
spark-nlp
State of the Art Natural Language Processing
Stars: 4048
Spark NLP is a state-of-the-art Natural Language Processing library built on top of Apache Spark. It provides simple, performant, and accurate NLP annotations for machine learning pipelines that scale easily in a distributed environment. Spark NLP comes with 36000+ pretrained pipelines and models in more than 200+ languages. It offers tasks such as Tokenization, Word Segmentation, Part-of-Speech Tagging, Named Entity Recognition, Dependency Parsing, Spell Checking, Text Classification, Sentiment Analysis, Token Classification, Machine Translation, Summarization, Question Answering, Table Question Answering, Text Generation, Image Classification, Image to Text (captioning), Automatic Speech Recognition, Zero-Shot Learning, and many more NLP tasks. Spark NLP is the only open-source NLP library in production that offers state-of-the-art transformers such as BERT, CamemBERT, ALBERT, ELECTRA, XLNet, DistilBERT, RoBERTa, DeBERTa, XLM-RoBERTa, Longformer, ELMO, Universal Sentence Encoder, Llama-2, M2M100, BART, Instructor, E5, Google T5, MarianMT, OpenAI GPT2, Vision Transformers (ViT), OpenAI Whisper, and many more not only to Python and R, but also to JVM ecosystem (Java, Scala, and Kotlin) at scale by extending Apache Spark natively.
README:
Spark NLP is a state-of-the-art Natural Language Processing library built on top of Apache Spark. It provides simple, performant & accurate NLP annotations for machine learning pipelines that scale easily in a distributed environment.
Spark NLP comes with 100000+ pretrained pipelines and models in more than 200+ languages. It also offers tasks such as Tokenization, Word Segmentation, Part-of-Speech Tagging, Word and Sentence Embeddings, Named Entity Recognition, Dependency Parsing, Spell Checking, Text Classification, Sentiment Analysis, Token Classification, Machine Translation (+180 languages), Summarization, Question Answering, Table Question Answering, Text Generation, Image Classification, Image to Text (captioning), Automatic Speech Recognition, Zero-Shot Learning, and many more NLP tasks.
Spark NLP is the only open-source NLP library in production that offers state-of-the-art transformers such as BERT, CamemBERT, ALBERT, ELECTRA, XLNet, DistilBERT, RoBERTa, DeBERTa, XLM-RoBERTa, Longformer, ELMO, Universal Sentence Encoder, Llama-2, M2M100, BART, Instructor, E5, Google T5, MarianMT, OpenAI GPT2, Vision Transformers (ViT), OpenAI Whisper, Llama, Mistral, Phi, Qwen2, and many more not only to Python and R, but also to JVM ecosystem (Java, Scala, and Kotlin) at scale by extending Apache Spark natively.
Spark NLP provides easy support for importing models from various popular frameworks:
- TensorFlow
- ONNX
- OpenVINO
- Llama.cpp (GGUF)
This wide range of support allows you to seamlessly integrate models from different sources into your Spark NLP workflows, enhancing flexibility and compatibility with existing machine learning ecosystems.
Take a look at our official Spark NLP page: https://sparknlp.org/ for user documentation and examples
- Text Preprocessing
- Parsing and Analysis
- Sentiment and Classification
- Embeddings
- Classification and Question Answering
- Machine Translation and Generation
- Image and Speech
- Integration and Interoperability (ONNX, OpenVINO)
- Pre-trained Models (36000+ in +200 languages)
- Multi-lingual Support
This is a quick example of how to use a Spark NLP pre-trained pipeline in Python and PySpark:
$ java -version
# should be Java 8 or 11 (Oracle or OpenJDK)
$ conda create -n sparknlp python=3.7 -y
$ conda activate sparknlp
# spark-nlp by default is based on pyspark 3.x
$ pip install spark-nlp==6.1.4 pyspark==3.3.1In Python console or Jupyter Python3 kernel:
# Import Spark NLP
from sparknlp.base import *
from sparknlp.annotator import *
from sparknlp.pretrained import PretrainedPipeline
import sparknlp
# Start SparkSession with Spark NLP
# start() functions has 3 parameters: gpu, apple_silicon, and memory
# sparknlp.start(gpu=True) will start the session with GPU support
# sparknlp.start(apple_silicon=True) will start the session with macOS M1 & M2 support
# sparknlp.start(memory="16G") to change the default driver memory in SparkSession
spark = sparknlp.start()
# Download a pre-trained pipeline
pipeline = PretrainedPipeline('explain_document_dl', lang='en')
# Your testing dataset
text = """
The Mona Lisa is a 16th century oil painting created by Leonardo.
It's held at the Louvre in Paris.
"""
# Annotate your testing dataset
result = pipeline.annotate(text)
# What's in the pipeline
list(result.keys())
Output: ['entities', 'stem', 'checked', 'lemma', 'document',
'pos', 'token', 'ner', 'embeddings', 'sentence']
# Check the results
result['entities']
Output: ['Mona Lisa', 'Leonardo', 'Louvre', 'Paris']For more examples, you can visit our dedicated examples to showcase all Spark NLP use cases!
This is a cheatsheet for corresponding Spark NLP Maven package to Apache Spark / PySpark major version:
| Apache Spark | Spark NLP on CPU | Spark NLP on GPU | Spark NLP on AArch64 (linux) | Spark NLP on Apple Silicon |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.0/3.1/3.2/3.3/3.4/3.5 | spark-nlp |
spark-nlp-gpu |
spark-nlp-aarch64 |
spark-nlp-silicon |
| Start Function | sparknlp.start() |
sparknlp.start(gpu=True) |
sparknlp.start(aarch64=True) |
sparknlp.start(apple_silicon=True) |
NOTE: M1/M2 and AArch64 are under experimental support. Access and support to these architectures are limited by the
community and we had to build most of the dependencies by ourselves to make them compatible. We support these two
architectures, however, they may not work in some environments.
For a quick example of using pipelines and models take a look at our official documentation
Please check out our Models Hub for the full list of pre-trained models with examples, demo, benchmark, and more
Spark NLP 6.1.4 has been built on top of Apache Spark 3.4 while fully supports Apache Spark 3.0.x, 3.1.x, 3.2.x, 3.3.x, 3.4.x, and 3.5.x
| Spark NLP | Apache Spark 3.5.x | Apache Spark 3.4.x | Apache Spark 3.3.x | Apache Spark 3.2.x | Apache Spark 3.1.x | Apache Spark 3.0.x | Apache Spark 2.4.x | Apache Spark 2.3.x |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6.x.x and up | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | NO | NO |
| 5.5.x | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | NO | NO |
| 5.4.x | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | NO | NO |
| 5.3.x | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | NO | NO |
| 5.2.x | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | NO | NO |
| 5.1.x | Partially | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | NO | NO |
| 5.0.x | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | NO | NO |
Find out more about Spark NLP versions from our release notes.
| Spark NLP | Python 3.6 | Python 3.7 | Python 3.8 | Python 3.9 | Python 3.10 | Scala 2.11 | Scala 2.12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6.0.x | NO | YES | YES | YES | YES | NO | YES |
| 5.5.x | NO | YES | YES | YES | YES | NO | YES |
| 5.4.x | NO | YES | YES | YES | YES | NO | YES |
| 5.3.x | NO | YES | YES | YES | YES | NO | YES |
| 5.2.x | NO | YES | YES | YES | YES | NO | YES |
| 5.1.x | NO | YES | YES | YES | YES | NO | YES |
| 5.0.x | NO | YES | YES | YES | YES | NO | YES |
Find out more about 4.x SparkNLP versions in our official documentation
Spark NLP 6.1.4 has been tested and is compatible with the following runtimes:
| CPU | GPU |
|---|---|
| 14.1 / 14.1 ML | 14.1 ML & GPU |
| 14.2 / 14.2 ML | 14.2 ML & GPU |
| 14.3 / 14.3 ML | 14.3 ML & GPU |
| 15.0 / 15.0 ML | 15.0 ML & GPU |
| 15.1 / 15.1 ML | 15.1 ML & GPU |
| 15.2 / 15.2 ML | 15.2 ML & GPU |
| 15.3 / 15.3 ML | 15.3 ML & GPU |
| 15.4 / 15.4 ML | 15.4 ML & GPU |
| 16.4 / 16.4 ML | 16.4 ML & GPU |
We are compatible with older runtimes. For a full list check databricks support in our official documentation
Spark NLP 6.1.4 has been tested and is compatible with the following EMR releases:
| EMR Release |
|---|
| emr-6.13.0 |
| emr-6.14.0 |
| emr-6.15.0 |
| emr-7.0.0 |
| emr-7.1.0 |
| emr-7.2.0 |
| emr-7.3.0 |
| emr-7.4.0 |
| emr-7.5.0 |
| emr-7.6.0 |
| emr-7.7.0 |
| emr-7.8.0 |
We are compatible with older EMR releases. For a full list check EMR support in our official documentation
Full list of Amazon EMR 6.x releases Full list of Amazon EMR 7.x releases
NOTE: The EMR 6.1.0 and 6.1.1 are not supported.
To install spark-nlp packages through command line follow these instructions from our official documentation
Spark NLP supports Scala 2.12.15 if you are using Apache Spark 3.0.x, 3.1.x, 3.2.x, 3.3.x, and 3.4.x versions. Our packages are deployed to Maven central. To add any of our packages as a dependency in your application you can follow these instructions from our official documentation.
If you are interested, there is a simple SBT project for Spark NLP to guide you on how to use it in your projects Spark NLP Starter
Spark NLP supports Python 3.7.x and above depending on your major PySpark version. Check all available installations for Python in our official documentation
To compile the jars from source follow these instructions from our official documentation
For detailed instructions on how to use Spark NLP on supported platforms, please refer to our official documentation:
| Platform | Supported Language(s) |
|---|---|
| Apache Zeppelin | Scala, Python |
| Jupyter Notebook | Python |
| Google Colab Notebook | Python |
| Kaggle Kernel | Python |
| Databricks Cluster | Scala, Python |
| EMR Cluster | Scala, Python |
| GCP Dataproc Cluster | Scala, Python |
Spark NLP library and all the pre-trained models/pipelines can be used entirely offline with no access to the Internet. Please check these instructions from our official documentation to use Spark NLP offline.
You can change Spark NLP configurations via Spark properties configuration. Please check these instructions from our official documentation.
In Spark NLP we can define S3 locations to:
- Export log files of training models
- Store tensorflow graphs used in
NerDLApproach
Please check these instructions from our official documentation.
Need more examples? Check out our dedicated Spark NLP Examples repository to showcase all Spark NLP use cases!
Also, don't forget to check Spark NLP in Action built by Streamlit.
All examples: spark-nlp/examples
Check our Articles and Videos page here
We have published a paper that you can cite for the Spark NLP library:
@article{KOCAMAN2021100058,
title = {Spark NLP: Natural language understanding at scale},
journal = {Software Impacts},
pages = {100058},
year = {2021},
issn = {2665-9638},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.simpa.2021.100058},
url = {https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2665963.2.300063},
author = {Veysel Kocaman and David Talby},
keywords = {Spark, Natural language processing, Deep learning, Tensorflow, Cluster},
abstract = {Spark NLP is a Natural Language Processing (NLP) library built on top of Apache Spark ML. It provides simple, performant & accurate NLP annotations for machine learning pipelines that can scale easily in a distributed environment. Spark NLP comes with 1100+ pretrained pipelines and models in more than 192+ languages. It supports nearly all the NLP tasks and modules that can be used seamlessly in a cluster. Downloaded more than 2.7 million times and experiencing 9x growth since January 2020, Spark NLP is used by 54% of healthcare organizations as the world’s most widely used NLP library in the enterprise.}
}
}- Slack For live discussion with the Spark NLP community and the team
- GitHub Bug reports, feature requests, and contributions
- Discussions Engage with other community members, share ideas, and show off how you use Spark NLP!
- Medium Spark NLP articles
- YouTube Spark NLP video tutorials
We appreciate any sort of contributions:
- ideas
- feedback
- documentation
- bug reports
- NLP training and testing corpora
- Development and testing
Clone the repo and submit your pull-requests! Or directly create issues in this repo.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for spark-nlp
Similar Open Source Tools

spark-nlp
Spark NLP is a state-of-the-art Natural Language Processing library built on top of Apache Spark. It provides simple, performant, and accurate NLP annotations for machine learning pipelines that scale easily in a distributed environment. Spark NLP comes with 36000+ pretrained pipelines and models in more than 200+ languages. It offers tasks such as Tokenization, Word Segmentation, Part-of-Speech Tagging, Named Entity Recognition, Dependency Parsing, Spell Checking, Text Classification, Sentiment Analysis, Token Classification, Machine Translation, Summarization, Question Answering, Table Question Answering, Text Generation, Image Classification, Image to Text (captioning), Automatic Speech Recognition, Zero-Shot Learning, and many more NLP tasks. Spark NLP is the only open-source NLP library in production that offers state-of-the-art transformers such as BERT, CamemBERT, ALBERT, ELECTRA, XLNet, DistilBERT, RoBERTa, DeBERTa, XLM-RoBERTa, Longformer, ELMO, Universal Sentence Encoder, Llama-2, M2M100, BART, Instructor, E5, Google T5, MarianMT, OpenAI GPT2, Vision Transformers (ViT), OpenAI Whisper, and many more not only to Python and R, but also to JVM ecosystem (Java, Scala, and Kotlin) at scale by extending Apache Spark natively.

deepfabric
DeepFabric is a CLI tool and SDK designed for researchers and developers to generate high-quality synthetic datasets at scale using large language models. It leverages a graph and tree-based architecture to create diverse and domain-specific datasets while minimizing redundancy. The tool supports generating Chain of Thought datasets for step-by-step reasoning tasks and offers multi-provider support for using different language models. DeepFabric also allows for automatic dataset upload to Hugging Face Hub and uses YAML configuration files for flexibility in dataset generation.
pai-opencode
PAI-OpenCode is a complete port of Daniel Miessler's Personal AI Infrastructure (PAI) to OpenCode, an open-source, provider-agnostic AI coding assistant. It brings modular capabilities, dynamic multi-agent orchestration, session history, and lifecycle automation to personalize AI assistants for users. With support for 75+ AI providers, PAI-OpenCode offers dynamic per-task model routing, full PAI infrastructure, real-time session sharing, and multiple client options. The tool optimizes cost and quality with a 3-tier model strategy and a 3-tier research system, allowing users to switch presets for different routing strategies. PAI-OpenCode's architecture preserves PAI's design while adapting to OpenCode, documented through Architecture Decision Records (ADRs).

llm4ad
LLM4AD is an open-source Python-based platform leveraging Large Language Models (LLMs) for Automatic Algorithm Design (AD). It provides unified interfaces for methods, tasks, and LLMs, along with features like evaluation acceleration, secure evaluation, logs, GUI support, and more. The platform was originally developed for optimization tasks but is versatile enough to be used in other areas such as machine learning, science discovery, game theory, and engineering design. It offers various search methods and algorithm design tasks across different domains. LLM4AD supports remote LLM API, local HuggingFace LLM deployment, and custom LLM interfaces. The project is licensed under the MIT License and welcomes contributions, collaborations, and issue reports.
BharatMLStack
BharatMLStack is a comprehensive, production-ready machine learning infrastructure platform designed to democratize ML capabilities across India and beyond. It provides a robust, scalable, and accessible ML stack empowering organizations to build, deploy, and manage machine learning solutions at massive scale. It includes core components like Horizon, Trufflebox UI, Online Feature Store, Go SDK, Python SDK, and Numerix, offering features such as control plane, ML management console, real-time features, mathematical compute engine, and more. The platform is production-ready, cloud agnostic, and offers observability through built-in monitoring and logging.
MaixPy
MaixPy is a Python SDK that enables users to easily create AI vision projects on edge devices. It provides a user-friendly API for accessing NPU, making it suitable for AI Algorithm Engineers, STEM teachers, Makers, Engineers, Students, Enterprises, and Contestants. The tool supports Python programming, MaixVision Workstation, AI vision, video streaming, voice recognition, and peripheral usage. It also offers an online AI training platform called MaixHub. MaixPy is designed for new hardware platforms like MaixCAM, offering improved performance and features compared to older versions. The ecosystem includes hardware, software, tools, documentation, and a cloud platform.
BitBLAS
BitBLAS is a library for mixed-precision BLAS operations on GPUs, for example, the $W_{wdtype}A_{adtype}$ mixed-precision matrix multiplication where $C_{cdtype}[M, N] = A_{adtype}[M, K] \times W_{wdtype}[N, K]$. BitBLAS aims to support efficient mixed-precision DNN model deployment, especially the $W_{wdtype}A_{adtype}$ quantization in large language models (LLMs), for example, the $W_{UINT4}A_{FP16}$ in GPTQ, the $W_{INT2}A_{FP16}$ in BitDistiller, the $W_{INT2}A_{INT8}$ in BitNet-b1.58. BitBLAS is based on techniques from our accepted submission at OSDI'24.
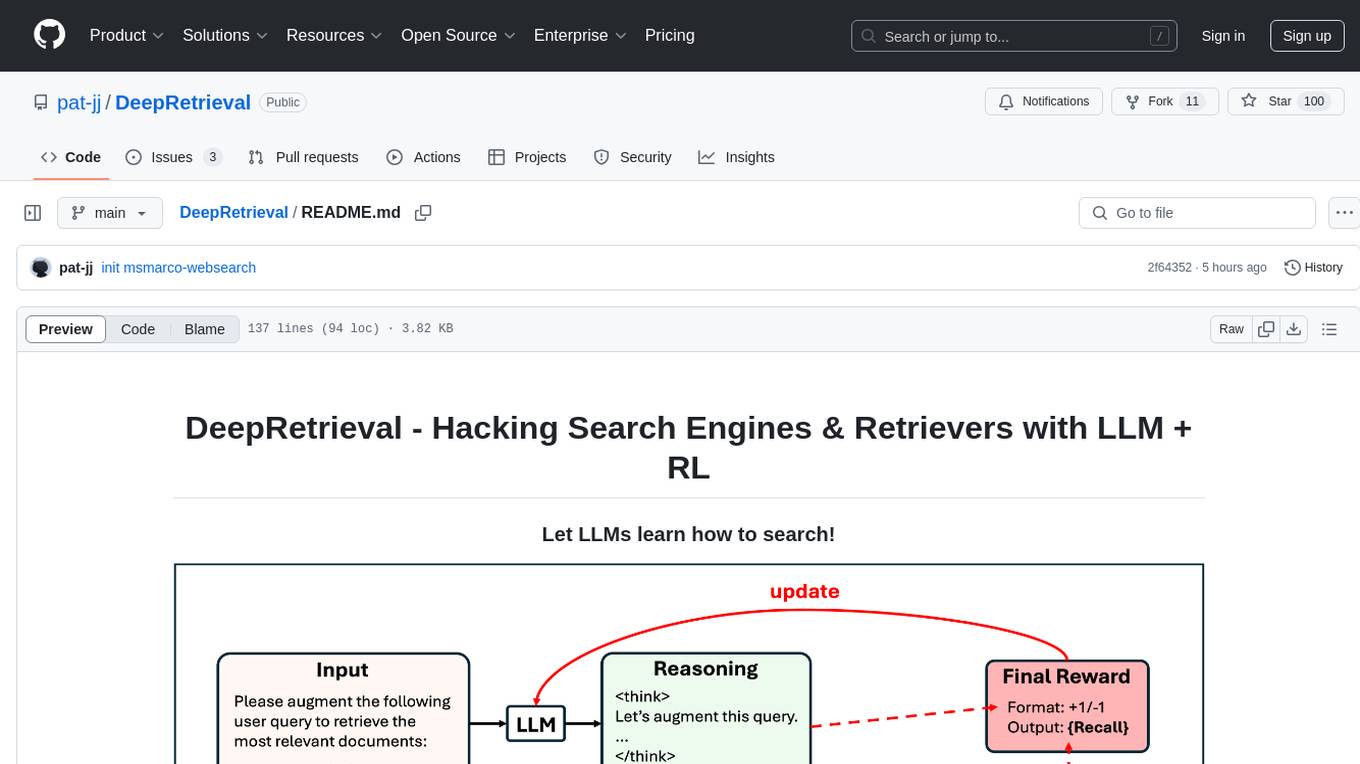
DeepRetrieval
DeepRetrieval is a tool designed to enhance search engines and retrievers using Large Language Models (LLMs) and Reinforcement Learning (RL). It allows LLMs to learn how to search effectively by integrating with search engine APIs and customizing reward functions. The tool provides functionalities for data preparation, training, evaluation, and monitoring search performance. DeepRetrieval aims to improve information retrieval tasks by leveraging advanced AI techniques.
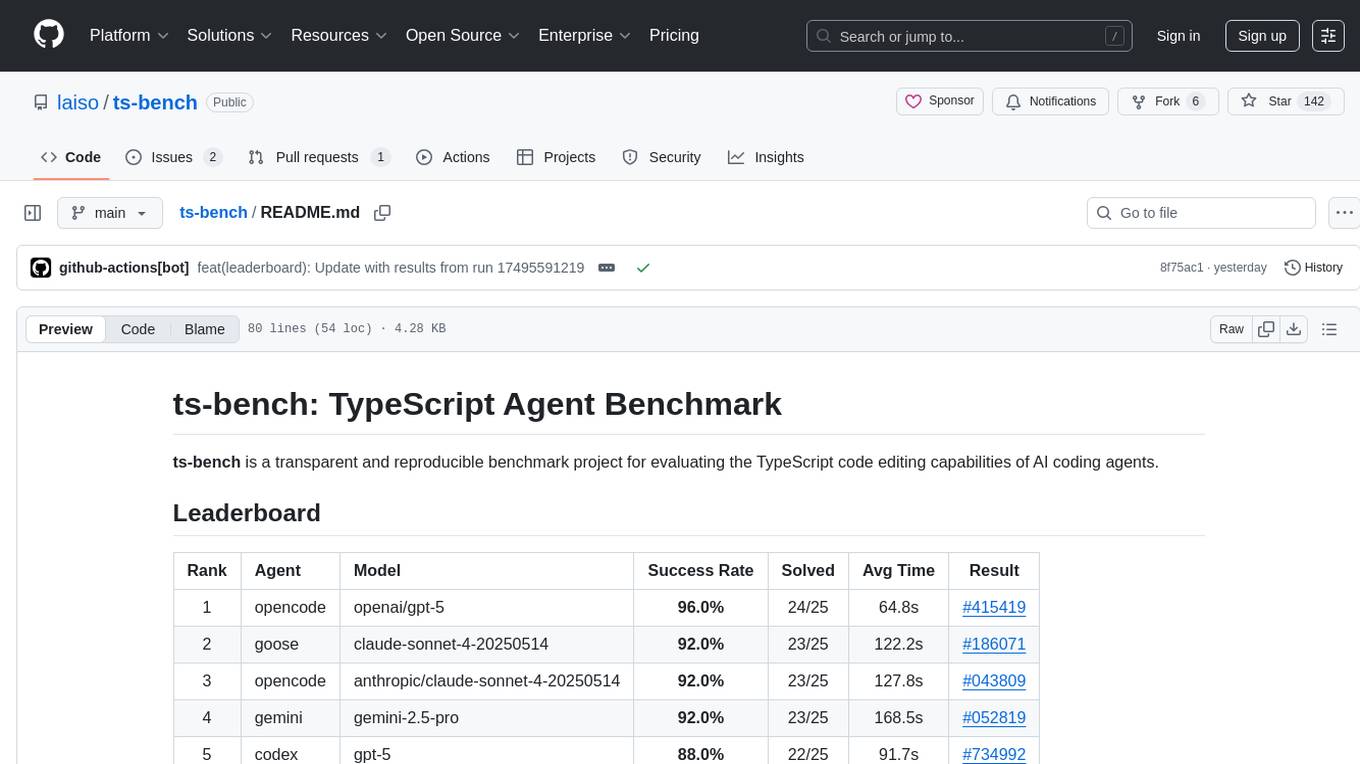
ts-bench
TS-Bench is a performance benchmarking tool for TypeScript projects. It provides detailed insights into the performance of TypeScript code, helping developers optimize their projects. With TS-Bench, users can measure and compare the execution time of different code snippets, functions, or modules. The tool offers a user-friendly interface for running benchmarks and analyzing the results. TS-Bench is a valuable asset for developers looking to enhance the performance of their TypeScript applications.

EasyEdit
EasyEdit is a Python package for edit Large Language Models (LLM) like `GPT-J`, `Llama`, `GPT-NEO`, `GPT2`, `T5`(support models from **1B** to **65B**), the objective of which is to alter the behavior of LLMs efficiently within a specific domain without negatively impacting performance across other inputs. It is designed to be easy to use and easy to extend.
UniCoT
Uni-CoT is a unified reasoning framework that extends Chain-of-Thought (CoT) principles to the multimodal domain, enabling Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) to perform interpretable, step-by-step reasoning across both text and vision. It decomposes complex multimodal tasks into structured, manageable steps that can be executed sequentially or in parallel, allowing for more scalable and systematic reasoning.
IDvs.MoRec
This repository contains the source code for the SIGIR 2023 paper 'Where to Go Next for Recommender Systems? ID- vs. Modality-based Recommender Models Revisited'. It provides resources for evaluating foundation, transferable, multi-modal, and LLM recommendation models, along with datasets, pre-trained models, and training strategies for IDRec and MoRec using in-batch debiased cross-entropy loss. The repository also offers large-scale datasets, code for SASRec with in-batch debias cross-entropy loss, and information on joining the lab for research opportunities.
AI-For-Beginners
AI-For-Beginners is a comprehensive 12-week, 24-lesson curriculum designed by experts at Microsoft to introduce beginners to the world of Artificial Intelligence (AI). The curriculum covers various topics such as Symbolic AI, Neural Networks, Computer Vision, Natural Language Processing, Genetic Algorithms, and Multi-Agent Systems. It includes hands-on lessons, quizzes, and labs using popular frameworks like TensorFlow and PyTorch. The focus is on providing a foundational understanding of AI concepts and principles, making it an ideal starting point for individuals interested in AI.
generative-ai-for-beginners
This course has 18 lessons. Each lesson covers its own topic so start wherever you like! Lessons are labeled either "Learn" lessons explaining a Generative AI concept or "Build" lessons that explain a concept and code examples in both **Python** and **TypeScript** when possible. Each lesson also includes a "Keep Learning" section with additional learning tools. **What You Need** * Access to the Azure OpenAI Service **OR** OpenAI API - _Only required to complete coding lessons_ * Basic knowledge of Python or Typescript is helpful - *For absolute beginners check out these Python and TypeScript courses. * A Github account to fork this entire repo to your own GitHub account We have created a **Course Setup** lesson to help you with setting up your development environment. Don't forget to star (🌟) this repo to find it easier later. ## 🧠 Ready to Deploy? If you are looking for more advanced code samples, check out our collection of Generative AI Code Samples in both **Python** and **TypeScript**. ## 🗣️ Meet Other Learners, Get Support Join our official AI Discord server to meet and network with other learners taking this course and get support. ## 🚀 Building a Startup? Sign up for Microsoft for Startups Founders Hub to receive **free OpenAI credits** and up to **$150k towards Azure credits to access OpenAI models through Azure OpenAI Services**. ## 🙏 Want to help? Do you have suggestions or found spelling or code errors? Raise an issue or Create a pull request ## 📂 Each lesson includes: * A short video introduction to the topic * A written lesson located in the README * Python and TypeScript code samples supporting Azure OpenAI and OpenAI API * Links to extra resources to continue your learning ## 🗃️ Lessons | | Lesson Link | Description | Additional Learning | | :-: | :------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: | :---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | | 00 | Course Setup | **Learn:** How to Setup Your Development Environment | Learn More | | 01 | Introduction to Generative AI and LLMs | **Learn:** Understanding what Generative AI is and how Large Language Models (LLMs) work. | Learn More | | 02 | Exploring and comparing different LLMs | **Learn:** How to select the right model for your use case | Learn More | | 03 | Using Generative AI Responsibly | **Learn:** How to build Generative AI Applications responsibly | Learn More | | 04 | Understanding Prompt Engineering Fundamentals | **Learn:** Hands-on Prompt Engineering Best Practices | Learn More | | 05 | Creating Advanced Prompts | **Learn:** How to apply prompt engineering techniques that improve the outcome of your prompts. | Learn More | | 06 | Building Text Generation Applications | **Build:** A text generation app using Azure OpenAI | Learn More | | 07 | Building Chat Applications | **Build:** Techniques for efficiently building and integrating chat applications. | Learn More | | 08 | Building Search Apps Vector Databases | **Build:** A search application that uses Embeddings to search for data. | Learn More | | 09 | Building Image Generation Applications | **Build:** A image generation application | Learn More | | 10 | Building Low Code AI Applications | **Build:** A Generative AI application using Low Code tools | Learn More | | 11 | Integrating External Applications with Function Calling | **Build:** What is function calling and its use cases for applications | Learn More | | 12 | Designing UX for AI Applications | **Learn:** How to apply UX design principles when developing Generative AI Applications | Learn More | | 13 | Securing Your Generative AI Applications | **Learn:** The threats and risks to AI systems and methods to secure these systems. | Learn More | | 14 | The Generative AI Application Lifecycle | **Learn:** The tools and metrics to manage the LLM Lifecycle and LLMOps | Learn More | | 15 | Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) and Vector Databases | **Build:** An application using a RAG Framework to retrieve embeddings from a Vector Databases | Learn More | | 16 | Open Source Models and Hugging Face | **Build:** An application using open source models available on Hugging Face | Learn More | | 17 | AI Agents | **Build:** An application using an AI Agent Framework | Learn More | | 18 | Fine-Tuning LLMs | **Learn:** The what, why and how of fine-tuning LLMs | Learn More |
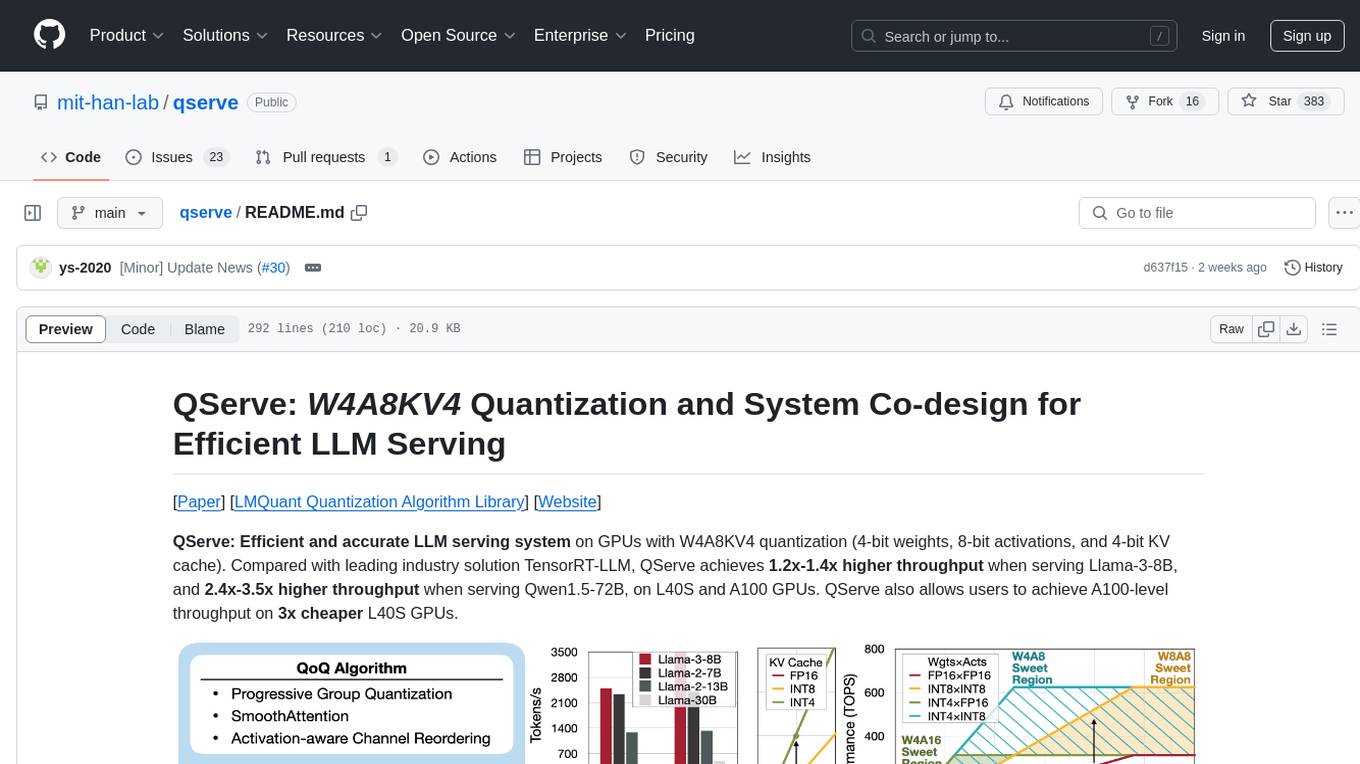
qserve
QServe is a serving system designed for efficient and accurate Large Language Models (LLM) on GPUs with W4A8KV4 quantization. It achieves higher throughput compared to leading industry solutions, allowing users to achieve A100-level throughput on cheaper L40S GPUs. The system introduces the QoQ quantization algorithm with 4-bit weight, 8-bit activation, and 4-bit KV cache, addressing runtime overhead challenges. QServe improves serving throughput for various LLM models by implementing compute-aware weight reordering, register-level parallelism, and fused attention memory-bound techniques.
squirrelscan
Squirrelscan is a website audit tool designed for SEO, performance, and security audits. It offers 230+ rules across 21 categories, AI-native design for Claude Code and AI workflows, smart incremental crawling, and multiple output formats. It provides E-E-A-T auditing, crawl history tracking, and is developer-friendly with a CLI. Users can run audits in the terminal, integrate with AI coding agents, or pipe output to AI assistants. The tool is available for macOS, Linux, Windows, npm, and npx installations, and is suitable for autonomous AI workflows.
For similar tasks
nlp-llms-resources
The 'nlp-llms-resources' repository is a comprehensive resource list for Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Large Language Models (LLMs). It covers a wide range of topics including traditional NLP datasets, data acquisition, libraries for NLP, neural networks, sentiment analysis, optical character recognition, information extraction, semantics, topic modeling, multilingual NLP, domain-specific LLMs, vector databases, ethics, costing, books, courses, surveys, aggregators, newsletters, papers, conferences, and societies. The repository provides valuable information and resources for individuals interested in NLP and LLMs.

adata
AData is a free and open-source A-share database that focuses on transaction-related data. It provides comprehensive data on stocks, including basic information, market data, and sentiment analysis. AData is designed to be easy to use and integrate with other applications, making it a valuable tool for quantitative trading and AI training.

PIXIU
PIXIU is a project designed to support the development, fine-tuning, and evaluation of Large Language Models (LLMs) in the financial domain. It includes components like FinBen, a Financial Language Understanding and Prediction Evaluation Benchmark, FIT, a Financial Instruction Dataset, and FinMA, a Financial Large Language Model. The project provides open resources, multi-task and multi-modal financial data, and diverse financial tasks for training and evaluation. It aims to encourage open research and transparency in the financial NLP field.

hezar
Hezar is an all-in-one AI library designed specifically for the Persian community. It brings together various AI models and tools, making it easy to use AI with just a few lines of code. The library seamlessly integrates with Hugging Face Hub, offering a developer-friendly interface and task-based model interface. In addition to models, Hezar provides tools like word embeddings, tokenizers, feature extractors, and more. It also includes supplementary ML tools for deployment, benchmarking, and optimization.
text-embeddings-inference
Text Embeddings Inference (TEI) is a toolkit for deploying and serving open source text embeddings and sequence classification models. TEI enables high-performance extraction for popular models like FlagEmbedding, Ember, GTE, and E5. It implements features such as no model graph compilation step, Metal support for local execution on Macs, small docker images with fast boot times, token-based dynamic batching, optimized transformers code for inference using Flash Attention, Candle, and cuBLASLt, Safetensors weight loading, and production-ready features like distributed tracing with Open Telemetry and Prometheus metrics.
CodeProject.AI-Server
CodeProject.AI Server is a standalone, self-hosted, fast, free, and open-source Artificial Intelligence microserver designed for any platform and language. It can be installed locally without the need for off-device or out-of-network data transfer, providing an easy-to-use solution for developers interested in AI programming. The server includes a HTTP REST API server, backend analysis services, and the source code, enabling users to perform various AI tasks locally without relying on external services or cloud computing. Current capabilities include object detection, face detection, scene recognition, sentiment analysis, and more, with ongoing feature expansions planned. The project aims to promote AI development, simplify AI implementation, focus on core use-cases, and leverage the expertise of the developer community.

spark-nlp
Spark NLP is a state-of-the-art Natural Language Processing library built on top of Apache Spark. It provides simple, performant, and accurate NLP annotations for machine learning pipelines that scale easily in a distributed environment. Spark NLP comes with 36000+ pretrained pipelines and models in more than 200+ languages. It offers tasks such as Tokenization, Word Segmentation, Part-of-Speech Tagging, Named Entity Recognition, Dependency Parsing, Spell Checking, Text Classification, Sentiment Analysis, Token Classification, Machine Translation, Summarization, Question Answering, Table Question Answering, Text Generation, Image Classification, Image to Text (captioning), Automatic Speech Recognition, Zero-Shot Learning, and many more NLP tasks. Spark NLP is the only open-source NLP library in production that offers state-of-the-art transformers such as BERT, CamemBERT, ALBERT, ELECTRA, XLNet, DistilBERT, RoBERTa, DeBERTa, XLM-RoBERTa, Longformer, ELMO, Universal Sentence Encoder, Llama-2, M2M100, BART, Instructor, E5, Google T5, MarianMT, OpenAI GPT2, Vision Transformers (ViT), OpenAI Whisper, and many more not only to Python and R, but also to JVM ecosystem (Java, Scala, and Kotlin) at scale by extending Apache Spark natively.
scikit-llm
Scikit-LLM is a tool that seamlessly integrates powerful language models like ChatGPT into scikit-learn for enhanced text analysis tasks. It allows users to leverage large language models for various text analysis applications within the familiar scikit-learn framework. The tool simplifies the process of incorporating advanced language processing capabilities into machine learning pipelines, enabling users to benefit from the latest advancements in natural language processing.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.


