
rig
⚙️🦀 Build modular and scalable LLM Applications in Rust
Stars: 6113
Rig is a Rust library designed for building scalable, modular, and user-friendly applications powered by large language models (LLMs). It provides full support for LLM completion and embedding workflows, offers simple yet powerful abstractions for LLM providers like OpenAI and Cohere, as well as vector stores such as MongoDB and in-memory storage. With Rig, users can easily integrate LLMs into their applications with minimal boilerplate code.
README:
📑 Docs • 🌐 Website • 🤝 Contribute • ✍🏽 Blogs
✨ If you would like to help spread the word about Rig, please consider starring the repo!
[!WARNING] Here be dragons! As we plan to ship a torrent of features in the following months, future updates will contain breaking changes. With Rig evolving, we'll annotate changes and highlight migration paths as we encounter them.
Rig is a Rust library for building scalable, modular, and ergonomic LLM-powered applications.
More information about this crate can be found in the official & crate (API Reference) documentations.
- Agentic workflows that can handle multi-turn streaming and prompting
- Full GenAI Semantic Convention compatibility
- 20+ model providers, all under one singular unified interface
- 10+ vector store integrations, all under one singular unified interface
- Full support for LLM completion and embedding workflows
- Support for transcription, audio generation and image generation model capabilities
- Integrate LLMs in your app with minimal boilerplate
- Full WASM compatibility (core library only)
Below is a non-exhaustive list of companies and people who are using Rig:
-
St Jude - Using Rig for a chatbot utility as part of
proteinpaint, a genomics visualisation tool. - Coral Protocol - Using Rig extensively, both internally as well as part of the Coral Rust SDK.
-
VT Code - VT Code is a Rust-based terminal coding agent with semantic code intelligence via Tree-sitter and ast-grep. VT Code uses
rigfor simplifying LLM calls and implement model picker. - Dria - a decentralised AI network. Currently using Rig as part of their compute node.
- Nethermind - Using Rig as part of their Neural Interconnected Nodes Engine framework.
- Neon - Using Rig for their app.build V2 reboot in Rust.
- Listen - A framework aiming to become the go-to framework for AI portfolio management agents. Powers the Listen app.
- Cairnify - helps users find documents, links, and information instantly through an intelligent search bar. Rig provides the agentic foundation behind Cairnify’s AI search experience, enabling tool-calling, reasoning, and retrieval workflows.
- Ryzome - Ryzome is a visual AI workspace that lets you build interconnected canvases of thoughts, research, and AI agents to orchestrate complex knowledge work.
- deepwiki-rs - Turn code into clarity. Generate accurate technical docs and AI-ready context in minutes—perfectly structured for human teams and intelligent agents.
- Cortex Memory - The production-ready memory system for intelligent agents. A complete solution for memory management, from extraction and vector search to automated optimization, with a REST API, MCP, CLI, and insights dashboard out-of-the-box.
- Ironclaw - A secure personal AI assistant
For a full list, check out our ECOSYSTEM.md file.
Are you also using Rig? Open an issue to have your name added!
cargo add rig-coreuse rig::client::{CompletionClient, ProviderClient};
use rig::completion::Prompt;
use rig::providers::openai;
#[tokio::main]
async fn main() -> Result<(), anyhow::Error> {
// Create OpenAI client
let client = openai::Client::from_env();
// Create agent with a single context prompt
let comedian_agent = client
.agent("gpt-5.2")
.preamble("You are a comedian here to entertain the user using humour and jokes.")
.build();
// Prompt the agent and print the response
let response = comedian_agent.prompt("Entertain me!").await?;
println!("{response}");
Ok(())
}Note using #[tokio::main] requires you enable tokio's macros and rt-multi-thread features
or just full to enable all features (cargo add tokio --features macros,rt-multi-thread).
You can find more examples each crate's examples (ie. rig/rig-core/examples) directory. More detailed use cases walkthroughs are regularly published on our Dev.to Blog and added to Rig's official documentation (docs.rig.rs).
Vector stores are available as separate companion-crates:
- MongoDB:
rig-mongodb - LanceDB:
rig-lancedb - Neo4j:
rig-neo4j - Qdrant:
rig-qdrant - SQLite:
rig-sqlite - SurrealDB:
rig-surrealdb - Milvus:
rig-milvus - ScyllaDB:
rig-scylladb - AWS S3Vectors:
rig-s3vectors - HelixDB:
rig-helixdb
The following providers are available as separate companion-crates:
- AWS Bedrock:
rig-bedrock - Fastembed:
rig-fastembed - Eternal AI:
rig-eternalai - Google Vertex:
rig-vertexai
We also have some other associated crates that have additional functionality you may find helpful when using Rig:
-
rig-onchain-kit- the Rig Onchain Kit. Intended to make interactions between Solana/EVM and Rig much easier to implement.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for rig
Similar Open Source Tools

rig
Rig is a Rust library designed for building scalable, modular, and user-friendly applications powered by large language models (LLMs). It provides full support for LLM completion and embedding workflows, offers simple yet powerful abstractions for LLM providers like OpenAI and Cohere, as well as vector stores such as MongoDB and in-memory storage. With Rig, users can easily integrate LLMs into their applications with minimal boilerplate code.
koog
Koog is a Kotlin-based framework for building and running AI agents entirely in idiomatic Kotlin. It allows users to create agents that interact with tools, handle complex workflows, and communicate with users. Key features include pure Kotlin implementation, MCP integration, embedding capabilities, custom tool creation, ready-to-use components, intelligent history compression, powerful streaming API, persistent agent memory, comprehensive tracing, flexible graph workflows, modular feature system, scalable architecture, and multiplatform support.
arcade-ai
Arcade AI is a developer-focused tooling and API platform designed to enhance the capabilities of LLM applications and agents. It simplifies the process of connecting agentic applications with user data and services, allowing developers to concentrate on building their applications. The platform offers prebuilt toolkits for interacting with various services, supports multiple authentication providers, and provides access to different language models. Users can also create custom toolkits and evaluate their tools using Arcade AI. Contributions are welcome, and self-hosting is possible with the provided documentation.
budibase
Budibase is an open-source low-code platform that allows users to build web applications visually without writing code. It provides a drag-and-drop interface for designing user interfaces and workflows, as well as a visual editor for defining data models and business logic. With Budibase, users can quickly create custom web applications for various purposes, such as data management, project tracking, and internal tools. The platform supports integrations with popular services and databases, making it easy to extend the functionality of applications. Budibase is suitable for both experienced developers looking to speed up their workflow and non-technical users who want to create web applications without coding.

langchain
LangChain is a framework for building LLM-powered applications that simplifies AI application development by chaining together interoperable components and third-party integrations. It helps developers connect LLMs to diverse data sources, swap models easily, and future-proof decisions as technology evolves. LangChain's ecosystem includes tools like LangSmith for agent evals, LangGraph for complex task handling, and LangGraph Platform for deployment and scaling. Additional resources include tutorials, how-to guides, conceptual guides, a forum, API reference, and chat support.
LocalLLMClient
LocalLLMClient is a Swift package designed to interact with local Large Language Models (LLMs) on Apple platforms. It supports GGUF, MLX models, and the FoundationModels framework, providing streaming API, multimodal capabilities, and tool calling functionalities. Users can easily integrate this tool to work with various models for text generation and processing. The package also includes advanced features for low-level API control and multimodal image processing. LocalLLMClient is experimental and subject to API changes, offering support for iOS, macOS, and Linux platforms.
Fast-LLM
Fast-LLM is an open-source library designed for training large language models with exceptional speed, scalability, and flexibility. Built on PyTorch and Triton, it offers optimized kernel efficiency, reduced overheads, and memory usage, making it suitable for training models of all sizes. The library supports distributed training across multiple GPUs and nodes, offers flexibility in model architectures, and is easy to use with pre-built Docker images and simple configuration. Fast-LLM is licensed under Apache 2.0, developed transparently on GitHub, and encourages contributions and collaboration from the community.
AimRT
AimRT is a basic runtime framework for modern robotics, developed in modern C++ with lightweight and easy deployment. It integrates research and development for robot applications in various deployment scenarios, providing debugging tools and observability support. AimRT offers a plug-in development interface compatible with ROS2, HTTP, Grpc, and other ecosystems for progressive system upgrades.
atomic-agents
The Atomic Agents framework is a modular and extensible tool designed for creating powerful applications. It leverages Pydantic for data validation and serialization. The framework follows the principles of Atomic Design, providing small and single-purpose components that can be combined. It integrates with Instructor for AI agent architecture and supports various APIs like Cohere, Anthropic, and Gemini. The tool includes documentation, examples, and testing features to ensure smooth development and usage.
llama_index
LlamaIndex is a data framework for building LLM applications. It provides tools for ingesting, structuring, and querying data, as well as integrating with LLMs and other tools. LlamaIndex is designed to be easy to use for both beginner and advanced users, and it provides a comprehensive set of features for building LLM applications.
Acontext
Acontext is a context data platform designed for production AI agents, offering unified storage, built-in context management, and observability features. It helps agents scale from local demos to production without the need to rebuild context infrastructure. The platform provides solutions for challenges like scattered context data, long-running agents requiring context management, and tracking states from multi-modal agents. Acontext offers core features such as context storage, session management, disk storage, agent skills management, and sandbox for code execution and analysis. Users can connect to Acontext, install SDKs, initialize clients, store and retrieve messages, perform context engineering, and utilize agent storage tools. The platform also supports building agents using end-to-end scripts in Python and Typescript, with various templates available. Acontext's architecture includes client layer, backend with API and core components, infrastructure with PostgreSQL, S3, Redis, and RabbitMQ, and a web dashboard. Join the Acontext community on Discord and follow updates on GitHub.

deeppowers
Deeppowers is a powerful Python library for deep learning applications. It provides a wide range of tools and utilities to simplify the process of building and training deep neural networks. With Deeppowers, users can easily create complex neural network architectures, perform efficient training and optimization, and deploy models for various tasks. The library is designed to be user-friendly and flexible, making it suitable for both beginners and experienced deep learning practitioners.
tensorzero
TensorZero is an open-source platform that helps LLM applications graduate from API wrappers into defensible AI products. It enables a data & learning flywheel for LLMs by unifying inference, observability, optimization, and experimentation. The platform includes a high-performance model gateway, structured schema-based inference, observability, experimentation, and data warehouse for analytics. TensorZero Recipes optimize prompts and models, and the platform supports experimentation features and GitOps orchestration for deployment.
Memori
Memori is a memory fabric designed for enterprise AI that seamlessly integrates into existing software and infrastructure. It is agnostic to LLM, datastore, and framework, providing support for major foundational models and databases. With features like vectorized memories, in-memory semantic search, and a knowledge graph, Memori simplifies the process of attributing LLM interactions and managing sessions. It offers Advanced Augmentation for enhancing memories at different levels and supports various platforms, frameworks, database integrations, and datastores. Memori is designed to reduce development overhead and provide efficient memory management for AI applications.
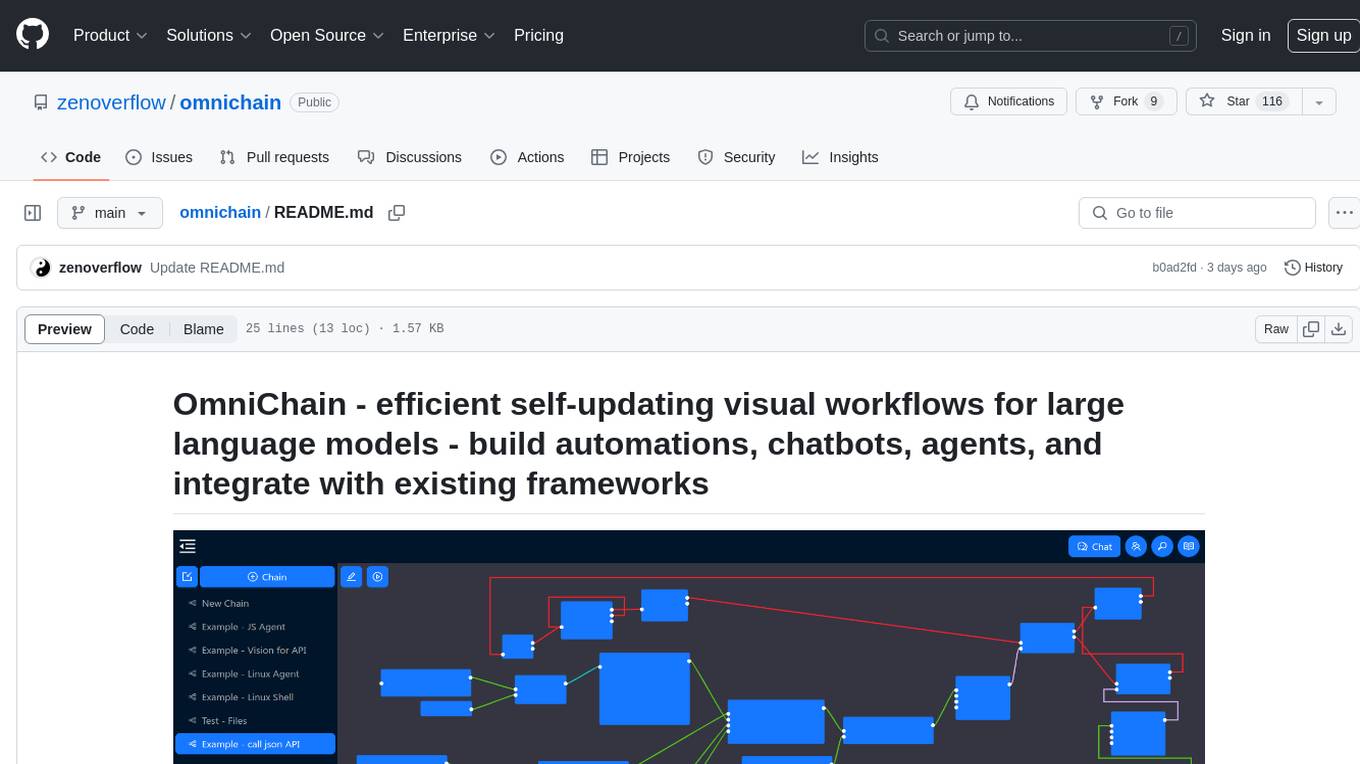
omnichain
OmniChain is a tool for building efficient self-updating visual workflows using AI language models, enabling users to automate tasks, create chatbots, agents, and integrate with existing frameworks. It allows users to create custom workflows guided by logic processes, store and recall information, and make decisions based on that information. The tool enables users to create tireless robot employees that operate 24/7, access the underlying operating system, generate and run NodeJS code snippets, and create custom agents and logic chains. OmniChain is self-hosted, open-source, and available for commercial use under the MIT license, with no coding skills required.
sdk-python
Strands Agents is a lightweight and flexible SDK that takes a model-driven approach to building and running AI agents. It supports various model providers, offers advanced capabilities like multi-agent systems and streaming support, and comes with built-in MCP server support. Users can easily create tools using Python decorators, integrate MCP servers seamlessly, and leverage multiple model providers for different AI tasks. The SDK is designed to scale from simple conversational assistants to complex autonomous workflows, making it suitable for a wide range of AI development needs.
For similar tasks
python-tutorial-notebooks
This repository contains Jupyter-based tutorials for NLP, ML, AI in Python for classes in Computational Linguistics, Natural Language Processing (NLP), Machine Learning (ML), and Artificial Intelligence (AI) at Indiana University.
open-parse
Open Parse is a Python library for visually discerning document layouts and chunking them effectively. It is designed to fill the gap in open-source libraries for handling complex documents. Unlike text splitting, which converts a file to raw text and slices it up, Open Parse visually analyzes documents for superior LLM input. It also supports basic markdown for parsing headings, bold, and italics, and has high-precision table support, extracting tables into clean Markdown formats with accuracy that surpasses traditional tools. Open Parse is extensible, allowing users to easily implement their own post-processing steps. It is also intuitive, with great editor support and completion everywhere, making it easy to use and learn.
MoonshotAI-Cookbook
The MoonshotAI-Cookbook provides example code and guides for accomplishing common tasks with the MoonshotAI API. To run these examples, you'll need an MoonshotAI account and associated API key. Most code examples are written in Python, though the concepts can be applied in any language.
AHU-AI-Repository
This repository is dedicated to the learning and exchange of resources for the School of Artificial Intelligence at Anhui University. Notes will be published on this website first: https://www.aoaoaoao.cn and will be synchronized to the repository regularly. You can also contact me at [email protected].
modern_ai_for_beginners
This repository provides a comprehensive guide to modern AI for beginners, covering both theoretical foundations and practical implementation. It emphasizes the importance of understanding both the mathematical principles and the code implementation of AI models. The repository includes resources on PyTorch, deep learning fundamentals, mathematical foundations, transformer-based LLMs, diffusion models, software engineering, and full-stack development. It also features tutorials on natural language processing with transformers, reinforcement learning, and practical deep learning for coders.
Building-AI-Applications-with-ChatGPT-APIs
This repository is for the book 'Building AI Applications with ChatGPT APIs' published by Packt. It provides code examples and instructions for mastering ChatGPT, Whisper, and DALL-E APIs through building innovative AI projects. Readers will learn to develop AI applications using ChatGPT APIs, integrate them with frameworks like Flask and Django, create AI-generated art with DALL-E APIs, and optimize ChatGPT models through fine-tuning.
examples
This repository contains a collection of sample applications and Jupyter Notebooks for hands-on experience with Pinecone vector databases and common AI patterns, tools, and algorithms. It includes production-ready examples for review and support, as well as learning-optimized examples for exploring AI techniques and building applications. Users can contribute, provide feedback, and collaborate to improve the resource.
lingoose
LinGoose is a modular Go framework designed for building AI/LLM applications. It offers the flexibility to import only the necessary modules, abstracts features for customization, and provides a comprehensive solution for developing AI/LLM applications from scratch. The framework simplifies the process of creating intelligent applications by allowing users to choose preferred implementations or create their own. LinGoose empowers developers to leverage its capabilities to streamline the development of cutting-edge AI and LLM projects.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.






