Me-LLaMA
A novel medical large language model family with 13/70B parameters, which have SOTA performances on various medical tasks
Stars: 126

Me LLaMA introduces a suite of open-source medical Large Language Models (LLMs), including Me LLaMA 13B/70B and their chat-enhanced versions. Developed through innovative continual pre-training and instruction tuning, these models leverage a vast medical corpus comprising PubMed papers, medical guidelines, and general domain data. Me LLaMA sets new benchmarks on medical reasoning tasks, making it a significant asset for medical NLP applications and research. The models are intended for computational linguistics and medical research, not for clinical decision-making without validation and regulatory approval.
README:
Me LLaMA introduces a groundbreaking suite of open-source medical Large Language Models (LLMs), including the foundation models Me LLaMA 13B/70B and their chat-enhanced versions, Me LLaMA 13B-chat/70B-chat. Developed through the innovative continual pre-training and instruction tuning of LLaMA2, these models leverage a vast medical corpus. This corpus encompasses selected PubMed papers and abstracts, a novel dataset of internationally-recognized medical guidelines, and a general domain corpus, positioning Me LLaMA at the forefront of medical AI research.
With its domain-specific advancements, Me LLaMA sets new benchmarks on a wide array of medical reasoning tasks. This makes Me LLaMA a significant asset for medical NLP applications and research.
The code, datasets, and models are available for non-commercial use.
- Code: See above.
- Datasets: Check our Hugging Face collection.
- Models: Please visit our PhysioNet repository. Note that a PhysioNet account, training, and data usage agreement are required.
This software and model are provided "as is", without warranty of any kind, express or implied, including but not limited to the warranties of merchantability, fitness for a particular purpose, and noninfringement. In no event shall the authors, contributors, or copyright holders be liable for any claim, damages, or other liability, whether in an action of contract, tort, or otherwise, arising from, out of, or in connection with the software or the use or other dealings in the software.
The Me LLaMA models are research tools intended for use in the field of computational linguistics and medicine. They are not intended to be used as diagnostic tools or for clinical decision-making without appropriate validation and regulatory approval. Users of the Me LLaMA models should be aware of their responsibilities to ensure the ethical and appropriate use of this technology, including adherence to any applicable legal and regulatory requirements.
The content and data provided with the models do not replace the expertise of healthcare professionals. Healthcare professionals should use their professional judgment in evaluating the outputs of the Me LLaMA models. Patients should not use the model outputs for self-diagnosis or treatment without consulting a qualified healthcare provider. The information is not intended for clinical decision making, is not intended to be used in the diagnosis or treatment of patients and may not be useful or appropriate for any clinical purpose.
Additionally, users are expressly prohibited from sharing or redistributing any outputs generated from the Me LLaMA models without explicit permission from the authors. This includes, but is not limited to, publishing, distributing, or making the generated outputs available to third parties in any form, whether for commercial purposes or not. This restriction is put in place to ensure responsible use of the technology and to respect the intellectual property rights associated with the models and their outputs. Violation of these terms may result in legal action and revocation of access to the models.
- Model License: PhysioNet Credentialed Health Data License 1.5.0
- Code License: MIT LICENSE
- Continued-pretrained from model: Llama-2 models, extensively adapted for the medical domain through targeted pre-training and instruction tuning
- Evaluation Datasets: Huggingface Evaluation Datasets Collection
- Paper: Me LLaMA: Foundation Large Language Models for Medical Applications
The development of Me LLaMA involved a meticulous process of continual pre-training and instruction tuning of the LLaMA2 models, incorporating an extensive 129B tokens and 214K instruction tuning samples from a diverse array of general, biomedical, and clinical domains. This comprehensive approach aimed to balance domain-specific knowledge with a broader understanding of general context, thereby effectively mitigating catastrophic forgetting issues.
The mixed continual pre-training dataset, comprising 129B tokens, includes a wide range of biomedical literature, clinical notes, and general domain data. This dataset is designed to ensure a deep focus on medical domain knowledge while incorporating a broad spectrum of general knowledge. The dataset's composition includes:
- Biomedical Papers: Integration of a vast collection from PubMed Central and PubMed Abstracts.
- Clinical Notes: Inclusion of de-identified free-text clinical notes from MIMIC-IV and MIMIC-CXR.
- General Domain Data: A subset from the RedPajama dataset, replicating LLaMA's pre-training data.
The pre-training utilized a ratio of 15:1:4 for biomedical, clinical to general domain data, aiming to maintain a strong medical focus while also broadening the model's understanding.
The Me LLaMA models, 13B and 70B, were developed through continuous pre-training and instruction tuning on the University of Florida's HiPerGator supercomputer, equipped with 160 A100 80GB GPUs. The process aimed to adapt the LLaMA2 models for enhanced comprehension and generation of medically relevant text. The training regimen involved:
- Optimization: Use of the AdamW optimizer with specific hyperparameters (β1=0.9, β2=0.95), a learning rate of 8e-6, and a weight decay of 0.00001.
- Learning Rate Scheduler: A cosine learning rate scheduler with a 0.05 warmup ratio for gradual adaptation.
- Precision and Efficiency: bf16 precision for computational efficiency and gradient accumulation over 16 steps, limited to one epoch.
- Model Parallelism: Utilization of DeepSpeed for effective model parallelism.
Following the pre-training phase, Me LLaMA models underwent instruction tuning using 8 H100 GPUs for 3 epochs, employing a learning rate of 1e-5. This phase focused on refining the models' ability to follow instructions and generalize across medical tasks, utilizing LoRA-based parameter-efficient fine-tuning for enhanced performance.
This detailed training procedure underscores the comprehensive approach taken in developing Me LLaMA models, leveraging advanced computational resources and methodologies to achieve state-of-the-art performance in the medical domain.
To utilize the Me LLaMA model locally, begin by acquiring the necessary model files from our PhysioNet project.
First, ensure that both the torch and transformers libraries are installed in your Python environment. These libraries are required for working with the model.
For basic text generation, you'll employ a pipeline from the transformers library. This method simplifies the process of generating text. Here's how you can set it up:
from transformers import pipeline
# Ensure you replace "FOLDER_PATH_TO_MODEL" with the actual path to your model files.
pipe = pipeline("text-generation", model="FOLDER_PATH_TO_MODEL")
# Example usage for generating text.
generated_text = pipe("The medical condition is characterized by", num_return_sequences=1)
print(generated_text)This code snippet demonstrates how to generate text based on a prompt. The num_return_sequences=1 argument specifies that you want to generate one sequence of text.
For tasks requiring more customization or fine-tuning capabilities, you might prefer directly loading the tokenizer and model. This approach gives you more control over the text generation process, allowing you to adjust parameters like the maximum length of the generated text. Here's a more detailed example:
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM
# Load the tokenizer and model from your local model directory.
# Don't forget to replace "FOLDER_PATH_TO_MODEL" with the actual path to your model files.
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("FOLDER_PATH_TO_MODEL")
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("FOLDER_PATH_TO_MODEL")
# Tokenizing input text for the model.
input_ids = tokenizer("[INPUT SENTENCE]", return_tensors="pt").input_ids
# Generating output based on the input_ids.
# You can adjust the max_length parameter as necessary for your use case.
generated_tokens = model.generate(input_ids, max_length=50)
# Decoding the generated tokens to produce readable text.
generated_text = tokenizer.decode(generated_tokens[0], skip_special_tokens=True)
print(generated_text)This setup allows for more nuanced interactions with the model, such as fine-tuning on specific datasets or modifying the generation parameters for different outputs. Remember to replace "[INPUT SENTENCE]" with the sentence or prompt you want the model to expand on or respond to.
git clone [email protected]:BIDS-Xu-Lab/Me-LLaMA.git --recursive
cd Me-LLaMA
pip install poetry
poetry install
cd src/medical-evaluation
poetry run pip install -e .[multilingual]
poetry run python -m spacy download en_core_web_lgBefore evaluation, please download BART checkpoint to src/metrics/BARTScore/bart_score.pth.
For automated evaluation, please follow these instructions:
-
Huggingface Transformer
To evaluate a model hosted on the HuggingFace Hub (for instance, llama2-7b-hf), change this command in
scripts/run_evaluation.sh:
poetry run python src/eval.py \
--model "hf-causal-vllm" \
--model_args "use_accelerate=True,pretrained=meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-chat-hf,use_fast=False" \
--tasks "PUBMEDQA,MedQA,MedMCQA,EmrQA,i2b2,DDI2013,hoc,MTSample,PUBMEDSUM,MimicSum,BioNLI,MedNLI"Then run bash command:
bash scripts/run_evaluation.shMore details can be found in the lm_eval documentation.
- Commercial APIs
Perform the same steps as the open-sourced models, first to change the bash file with:
export OPENAI_API_SECRET_KEY=YOUR_KEY_HERE
poetry run python src/eval.py \
--model gpt-4 \
--tasks "PUBMEDQA,MedQA,MedMCQA,EmrQA,i2b2,DDI2013,hoc,MTSample,PUBMEDSUM,MimicSum,BioNLI,MedNLI"Please note, for tasks such as NER, the automated evaluation is based on a specific pattern. This might fail to extract relevant information in zero-shot settings, resulting in relatively lower performance compared to previous human-annotated results.
@misc{xie2024llama,
title={Me LLaMA: Foundation Large Language Models for Medical Applications},
author={Qianqian Xie and Qingyu Chen and Aokun Chen and Cheng Peng and Yan Hu and Fongci Lin and Xueqing Peng and Jimin Huang and Jeffrey Zhang and Vipina Keloth and Huan He and Lucila Ohno-Machido and Yonghui Wu and Hua Xu and Jiang Bian},
year={2024},
eprint={2402.12749},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CL}
}
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for Me-LLaMA
Similar Open Source Tools

Me-LLaMA
Me LLaMA introduces a suite of open-source medical Large Language Models (LLMs), including Me LLaMA 13B/70B and their chat-enhanced versions. Developed through innovative continual pre-training and instruction tuning, these models leverage a vast medical corpus comprising PubMed papers, medical guidelines, and general domain data. Me LLaMA sets new benchmarks on medical reasoning tasks, making it a significant asset for medical NLP applications and research. The models are intended for computational linguistics and medical research, not for clinical decision-making without validation and regulatory approval.

kaapana
Kaapana is an open-source toolkit for state-of-the-art platform provisioning in the field of medical data analysis. The applications comprise AI-based workflows and federated learning scenarios with a focus on radiological and radiotherapeutic imaging. Obtaining large amounts of medical data necessary for developing and training modern machine learning methods is an extremely challenging effort that often fails in a multi-center setting, e.g. due to technical, organizational and legal hurdles. A federated approach where the data remains under the authority of the individual institutions and is only processed on-site is, in contrast, a promising approach ideally suited to overcome these difficulties. Following this federated concept, the goal of Kaapana is to provide a framework and a set of tools for sharing data processing algorithms, for standardized workflow design and execution as well as for performing distributed method development. This will facilitate data analysis in a compliant way enabling researchers and clinicians to perform large-scale multi-center studies. By adhering to established standards and by adopting widely used open technologies for private cloud development and containerized data processing, Kaapana integrates seamlessly with the existing clinical IT infrastructure, such as the Picture Archiving and Communication System (PACS), and ensures modularity and easy extensibility.
Taiyi-LLM
Taiyi (太一) is a bilingual large language model fine-tuned for diverse biomedical tasks. It aims to facilitate communication between healthcare professionals and patients, provide medical information, and assist in diagnosis, biomedical knowledge discovery, drug development, and personalized healthcare solutions. The model is based on the Qwen-7B-base model and has been fine-tuned using rich bilingual instruction data. It covers tasks such as question answering, biomedical dialogue, medical report generation, biomedical information extraction, machine translation, title generation, text classification, and text semantic similarity. The project also provides standardized data formats, model training details, model inference guidelines, and overall performance metrics across various BioNLP tasks.
RecAI
RecAI is a project that explores the integration of Large Language Models (LLMs) into recommender systems, addressing the challenges of interactivity, explainability, and controllability. It aims to bridge the gap between general-purpose LLMs and domain-specific recommender systems, providing a holistic perspective on the practical requirements of LLM4Rec. The project investigates various techniques, including Recommender AI agents, selective knowledge injection, fine-tuning language models, evaluation, and LLMs as model explainers, to create more sophisticated, interactive, and user-centric recommender systems.

asreview
The ASReview project implements active learning for systematic reviews, utilizing AI-aided pipelines to assist in finding relevant texts for search tasks. It accelerates the screening of textual data with minimal human input, saving time and increasing output quality. The software offers three modes: Oracle for interactive screening, Exploration for teaching purposes, and Simulation for evaluating active learning models. ASReview LAB is designed to support decision-making in any discipline or industry by improving efficiency and transparency in screening large amounts of textual data.
awesome-RLAIF
Reinforcement Learning from AI Feedback (RLAIF) is a concept that describes a type of machine learning approach where **an AI agent learns by receiving feedback or guidance from another AI system**. This concept is closely related to the field of Reinforcement Learning (RL), which is a type of machine learning where an agent learns to make a sequence of decisions in an environment to maximize a cumulative reward. In traditional RL, an agent interacts with an environment and receives feedback in the form of rewards or penalties based on the actions it takes. It learns to improve its decision-making over time to achieve its goals. In the context of Reinforcement Learning from AI Feedback, the AI agent still aims to learn optimal behavior through interactions, but **the feedback comes from another AI system rather than from the environment or human evaluators**. This can be **particularly useful in situations where it may be challenging to define clear reward functions or when it is more efficient to use another AI system to provide guidance**. The feedback from the AI system can take various forms, such as: - **Demonstrations** : The AI system provides demonstrations of desired behavior, and the learning agent tries to imitate these demonstrations. - **Comparison Data** : The AI system ranks or compares different actions taken by the learning agent, helping it to understand which actions are better or worse. - **Reward Shaping** : The AI system provides additional reward signals to guide the learning agent's behavior, supplementing the rewards from the environment. This approach is often used in scenarios where the RL agent needs to learn from **limited human or expert feedback or when the reward signal from the environment is sparse or unclear**. It can also be used to **accelerate the learning process and make RL more sample-efficient**. Reinforcement Learning from AI Feedback is an area of ongoing research and has applications in various domains, including robotics, autonomous vehicles, and game playing, among others.
LLMs-World-Models-for-Planning
This repository provides a Python implementation of a method that leverages pre-trained large language models to construct and utilize world models for model-based task planning. It includes scripts to generate domain models using natural language descriptions, correct domain models based on feedback, and support plan generation for tasks in different domains. The code has been refactored for better readability and includes tools for validating PDDL syntax and handling corrective feedback.
xlstm-jax
The xLSTM-jax repository contains code for training and evaluating the xLSTM model on language modeling using JAX. xLSTM is a Recurrent Neural Network architecture that improves upon the original LSTM through Exponential Gating, normalization, stabilization techniques, and a Matrix Memory. It is optimized for large-scale distributed systems with performant triton kernels for faster training and inference.
llmops-promptflow-template
LLMOps with Prompt flow is a template and guidance for building LLM-infused apps using Prompt flow. It provides centralized code hosting, lifecycle management, variant and hyperparameter experimentation, A/B deployment, many-to-many dataset/flow relationships, multiple deployment targets, comprehensive reporting, BYOF capabilities, configuration-based development, local prompt experimentation and evaluation, endpoint testing, and optional Human-in-loop validation. The tool is customizable to suit various application needs.
AutoWebGLM
AutoWebGLM is a project focused on developing a language model-driven automated web navigation agent. It extends the capabilities of the ChatGLM3-6B model to navigate the web more efficiently and address real-world browsing challenges. The project includes features such as an HTML simplification algorithm, hybrid human-AI training, reinforcement learning, rejection sampling, and a bilingual web navigation benchmark for testing AI web navigation agents.
uncheatable_eval
Uncheatable Eval is a tool designed to assess the language modeling capabilities of LLMs on real-time, newly generated data from the internet. It aims to provide a reliable evaluation method that is immune to data leaks and cannot be gamed. The tool supports the evaluation of Hugging Face AutoModelForCausalLM models and RWKV models by calculating the sum of negative log probabilities on new texts from various sources such as recent papers on arXiv, new projects on GitHub, news articles, and more. Uncheatable Eval ensures that the evaluation data is not included in the training sets of publicly released models, thus offering a fair assessment of the models' performance.
bocoel
BoCoEL is a tool that leverages Bayesian Optimization to efficiently evaluate large language models by selecting a subset of the corpus for evaluation. It encodes individual entries into embeddings, uses Bayesian optimization to select queries, retrieves from the corpus, and provides easily managed evaluations. The tool aims to reduce computation costs during evaluation with a dynamic budget, supporting models like GPT2, Pythia, and LLAMA through integration with Hugging Face transformers and datasets. BoCoEL offers a modular design and efficient representation of the corpus to enhance evaluation quality.
intelligence-toolkit
The Intelligence Toolkit is a suite of interactive workflows designed to help domain experts make sense of real-world data by identifying patterns, themes, relationships, and risks within complex datasets. It utilizes generative AI (GPT models) to create reports on findings of interest. The toolkit supports analysis of case, entity, and text data, providing various interactive workflows for different intelligence tasks. Users are expected to evaluate the quality of data insights and AI interpretations before taking action. The system is designed for moderate-sized datasets and responsible use of personal case data. It uses the GPT-4 model from OpenAI or Azure OpenAI APIs for generating reports and insights.
agentUniverse
agentUniverse is a framework for developing applications powered by multi-agent based on large language model. It provides essential components for building single agent and multi-agent collaboration mechanism for customizing collaboration patterns. Developers can easily construct multi-agent applications and share pattern practices from different fields. The framework includes pre-installed collaboration patterns like PEER and DOE for complex task breakdown and data-intensive tasks.

aitlas
The AiTLAS toolbox (Artificial Intelligence Toolbox for Earth Observation) includes state-of-the-art machine learning methods for exploratory and predictive analysis of satellite imagery as well as a repository of AI-ready Earth Observation (EO) datasets. It can be easily applied for a variety of Earth Observation tasks, such as land use and cover classification, crop type prediction, localization of specific objects (semantic segmentation), etc. The main goal of AiTLAS is to facilitate better usability and adoption of novel AI methods (and models) by EO experts, while offering easy access and standardized format of EO datasets to AI experts which allows benchmarking of various existing and novel AI methods tailored for EO data.
For similar tasks

Me-LLaMA
Me LLaMA introduces a suite of open-source medical Large Language Models (LLMs), including Me LLaMA 13B/70B and their chat-enhanced versions. Developed through innovative continual pre-training and instruction tuning, these models leverage a vast medical corpus comprising PubMed papers, medical guidelines, and general domain data. Me LLaMA sets new benchmarks on medical reasoning tasks, making it a significant asset for medical NLP applications and research. The models are intended for computational linguistics and medical research, not for clinical decision-making without validation and regulatory approval.
MedicalGPT
MedicalGPT is a training medical GPT model with ChatGPT training pipeline, implement of Pretraining, Supervised Finetuning, RLHF(Reward Modeling and Reinforcement Learning) and DPO(Direct Preference Optimization).
For similar jobs

Me-LLaMA
Me LLaMA introduces a suite of open-source medical Large Language Models (LLMs), including Me LLaMA 13B/70B and their chat-enhanced versions. Developed through innovative continual pre-training and instruction tuning, these models leverage a vast medical corpus comprising PubMed papers, medical guidelines, and general domain data. Me LLaMA sets new benchmarks on medical reasoning tasks, making it a significant asset for medical NLP applications and research. The models are intended for computational linguistics and medical research, not for clinical decision-making without validation and regulatory approval.
LLM-for-Healthcare
The repository 'LLM-for-Healthcare' provides a comprehensive survey of large language models (LLMs) for healthcare, covering data, technology, applications, and accountability and ethics. It includes information on various LLM models, training data, evaluation methods, and computation costs. The repository also discusses tasks such as NER, text classification, question answering, dialogue systems, and generation of medical reports from images in the healthcare domain.
HuatuoGPT-II
HuatuoGPT2 is an innovative domain-adapted medical large language model that excels in medical knowledge and dialogue proficiency. It showcases state-of-the-art performance in various medical benchmarks, surpassing GPT-4 in expert evaluations and fresh medical licensing exams. The open-source release includes HuatuoGPT2 models in 7B, 13B, and 34B versions, training code for one-stage adaptation, partial pre-training and fine-tuning instructions, and evaluation methods for medical response capabilities and professional pharmacist exams. The tool aims to enhance LLM capabilities in the Chinese medical field through open-source principles.
azure-health-data-and-ai-samples
The Azure Health Data and AI Samples Repo is a collection of sample apps and code to help users start with Azure Health Data and AI services, learn product usage, and speed up implementations. It includes samples for various health data workflows, such as data ingestion, analytics, machine learning, SMART on FHIR, patient services, FHIR service integration, Azure AD B2C access, DICOM service, MedTech service, and healthcare data solutions in Microsoft Fabric. These samples are simplified scenarios for testing purposes only.

fuse-med-ml
FuseMedML is a Python framework designed to accelerate machine learning-based discovery in the medical field by promoting code reuse. It provides a flexible design concept where data is stored in a nested dictionary, allowing easy handling of multi-modality information. The framework includes components for creating custom models, loss functions, metrics, and data processing operators. Additionally, FuseMedML offers 'batteries included' key components such as fuse.data for data processing, fuse.eval for model evaluation, and fuse.dl for reusable deep learning components. It supports PyTorch and PyTorch Lightning libraries and encourages the creation of domain extensions for specific medical domains.
MedLLMsPracticalGuide
This repository serves as a practical guide for Medical Large Language Models (Medical LLMs) and provides resources, surveys, and tools for building, fine-tuning, and utilizing LLMs in the medical domain. It covers a wide range of topics including pre-training, fine-tuning, downstream biomedical tasks, clinical applications, challenges, future directions, and more. The repository aims to provide insights into the opportunities and challenges of LLMs in medicine and serve as a practical resource for constructing effective medical LLMs.
hi-ml
The Microsoft Health Intelligence Machine Learning Toolbox is a repository that provides low-level and high-level building blocks for Machine Learning / AI researchers and practitioners. It simplifies and streamlines work on deep learning models for healthcare and life sciences by offering tested components such as data loaders, pre-processing tools, deep learning models, and cloud integration utilities. The repository includes two Python packages, 'hi-ml-azure' for helper functions in AzureML, 'hi-ml' for ML components, and 'hi-ml-cpath' for models and workflows related to histopathology images.
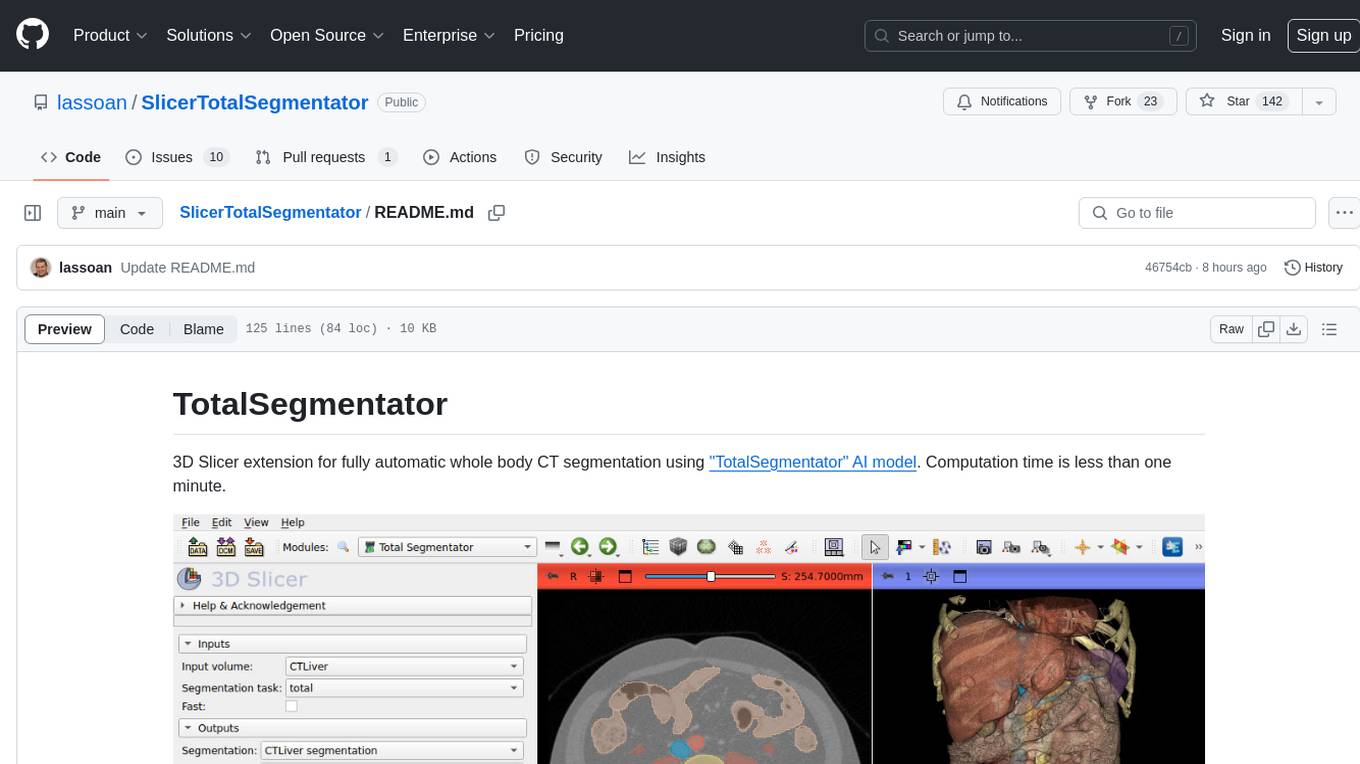
SlicerTotalSegmentator
TotalSegmentator is a 3D Slicer extension designed for fully automatic whole body CT segmentation using the 'TotalSegmentator' AI model. The computation time is less than one minute, making it efficient for research purposes. Users can set up GPU acceleration for faster segmentation. The tool provides a user-friendly interface for loading CT images, creating segmentations, and displaying results in 3D. Troubleshooting steps are available for common issues such as failed computation, GPU errors, and inaccurate segmentations. Contributions to the extension are welcome, following 3D Slicer contribution guidelines.