
cl-waffe2
[Experimental] Graph and Tensor Abstraction for Deep Learning all in Common Lisp
Stars: 119

cl-waffe2 is an experimental deep learning framework in Common Lisp, providing fast, systematic, and customizable matrix operations, reverse mode tape-based Automatic Differentiation, and neural network model building and training features accelerated by a JIT Compiler. It offers abstraction layers, extensibility, inlining, graph-level optimization, visualization, debugging, systematic nodes, and symbolic differentiation. Users can easily write extensions and optimize their networks without overheads. The framework is designed to eliminate barriers between users and developers, allowing for easy customization and extension.
README:
Visit the docs »
Concepts
·
Install
·
Examples
⚠️ cl-waffe2 is still in the experimental stage. Things are subject to change, and APIs can be changed without warnings. DO NOT USE CL-WAFFE2 IN YOUR PRODUCT.I actually have a repository cl-waffe(DEPRECATED UNSUPPORTED!) with a similar name. Note that cl-waffe2 is the latest one and all features are inherited from the old one.
cl-waffe2 provides fast, systematic, easy to optimize, customizable, device independent abstract matrix operations, and reverse mode tape-based Automatic Differentiation on Common Lisp. Plus, we also provide features for building and training neural network models, accelerated by a JIT Compiler.
Roughly speaking, this is a framework for the graph and tensor abstraction without overheads. All features provided here can be extended by users without exceptions - and with minimal code. In fact, cl-waffe2 is designed as the truly easiest framework to write extensions by users. There is no barrier between users and developers. There is no restriction imposed by the framework ignoring the developing language is limited to Common Lisp.
As of this writing, its abstraction layers are almost reaching the goals and working enough, but there is still a serious lack of backend functionality, and documentation. Contributions are welcome and I would appreciate if somebody who is interested in by project contact me: hikettei.
- Abstraction cl-waffe2 brings AbstractTensor (and AbstractNode!) to Common Lisp.
- Extensible All operations can be reimplemented with any matrix operation libraries you like! Plus, AbstractNode guarantees that no code rewriting is needed when changing devices.
- Inlining Anyone can write an optimized loop calling foreign libraries; an order is collapsed and shuffled depending on the ranks and offsets.
- Graph-Level Optimization cl-waffe2 provides a powerful abstract graph optimization tool that can be used on any devices. For example, it optimizes the locality of memory, and make operations in-place as much as possible.
-
Visualize Super easy to know the bottleneck in your network, because a
proceed-benchfunction profiles every instruction. - Debugging cl-waffe2 is enough clever by not only detecting all Shaping-Error before the execution but it also suggests alternatives! In addition, all objects in cl-waffe2 are nicely rendered on your REPL.
- Systematic Nodes AbstractNodes and Models are based on small and elegant macros.
- Symbolic Differentiation In the first place, cl-waffe2 does not create nodes that are later modified. Compiler macros eliminate functions producing such nodes.
As the simplest example, the build function traces and compiles the network from the endpoints of the computation nodes.
Example1. Compiling nodes
(let ((a (make-input `(A B) :A))
(b (make-input `(A B) :B)))
(let ((model (build (!sum (!mul a b)) :inputs `(:A :B))))
(print model)
;; model is a compiled function: f(a b)
(forward model (randn `(3 3)) (randn `(3 3)))))
;;<Compiled-Composite(allocated-p=NIL)
;; forward : forward(model A B) -> CPUTENSOR{FLOAT}(1 1)
;; backward : backward(model) -> t
;; memory-pool : two tensor(s)
;; L {8.0e-6+((A B) x 4.0e-6)}MB
;; inputs:
;; A -> (A B)
;; B -> (A B)
;;>
;;{CPUTENSOR[float] :shape (1 1) -> :view (<(BROADCAST 1)> <(BROADCAST 1)>) -> :visible-shape (1 1) :named ChainTMP646587
;; ((1.0858848))
;; :facet :input
;; :requires-grad NIL
;; :backward NIL} The advantages of using Common Lisp are numerous:
- The shape of tensors is not limited to numbers, but can also include symbols and even S-expressions!
- Automatic Generation of Iterators, ShapeError, etc.
- Works as a Domain Specific Language for Deep Learning embedded in Common Lisp
Example2. MLP Model
;; From https://github.com/hikettei/cl-waffe2/blob/master/examples/mnist/mlp.lisp
(defsequence MLP (in-features hidden-dim out-features
&key (activation #'!relu))
"Three Layers MLP Model"
(LinearLayer in-features hidden-dim)
(asnode activation)
(LinearLayer hidden-dim hidden-dim)
(asnode activation)
(LinearLayer hidden-dim out-features))
(defun build-mlp-model (in-class out-class &key (hidden-size 256) (activation #'!relu) (lr 1e-3))
(let* ((mlp (MLP in-class hidden-size out-class :activation activation))
(lazy-loss (criterion #'softmax-cross-entropy
(call mlp
(make-input `(batch-size ,in-class) :X))
(make-input `(batch-size ,out-class) :Y)
:reductions (list #'!sum #'->scal)))
(model (build lazy-loss :inputs `(:X :Y))))
(mapc (hooker x (Adam x :lr lr)) (model-parameters model))
(values model mlp)))
(defun step-train-mlp (model x y)
(let ((act-loss (forward model x y)))
(backward model)
(mapc #'call-optimizer! (model-parameters model))
(/ (tensor-vec act-loss) 100)))
(defmethod accuracy ((model MLP) x y)
(let* ((out (!argmax (call model x)))
(label (!argmax y))
(total (proceed (->scal (!sum (A=B out label))))))
(float (/ (tensor-vec total) (nth 0 (shape out))))))Example3. reshape and transform
(!reshape (make-input `(N C H W) nil) (~ N C H W -> (* N C H) W))
(%transform (ax+b `(3) 1 0)[i] -> [~ i])We also provide example projects here!
Don't underestimate the power of lazy evaluation. Nodes are first converted to fully optimized IRs before doing forward and backward propagations.
Since cl-waffe2 is still under development, there are still many optimization techniques remains to be implemented. Even these benchmarks were measured under single-core but shows enough performance!
optimizers=Adam, hidden_size=256
| n_epoch | cl-waffe2 | Keras | PyTorch | JAX |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3.111s | 3.662s | 3.418 | 4.039s |
| 10 | 32.437s | 31.352s | 28.403s | 30.801s |
| 100 | 304.864s | 274.854s | 338.031s | 275.875s |
optimizers=Adam hidden=512
| n_epoch | cl-waffe2 | Keras | PyTorch | JAX |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6.075s | 7.55s | 7.29s | 6.90s |
| 10 | 61.703s | 56.283s | 51.140s | 65.682s |
(Coming Soon...)
(Coming Soon...)
-
All comments on this Reddit post: Does anyone have any interest in my deep-learning framework?.
-
digikar99 for giving me intriguing perspectives on some semantics and the publication of a large number of valuable references.
-
Some of the algorithms implemented within the source code are referenced below:
-
Marsaglia, G., & Tsang, W. W. (2000). The ziggurat method for generating random variables. Journal of statistical software.
-
Previous works of JIT Compiler for Deep Learning:
-
See also my reading list: https://github.com/hikettei/cl-waffe2/issues/47
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for cl-waffe2
Similar Open Source Tools

cl-waffe2
cl-waffe2 is an experimental deep learning framework in Common Lisp, providing fast, systematic, and customizable matrix operations, reverse mode tape-based Automatic Differentiation, and neural network model building and training features accelerated by a JIT Compiler. It offers abstraction layers, extensibility, inlining, graph-level optimization, visualization, debugging, systematic nodes, and symbolic differentiation. Users can easily write extensions and optimize their networks without overheads. The framework is designed to eliminate barriers between users and developers, allowing for easy customization and extension.

rl
TorchRL is an open-source Reinforcement Learning (RL) library for PyTorch. It provides pytorch and **python-first** , low and high level abstractions for RL that are intended to be **efficient** , **modular** , **documented** and properly **tested**. The code is aimed at supporting research in RL. Most of it is written in python in a highly modular way, such that researchers can easily swap components, transform them or write new ones with little effort.
RWKV-LM
RWKV is an RNN with Transformer-level LLM performance, which can also be directly trained like a GPT transformer (parallelizable). And it's 100% attention-free. You only need the hidden state at position t to compute the state at position t+1. You can use the "GPT" mode to quickly compute the hidden state for the "RNN" mode. So it's combining the best of RNN and transformer - **great performance, fast inference, saves VRAM, fast training, "infinite" ctx_len, and free sentence embedding** (using the final hidden state).
awesome-production-llm
This repository is a curated list of open-source libraries for production large language models. It includes tools for data preprocessing, training/finetuning, evaluation/benchmarking, serving/inference, application/RAG, testing/monitoring, and guardrails/security. The repository also provides a new category called LLM Cookbook/Examples for showcasing examples and guides on using various LLM APIs.

towhee
Towhee is a cutting-edge framework designed to streamline the processing of unstructured data through the use of Large Language Model (LLM) based pipeline orchestration. It can extract insights from diverse data types like text, images, audio, and video files using generative AI and deep learning models. Towhee offers rich operators, prebuilt ETL pipelines, and a high-performance backend for efficient data processing. With a Pythonic API, users can build custom data processing pipelines easily. Towhee is suitable for tasks like sentence embedding, image embedding, video deduplication, question answering with documents, and cross-modal retrieval based on CLIP.

catalyst
Catalyst is a C# Natural Language Processing library designed for speed, inspired by spaCy's design. It provides pre-trained models, support for training word and document embeddings, and flexible entity recognition models. The library is fast, modern, and pure-C#, supporting .NET standard 2.0. It is cross-platform, running on Windows, Linux, macOS, and ARM. Catalyst offers non-destructive tokenization, named entity recognition, part-of-speech tagging, language detection, and efficient binary serialization. It includes pre-built models for language packages and lemmatization. Users can store and load models using streams. Getting started with Catalyst involves installing its NuGet Package and setting the storage to use the online repository. The library supports lazy loading of models from disk or online. Users can take advantage of C# lazy evaluation and native multi-threading support to process documents in parallel. Training a new FastText word2vec embedding model is straightforward, and Catalyst also provides algorithms for fast embedding search and dimensionality reduction.
mobius
Mobius is an AI infra platform including realtime computing and training. It is built on Ray, a distributed computing framework, and provides a number of features that make it well-suited for online machine learning tasks. These features include: * **Cross Language**: Mobius can run in multiple languages (only Python and Java are supported currently) with high efficiency. You can implement your operator in different languages and run them in one job. * **Single Node Failover**: Mobius has a special failover mechanism that only needs to rollback the failed node itself, in most cases, to recover the job. This is a huge benefit if your job is sensitive about failure recovery time. * **AutoScaling**: Mobius can generate a new graph with different configurations in runtime without stopping the job. * **Fusion Training**: Mobius can combine TensorFlow/Pytorch and streaming, then building an e2e online machine learning pipeline. Mobius is still under development, but it has already been used to power a number of real-world applications, including: * A real-time recommendation system for a major e-commerce company * A fraud detection system for a large financial institution * A personalized news feed for a major news organization If you are interested in using Mobius for your own online machine learning projects, you can find more information in the documentation.
superlinked
Superlinked is a compute framework for information retrieval and feature engineering systems, focusing on converting complex data into vector embeddings for RAG, Search, RecSys, and Analytics stack integration. It enables custom model performance in machine learning with pre-trained model convenience. The tool allows users to build multimodal vectors, define weights at query time, and avoid postprocessing & rerank requirements. Users can explore the computational model through simple scripts and python notebooks, with a future release planned for production usage with built-in data infra and vector database integrations.

cleanlab
Cleanlab helps you **clean** data and **lab** els by automatically detecting issues in a ML dataset. To facilitate **machine learning with messy, real-world data** , this data-centric AI package uses your _existing_ models to estimate dataset problems that can be fixed to train even _better_ models.
superagentx
SuperAgentX is a lightweight open-source AI framework designed for multi-agent applications with Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) capabilities. It offers goal-oriented multi-agents with retry mechanisms, easy deployment through WebSocket, RESTful API, and IO console interfaces, streamlined architecture with no major dependencies, contextual memory using SQL + Vector databases, flexible LLM configuration supporting various Gen AI models, and extendable handlers for integration with diverse APIs and data sources. It aims to accelerate the development of AGI by providing a powerful platform for building autonomous AI agents capable of executing complex tasks with minimal human intervention.
dom-to-semantic-markdown
DOM to Semantic Markdown is a tool that converts HTML DOM to Semantic Markdown for use in Large Language Models (LLMs). It maximizes semantic information, token efficiency, and preserves metadata to enhance LLMs' processing capabilities. The tool captures rich web content structure, including semantic tags, image metadata, table structures, and link destinations. It offers customizable conversion options and supports both browser and Node.js environments.
MarkLLM
MarkLLM is an open-source toolkit designed for watermarking technologies within large language models (LLMs). It simplifies access, understanding, and assessment of watermarking technologies, supporting various algorithms, visualization tools, and evaluation modules. The toolkit aids researchers and the community in ensuring the authenticity and origin of machine-generated text.

KULLM
KULLM (구름) is a Korean Large Language Model developed by Korea University NLP & AI Lab and HIAI Research Institute. It is based on the upstage/SOLAR-10.7B-v1.0 model and has been fine-tuned for instruction. The model has been trained on 8×A100 GPUs and is capable of generating responses in Korean language. KULLM exhibits hallucination and repetition phenomena due to its decoding strategy. Users should be cautious as the model may produce inaccurate or harmful results. Performance may vary in benchmarks without a fixed system prompt.
DriveLM
DriveLM is a multimodal AI model that enables autonomous driving by combining computer vision and natural language processing. It is designed to understand and respond to complex driving scenarios using visual and textual information. DriveLM can perform various tasks related to driving, such as object detection, lane keeping, and decision-making. It is trained on a massive dataset of images and text, which allows it to learn the relationships between visual cues and driving actions. DriveLM is a powerful tool that can help to improve the safety and efficiency of autonomous vehicles.
map-anything
MapAnything is an end-to-end trained transformer model for 3D reconstruction tasks, supporting over 12 different tasks including multi-image sfm, multi-view stereo, monocular metric depth estimation, and more. It provides a simple and efficient way to regress the factored metric 3D geometry of a scene from various inputs like images, calibration, poses, or depth. The tool offers flexibility in combining different geometric inputs for enhanced reconstruction results. It includes interactive demos, support for COLMAP & GSplat, data processing for training & benchmarking, and pre-trained models on Hugging Face Hub with different licensing options.
Eco2AI
Eco2AI is a python library for CO2 emission tracking that monitors energy consumption of CPU & GPU devices and estimates equivalent carbon emissions based on regional emission coefficients. Users can easily integrate Eco2AI into their Python scripts by adding a few lines of code. The library records emissions data and device information in a local file, providing detailed session logs with project names, experiment descriptions, start times, durations, power consumption, CO2 emissions, CPU and GPU names, operating systems, and countries.
For similar tasks

cl-waffe2
cl-waffe2 is an experimental deep learning framework in Common Lisp, providing fast, systematic, and customizable matrix operations, reverse mode tape-based Automatic Differentiation, and neural network model building and training features accelerated by a JIT Compiler. It offers abstraction layers, extensibility, inlining, graph-level optimization, visualization, debugging, systematic nodes, and symbolic differentiation. Users can easily write extensions and optimize their networks without overheads. The framework is designed to eliminate barriers between users and developers, allowing for easy customization and extension.
xlang
XLang™ is a cutting-edge language designed for AI and IoT applications, offering exceptional dynamic and high-performance capabilities. It excels in distributed computing and seamless integration with popular languages like C++, Python, and JavaScript. Notably efficient, running 3 to 5 times faster than Python in AI and deep learning contexts. Features optimized tensor computing architecture for constructing neural networks through tensor expressions. Automates tensor data flow graph generation and compilation for specific targets, enhancing GPU performance by 6 to 10 times in CUDA environments.
AI-resources
AI-resources is a repository containing links to various resources for learning Artificial Intelligence. It includes video lectures, courses, tutorials, and open-source libraries related to deep learning, reinforcement learning, machine learning, and more. The repository categorizes resources for beginners, average users, and advanced users/researchers, providing a comprehensive collection of materials to enhance knowledge and skills in AI.
ai-hands-on
A complete, hands-on guide to becoming an AI Engineer. This repository is designed to help you learn AI from first principles, build real neural networks, and understand modern LLM systems end-to-end. Progress through math, PyTorch, deep learning, transformers, RAG, and OCR with clean, intuitive Jupyter notebooks guiding you at every step. Suitable for beginners and engineers leveling up, providing clarity, structure, and intuition to build real AI systems.
aistore
AIStore is a lightweight object storage system designed for AI applications. It is highly scalable, reliable, and easy to use. AIStore can be deployed on any commodity hardware, and it can be used to store and manage large datasets for deep learning and other AI applications.
aigt
AIGT is a repository containing scripts for deep learning in guided medical interventions, focusing on ultrasound imaging. It provides a complete workflow from formatting and annotations to real-time model deployment. Users can set up an Anaconda environment, run Slicer notebooks, acquire tracked ultrasound data, and process exported data for training. The repository includes tools for segmentation, image export, and annotation creation.
DeepLearing-Interview-Awesome-2024
DeepLearning-Interview-Awesome-2024 is a repository that covers various topics related to deep learning, computer vision, big models (LLMs), autonomous driving, smart healthcare, and more. It provides a collection of interview questions with detailed explanations sourced from recent academic papers and industry developments. The repository is aimed at assisting individuals in academic research, work innovation, and job interviews. It includes six major modules covering topics such as large language models (LLMs), computer vision models, common problems in computer vision and perception algorithms, deep learning basics and frameworks, as well as specific tasks like 3D object detection, medical image segmentation, and more.
PINNACLE
PINNACLE is a flexible geometric deep learning approach that trains on contextualized protein interaction networks to generate context-aware protein representations. It provides protein representations split across various cell-type contexts from different tissues and organs. The tool can be fine-tuned to study the genomic effects of drugs and nominate promising protein targets and cell-type contexts for further investigation. PINNACLE exemplifies the paradigm of incorporating context-specific effects for studying biological systems, especially the impact of disease and therapeutics.
For similar jobs
Qwen-TensorRT-LLM
Qwen-TensorRT-LLM is a project developed for the NVIDIA TensorRT Hackathon 2023, focusing on accelerating inference for the Qwen-7B-Chat model using TRT-LLM. The project offers various functionalities such as FP16/BF16 support, INT8 and INT4 quantization options, Tensor Parallel for multi-GPU parallelism, web demo setup with gradio, Triton API deployment for maximum throughput/concurrency, fastapi integration for openai requests, CLI interaction, and langchain support. It supports models like qwen2, qwen, and qwen-vl for both base and chat models. The project also provides tutorials on Bilibili and blogs for adapting Qwen models in NVIDIA TensorRT-LLM, along with hardware requirements and quick start guides for different model types and quantization methods.
dl_model_infer
This project is a c++ version of the AI reasoning library that supports the reasoning of tensorrt models. It provides accelerated deployment cases of deep learning CV popular models and supports dynamic-batch image processing, inference, decode, and NMS. The project has been updated with various models and provides tutorials for model exports. It also includes a producer-consumer inference model for specific tasks. The project directory includes implementations for model inference applications, backend reasoning classes, post-processing, pre-processing, and target detection and tracking. Speed tests have been conducted on various models, and onnx downloads are available for different models.
joliGEN
JoliGEN is an integrated framework for training custom generative AI image-to-image models. It implements GAN, Diffusion, and Consistency models for various image translation tasks, including domain and style adaptation with conservation of semantics. The tool is designed for real-world applications such as Controlled Image Generation, Augmented Reality, Dataset Smart Augmentation, and Synthetic to Real transforms. JoliGEN allows for fast and stable training with a REST API server for simplified deployment. It offers a wide range of options and parameters with detailed documentation available for models, dataset formats, and data augmentation.
ai-edge-torch
AI Edge Torch is a Python library that supports converting PyTorch models into a .tflite format for on-device applications on Android, iOS, and IoT devices. It offers broad CPU coverage with initial GPU and NPU support, closely integrating with PyTorch and providing good coverage of Core ATen operators. The library includes a PyTorch converter for model conversion and a Generative API for authoring mobile-optimized PyTorch Transformer models, enabling easy deployment of Large Language Models (LLMs) on mobile devices.
awesome-RK3588
RK3588 is a flagship 8K SoC chip by Rockchip, integrating Cortex-A76 and Cortex-A55 cores with NEON coprocessor for 8K video codec. This repository curates resources for developing with RK3588, including official resources, RKNN models, projects, development boards, documentation, tools, and sample code.

cl-waffe2
cl-waffe2 is an experimental deep learning framework in Common Lisp, providing fast, systematic, and customizable matrix operations, reverse mode tape-based Automatic Differentiation, and neural network model building and training features accelerated by a JIT Compiler. It offers abstraction layers, extensibility, inlining, graph-level optimization, visualization, debugging, systematic nodes, and symbolic differentiation. Users can easily write extensions and optimize their networks without overheads. The framework is designed to eliminate barriers between users and developers, allowing for easy customization and extension.
TensorRT-Model-Optimizer
The NVIDIA TensorRT Model Optimizer is a library designed to quantize and compress deep learning models for optimized inference on GPUs. It offers state-of-the-art model optimization techniques including quantization and sparsity to reduce inference costs for generative AI models. Users can easily stack different optimization techniques to produce quantized checkpoints from torch or ONNX models. The quantized checkpoints are ready for deployment in inference frameworks like TensorRT-LLM or TensorRT, with planned integrations for NVIDIA NeMo and Megatron-LM. The tool also supports 8-bit quantization with Stable Diffusion for enterprise users on NVIDIA NIM. Model Optimizer is available for free on NVIDIA PyPI, and this repository serves as a platform for sharing examples, GPU-optimized recipes, and collecting community feedback.
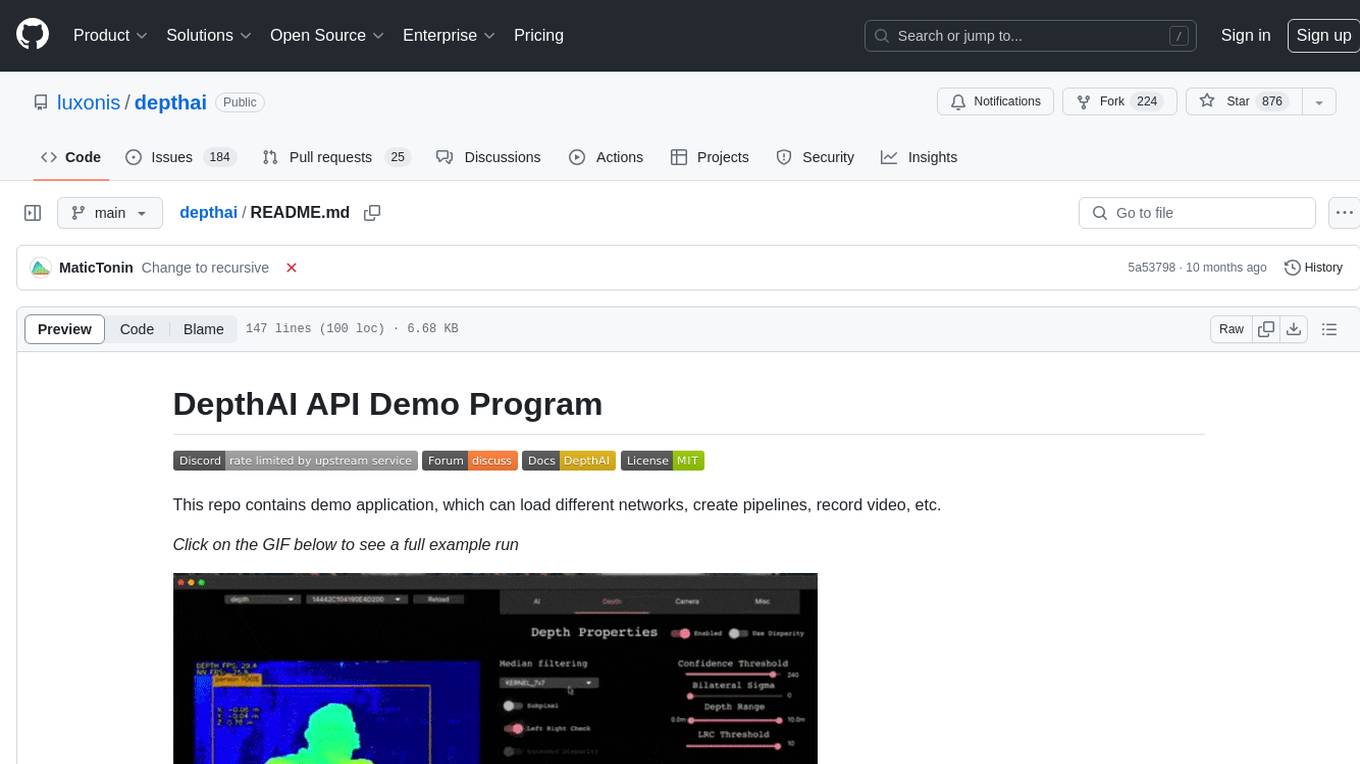
depthai
This repository contains a demo application for DepthAI, a tool that can load different networks, create pipelines, record video, and more. It provides documentation for installation and usage, including running programs through Docker. Users can explore DepthAI features via command line arguments or a clickable QT interface. Supported models include various AI models for tasks like face detection, human pose estimation, and object detection. The tool collects anonymous usage statistics by default, which can be disabled. Users can report issues to the development team for support and troubleshooting.

