
COLD-Attack
[ICML 2024] COLD-Attack: Jailbreaking LLMs with Stealthiness and Controllability
Stars: 84
COLD-Attack is a framework designed for controllable jailbreaks on large language models (LLMs). It formulates the controllable attack generation problem and utilizes the Energy-based Constrained Decoding with Langevin Dynamics (COLD) algorithm to automate the search of adversarial LLM attacks with control over fluency, stealthiness, sentiment, and left-right-coherence. The framework includes steps for energy function formulation, Langevin dynamics sampling, and decoding process to generate discrete text attacks. It offers diverse jailbreak scenarios such as fluent suffix attacks, paraphrase attacks, and attacks with left-right-coherence.
README:
We study the controllable jailbreaks on large language models (LLMs). Specifically, we focus on how to enforce control on LLM attacks. In this work, we formally formulate the controllable attack generation problem, and build a novel connection between this problem and controllable text generation, a well-explored topic of natural language processing. Based on this connection, we adapt the Energy-based Constrained Decoding with Langevin Dynamics (COLD), a state-of-the-art, highly efficient algorithm in controllable text generation, and introduce the COLD-Attack framework which unifies and automates the search of adversarial LLM attacks under a variety of control requirements such as fluency, stealthiness, sentiment, and left-right-coherence. The controllability enabled by COLD-Attack leads to diverse new jailbreak scenarios including:
- Fluent suffix attacks (standard attack setting which append the adversarial prompt to the original malicious user query).
- Paraphrase attack with and without sentiment steering (revising a user query adversarially with minimal paraphrasing).
- Attack with left-right-coherence (inserting stealthy attacks in context with left-right-coherence).
More details can be found in our paper: Xingang Guo*, Fangxu Yu*, Huan Zhang, Lianhui Qin, Bin Hu, "COLD-Attack: Jailbreaking LLMs with Stealthiness and Controllability" (* Equal contribution)
As illustrated in the above diagram, our COLD-Attack framework includes three main steps:
- Energy function formulation: specify energy functions properly to capture the attack constraints such as fluency, stealthiness, sentiment, and left-right-coherence.
- Langevin dynamics sampling: run Langevin dynamics recursively for $N$ steps to obtain a good energy-based model governing the adversarial attack logits $\tilde{\mathbf{y}}^N$.
- Decoding process: leverage an LLM-guided decoding process to covert the continuous logit $\tilde{\mathbf{y}}^N$ into discrete text attacks $\mathbf{y}$.
Here are some examples that generated by COLD-Attack:
We evaluate the performance of COLD-Attack on four popular white-box LLMs: Vicuna-7b-v1.5 (Vicuna), Llama-2-7b-Chat-hf (Llama2), Guanaco-7b (Guanaco), and Mistral-7b-Instruct-v0.2 (Mistral). In addition, we use the following three main evaluation metrics:
- Attack Successful Rate (ASR): the percentage of instructions that elicit corresponding harmful outputs using sub-string matching method.
- GPT-4 based ASR (ASR-G): We develop a prompt template and utilize GPT-4 to assess whether a response accurately fulfills the malicious instruction. Based on our observations, ASR-G has shown higher correlation with human annotations, providing a more reliable measure of attack effectiveness.
- Perplexity (PPL): We use PPL to evaluate the fluency of the generated prompts and use Vicuna-7b to do the PPL calculation.
To ensure the generated adversarial prompts meet specific criteria, we apply controls over various features, including sentiment and vocabulary. We evaluate how well these controls work using a metric called Succ, which represents the percentage of samples that successfully adhere to our set requirements. Additionally, a range of NLP-related evaluation metrics including BERTScore, BLEU, and ROUGE are applied to evaluate the quality of generated controllable attacks.
| Models | ASR ↑ | ASR-G ↑ | PPL ↓ |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vicuna | 100.0 | 86.00 | 32.96 |
| Guanaco | 96.00 | 84.00 | 30.55 |
| Mistral | 92.00 | 90.00 | 26.24 |
| Llama2 | 92.00 | 66.00 | 24.83 |
| Models | ASR ↑ | ASR-G ↑ | PPL ↓ | BLEU ↑ | ROUGE ↑ | BERTScore ↑ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vicuna | 96.00 | 80.00 | 31.11 | 0.52 | 0.57 | 0.72 |
| Guanaco | 98.00 | 78.00 | 29.23 | 0.47 | 0.55 | 0.74 |
| Mistral | 98.00 | 90.00 | 37.21 | 0.41 | 0.55 | 0.72 |
| Llama2 | 86.00 | 74.00 | 39.26 | 0.60 | 0.54 | 0.71 |
| Models | ASR ↑ | ASR-G ↑ | Succ ↑ | PPL ↓ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sentiment Constraint | ||||
| Vicuna | 90.00 | 96.00 | 84.00 | 66.48 |
| Guanaco | 96.00 | 94.00 | 82.00 | 74.05 |
| Mistral | 92.00 | 96.00 | 92.00 | 67.61 |
| Llama2 | 80.00 | 88.00 | 64.00 | 59.53 |
| Lexical Constraint | ||||
| Vicuna | 92.00 | 100.00 | 82.00 | 76.69 |
| Guanaco | 92.00 | 96.00 | 82.00 | 99.03 |
| Mistral | 94.00 | 84.00 | 92.00 | 96.06 |
| Llama2 | 88.00 | 86.00 | 68.00 | 68.23 |
| Format Constraint | ||||
| Vicuna | 92.00 | 94.00 | 88.00 | 67.63 |
| Guanaco | 92.00 | 94.00 | 72.00 | 72.97 |
| Mistral | 94.00 | 86.00 | 84.00 | 44.56 |
| Llama2 | 80.00 | 86.00 | 72.00 | 57.70 |
| Style Constraint | ||||
| Vicuna | 94.00 | 96.00 | 80.00 | 81.54 |
| Guanaco | 94.00 | 92.00 | 70.00 | 75.25 |
| Mistral | 92.00 | 90.00 | 86.00 | 54.50 |
| Llama2 | 80.00 | 80.00 | 68.00 | 58.93 |
Please see more detaieled evaluation results and discussions in our paper.
1) Download this GitHub
git clone https://github.com/Yu-Fangxu/COLD-Attack.git
2) Setup Environment
We recommend conda for setting up a reproducible experiment environment.
We include environment.yaml for creating a working environment:
conda env create -f environment.yaml -n cold-attackYou will then need to setup NLTK and hugging face:
conda activate cold-attack
python3 -c "import nltk; nltk.download('stopwords', 'averaged_perceptron_tagger', 'punkt'); "To run the Llama-2 model, you will need to request access at Hugging face and setup account login:
huggingface-cli login --token [Your Hugging face token]3) Run Command for COLD-Attack
- Fluent suffix attack
bash attack.sh "suffix"
- Paraphrase attack
bash attack.sh "paraphrase"
- Left-right-coherence control
bash attack.sh "control"
If you find our repository helpful to your research, please consider citing:
@article{guo2024cold,
title={Cold-attack: Jailbreaking llms with stealthiness and controllability},
author={Guo, Xingang and Yu, Fangxu and Zhang, Huan and Qin, Lianhui and Hu, Bin},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.08679},
year={2024}
}
@article{qin2022cold,
title={Cold decoding: Energy-based constrained text generation with langevin dynamics},
author={Qin, Lianhui and Welleck, Sean and Khashabi, Daniel and Choi, Yejin},
journal={Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems},
volume={35},
pages={9538--9551},
year={2022}
}
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for COLD-Attack
Similar Open Source Tools

COLD-Attack
COLD-Attack is a framework designed for controllable jailbreaks on large language models (LLMs). It formulates the controllable attack generation problem and utilizes the Energy-based Constrained Decoding with Langevin Dynamics (COLD) algorithm to automate the search of adversarial LLM attacks with control over fluency, stealthiness, sentiment, and left-right-coherence. The framework includes steps for energy function formulation, Langevin dynamics sampling, and decoding process to generate discrete text attacks. It offers diverse jailbreak scenarios such as fluent suffix attacks, paraphrase attacks, and attacks with left-right-coherence.

TrustLLM
TrustLLM is a comprehensive study of trustworthiness in LLMs, including principles for different dimensions of trustworthiness, established benchmark, evaluation, and analysis of trustworthiness for mainstream LLMs, and discussion of open challenges and future directions. Specifically, we first propose a set of principles for trustworthy LLMs that span eight different dimensions. Based on these principles, we further establish a benchmark across six dimensions including truthfulness, safety, fairness, robustness, privacy, and machine ethics. We then present a study evaluating 16 mainstream LLMs in TrustLLM, consisting of over 30 datasets. The document explains how to use the trustllm python package to help you assess the performance of your LLM in trustworthiness more quickly. For more details about TrustLLM, please refer to project website.
rubra
Rubra is a collection of open-weight large language models enhanced with tool-calling capability. It allows users to call user-defined external tools in a deterministic manner while reasoning and chatting, making it ideal for agentic use cases. The models are further post-trained to teach instruct-tuned models new skills and mitigate catastrophic forgetting. Rubra extends popular inferencing projects for easy use, enabling users to run the models easily.
YuLan-Mini
YuLan-Mini is a lightweight language model with 2.4 billion parameters that achieves performance comparable to industry-leading models despite being pre-trained on only 1.08T tokens. It excels in mathematics and code domains. The repository provides pre-training resources, including data pipeline, optimization methods, and annealing approaches. Users can pre-train their own language models, perform learning rate annealing, fine-tune the model, research training dynamics, and synthesize data. The team behind YuLan-Mini is AI Box at Renmin University of China. The code is released under the MIT License with future updates on model weights usage policies. Users are advised on potential safety concerns and ethical use of the model.
UniCoT
Uni-CoT is a unified reasoning framework that extends Chain-of-Thought (CoT) principles to the multimodal domain, enabling Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) to perform interpretable, step-by-step reasoning across both text and vision. It decomposes complex multimodal tasks into structured, manageable steps that can be executed sequentially or in parallel, allowing for more scalable and systematic reasoning.
jailbreak_llms
This is the official repository for the ACM CCS 2024 paper 'Do Anything Now': Characterizing and Evaluating In-The-Wild Jailbreak Prompts on Large Language Models. The project employs a new framework called JailbreakHub to conduct the first measurement study on jailbreak prompts in the wild, collecting 15,140 prompts from December 2022 to December 2023, including 1,405 jailbreak prompts. The dataset serves as the largest collection of in-the-wild jailbreak prompts. The repository contains examples of harmful language and is intended for research purposes only.
llm-compression-intelligence
This repository presents the findings of the paper "Compression Represents Intelligence Linearly". The study reveals a strong linear correlation between the intelligence of LLMs, as measured by benchmark scores, and their ability to compress external text corpora. Compression efficiency, derived from raw text corpora, serves as a reliable evaluation metric that is linearly associated with model capabilities. The repository includes the compression corpora used in the paper, code for computing compression efficiency, and data collection and processing pipelines.
FlipAttack
FlipAttack is a jailbreak attack tool designed to exploit black-box Language Model Models (LLMs) by manipulating text inputs. It leverages insights into LLMs' autoregressive nature to construct noise on the left side of the input text, deceiving the model and enabling harmful behaviors. The tool offers four flipping modes to guide LLMs in denoising and executing malicious prompts effectively. FlipAttack is characterized by its universality, stealthiness, and simplicity, allowing users to compromise black-box LLMs with just one query. Experimental results demonstrate its high success rates against various LLMs, including GPT-4o and guardrail models.
amber-train
Amber is the first model in the LLM360 family, an initiative for comprehensive and fully open-sourced LLMs. It is a 7B English language model with the LLaMA architecture. The model type is a language model with the same architecture as LLaMA-7B. It is licensed under Apache 2.0. The resources available include training code, data preparation, metrics, and fully processed Amber pretraining data. The model has been trained on various datasets like Arxiv, Book, C4, Refined-Web, StarCoder, StackExchange, and Wikipedia. The hyperparameters include a total of 6.7B parameters, hidden size of 4096, intermediate size of 11008, 32 attention heads, 32 hidden layers, RMSNorm ε of 1e^-6, max sequence length of 2048, and a vocabulary size of 32000.
IDvs.MoRec
This repository contains the source code for the SIGIR 2023 paper 'Where to Go Next for Recommender Systems? ID- vs. Modality-based Recommender Models Revisited'. It provides resources for evaluating foundation, transferable, multi-modal, and LLM recommendation models, along with datasets, pre-trained models, and training strategies for IDRec and MoRec using in-batch debiased cross-entropy loss. The repository also offers large-scale datasets, code for SASRec with in-batch debias cross-entropy loss, and information on joining the lab for research opportunities.

EasyEdit
EasyEdit is a Python package for edit Large Language Models (LLM) like `GPT-J`, `Llama`, `GPT-NEO`, `GPT2`, `T5`(support models from **1B** to **65B**), the objective of which is to alter the behavior of LLMs efficiently within a specific domain without negatively impacting performance across other inputs. It is designed to be easy to use and easy to extend.
qserve
QServe is a serving system designed for efficient and accurate Large Language Models (LLM) on GPUs with W4A8KV4 quantization. It achieves higher throughput compared to leading industry solutions, allowing users to achieve A100-level throughput on cheaper L40S GPUs. The system introduces the QoQ quantization algorithm with 4-bit weight, 8-bit activation, and 4-bit KV cache, addressing runtime overhead challenges. QServe improves serving throughput for various LLM models by implementing compute-aware weight reordering, register-level parallelism, and fused attention memory-bound techniques.
PredictorLLM
PredictorLLM is an advanced trading agent framework that utilizes large language models to automate trading in financial markets. It includes a profiling module to establish agent characteristics, a layered memory module for retaining and prioritizing financial data, and a decision-making module to convert insights into trading strategies. The framework mimics professional traders' behavior, surpassing human limitations in data processing and continuously evolving to adapt to market conditions for superior investment outcomes.
llm4regression
This project explores the capability of Large Language Models (LLMs) to perform regression tasks using in-context examples. It compares the performance of LLMs like GPT-4 and Claude 3 Opus with traditional supervised methods such as Linear Regression and Gradient Boosting. The project provides preprints and results demonstrating the strong performance of LLMs in regression tasks. It includes datasets, models used, and experiments on adaptation and contamination. The code and data for the experiments are available for interaction and analysis.
AI-For-Beginners
AI-For-Beginners is a comprehensive 12-week, 24-lesson curriculum designed by experts at Microsoft to introduce beginners to the world of Artificial Intelligence (AI). The curriculum covers various topics such as Symbolic AI, Neural Networks, Computer Vision, Natural Language Processing, Genetic Algorithms, and Multi-Agent Systems. It includes hands-on lessons, quizzes, and labs using popular frameworks like TensorFlow and PyTorch. The focus is on providing a foundational understanding of AI concepts and principles, making it an ideal starting point for individuals interested in AI.
DeepRetrieval
DeepRetrieval is a tool designed to enhance search engines and retrievers using Large Language Models (LLMs) and Reinforcement Learning (RL). It allows LLMs to learn how to search effectively by integrating with search engine APIs and customizing reward functions. The tool provides functionalities for data preparation, training, evaluation, and monitoring search performance. DeepRetrieval aims to improve information retrieval tasks by leveraging advanced AI techniques.
For similar tasks

COLD-Attack
COLD-Attack is a framework designed for controllable jailbreaks on large language models (LLMs). It formulates the controllable attack generation problem and utilizes the Energy-based Constrained Decoding with Langevin Dynamics (COLD) algorithm to automate the search of adversarial LLM attacks with control over fluency, stealthiness, sentiment, and left-right-coherence. The framework includes steps for energy function formulation, Langevin dynamics sampling, and decoding process to generate discrete text attacks. It offers diverse jailbreak scenarios such as fluent suffix attacks, paraphrase attacks, and attacks with left-right-coherence.
For similar jobs
prometheus-eval
Prometheus-Eval is a repository dedicated to evaluating large language models (LLMs) in generation tasks. It provides state-of-the-art language models like Prometheus 2 (7B & 8x7B) for assessing in pairwise ranking formats and achieving high correlation scores with benchmarks. The repository includes tools for training, evaluating, and using these models, along with scripts for fine-tuning on custom datasets. Prometheus aims to address issues like fairness, controllability, and affordability in evaluations by simulating human judgments and proprietary LM-based assessments.
cladder
CLadder is a repository containing the CLadder dataset for evaluating causal reasoning in language models. The dataset consists of yes/no questions in natural language that require statistical and causal inference to answer. It includes fields such as question_id, given_info, question, answer, reasoning, and metadata like query_type and rung. The dataset also provides prompts for evaluating language models and example questions with associated reasoning steps. Additionally, it offers dataset statistics, data variants, and code setup instructions for using the repository.
awesome-llm-unlearning
This repository tracks the latest research on machine unlearning in large language models (LLMs). It offers a comprehensive list of papers, datasets, and resources relevant to the topic.

COLD-Attack
COLD-Attack is a framework designed for controllable jailbreaks on large language models (LLMs). It formulates the controllable attack generation problem and utilizes the Energy-based Constrained Decoding with Langevin Dynamics (COLD) algorithm to automate the search of adversarial LLM attacks with control over fluency, stealthiness, sentiment, and left-right-coherence. The framework includes steps for energy function formulation, Langevin dynamics sampling, and decoding process to generate discrete text attacks. It offers diverse jailbreak scenarios such as fluent suffix attacks, paraphrase attacks, and attacks with left-right-coherence.
Awesome-LLM-in-Social-Science
Awesome-LLM-in-Social-Science is a repository that compiles papers evaluating Large Language Models (LLMs) from a social science perspective. It includes papers on evaluating, aligning, and simulating LLMs, as well as enhancing tools in social science research. The repository categorizes papers based on their focus on attitudes, opinions, values, personality, morality, and more. It aims to contribute to discussions on the potential and challenges of using LLMs in social science research.
awesome-llm-attributions
This repository focuses on unraveling the sources that large language models tap into for attribution or citation. It delves into the origins of facts, their utilization by the models, the efficacy of attribution methodologies, and challenges tied to ambiguous knowledge reservoirs, biases, and pitfalls of excessive attribution.
context-cite
ContextCite is a tool for attributing statements generated by LLMs back to specific parts of the context. It allows users to analyze and understand the sources of information used by language models in generating responses. By providing attributions, users can gain insights into how the model makes decisions and where the information comes from.
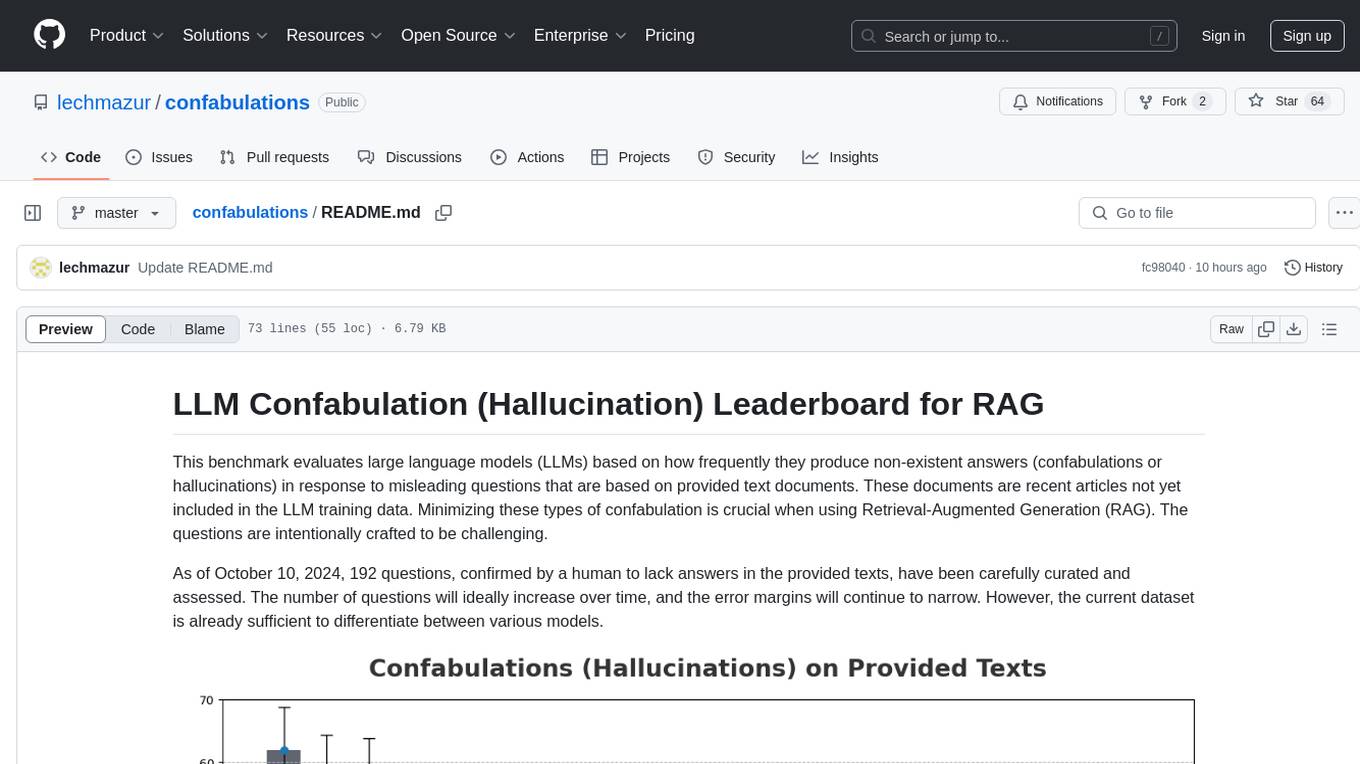
confabulations
LLM Confabulation Leaderboard evaluates large language models based on confabulations and non-response rates to challenging questions. It includes carefully curated questions with no answers in provided texts, aiming to differentiate between various models. The benchmark combines confabulation and non-response rates for comprehensive ranking, offering insights into model performance and tendencies. Additional notes highlight the meticulous human verification process, challenges faced by LLMs in generating valid responses, and the use of temperature settings. Updates and other benchmarks are also mentioned, providing a holistic view of the evaluation landscape.

