HuatuoGPT-II
HuatuoGPT2, One-stage Training for Medical Adaption of LLMs. (An Open Medical GPT)
Stars: 308
HuatuoGPT2 is an innovative domain-adapted medical large language model that excels in medical knowledge and dialogue proficiency. It showcases state-of-the-art performance in various medical benchmarks, surpassing GPT-4 in expert evaluations and fresh medical licensing exams. The open-source release includes HuatuoGPT2 models in 7B, 13B, and 34B versions, training code for one-stage adaptation, partial pre-training and fine-tuning instructions, and evaluation methods for medical response capabilities and professional pharmacist exams. The tool aims to enhance LLM capabilities in the Chinese medical field through open-source principles.
README:
🖥️ Online Demo (7B) |⬇️ 7B Model |⬇️ 13B Model | ⬇️ 34B Model | 📃 Paper
- [07/10/2024]: 🎉🎉🎉 Our paper is accepted for COLM 2024!
- [06/24/2024] We have made all training data for HuatuoGPT2 publicly available. This includes the Pretraining dataset and the SFT dataset).
- [01/10/2024] The HuatuoGPT2 model is now available on the Wisemodel platform.
- [12/04/2023] We released the code and dataset for our evaluation.
- [11/24/2023] We released the quantitative version of HuatuoGPT-II.
- [11/21/2023] We released HuatuoGPT-II models. The HuatuoGPT-II will be available in 7B, 13B, and 34B versions.
- [11/17/2023] We released the HuatuoGPT-II paper, achieving a new state-of-the-art in Chinese medical applications! Try our demo!
Hello! Welcome to the repository for HuatuoGPT2.
HuatuoGPT2 employs an innovative domain adaptation method to significantly boost its medical knowledge and dialogue proficiency. It showcases state-of-the-art performance in several medical benchmarks, especially surpassing GPT-4 in expert evaluations and the fresh medical licensing exams.
The open-source release of HuatuoGPT-2 includes:
- HuatuoGPT2 Model: Open-sourcing of 7B, 13B, and 34B versions.
- Training Code: Training code for one-stage adaptation will be provided, enabling better model adaptation across various languages and domains.
- HuatuoGPT2 Data: Release of partial pre-training and fine-tuning instructions.
- Evaluation for Chinese Medical LLM: Comprehensive automatic evaluation methods for medical response capabilities of LLM and the fresh professional pharmacist exam assessment.
Note that we're still actively organizing our code and data. Please stay tuned for updates coming soon!
Compared with representative open-source models and closed-source models (including GPT-4), HuatuoGPT2 showed impressive performance on medical benchmarks. Here, we present two of the results.
- Expert Evaluation: In assessments by medical professionals, HuatuoGPT-II's responses in Chinese medical contexts were favored over counterparts like GPT-4:
| HuatuoGPT-II Win Rate | Win | Tie | Fail |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single-round Medical Response | |||
| HuatuoGPT-II(7B) vs GPT-4 | 38 | 38 | 24 |
| HuatuoGPT-II(7B) vs ChatGPT | 52 | 33 | 15 |
| HuatuoGPT-II(7B) vs Baichuan2-13B-Chat | 63 | 19 | 18 |
| HuatuoGPT-II(7B) vs HuatuoGPT | 81 | 11 | 8 |
| Multi-round Medical Dialogue | |||
| HuatuoGPT-II(7B) vs GPT-4 | 53 | 17 | 30 |
| HuatuoGPT-II(7B) vs ChatGPT | 56 | 11 | 33 |
| HuatuoGPT-II(7B) vs Baichuan2-13B-Chat | 63 | 19 | 18 |
| HuatuoGPT-II(7B) vs HuatuoGPT | 68 | 6 | 26 |
- The Fresh Medical Exams: We collected the fresh 2023 Chinese National Pharmacist Licensure Examination, which started on October 21, 2023. This date is later than our data finalization. HuatuoGPT2 achieved the best results in this exam, as shown below.
Our model is now available on Huggingface. You can Try our model in https://www.huatuogpt.cn/.
| Model | Backbone | Checkpoint |
|---|---|---|
| HuatuoGPT2-7B | Baichuan2-7B-Base | HF Lnik |
| HuatuoGPT2-13B | Baichuan2-13B-Base | HF Lnik |
| HuatuoGPT2-34B | Yi-34B | HF Lnik |
A quantized version of HuatuoGPT2 is also provided, allowing users with constrained memory or computing resources to access our HuatuoGPT2.
| Quantization | Backbone | Checkpoint |
|---|---|---|
| HuatuoGPT2-7B-4bits | Baichuan2-7B-Base | HF Lnik |
| HuatuoGPT2-7B-8bits | Baichuan2-7B-Base | HF Lnik |
| HuatuoGPT2-34B-4bits | Yi-34B | HF Lnik |
| HuatuoGPT2-34B-8bits | Yi-34B | HF Lnik |
import torch
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("FreedomIntelligence/HuatuoGPT2-7B", use_fast=True, trust_remote_code=True)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("FreedomIntelligence/HuatuoGPT2-7B", device_map="auto", torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16, trust_remote_code=True)
messages = []
messages.append({"role": "user", "content": "肚子疼怎么办?"})
response = model.HuatuoChat(tokenizer, messages)
print(response)python cli_demo.py --model_name FreedomIntelligence/HuatuoGPT2-7BWe open source part of the training data.
| Data Type | # Training data | Link |
|---|---|---|
| Medical Fine-tuning Instruction (GPT-4) | 142,248 | HF Link |
| Medical Pre-training Instruction | 5,286,308 | HF Link |
- HuatuoGPT2 transforms the pre-training corpus into (instruction, output) pairs using LLM. Utilize the script for Data Unification.
python adaption/data_unification/rewrite.py- We introduce a priority sampling approach, pre-processing data with this algorithm:
python adaption/one_stage_training/data_process.py- Then, training is conducted using one-stage training:
bash adaption/one_stage_training/train.shBy adopting the One-stage Adaptation method, you will observe the following loss curve:
-- Evaluation code for the QA benchmarks.
accelerate launch evaluation/eval_qa.py --model_path=FreedomIntelligence/HuatuoGPT2-7B --data_path=./evaluation/data/eval_qa.json- Single-turn response evaluation using GPT-4:
python evaluation/eval_huatuo_inst.py- Multi-turn dialogue evaluation using GPT-4:
python evaluation/eval_huatuo_conv.pyAccess our newest medical exam dataset via the link provided. The dataset includes complete exam questions, with exam dates noted to alert for potential leaks. We plan to release more updated exams in the future.
| Examination | #Question | Exam Time | Links |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2023 Chinese National Pharmacist Licensure Examination (Pharmacy) | 480 | 2023.10.22 | huggingface |
| 2023 Chinese National Pharmacist Licensure Examination (TCM) | 480 | 2023.10.22 | huggingface |
| Other Fresh Medical Examinations is in coming |
The HuatuoGPT series has so far launched two generations:
- HuatuoGPT: A Doctor-like Medical Large Language Model
- HuatuoGPT-II: An Domain-enhanced Medical Large Language Model
In the future, we will continue to release new versions of HuatuoGPT. Our goal is to enhance the capabilities of LLM in the Chinese medical field and to adhere to open-source principles (aligned with the ethos of FreedomIntelligence). We hope to work together with everyone to promote the development of medical LLM!
We are from the School of Data Science, the Chinese University of Hong Kong, Shenzhen (CUHKSZ) and the Shenzhen Research Institute of Big Data (SRIBD).
@misc{chen2023huatuogptii,
title={HuatuoGPT-II, One-stage Training for Medical Adaption of LLMs},
author={Junying Chen and Xidong Wang and Anningzhe Gao and Feng Jiang and Shunian Chen and Hongbo Zhang and Dingjie Song and Wenya Xie and Chuyi Kong and Jianquan Li and Xiang Wan and Haizhou Li and Benyou Wang},
year={2023},
eprint={2311.09774},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CL}
}
@article{huatuogpt-2023,
title={HuatuoGPT, Towards Taming Language Models To Be a Doctor},
author={Hongbo Zhang and Junying Chen and Feng Jiang and Fei Yu and Zhihong Chen and Jianquan Li and Guiming Chen and Xiangbo Wu and Zhiyi Zhang and Qingying Xiao and Xiang Wan and Benyou Wang and Haizhou Li},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.15075},
year={2023}
}
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for HuatuoGPT-II
Similar Open Source Tools

HuatuoGPT-II
HuatuoGPT2 is an innovative domain-adapted medical large language model that excels in medical knowledge and dialogue proficiency. It showcases state-of-the-art performance in various medical benchmarks, surpassing GPT-4 in expert evaluations and fresh medical licensing exams. The open-source release includes HuatuoGPT2 models in 7B, 13B, and 34B versions, training code for one-stage adaptation, partial pre-training and fine-tuning instructions, and evaluation methods for medical response capabilities and professional pharmacist exams. The tool aims to enhance LLM capabilities in the Chinese medical field through open-source principles.
IDvs.MoRec
This repository contains the source code for the SIGIR 2023 paper 'Where to Go Next for Recommender Systems? ID- vs. Modality-based Recommender Models Revisited'. It provides resources for evaluating foundation, transferable, multi-modal, and LLM recommendation models, along with datasets, pre-trained models, and training strategies for IDRec and MoRec using in-batch debiased cross-entropy loss. The repository also offers large-scale datasets, code for SASRec with in-batch debias cross-entropy loss, and information on joining the lab for research opportunities.

EasyEdit
EasyEdit is a Python package for edit Large Language Models (LLM) like `GPT-J`, `Llama`, `GPT-NEO`, `GPT2`, `T5`(support models from **1B** to **65B**), the objective of which is to alter the behavior of LLMs efficiently within a specific domain without negatively impacting performance across other inputs. It is designed to be easy to use and easy to extend.
UniCoT
Uni-CoT is a unified reasoning framework that extends Chain-of-Thought (CoT) principles to the multimodal domain, enabling Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) to perform interpretable, step-by-step reasoning across both text and vision. It decomposes complex multimodal tasks into structured, manageable steps that can be executed sequentially or in parallel, allowing for more scalable and systematic reasoning.

TrustLLM
TrustLLM is a comprehensive study of trustworthiness in LLMs, including principles for different dimensions of trustworthiness, established benchmark, evaluation, and analysis of trustworthiness for mainstream LLMs, and discussion of open challenges and future directions. Specifically, we first propose a set of principles for trustworthy LLMs that span eight different dimensions. Based on these principles, we further establish a benchmark across six dimensions including truthfulness, safety, fairness, robustness, privacy, and machine ethics. We then present a study evaluating 16 mainstream LLMs in TrustLLM, consisting of over 30 datasets. The document explains how to use the trustllm python package to help you assess the performance of your LLM in trustworthiness more quickly. For more details about TrustLLM, please refer to project website.

llm4ad
LLM4AD is an open-source Python-based platform leveraging Large Language Models (LLMs) for Automatic Algorithm Design (AD). It provides unified interfaces for methods, tasks, and LLMs, along with features like evaluation acceleration, secure evaluation, logs, GUI support, and more. The platform was originally developed for optimization tasks but is versatile enough to be used in other areas such as machine learning, science discovery, game theory, and engineering design. It offers various search methods and algorithm design tasks across different domains. LLM4AD supports remote LLM API, local HuggingFace LLM deployment, and custom LLM interfaces. The project is licensed under the MIT License and welcomes contributions, collaborations, and issue reports.
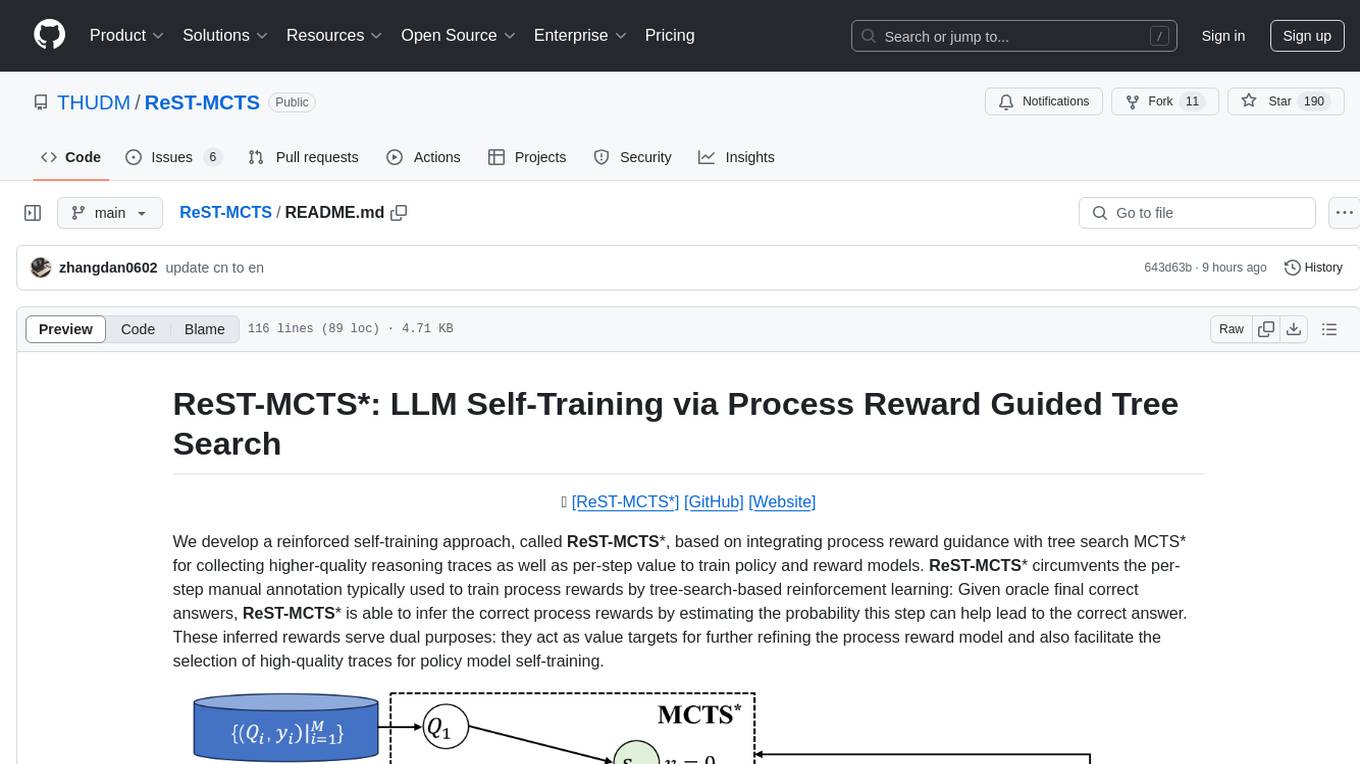
ReST-MCTS
ReST-MCTS is a reinforced self-training approach that integrates process reward guidance with tree search MCTS to collect higher-quality reasoning traces and per-step value for training policy and reward models. It eliminates the need for manual per-step annotation by estimating the probability of steps leading to correct answers. The inferred rewards refine the process reward model and aid in selecting high-quality traces for policy model self-training.
BitBLAS
BitBLAS is a library for mixed-precision BLAS operations on GPUs, for example, the $W_{wdtype}A_{adtype}$ mixed-precision matrix multiplication where $C_{cdtype}[M, N] = A_{adtype}[M, K] \times W_{wdtype}[N, K]$. BitBLAS aims to support efficient mixed-precision DNN model deployment, especially the $W_{wdtype}A_{adtype}$ quantization in large language models (LLMs), for example, the $W_{UINT4}A_{FP16}$ in GPTQ, the $W_{INT2}A_{FP16}$ in BitDistiller, the $W_{INT2}A_{INT8}$ in BitNet-b1.58. BitBLAS is based on techniques from our accepted submission at OSDI'24.
pai-opencode
PAI-OpenCode is a complete port of Daniel Miessler's Personal AI Infrastructure (PAI) to OpenCode, an open-source, provider-agnostic AI coding assistant. It brings modular capabilities, dynamic multi-agent orchestration, session history, and lifecycle automation to personalize AI assistants for users. With support for 75+ AI providers, PAI-OpenCode offers dynamic per-task model routing, full PAI infrastructure, real-time session sharing, and multiple client options. The tool optimizes cost and quality with a 3-tier model strategy and a 3-tier research system, allowing users to switch presets for different routing strategies. PAI-OpenCode's architecture preserves PAI's design while adapting to OpenCode, documented through Architecture Decision Records (ADRs).
MiniCPM-V
MiniCPM-V is a series of end-side multimodal LLMs designed for vision-language understanding. The models take image and text inputs to provide high-quality text outputs. The series includes models like MiniCPM-Llama3-V 2.5 with 8B parameters surpassing proprietary models, and MiniCPM-V 2.0, a lighter model with 2B parameters. The models support over 30 languages, efficient deployment on end-side devices, and have strong OCR capabilities. They achieve state-of-the-art performance on various benchmarks and prevent hallucinations in text generation. The models can process high-resolution images efficiently and support multilingual capabilities.

deepfabric
DeepFabric is a CLI tool and SDK designed for researchers and developers to generate high-quality synthetic datasets at scale using large language models. It leverages a graph and tree-based architecture to create diverse and domain-specific datasets while minimizing redundancy. The tool supports generating Chain of Thought datasets for step-by-step reasoning tasks and offers multi-provider support for using different language models. DeepFabric also allows for automatic dataset upload to Hugging Face Hub and uses YAML configuration files for flexibility in dataset generation.
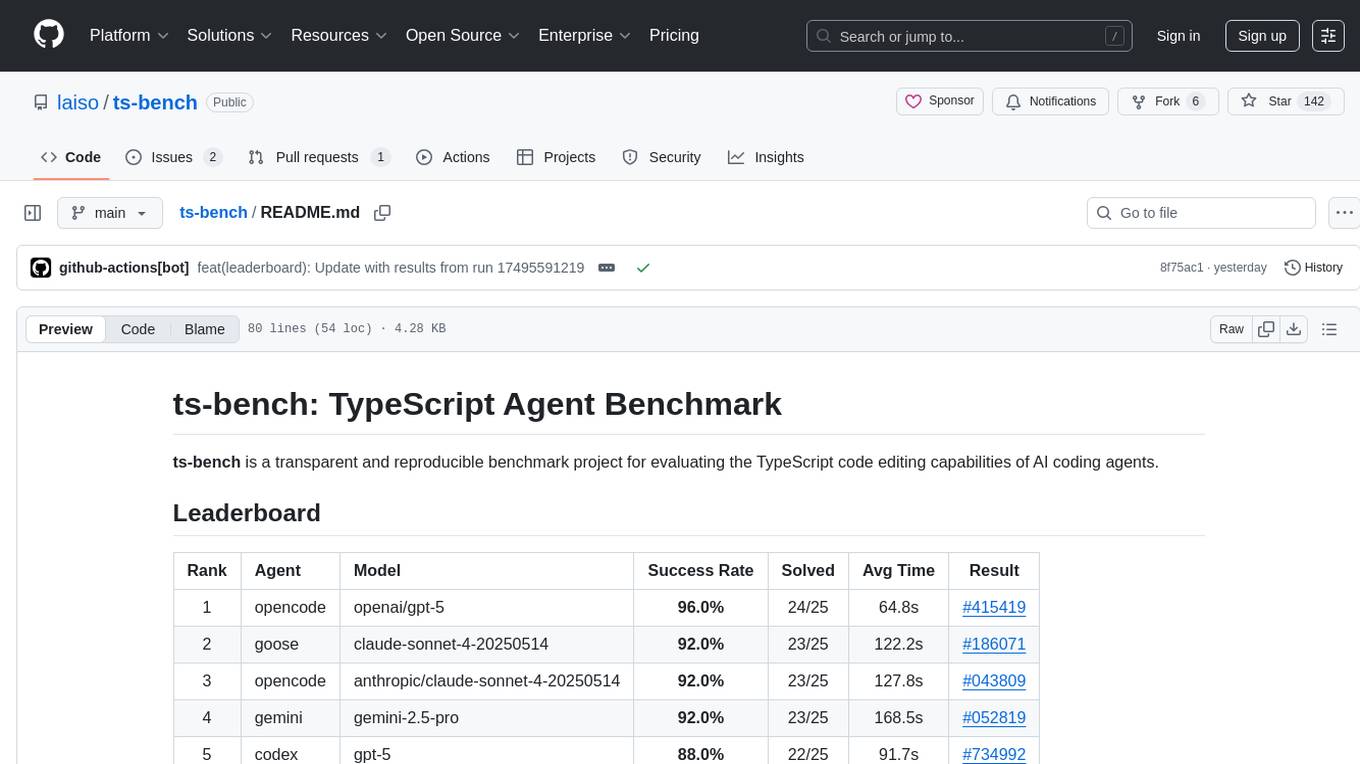
ts-bench
TS-Bench is a performance benchmarking tool for TypeScript projects. It provides detailed insights into the performance of TypeScript code, helping developers optimize their projects. With TS-Bench, users can measure and compare the execution time of different code snippets, functions, or modules. The tool offers a user-friendly interface for running benchmarks and analyzing the results. TS-Bench is a valuable asset for developers looking to enhance the performance of their TypeScript applications.
amber-train
Amber is the first model in the LLM360 family, an initiative for comprehensive and fully open-sourced LLMs. It is a 7B English language model with the LLaMA architecture. The model type is a language model with the same architecture as LLaMA-7B. It is licensed under Apache 2.0. The resources available include training code, data preparation, metrics, and fully processed Amber pretraining data. The model has been trained on various datasets like Arxiv, Book, C4, Refined-Web, StarCoder, StackExchange, and Wikipedia. The hyperparameters include a total of 6.7B parameters, hidden size of 4096, intermediate size of 11008, 32 attention heads, 32 hidden layers, RMSNorm ε of 1e^-6, max sequence length of 2048, and a vocabulary size of 32000.
AI-For-Beginners
AI-For-Beginners is a comprehensive 12-week, 24-lesson curriculum designed by experts at Microsoft to introduce beginners to the world of Artificial Intelligence (AI). The curriculum covers various topics such as Symbolic AI, Neural Networks, Computer Vision, Natural Language Processing, Genetic Algorithms, and Multi-Agent Systems. It includes hands-on lessons, quizzes, and labs using popular frameworks like TensorFlow and PyTorch. The focus is on providing a foundational understanding of AI concepts and principles, making it an ideal starting point for individuals interested in AI.
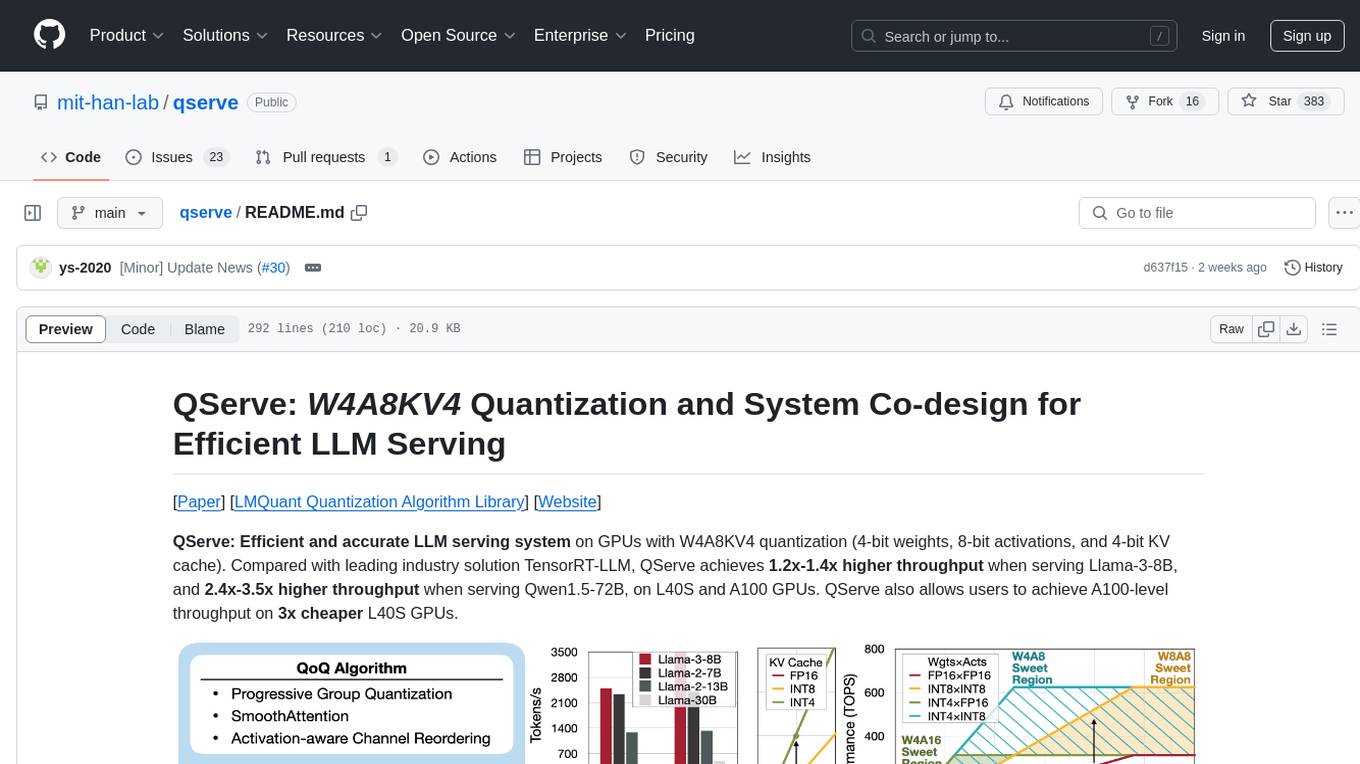
qserve
QServe is a serving system designed for efficient and accurate Large Language Models (LLM) on GPUs with W4A8KV4 quantization. It achieves higher throughput compared to leading industry solutions, allowing users to achieve A100-level throughput on cheaper L40S GPUs. The system introduces the QoQ quantization algorithm with 4-bit weight, 8-bit activation, and 4-bit KV cache, addressing runtime overhead challenges. QServe improves serving throughput for various LLM models by implementing compute-aware weight reordering, register-level parallelism, and fused attention memory-bound techniques.
For similar tasks
CareGPT
CareGPT is a medical large language model (LLM) that explores medical data, training, and deployment related research work. It integrates resources, open-source models, rich data, and efficient deployment methods. It supports various medical tasks, including patient diagnosis, medical dialogue, and medical knowledge integration. The model has been fine-tuned on diverse medical datasets to enhance its performance in the healthcare domain.

HuatuoGPT-II
HuatuoGPT2 is an innovative domain-adapted medical large language model that excels in medical knowledge and dialogue proficiency. It showcases state-of-the-art performance in various medical benchmarks, surpassing GPT-4 in expert evaluations and fresh medical licensing exams. The open-source release includes HuatuoGPT2 models in 7B, 13B, and 34B versions, training code for one-stage adaptation, partial pre-training and fine-tuning instructions, and evaluation methods for medical response capabilities and professional pharmacist exams. The tool aims to enhance LLM capabilities in the Chinese medical field through open-source principles.
IvyGPT
IvyGPT is a medical large language model that aims to generate the most realistic doctor consultation effects. It has been fine-tuned on high-quality medical Q&A data and trained using human feedback reinforcement learning. The project features full-process training on medical Q&A LLM, multiple fine-tuning methods support, efficient dataset creation tools, and a dataset of over 300,000 high-quality doctor-patient dialogues for training.
For similar jobs
LLM-for-Healthcare
The repository 'LLM-for-Healthcare' provides a comprehensive survey of large language models (LLMs) for healthcare, covering data, technology, applications, and accountability and ethics. It includes information on various LLM models, training data, evaluation methods, and computation costs. The repository also discusses tasks such as NER, text classification, question answering, dialogue systems, and generation of medical reports from images in the healthcare domain.

HuatuoGPT-II
HuatuoGPT2 is an innovative domain-adapted medical large language model that excels in medical knowledge and dialogue proficiency. It showcases state-of-the-art performance in various medical benchmarks, surpassing GPT-4 in expert evaluations and fresh medical licensing exams. The open-source release includes HuatuoGPT2 models in 7B, 13B, and 34B versions, training code for one-stage adaptation, partial pre-training and fine-tuning instructions, and evaluation methods for medical response capabilities and professional pharmacist exams. The tool aims to enhance LLM capabilities in the Chinese medical field through open-source principles.

Me-LLaMA
Me LLaMA introduces a suite of open-source medical Large Language Models (LLMs), including Me LLaMA 13B/70B and their chat-enhanced versions. Developed through innovative continual pre-training and instruction tuning, these models leverage a vast medical corpus comprising PubMed papers, medical guidelines, and general domain data. Me LLaMA sets new benchmarks on medical reasoning tasks, making it a significant asset for medical NLP applications and research. The models are intended for computational linguistics and medical research, not for clinical decision-making without validation and regulatory approval.
azure-health-data-and-ai-samples
The Azure Health Data and AI Samples Repo is a collection of sample apps and code to help users start with Azure Health Data and AI services, learn product usage, and speed up implementations. It includes samples for various health data workflows, such as data ingestion, analytics, machine learning, SMART on FHIR, patient services, FHIR service integration, Azure AD B2C access, DICOM service, MedTech service, and healthcare data solutions in Microsoft Fabric. These samples are simplified scenarios for testing purposes only.
HuatuoGPT-o1
HuatuoGPT-o1 is a medical language model designed for advanced medical reasoning. It can identify mistakes, explore alternative strategies, and refine answers. The model leverages verifiable medical problems and a specialized medical verifier to guide complex reasoning trajectories and enhance reasoning through reinforcement learning. The repository provides access to models, data, and code for HuatuoGPT-o1, allowing users to deploy the model for medical reasoning tasks.

fuse-med-ml
FuseMedML is a Python framework designed to accelerate machine learning-based discovery in the medical field by promoting code reuse. It provides a flexible design concept where data is stored in a nested dictionary, allowing easy handling of multi-modality information. The framework includes components for creating custom models, loss functions, metrics, and data processing operators. Additionally, FuseMedML offers 'batteries included' key components such as fuse.data for data processing, fuse.eval for model evaluation, and fuse.dl for reusable deep learning components. It supports PyTorch and PyTorch Lightning libraries and encourages the creation of domain extensions for specific medical domains.
MedLLMsPracticalGuide
This repository serves as a practical guide for Medical Large Language Models (Medical LLMs) and provides resources, surveys, and tools for building, fine-tuning, and utilizing LLMs in the medical domain. It covers a wide range of topics including pre-training, fine-tuning, downstream biomedical tasks, clinical applications, challenges, future directions, and more. The repository aims to provide insights into the opportunities and challenges of LLMs in medicine and serve as a practical resource for constructing effective medical LLMs.
hi-ml
The Microsoft Health Intelligence Machine Learning Toolbox is a repository that provides low-level and high-level building blocks for Machine Learning / AI researchers and practitioners. It simplifies and streamlines work on deep learning models for healthcare and life sciences by offering tested components such as data loaders, pre-processing tools, deep learning models, and cloud integration utilities. The repository includes two Python packages, 'hi-ml-azure' for helper functions in AzureML, 'hi-ml' for ML components, and 'hi-ml-cpath' for models and workflows related to histopathology images.