabilirsiniz...
2.13. "D1_Python_ilk_ayarlar.ipynb" dosyasına çift tıklayıp açtığımızda karşımıza gelen çalışma ortamı...
2.14. Çalışma ortamında ilk python kodumuzu yazıyoruz..
print("Merhaba, İGÜ - YAPAY ZEKA") # print ekrana çıktı veren bir koddur.
2.15. Python'da kütüphane ekleme komutu "import" dur. import sys diyerek çalışma ortamında python programının hangi sürümde oluğunu öğreneceğiz.
import sys # import python programlama dilinde yazılıma kütüphane eklemeye yarayan bir kod blogudur.
print(sys.version)
2.16. Google Colab üzerinde drive alanına erişim için ayarlamaları yapıyoruz..
from google.colab import drive # google colab - drive bağlantısı
drive.mount('/content/drive')
2.17. Drive Erişim izni..
2.18. Mail adresine erişim izni..
2.19. Mail adresine erişim izni..
2.20. Mail adresine erişim izni..
2.21. Gerekli izinler onaylandıktan sonra karşılaşılaçak ekran..
2.22. Google Drive klasör alanınıza erişim izni sağlanıyor. "!pwd" derlenen kodun tam derlendiğinde yaptığı işin ekran çıktısını sağlar. Silip denerseniz farklı görürsünüz.
GOOGLE DRIVE ve GOOGLE COLAB SİSTEMLERİNİN BAĞLANTILARI GERÇEKLEŞTİRİLMİŞTİR. BU AŞAMADAN SONRAKİ TÜM DERSLERİMİZDE BU BÖLÜMLER ATLANARAK KONUYA DEVAM EDİLECEKTİR. BAĞLANTI KISMINDA HATA ALAN veya ALANLAR DERS ANINDA İLETİŞİME GEÇSİN!!!!
DERS 3 -> YZ Uygulamalarında Python Programlama Dili Kütüphaneleri 2 - Scikit-Learn, Tensorflow, Pytorch ve Keras Kütüphanelerinin Uygulamaları
DERS 4 -> Python Programlama Dili ile Görüntü İşleme ile Plaka Okuma, Görüntüden Metinsel İçerik Alma, Matematiksel İşlem Algılaması ve Nesne (Araç) Tespit Uygulamasının Gerçekleştirilmesi
DERS 5 -> Python Programlama Dili ile Makine Öğrenmesi Tabanlı İBB Su Veri Seti üzerinden YZ Su Analizi ve Tahmini Uygulamasının Gerçekleştirilmesi
DERS 6 -> Python Programlama Dili ile Bulanık Mantık Tabanlı Komisyon Hesaplaması YZ Uygulamasının Gerçekleştirilmesi
DERS 7 -> Python Programlama Dili ile Makine Öğrenmesi Tabanlı Titanik Veri Seti üzerinden YZ Uygulamasının Gerçekleştirilmesi
DERS 8 -> Python Programlama Dili ile Derin Öğrenme Tabanlı MNIST Veri Seti üzerinden YZ Uygulamasının Gerçekleştirilmesi
DERS 9 -> Python Programlama Dili ile API ve ENDPOINT Kullanarak Uygulama Geliştirme: Web Hizmetlerinde Bütünlük ve Erişilebilirlik
DERS 10 -> Python Programlama Dili ile Derin Öğrenme Tabanlı Araç Veri Seti üzerinden YZ Fiyat Tahmini Uygulamasının Gerçekleştirilmesi
DERS 11 -> Python Programlama Dili ile Derin Öğrenme Tabanlı NLP Veri Seti üzerinden YZ Metin Analizi Uygulamasının Gerçekleştirilmesi
Hz. Mevlana'nın Sözleriyle Eğitim serimizi tamamlıyoruz.
Mum olmak kolay değildir !!
Işık saçmak için önce yanmak gerekir.
Hz. Mevlana
Arkadaşlar çalışmalarınızda başarılar dilerim. Öğr. Gör. Ali ÇETİNKAYA
Bu Çalışmayı Oluşturulması İçin Kullanılan Referans Kaynaklar:
NOT: Bu kitaplar ülkemizin yapay zeka alanında ortaya çıkardığı çalışmalardan önemli kaynaklardır. Her yazılımcının, mezun ve / veye öğrencilerinin mutlaka kütüphanelerinde olması gereken kitaplardır.
Ord. Prof. Dr. Cahit ARF, "Makine düşünebilir mi ve nasıl düşünebilir", Atatürk Üniversitesi-Üniversite Çalışmalarını Muhite Yayma ve Halk Eğitimi Yayınları Konferanslar Serisi, (1), 91-103. Erzurum, 1959.
Prof. Dr. Vasıf NABİYEV, "Teoriden Uygulamalara Algoritmalar", Seçkin Yayınları, Ankara, 2011.
Prof. Dr. Vasıf NABİYEV, "Yapay zeka: insan-bilgisayar etkileşimi", Seçkin Yayınları, Ankara, 2021.
Prof. Dr. Ali OKATAN, Tamer KARATEKİN, Dr. Kağan OKATAN, "100 Sayfada Makine Öğrenmesi Kitabı", Papatya Bilim Yayıncılık, İstanbul, 2020.
Prof. Dr. Vasıf NABİYEV, "Teoriden Uygulamalara Algoritmalar", Seçkin Yayınları, Ankara, 2011.
Prof. Dr. Ercan Nurcan YILMAZ & Dr. Öğr. Üyesi Serkan GÖNEN, "Örneklerle Uygulamalı C ve C++ - 2023", İstanbul Gelişim Üniversitesi Yayınları, İstanbul, 2023.
Prof. Dr. Çetin ELMAS, "Yapay Zeka Uygulamaları", Seçkin Yayıncılık, İstanbul, 2021.
Prof. Dr. Şadi Evren ŞEKER, "Algoritmalar", Nobel Akademik Yayıncılık, Ankara, 2021.
Prof. Dr. Eşref ADALI, "Bilişim Etiği ve Hukuku", İTÜ Ulusal Yazılım ve Sertifikasyon Merkezi, İstanbul, 2017.
Doç. Dr. Yılmaz KAYA, "Python ile Veri YAPILARI ve ALGORİTMA ANALİZİ", Nobel Yayınevi, Ankara, 2023.
Dr. Atınç YILMAZ, Öğr. Gör. Umut KAYA, "Derin Öğrenme", KODLAB Yayıncılık, İstanbul, 2022.
Dr. Yalçın ÖZKAN, "Uygulamalı Derin Öğrenme", Papatya Bilim Yayıncılık, İstanbul, 2021.
Dr. Andriy BURKOV, "The hundred-page machine learning" book (Vol. 1, p. 32). Quebec City, QC, Canada: Andriy Burkov, 2019.
Dr. Öğr. Üyesi Fahri VATANSEVER, "Algoritma Geliştirme ve Programlamaya Giriş", Seçkin Yayınları, Ankara, 2009.
Dr. Öğr. Üyesi Selçuk ALP & Arzu KİLİTCİ, "Algoritmalar ve Programlamaya Giriş", Umuttepe Yayınları, Kocaeli, 2015.
Dr. Öğr. Üyesi Ebubekir YAŞAR, "Algoritma Ve Programlamaya Giriş", Ekin Basım Yayın, Bursa, 2015.
Öğr. Gör. Ali ÇETİNKAYA, "Bulanık Mantık ve Python Uygulamaları". İstanbul Gelişim Üniversitesi Yayınları, 2023.
Öğr. Gör. Tuğba SARAY ÇETİNKAYA & Öğr. Gör. Ali ÇETİNKAYA, Algorithm Design in Programming Language Education - Özgür Yayınları, Gaziantep, 2023.
Öğr. Gör. Ali ÇETİNKAYA, Mühendislik Alanında Yapay Zeka (YZ) İçerikli Araştırmalarda Yaklaşımlar - Serüven Yayınevi, İzmir, 2022.
Öğr. Gör. Ali ÇETİNKAYA, Approaches with Artificial Intelligence (AI) Algorithms to Smart System Works - Platanus Publishing, Ankara, 2023.
Öğr. Gör. Ali ÇETİNKAYA’nın internet sayfaları:
https://scholar.google.com.tr/citations?hl=tr&user=XSEW-NcAAAAJ
https://avesis.gelisim.edu.tr/alcetinkaya
https://github.com/acetinkaya/
https://alicetinkaya.site/
Tablo 1 içerisinde yer alan çalışmaların referans kaynak listesi:
-
Arf, C. (1959). Makineler Düşünebilir mi ve Nasıl Düşünebilir?. Atatürk Üniversitesi 1958-1959 Öğretim Yılı Halk Konferansları, (1), 91-103.
-
Widrow, B., & Hoff, M. E. (1960). Adaptative Switching Circuits. Wetscon Convention Record. Institute for Research and Education. New York.
-
Zadeh, L. A. (1965). Fuzzy sets. Information and control, 8(3), 338-353.
-
Brezina, C. (2006). Al-Khwarizmi: The inventor of algebra. The Rosen Publishing Group.
-
Campbell, M., Hoane Jr, A. J., & Hsu, F. H. (2002). Deep blue. Artificial intelligence, 134(1-2), 57-83.
-
Allahverdi, N. (2002). Uzman Sistemler Bir Yapay Zeka Uygulaması, Atlas Yayın Dağıtım, Ankara.
-
James, W. (1984). Psychology, briefer course (Vol. 14). Harvard University Press.
-
Nilsson NJ (1965). Foundations of trainable pattern classifying systems. McGraw-Hill, New York
-
Taştan, A. (2001). Nasreddin Tusi: hayatı, eserleri, din ve toplum Görüşü. Erciyes Üniversitesi Sosyal Bilimler Enstitüsü Dergisi, 1(11), 1-13.
-
Hebb, D. O. (1949). The first stage of perception: growth of the assembly. The Organization of Behavior, 4, 60-78.
-
Farley, B. W. A. C., & Clark, W. D. (1954). Simulation of self-organizing systems by digital computer. Transactions of the IRE Professional Group on Information Theory, 4(4), 76-84.
-
Uyanık, M. (2022). El-Hârezmî Ebû Ca‘Fer Muhammed B. Mûsâ. Bilgeler ve Bilginler: Cumhuriyetin 100. Yılına Armağan, Türk Kültürüne Hizmet Vakfı Yayın Evi, 250.
-
McCulloch, W. S., & Pitts, W. (1943). A logical calculus of the ideas immanent in nervous activity. The bulletin of mathematical biophysics, 5(4), 115-133.
-
Yang, S., Lee, J., Sezgin, E., Bridge, J., & Lin, S. (2021). Clinical Advice by Voice Assistants on Postpartum Depression: Cross-Sectional Investigation Using Apple Siri, Amazon Alexa, Google Assistant, and ,
-
Microsoft Cortana. JMIR mHealth and uHealth, 9(1), e24045. https://doi.org/10.2196/24045
-
McFarlane, M. D. (1972). Digital pictures fifty years ago. Proceedings of the IEEE, 60(7), 768-770.
-
Turing, A. M. (1940). Mathematical theory of enigma machine. Public Record Office, London, 3, 150.
-
Turing, A. M. (1948). Intelligent machinery. report for national physical laboratory. reprinted in ince, dc (editor). 1992. mechanical intelligence: Collected works of am turing.
-
McCarthy, J. (1955). Human-Level Ai Is Harder Than It Seemed.
-
Rosenblatt, F. (1957). The perceptron, a perceiving and recognizing automaton Project Para. Cornell Aeronautical Laboratory.
-
Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., & Hinton, G. E. (2017). Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Communications of the ACM, 60(6), 84-90.
-
Goodfellow, I., Pouget-Abadie, J., Mirza, M., Xu, B., Warde-Farley, D., Ozair, S., ... & Bengio, Y. (2020). Generative adversarial networks. Communications of the ACM, 63(11), 139-144.
-
Özşahin, M. S. (2017). Türk minyatür tekniği ile çizgi roman tasarımı (Master's thesis). Kütahya Dumlupınar Üniversitesi, Sosyal Bilimler Enstitüsü.
-
Devlin, J., Chang, M. W., Lee, K., & Toutanova, K. (2018). Bert: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. arXiv preprint arXiv:1810.04805.
-
Radford, A., Wu, J., Child, R., Luan, D., Amodei, D., & Sutskever, I. (2019). Language models are unsupervised multitask learners. OpenAI blog, 1(8), 9.
-
Ramesh, A., Pavlov, M., Goh, G., Gray, S., Voss, C., Radford, A., ... & Sutskever, I. (2021). Zero-shot text-to-image generation. In International Conference on Machine Learning (pp. 8821-8831). PMLR.
-
Topdemir, H. G. (2022). Takiyüddin İbn Ma'ruf. Bilgeler ve Bilginler: Cumhuriyetin 100. Yılına Armağan, Türk Kültürüne Hizmet Vakfı Yayın Evi, 524.
-
LeCun, Y., Bottou, L., Bengio, Y., & Haffner, P. (1998). Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proceedings of the IEEE, 86(11), 2278-2324.
-
Vacroux, A. G. (1975). Microcomputers. Scientific American, 232(5), 32-41.
-
Deng, J., Dong, W., Socher, R., Li, L. J., Li, K., & Fei-Fei, L. (2009). Imagenet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In 2009 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 248-255). Ieee.
-
Çırak, B., & Yörük, A. (2016). Mekatronik biliminin öncüsü İsmail El-Cezeri. Siirt Üniversitesi Sosyal Bilimler Enstitüsü Dergisi, (4), 175-194.
-
Kato, I., Ohteru, S., Shirai, K., Matsushima, T., Narita, S., Sugano, S., ... & Fujisawa, E. (1987). The robot musician ‘wabot-2’(waseda robot-2). Robotics, 3(2), 143-155.
-
Spenko, M., Buerger, S., & Iagnemma, K. (Eds.). (2018). The DARPA robotics challenge finals: humanoid robots to the rescue (Vol. 121). Springer.
-
Lin, R., Ma, L., & Zhang, W. (2018). An interview study exploring Tesla drivers' behavioural adaptation. Applied ergonomics, 72, 37-47.
-
Google, (2017). Teachable machine v1. https://teachablemachine.withgoogle.com/v1/ Son Erişim Tarihi: 19.12.2022
-
Yang, Z., Gan, Z., Wang, J., Hu, X., Lu, Y., Liu, Z., & Wang, L. (2022). An empirical study of gpt-3 for few-shot knowledge-based vqa. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (Vol. 36, No. 3, pp. 3081-3089).
<-- Saygılarımla Öğr. Gör. Ali ÇETİNKAYA - Eylül 2024 -->
Yukarıdaki bilgi, resim ve kod çalışmaları açık kaynak paylaşım olarak github "acetinkaya" alanında paylaşımı yapılmıştır.
Github alanından; star - yıldız ile beğenme bildirimi ile paylaşımlarıma destek verebilirsiniz.
Bilgi paylaşıldıkça çoğalır ve gelişir. İyi çalışmalar dilerim.
## Yazdığınız kodun hakkını verin !!!
## Öğr. Gör. Ali ÇETİNKAYA İstanbul, 2024
IEEE--> A. Cetinkaya, "AI-IGU" GitHub, [Online]. Erişim Linki: https://github.com/acetinkaya/ai_igu. Son Erişim Tarihi: Gün Ay Yıl.
APA--> Cetinkaya, A. (2024). AI-IGU [GitHub Deposu]. GitHub. Erişim Linki: https://github.com/acetinkaya/ai_igu. Son Erişim Tarihi: Gün Ay Yıl.
Proje Durumu: İlgili paylaşımlar ve Python programlama dilinde yazılmış yazılım kodlarına sürüm güncellemeleri yaptıkça bu paylaşımları güncelleyeceğiz. GitHub bölümünden beğeni bildirimi olarak bir yıldız vererek çalışmalarımı destekleyebilirsiniz. Bilgi paylaşıldıkça büyür ve gelişir.
Katkıda Bulunma: Çekme istekleri memnuniyetle karşılanır. Büyük değişiklikler için lütfen önce neyi değiştirmek istediğinizi görüşmek üzere ilgili Python kodunu belirttiğiniz bir soru - yanıt bölümü açın.
Lisans: MIT Lisansı altında yayımlandı
Yazar ve Güncelleme Yapan: Öğr. Gör. Ali Çetinkaya (MSc.) - 2024
Project Status: We will update these shares as we make version updates to the related dependencies and software code written in Python programming language. You can support my work by giving a star as a like notification from the GitHub section. Knowledge grows and develops as it is shared.
Contributing: Pull requests are welcome. For major changes, please open a question-and-answer section indicating the relevant Python code to discuss what you'd like to change first.
License: Released under the MIT License
Authored and Maintained by Lect. Ali Cetinkaya (MSc.) - 2024
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for ai_igu
Similar Open Source Tools

ai_igu
AI-IGU is a GitHub repository focused on Artificial Intelligence (AI) concepts, technology, software development, and algorithm improvement for all ages and professions. It emphasizes the importance of future software for future scientists and the increasing need for software developers in the industry. The repository covers various topics related to AI, including machine learning, deep learning, data mining, data science, big data, and more. It provides educational materials, practical examples, and hands-on projects to enhance software development skills and create awareness in the field of AI.
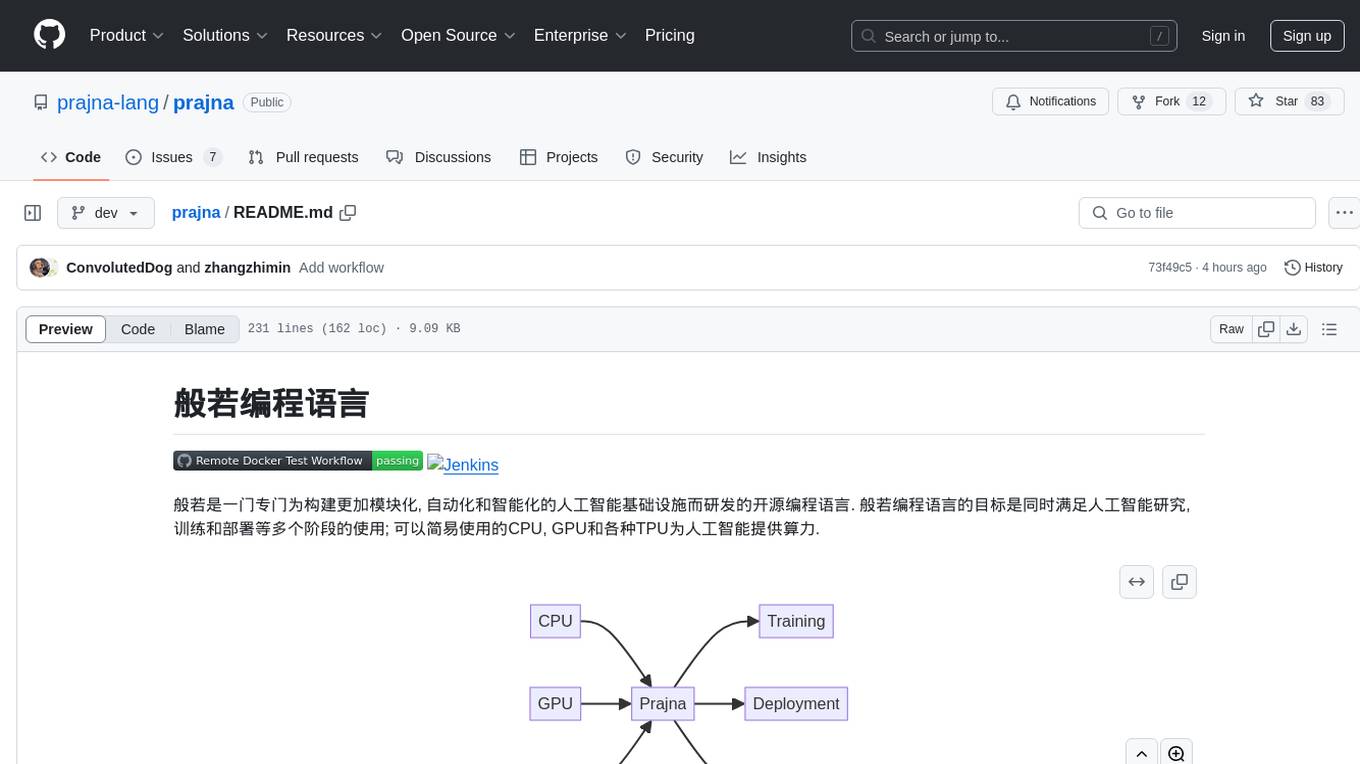
prajna
Prajna is an open-source programming language specifically developed for building more modular, automated, and intelligent artificial intelligence infrastructure. It aims to cater to various stages of AI research, training, and deployment by providing easy access to CPU, GPU, and various TPUs for AI computing. Prajna features just-in-time compilation, GPU/heterogeneous programming support, tensor computing, syntax improvements, and user-friendly interactions through main functions, Repl, and Jupyter, making it suitable for algorithm development and deployment in various scenarios.
langchat
LangChat is an enterprise AIGC project solution in the Java ecosystem. It integrates AIGC large model functionality on top of the RBAC permission system to help enterprises quickly customize AI knowledge bases and enterprise AI robots. It supports integration with various large models such as OpenAI, Gemini, Ollama, Azure, Zhifu, Alibaba Tongyi, Baidu Qianfan, etc. The project is developed solely by TyCoding and is continuously evolving. It features multi-modality, dynamic configuration, knowledge base support, advanced RAG capabilities, function call customization, multi-channel deployment, workflows visualization, AIGC client application, and more.
LLM-SFT
LLM-SFT is a Chinese large model fine-tuning tool that supports models such as ChatGLM, LlaMA, Bloom, Baichuan-7B, and frameworks like LoRA, QLoRA, DeepSpeed, UI, and TensorboardX. It facilitates tasks like fine-tuning, inference, evaluation, and API integration. The tool provides pre-trained weights for various models and datasets for Chinese language processing. It requires specific versions of libraries like transformers and torch for different functionalities.
knowledge
This repository serves as a personal knowledge base for the owner's reference and use. It covers a wide range of topics including cloud-native operations, Kubernetes ecosystem, networking, cloud services, telemetry, CI/CD, electronic engineering, hardware projects, operating systems, homelab setups, high-performance computing applications, openwrt router usage, programming languages, music theory, blockchain, distributed systems principles, and various other knowledge domains. The content is periodically refined and published on the owner's blog for maintenance purposes.
Awesome-Latent-CoT
This repository contains a regularly updated paper list for Large Language Models (LLMs) reasoning in latent space. Reasoning in latent space allows for more flexible and efficient thought representation beyond language tokens, bringing AI closer to human-like cognition. The repository covers various aspects of LLMs, including pre-training, supervised finetuning, analysis, interpretability, multimodal reasoning, and applications. It aims to showcase the advancements in reasoning with latent thoughts and continuous concepts in AI models.
500
Simple Config GeoIP for Quantumult X is a pre-configured file package containing rules for unlocking Apple News, ad blocking, TikTok unlock Rewrite, machine routing rules, and VIP video resolution rewriting. It integrates multiple rewrite configurations using Quantumult X and GeoIP features to remove most rules to save resources, and provides corresponding shortcuts for rule and configuration simplification through Vercel redirection.
Awesome-Efficient-LLM
Awesome-Efficient-LLM is a curated list focusing on efficient large language models. It includes topics such as knowledge distillation, network pruning, quantization, inference acceleration, efficient MOE, efficient architecture of LLM, KV cache compression, text compression, low-rank decomposition, hardware/system, tuning, and survey. The repository provides a collection of papers and projects related to improving the efficiency of large language models through various techniques like sparsity, quantization, and compression.
aiwechat-vercel
aiwechat-vercel is a tool that integrates AI capabilities into WeChat public accounts using Vercel functions. It requires minimal server setup, low entry barriers, and only needs a domain name that can be bound to Vercel, with almost zero cost. The tool supports various AI models, continuous Q&A sessions, chat functionality, system prompts, and custom commands. It aims to provide a platform for learning and experimentation with AI integration in WeChat public accounts.
MING
MING is an open-sourced Chinese medical consultation model fine-tuned based on medical instructions. The main functions of the model are as follows: Medical Q&A: answering medical questions and analyzing cases. Intelligent consultation: giving diagnosis results and suggestions after multiple rounds of consultation.
Wechat-AI-Assistant
Wechat AI Assistant is a project that enables multi-modal interaction with ChatGPT AI assistant within WeChat. It allows users to engage in conversations, role-playing, respond to voice messages, analyze images and videos, summarize articles and web links, and search the internet. The project utilizes the WeChatFerry library to control the Windows PC desktop WeChat client and leverages the OpenAI Assistant API for intelligent multi-modal message processing. Users can interact with ChatGPT AI in WeChat through text or voice, access various tools like bing_search, browse_link, image_to_text, text_to_image, text_to_speech, video_analysis, and more. The AI autonomously determines which code interpreter and external tools to use to complete tasks. Future developments include file uploads for AI to reference content, integration with other APIs, and login support for enterprise WeChat and WeChat official accounts.
hdu-cs-wiki
The HDU Computer Science Lecture Notes is a comprehensive guide designed to help students navigate through various challenges in the field of computer science. It covers topics such as programming languages, artificial intelligence, software development, and more. The notes provide insights on how to effectively utilize university time, balance grades with project experience, and make informed decisions regarding career paths. Created by a collaborative effort involving students, teachers, and industry experts, the lecture notes aim to serve as a guiding tool for individuals seeking guidance in the computer science domain.
xiaozhi-esp32
The xiaozhi-esp32 repository is the first hardware project by Xia Ge, focusing on creating an AI chatbot using ESP32, SenseVoice, and Qwen72B. The project aims to help beginners in AI hardware development understand how to apply language models to hardware devices. It supports various functionalities such as Wi-Fi configuration, offline voice wake-up, multilingual speech recognition, voiceprint recognition, TTS using large models, and more. The project encourages participation for learning and improvement, providing resources for hardware and firmware development.
Verbiverse
Verbiverse is a tool that uses a large language model to assist in reading PDFs and watching videos, aimed at improving language proficiency. It provides a more convenient and efficient way to use large models through predefined prompts, designed for those looking to enhance their language skills. The tool analyzes unfamiliar words and sentences in foreign language PDFs or video subtitles, providing better contextual understanding compared to traditional dictionary translations or ambiguous meanings. It offers features such as automatic loading of subtitles, word analysis by clicking or double-clicking, and a word database for collecting words. Users can run the tool on Windows x86_64 or ubuntu_22.04 x86_64 platforms by downloading the precompiled packages or by cloning the source code and setting up a virtual environment with Python. It is recommended to use a local model or smaller PDF files for testing due to potential token consumption issues with large files.
ai-paint-today-BE
AI Paint Today is an API server repository that allows users to record their emotions and daily experiences, and based on that, AI generates a beautiful picture diary of their day. The project includes features such as generating picture diaries from written entries, utilizing DALL-E 2 model for image generation, and deploying on AWS and Cloudflare. The project also follows specific conventions and collaboration strategies for development.
For similar tasks

ai_igu
AI-IGU is a GitHub repository focused on Artificial Intelligence (AI) concepts, technology, software development, and algorithm improvement for all ages and professions. It emphasizes the importance of future software for future scientists and the increasing need for software developers in the industry. The repository covers various topics related to AI, including machine learning, deep learning, data mining, data science, big data, and more. It provides educational materials, practical examples, and hands-on projects to enhance software development skills and create awareness in the field of AI.

Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement
The Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement repository provides packaged Industry Scenario DREAM Demos with ARM templates (Containing a demo web application, Power BI reports, Synapse resources, AML Notebooks etc.) that can be deployed in a customer’s subscription using the CAPE tool within a matter of few hours. Partners can also deploy DREAM Demos in their own subscriptions using DPoC.
SQLAgent
DataAgent is a multi-agent system for data analysis, capable of understanding data development and data analysis requirements, understanding data, and generating SQL and Python code for tasks such as data query, data visualization, and machine learning.
100days_AI
The 100 Days in AI repository provides a comprehensive roadmap for individuals to learn Artificial Intelligence over a period of 100 days. It covers topics ranging from basic programming in Python to advanced concepts in AI, including machine learning, deep learning, and specialized AI topics. The repository includes daily tasks, resources, and exercises to ensure a structured learning experience. By following this roadmap, users can gain a solid understanding of AI and be prepared to work on real-world AI projects.

marimo
Marimo is a reactive Python notebook that ensures code and outputs consistency by automatically running dependent cells or marking them as stale. It replaces various tools like Jupyter, streamlit, and more, offering an interactive environment with features like binding UI elements to Python, reproducibility, executability as scripts or apps, shareability, and designed for data tasks. It is git-friendly, offers a modern editor with AI assistants, and comes with built-in package management. Marimo provides deterministic execution order, dynamic markdown and SQL capabilities, and a performant runtime. It is easy to get started with and suitable for both beginners and power users.
Ultimate-Data-Science-Toolkit---From-Python-Basics-to-GenerativeAI
Ultimate Data Science Toolkit is a comprehensive repository covering Python basics to Generative AI. It includes modules on Python programming, data analysis, statistics, machine learning, MLOps, case studies, and deep learning. The repository provides detailed tutorials on various topics such as Python data structures, control statements, functions, modules, object-oriented programming, exception handling, file handling, web API, databases, list comprehension, lambda functions, Pandas, Numpy, data visualization, statistical analysis, supervised and unsupervised machine learning algorithms, model serialization, ML pipeline orchestration, case studies, and deep learning concepts like neural networks and autoencoders.
mlforpublicpolicylab
The Machine Learning for Public Policy Lab is a project-based course focused on solving real-world problems using machine learning in the context of public policy and social good. Students will gain hands-on experience building end-to-end machine learning systems, developing skills in problem formulation, working with messy data, communicating with non-technical stakeholders, model interpretability, and understanding algorithmic bias & disparities. The course covers topics such as project scoping, data acquisition, feature engineering, model evaluation, bias and fairness, and model interpretability. Students will work in small groups on policy projects, with graded components including project proposals, presentations, and final reports.
ml-road-map
The Machine Learning Road Map is a comprehensive guide designed to take individuals from various levels of machine learning knowledge to a basic understanding of machine learning principles using high-quality, free resources. It aims to simplify the complex and rapidly growing field of machine learning by providing a structured roadmap for learning. The guide emphasizes the importance of understanding AI for everyone, the need for patience in learning machine learning due to its complexity, and the value of learning from experts in the field. It covers five different paths to learning about machine learning, catering to consumers, aspiring AI researchers, ML engineers, developers interested in building ML applications, and companies looking to implement AI solutions.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.