
PINNACLE
Contextual AI models for single-cell protein biology
Stars: 70
PINNACLE is a flexible geometric deep learning approach that trains on contextualized protein interaction networks to generate context-aware protein representations. It provides protein representations split across various cell-type contexts from different tissues and organs. The tool can be fine-tuned to study the genomic effects of drugs and nominate promising protein targets and cell-type contexts for further investigation. PINNACLE exemplifies the paradigm of incorporating context-specific effects for studying biological systems, especially the impact of disease and therapeutics.
README:
Authors:
- Michelle M. Li
- Yepeng Huang
- Marissa Sumathipala
- Man Qing Liang
- Alberto Valdeolivas
- Ashwin Ananthakrishnan
- Katherine Liao
- Daniel Marbach
- Marinka Zitnik
Protein interaction networks are a critical component in studying the function and therapeutic potential of proteins. However, accurately modeling protein interactions across diverse biological contexts, such as tissues and cell types, remains a significant challenge for existing algorithms.
We introduce PINNACLE, a flexible geometric deep learning approach that trains on contextualized protein interaction networks to generate context-aware protein representations. Leveraging a multi-organ single-cell transcriptomic atlas of humans, PINNACLE provides 394,760 protein representations split across 156 cell-type contexts from 24 tissues and organs. We demonstrate that PINNACLE's contextualized representations of proteins reflect cellular and tissue organization and PINNACLE's tissue representations enable zero-shot retrieval of tissue hierarchy. Infused with cellular and tissue organization, our contextualized protein representations can easily be adapted for diverse downstream tasks.
We fine-tune PINNACLE to study the genomic effects of drugs in multiple cellular contexts and show that our context-aware model significantly outperforms state-of-the-art, yet context-agnostic, models. Enabled by our context-aware modeling of proteins, PINNACLE is able to nominate promising protein targets and cell-type contexts for further investigation. PINNACLE exemplifies and empowers the long-standing paradigm of incorporating context-specific effects for studying biological systems, especially the impact of disease and therapeutics.
PINNACLE is a self-supervised geometric deep learning model that can generate protein representations in diverse celltype contexts. It is trained on a set of context-aware protein interaction networks unified by a cellular and tissue network to produce contextualized protein representations based cell type activation. Unlike existing approaches, which do not consider biological context, PINNACLE produces multiple representations of proteins based on their cell type context, representations of the cell type contexts themselves, and representations of the tissue hierarchy.
Given the multi-scale nature of the model inputs, PINNACLE is equipped to learn the topology of proteins, cell types, and tissues in a single unified embedding space. PINNACLE uses protein-, cell type-, and tissue-level attention mechanisms and objective functions to inject cellular and tissue organization into the embedding space. Intuitively, pairs of nodes that share an edge should be embedded nearby, proteins of the same cell type context should be embedded nearby (and far from proteins in other cell type contexts), and proteins should be embedded close to their cell type context (and far from other cell type contexts).
First, clone the GitHub repository:
git clone https://github.com/mims-harvard/PINNACLE
cd PINNACLE
This codebase leverages Python, Pytorch, Pytorch Geometric, etc. To create an environment with all of the required packages, please ensure that conda is installed and then execute the commands:
conda env create -f environment.yml
conda activate pinnacle
bash install_pyg.sh
The data is hosted on Figshare. To maintain the directory structure while downloading the files, make sure to select all files and download in the original format. Make sure to also unzip all files in the download.
We provide the following datasets for training PINNACLE:
- Global reference protein interaction network
- Cell type specific protein interaction networks
- Metagraph of cell type and tissue relationships
The networks are provided in the appropriate format for PINNACLE. If you would like to use your own set of contextualized networks, please adhere to the format used in the cell type specific protein interaction networks (see README in data_prep folder for more details). The file should be structured as a tab-delimited table, where each line contains information for a single context. Each line must contain the following elements (in this order): index, context name (e.g., cell type name), comma-delimited list of nodes. The lists of nodes are used to extract a subgraph from the global reference network (e.g., global reference protein interaction network).
We also provide checkpoints for PINNACLE after pretraining. The checkpoints for PINNACLE can be found here. Make sure all downloaded files are unzipped. You can use these checkpoints (and/or embeddings) directly with the scripts in the finetune_pinnacle folder instead of training the models yourself.
You can finetune PINNACLE on your own datasets by using our provided model checkpoints or contextualized representations (i.e., no re-training needed). Please review this README to learn how to preprocess and finetune PINNACLE on your own datasets.
You can reproduce our results or pretrain PINNACLE on your own networks:
cd pinnacle
python train.py \
--G_f ../data/networks/global_ppi_edgelist.txt \
--ppi_dir ../data/networks/ppi_edgelists/ \
--mg_f ../data/networks/mg_edgelist.txt \
--save_prefix ../data/pinnacle_embeds/
To see and/or modify the default hyperparameters, please see the get_hparams() function in pinnacle/parse_args.py.
An example bash script is provided in pinnacle/run_pinnacle.sh.
After training PINNACLE, you can visualize PINNACLE's representations using evaluate/visualize_representations.py.
After training PINNACLE (you may also simply use our already-trained models), you can finetune PINNACLE for any downstream biomedical task of interest. Here, we provide instructions for nominating therapeutic targets. An example bash script can be found here.
✨ To finetune PINNACLE for nominating therapeutic targets of rheumatoid arthritis:
cd finetune_pinnacle
python train.py \
--disease EFO_0000685 \
--embeddings_dir ./data/pinnacle_embeds/
✨ To finetune PINNACLE for nominating therapeutic targets of inflammatory bowel disease:
cd finetune_pinnacle
python train.py \
--disease EFO_0003767 \
--embeddings_dir ./data/pinnacle_embeds/
To generate predictions on a different therapeutic area, simply find the disease ID from OpenTargets and change the ---disease flag.
To see and/or modify the default hyperparameters, please see the get_hparams() function in finetune_pinnacle/train_utils.py.
@article{pinnacle,
title={Contextual AI models for single-cell protein biology},
author={Li, Michelle M and Huang, Yepeng and Sumathipala, Marissa and Liang, Man Qing and Valdeolivas, Alberto and Ananthakrishnan, Ashwin N and Liao, Katherine and Marbach, Daniel and Zitnik, Marinka},
journal={Nature Methods},
pages={1--12},
year={2024},
publisher={Nature Publishing Group US New York}
}
Please leave a Github issue or contact Michelle Li at [email protected].
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for PINNACLE
Similar Open Source Tools

PINNACLE
PINNACLE is a flexible geometric deep learning approach that trains on contextualized protein interaction networks to generate context-aware protein representations. It provides protein representations split across various cell-type contexts from different tissues and organs. The tool can be fine-tuned to study the genomic effects of drugs and nominate promising protein targets and cell-type contexts for further investigation. PINNACLE exemplifies the paradigm of incorporating context-specific effects for studying biological systems, especially the impact of disease and therapeutics.

DNAnalyzer
DNAnalyzer is a nonprofit organization dedicated to revolutionizing DNA analysis through AI-powered tools. It aims to democratize access to DNA analysis for a deeper understanding of human health and disease. The tool provides innovative AI-powered analysis and interpretive tools to empower geneticists, physicians, and researchers to gain deep insights into DNA sequences, revolutionizing how we understand human health and disease.

Me-LLaMA
Me LLaMA introduces a suite of open-source medical Large Language Models (LLMs), including Me LLaMA 13B/70B and their chat-enhanced versions. Developed through innovative continual pre-training and instruction tuning, these models leverage a vast medical corpus comprising PubMed papers, medical guidelines, and general domain data. Me LLaMA sets new benchmarks on medical reasoning tasks, making it a significant asset for medical NLP applications and research. The models are intended for computational linguistics and medical research, not for clinical decision-making without validation and regulatory approval.
ManipVQA
ManipVQA is a framework that enhances Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) with manipulation-centric knowledge through a Visual Question-Answering (VQA) format. It addresses the deficiency of conventional MLLMs in understanding affordances and physical concepts crucial for manipulation tasks. By infusing robotics-specific knowledge, including tool detection, affordance recognition, and physical concept comprehension, ManipVQA improves the performance of robots in manipulation tasks. The framework involves fine-tuning MLLMs with a curated dataset of interactive objects, enabling robots to understand and execute natural language instructions more effectively.
aika
AIKA (Artificial Intelligence for Knowledge Acquisition) is a new type of artificial neural network designed to mimic the behavior of a biological brain more closely and bridge the gap to classical AI. The network conceptually separates activations from neurons, creating two separate graphs to represent acquired knowledge and inferred information. It uses different types of neurons and synapses to propagate activation values, binding signals, causal relations, and training gradients. The network structure allows for flexible topology and supports the gradual population of neurons and synapses during training.
llama3_interpretability_sae
This project focuses on implementing Sparse Autoencoders (SAEs) for mechanistic interpretability in Large Language Models (LLMs) like Llama 3.2-3B. The SAEs aim to untangle superimposed representations in LLMs into separate, interpretable features for each neuron activation. The project provides an end-to-end pipeline for capturing training data, training the SAEs, analyzing learned features, and verifying results experimentally. It includes comprehensive logging, visualization, and checkpointing of SAE training, interpretability analysis tools, and a pure PyTorch implementation of Llama 3.1/3.2 chat and text completion. The project is designed for scalability, efficiency, and maintainability.
EScAIP
EScAIP is an Efficiently Scaled Attention Interatomic Potential that leverages a novel multi-head self-attention formulation within graph neural networks to predict energy and forces between atoms in molecules and materials. It achieves substantial gains in efficiency, at least 10x speed up in inference time and 5x less memory usage compared to existing models. EScAIP represents a philosophy towards developing general-purpose Neural Network Interatomic Potentials that achieve better expressivity through scaling and continue to scale efficiently with increased computational resources and training data.
context-cite
ContextCite is a tool for attributing statements generated by LLMs back to specific parts of the context. It allows users to analyze and understand the sources of information used by language models in generating responses. By providing attributions, users can gain insights into how the model makes decisions and where the information comes from.
Electronic-Component-Sorter
The Electronic Component Classifier is a project that uses machine learning and artificial intelligence to automate the identification and classification of electrical and electronic components. It features component classification into seven classes, user-friendly design, and integration with Flask for a user-friendly interface. The project aims to reduce human error in component identification, make the process safer and more reliable, and potentially help visually impaired individuals in identifying electronic components.

eureka-ml-insights
The Eureka ML Insights Framework is a repository containing code designed to help researchers and practitioners run reproducible evaluations of generative models efficiently. Users can define custom pipelines for data processing, inference, and evaluation, as well as utilize pre-defined evaluation pipelines for key benchmarks. The framework provides a structured approach to conducting experiments and analyzing model performance across various tasks and modalities.

aitlas
The AiTLAS toolbox (Artificial Intelligence Toolbox for Earth Observation) includes state-of-the-art machine learning methods for exploratory and predictive analysis of satellite imagery as well as a repository of AI-ready Earth Observation (EO) datasets. It can be easily applied for a variety of Earth Observation tasks, such as land use and cover classification, crop type prediction, localization of specific objects (semantic segmentation), etc. The main goal of AiTLAS is to facilitate better usability and adoption of novel AI methods (and models) by EO experts, while offering easy access and standardized format of EO datasets to AI experts which allows benchmarking of various existing and novel AI methods tailored for EO data.
LongRoPE
LongRoPE is a method to extend the context window of large language models (LLMs) beyond 2 million tokens. It identifies and exploits non-uniformities in positional embeddings to enable 8x context extension without fine-tuning. The method utilizes a progressive extension strategy with 256k fine-tuning to reach a 2048k context. It adjusts embeddings for shorter contexts to maintain performance within the original window size. LongRoPE has been shown to be effective in maintaining performance across various tasks from 4k to 2048k context lengths.
Graph-CoT
This repository contains the source code and datasets for Graph Chain-of-Thought: Augmenting Large Language Models by Reasoning on Graphs accepted to ACL 2024. It proposes a framework called Graph Chain-of-thought (Graph-CoT) to enable Language Models to traverse graphs step-by-step for reasoning, interaction, and execution. The motivation is to alleviate hallucination issues in Language Models by augmenting them with structured knowledge sources represented as graphs.
xlstm-jax
The xLSTM-jax repository contains code for training and evaluating the xLSTM model on language modeling using JAX. xLSTM is a Recurrent Neural Network architecture that improves upon the original LSTM through Exponential Gating, normalization, stabilization techniques, and a Matrix Memory. It is optimized for large-scale distributed systems with performant triton kernels for faster training and inference.
matchem-llm
A public repository collecting links to state-of-the-art training sets, QA, benchmarks and other evaluations for various ML and LLM applications in materials science and chemistry. It includes datasets related to chemistry, materials, multimodal data, and knowledge graphs in the field. The repository aims to provide resources for training and evaluating machine learning models in the materials science and chemistry domains.
LLMs-World-Models-for-Planning
This repository provides a Python implementation of a method that leverages pre-trained large language models to construct and utilize world models for model-based task planning. It includes scripts to generate domain models using natural language descriptions, correct domain models based on feedback, and support plan generation for tasks in different domains. The code has been refactored for better readability and includes tools for validating PDDL syntax and handling corrective feedback.
For similar tasks

PINNACLE
PINNACLE is a flexible geometric deep learning approach that trains on contextualized protein interaction networks to generate context-aware protein representations. It provides protein representations split across various cell-type contexts from different tissues and organs. The tool can be fine-tuned to study the genomic effects of drugs and nominate promising protein targets and cell-type contexts for further investigation. PINNACLE exemplifies the paradigm of incorporating context-specific effects for studying biological systems, especially the impact of disease and therapeutics.
ToolUniverse
ToolUniverse is a collection of 211 biomedical tools designed for Agentic AI, providing access to biomedical knowledge for solving therapeutic reasoning tasks. The tools cover various aspects of drugs and diseases, linked to trusted sources like US FDA-approved drugs since 1939, Open Targets, and Monarch Initiative.
aistore
AIStore is a lightweight object storage system designed for AI applications. It is highly scalable, reliable, and easy to use. AIStore can be deployed on any commodity hardware, and it can be used to store and manage large datasets for deep learning and other AI applications.

cl-waffe2
cl-waffe2 is an experimental deep learning framework in Common Lisp, providing fast, systematic, and customizable matrix operations, reverse mode tape-based Automatic Differentiation, and neural network model building and training features accelerated by a JIT Compiler. It offers abstraction layers, extensibility, inlining, graph-level optimization, visualization, debugging, systematic nodes, and symbolic differentiation. Users can easily write extensions and optimize their networks without overheads. The framework is designed to eliminate barriers between users and developers, allowing for easy customization and extension.
aigt
AIGT is a repository containing scripts for deep learning in guided medical interventions, focusing on ultrasound imaging. It provides a complete workflow from formatting and annotations to real-time model deployment. Users can set up an Anaconda environment, run Slicer notebooks, acquire tracked ultrasound data, and process exported data for training. The repository includes tools for segmentation, image export, and annotation creation.
DeepLearing-Interview-Awesome-2024
DeepLearning-Interview-Awesome-2024 is a repository that covers various topics related to deep learning, computer vision, big models (LLMs), autonomous driving, smart healthcare, and more. It provides a collection of interview questions with detailed explanations sourced from recent academic papers and industry developments. The repository is aimed at assisting individuals in academic research, work innovation, and job interviews. It includes six major modules covering topics such as large language models (LLMs), computer vision models, common problems in computer vision and perception algorithms, deep learning basics and frameworks, as well as specific tasks like 3D object detection, medical image segmentation, and more.
ai-hands-on
A complete, hands-on guide to becoming an AI Engineer. This repository is designed to help you learn AI from first principles, build real neural networks, and understand modern LLM systems end-to-end. Progress through math, PyTorch, deep learning, transformers, RAG, and OCR with clean, intuitive Jupyter notebooks guiding you at every step. Suitable for beginners and engineers leveling up, providing clarity, structure, and intuition to build real AI systems.
For similar jobs

NoLabs
NoLabs is an open-source biolab that provides easy access to state-of-the-art models for bio research. It supports various tasks, including drug discovery, protein analysis, and small molecule design. NoLabs aims to accelerate bio research by making inference models accessible to everyone.
OpenCRISPR
OpenCRISPR is a set of free and open gene editing systems designed by Profluent Bio. The OpenCRISPR-1 protein maintains the prototypical architecture of a Type II Cas9 nuclease but is hundreds of mutations away from SpCas9 or any other known natural CRISPR-associated protein. You can view OpenCRISPR-1 as a drop-in replacement for many protocols that need a cas9-like protein with an NGG PAM and you can even use it with canonical SpCas9 gRNAs. OpenCRISPR-1 can be fused in a deactivated or nickase format for next generation gene editing techniques like base, prime, or epigenome editing.
ersilia
The Ersilia Model Hub is a unified platform of pre-trained AI/ML models dedicated to infectious and neglected disease research. It offers an open-source, low-code solution that provides seamless access to AI/ML models for drug discovery. Models housed in the hub come from two sources: published models from literature (with due third-party acknowledgment) and custom models developed by the Ersilia team or contributors.

ontogpt
OntoGPT is a Python package for extracting structured information from text using large language models, instruction prompts, and ontology-based grounding. It provides a command line interface and a minimal web app for easy usage. The tool has been evaluated on test data and is used in related projects like TALISMAN for gene set analysis. OntoGPT enables users to extract information from text by specifying relevant terms and provides the extracted objects as output.
bia-bob
BIA `bob` is a Jupyter-based assistant for interacting with data using large language models to generate Python code. It can utilize OpenAI's chatGPT, Google's Gemini, Helmholtz' blablador, and Ollama. Users need respective accounts to access these services. Bob can assist in code generation, bug fixing, code documentation, GPU-acceleration, and offers a no-code custom Jupyter Kernel. It provides example notebooks for various tasks like bio-image analysis, model selection, and bug fixing. Installation is recommended via conda/mamba environment. Custom endpoints like blablador and ollama can be used. Google Cloud AI API integration is also supported. The tool is extensible for Python libraries to enhance Bob's functionality.
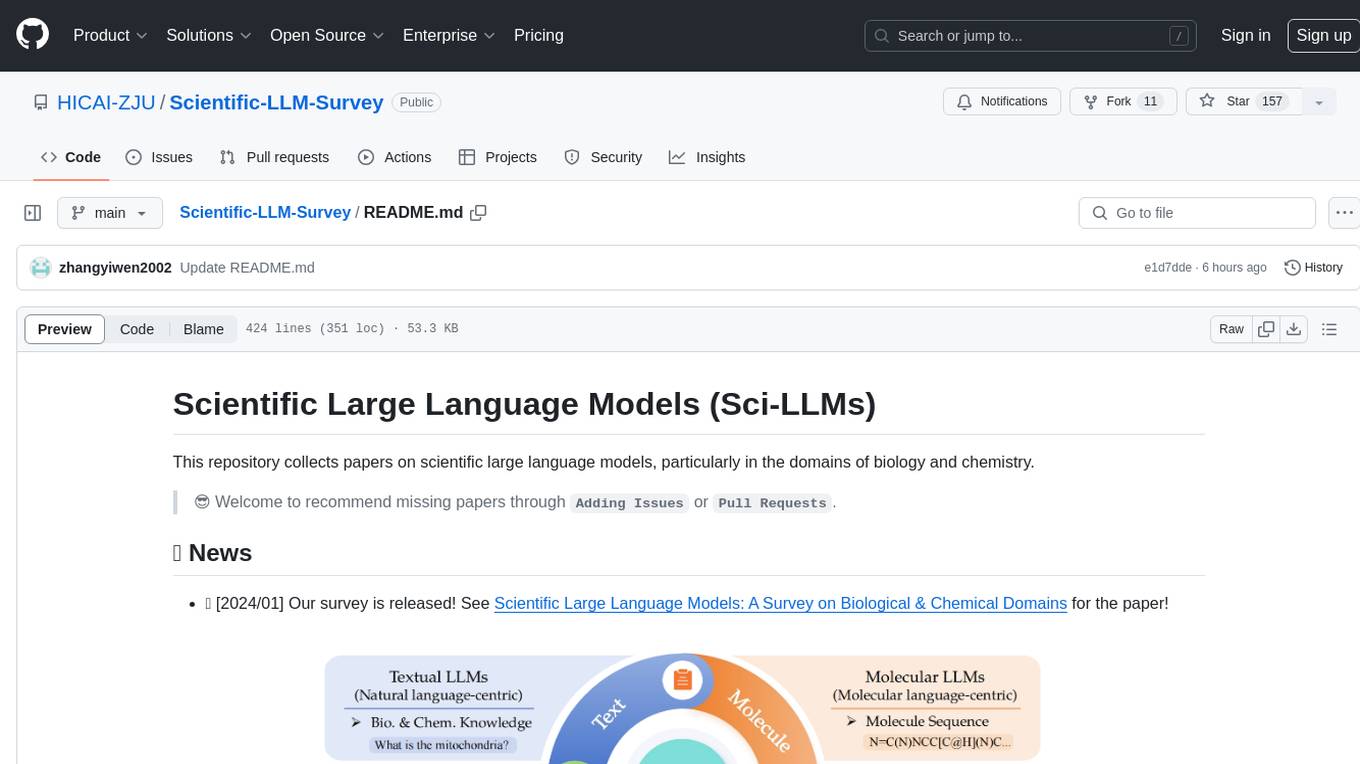
Scientific-LLM-Survey
Scientific Large Language Models (Sci-LLMs) is a repository that collects papers on scientific large language models, focusing on biology and chemistry domains. It includes textual, molecular, protein, and genomic languages, as well as multimodal language. The repository covers various large language models for tasks such as molecule property prediction, interaction prediction, protein sequence representation, protein sequence generation/design, DNA-protein interaction prediction, and RNA prediction. It also provides datasets and benchmarks for evaluating these models. The repository aims to facilitate research and development in the field of scientific language modeling.
polaris
Polaris establishes a novel, industry‑certified standard to foster the development of impactful methods in AI-based drug discovery. This library is a Python client to interact with the Polaris Hub. It allows you to download Polaris datasets and benchmarks, evaluate a custom method against a Polaris benchmark, and create and upload new datasets and benchmarks.
awesome-AI4MolConformation-MD
The 'awesome-AI4MolConformation-MD' repository focuses on protein conformations and molecular dynamics using generative artificial intelligence and deep learning. It provides resources, reviews, datasets, packages, and tools related to AI-driven molecular dynamics simulations. The repository covers a wide range of topics such as neural networks potentials, force fields, AI engines/frameworks, trajectory analysis, visualization tools, and various AI-based models for protein conformational sampling. It serves as a comprehensive guide for researchers and practitioners interested in leveraging AI for studying molecular structures and dynamics.
