
confabulations
Hallucinations (Confabulations) Document-Based Benchmark for RAG
Stars: 90
LLM Confabulation Leaderboard evaluates large language models based on confabulations and non-response rates to challenging questions. It includes carefully curated questions with no answers in provided texts, aiming to differentiate between various models. The benchmark combines confabulation and non-response rates for comprehensive ranking, offering insights into model performance and tendencies. Additional notes highlight the meticulous human verification process, challenges faced by LLMs in generating valid responses, and the use of temperature settings. Updates and other benchmarks are also mentioned, providing a holistic view of the evaluation landscape.
README:
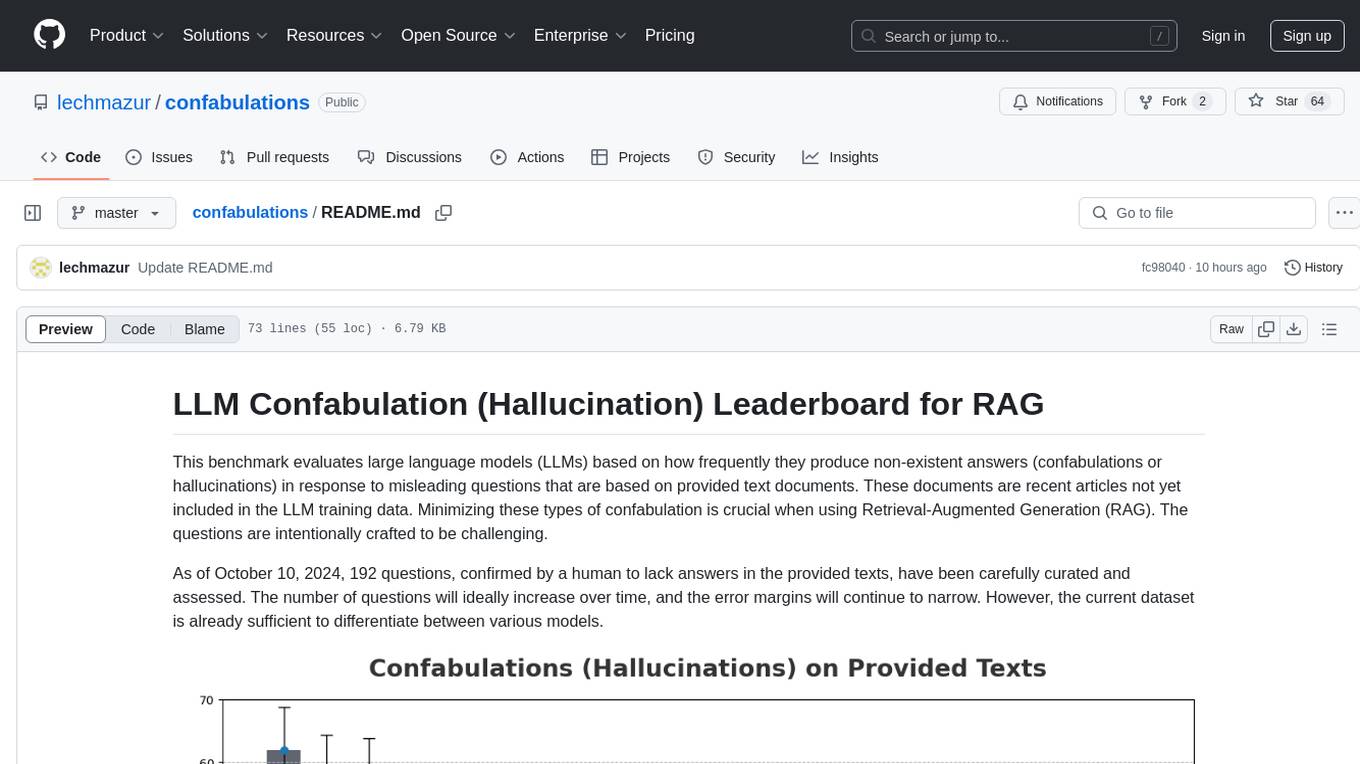
This benchmark evaluates large language models (LLMs) based on how frequently they produce non-existent answers (confabulations or hallucinations) in response to misleading questions that are based on provided text documents. These documents are recent articles not yet included in the LLM training data. Minimizing these types of confabulation is crucial when using Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG). The questions are intentionally crafted to be challenging.
As of Feb 10, 2025, 201 questions, confirmed by a human to lack answers in the provided texts, have been carefully curated and assessed. The number of questions will ideally increase over time, and the error margins will continue to narrow. However, the current dataset is already sufficient to differentiate between various models.
Combining confabulation and non-response rates enables a comprehensive ranking. Depending on your priorities, you may prefer fewer confabulations or fewer non-responses.
| Rank | Model | Confab % | Non-Resp % | Weighted |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | o1 | 10.9 | 12.6 | 11.74 |
| 2 | Gemini 2.0 Flash Think Exp 01-21 | 14.9 | 10.0 | 12.43 |
| 3 | DeepSeek R1 | 17.3 | 8.0 | 12.65 |
| 4 | o1-preview | 18.3 | 7.8 | 13.04 |
| 5 | Gemini 1.5 Pro (Sept) | 16.8 | 10.2 | 13.54 |
| 6 | GPT-4o | 22.3 | 8.4 | 15.34 |
| 7 | Llama 3.1 405B | 14.4 | 20.9 | 17.62 |
| 8 | o3-mini (medium reasoning) | 27.2 | 8.6 | 17.91 |
| 9 | Gemini 2.0 Pro Exp 02-05 | 15.8 | 21.0 | 18.43 |
| 10 | o1-mini | 26.2 | 10.9 | 18.55 |
| 11 | Qwen 2.5 72B | 32.2 | 6.0 | 19.09 |
| 12 | DeepSeek-V3 | 24.3 | 14.2 | 19.23 |
| 13 | Claude 3.5 Sonnet 2024-10-22 | 12.9 | 27.0 | 19.94 |
| 14 | Grok 2 12-12 | 25.7 | 14.5 | 20.14 |
| 15 | Mistral Large 2 | 32.2 | 10.6 | 21.40 |
| 16 | Qwen 2.5 Max | 31.2 | 12.4 | 21.78 |
| 17 | Claude 3 Opus | 28.2 | 17.2 | 22.70 |
| 18 | Llama 3.3 70B | 17.8 | 27.8 | 22.81 |
| 19 | MiniMax-Text-01 | 44.6 | 3.3 | 23.92 |
| 20 | Mistral Small 3 | 38.6 | 11.8 | 25.21 |
| 21 | Gemini 2.0 Flash | 24.3 | 29.4 | 26.85 |
| 22 | Gemma 2 27B | 47.3 | 7.2 | 27.24 |
| 23 | GPT-4 Turbo | 26.7 | 30.1 | 28.42 |
| 24 | Microsoft Phi-4 | 52.5 | 6.5 | 29.49 |
| 25 | Amazon Nova Pro | 54.5 | 5.6 | 30.05 |
| 26 | Claude 3 Haiku | 56.9 | 11.5 | 34.21 |
| 27 | Claude 3.5 Haiku | 65.8 | 7.6 | 36.74 |
| 28 | GPT-4o mini | 60.9 | 13.5 | 37.21 |
The raw confabulation rate alone isn't sufficient for meaningful evaluation. A model that simply declines to answer most questions would achieve a low confabulation rate. To address this, the benchmark also tracks the LLM non-response rate using the same prompts and documents but specific questions with answers that are present in the text. Currently, 2,612 hard questions (see the prompts) with known answers in the texts are included in this analysis.
Accuracy benchmarks can also be considered for a more comprehensive assessment. This benchmark currently focuses solely on pure confabulations to keep it distinct for now. However, I have created a separate benchmark to test LLMs using the extended version of the New York Times Connections.
- Reasoning appears to help. For example, DeepSeek R1 performs better than DeepSeek-V3 and Gemini 2.0 Flash Thinking Exp 01-21 performs better than Gemini 2.0 Flash.
- OpenAI o1 confabulates less than DeepSeek R1, but R1 answers questions with known answers more frequently.
- GPT-4o shows a significant improvement over GPT-4 Turbo.
- Gemini 1.5 Pro (September) performs better than Claude models, but there is no improvement with Gemini 2.0 Pro Exp 02-05.
- Llama models tend to respond cautiously, resulting in fewer confabulations but higher non-response rates
- A popular hallucination leaderboard on GitHub uses a model for evaluation of document summaries, but I found this to lead to a very high error rate and different rankings. This approach can be very misleading.
- While the initial set of questions was suggested by LLMs, the final 201 questions were all painstakingly human-verified to have no answers in the provided texts. Only a percentage of LLM-suggested questions were unequivocally answer-free.
- Despite clear prompts, LLMs often generated compound questions that effectively asked for two answers. These were removed in a separate judging step.
- The benchmark includes questions where at least one LLM confabulated, in order to minimize the number of questions requiring human assessment. Because of this, and since the questions are intentionally adversarial, the absolute percentage should not be used to infer that LLMs frequently confabulate. This leaderboard does not reflect a "typical" hallucination rate.
- In some cases, LLMs failed to provide valid responses to the questions, such as skipping certain questions altogether. This occurred only once for the human-selected questions without valid answers in the text (bad Gemma, bad), but happened more frequently for questions with valid answers. These questions were discarded.
- A temperature setting of 0 was used
- Multi-turn ensemble is my unpublished system. It utilizes multiple LLMs (that existed in Oct 2024), multi-turn dialogues, and other proprietary techniques. It is slower and more costly to run but it does very well. It outperforms non-o1 LLMs on MMLU-Pro and GPQA.
- Feb 10, 2025: 17 human-verified questions based on Jan 2025-Feb 2025 articles added. 176 answerable questions added.
- Feb 7, 2025: DeepSeek R1, o1, o3-mini (medium reasoning effort), DeepSeek-V3, Gemini 2.0 Flash Thinking Exp 01-21, Qwen 2.5 Max, Microsoft Phi-4, Amazon Nova Pro, Mistral Small 3, MiniMax-Text-01 added.
- Nov. 5, 2024: Claude 3.5 Haiku added
- Oct. 23, 2024: Grok Beta added
- Oct. 23, 2024: Claude 3.5 Sonnet (2024-10-22) added
- Oct. 15, 2024: Grok 2 added
- Also check out Multi-Agent Elimination Game LLM Benchmark, LLM Public Goods Game, LLM Step Game, LLM Thematic Generalization Benchmark, LLM Creative Story-Writing Benchmark, LLM Deception Benchmark and LLM Divergent Thinking Creativity Benchmark.
- Follow @lechmazur on X (Twitter) for other upcoming benchmarks and more.
| Rank | Model | Confab % | Non-Resp % | Weighted |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Multi-turn ensemble | 11.4 | 8.5 | 9.94 |
| 2 | DeepSeek R1 | 14.6 | 7.7 | 11.13 |
| 3 | o1 | 10.3 | 12.2 | 11.21 |
| 4 | Gemini 2.0 Flash Think Exp 01-21 | 13.0 | 10.1 | 11.56 |
| 5 | o1-preview | 16.8 | 7.4 | 12.07 |
| 6 | Gemini 1.5 Pro (Sept) | 16.8 | 9.7 | 13.24 |
| 7 | GPT-4o | 18.4 | 8.5 | 13.44 |
| 8 | Llama 3.1 405B | 11.9 | 20.8 | 16.35 |
| 9 | o3-mini (medium reasoning) | 24.3 | 8.5 | 16.43 |
| 10 | Gemini 2.0 Pro Exp 02-05 | 13.0 | 21.0 | 16.97 |
| 11 | o1-mini | 24.3 | 10.2 | 17.25 |
| 12 | DeepSeek-V3 | 21.1 | 14.5 | 17.79 |
| 13 | Qwen 2.5 72B | 30.3 | 5.8 | 18.03 |
| 14 | Grok 2 12-12 | 24.3 | 14.5 | 19.43 |
| 15 | Claude 3.5 Sonnet 2024-10-22 | 11.9 | 27.8 | 19.82 |
| 16 | Mistral Large 2 | 30.8 | 9.2 | 19.98 |
| 17 | Qwen 2.5 Max | 28.1 | 12.3 | 20.20 |
| 18 | Claude 3 Opus | 26.5 | 15.9 | 21.21 |
| 19 | MiniMax-Text-01 | 40.0 | 3.1 | 21.54 |
| 20 | Claude 3.5 Sonnet Old | 27.0 | 16.1 | 21.58 |
| 21 | Llama 3.1 70B | 13.5 | 31.4 | 22.46 |
| 22 | Llama 3.3 70B | 16.2 | 29.4 | 22.78 |
| 23 | Grok 2 | 24.3 | 22.7 | 23.53 |
| 24 | Gemini 1.5 Flash | 42.2 | 5.2 | 23.69 |
| 25 | Grok Beta | 24.3 | 23.4 | 23.84 |
| 26 | Mistral Small 3 | 35.7 | 12.5 | 24.10 |
| 27 | Gemma 2 27B | 44.3 | 7.1 | 25.71 |
| 28 | Gemini 2.0 Flash Exp | 23.2 | 29.9 | 26.58 |
| 29 | Gemini 2.0 Flash | 23.2 | 30.3 | 26.75 |
| 30 | Microsoft Phi-4 | 48.6 | 6.0 | 27.28 |
| 31 | GPT-4 Turbo | 23.8 | 31.4 | 27.59 |
| 32 | Amazon Nova Pro | 51.4 | 5.8 | 28.58 |
| 33 | DeepSeek-V2.5 | 33.5 | 25.6 | 29.54 |
| 34 | Claude 3 Haiku | 57.3 | 10.4 | 33.86 |
| 35 | Claude 3.5 Haiku | 63.2 | 6.8 | 35.03 |
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for confabulations
Similar Open Source Tools

confabulations
LLM Confabulation Leaderboard evaluates large language models based on confabulations and non-response rates to challenging questions. It includes carefully curated questions with no answers in provided texts, aiming to differentiate between various models. The benchmark combines confabulation and non-response rates for comprehensive ranking, offering insights into model performance and tendencies. Additional notes highlight the meticulous human verification process, challenges faced by LLMs in generating valid responses, and the use of temperature settings. Updates and other benchmarks are also mentioned, providing a holistic view of the evaluation landscape.
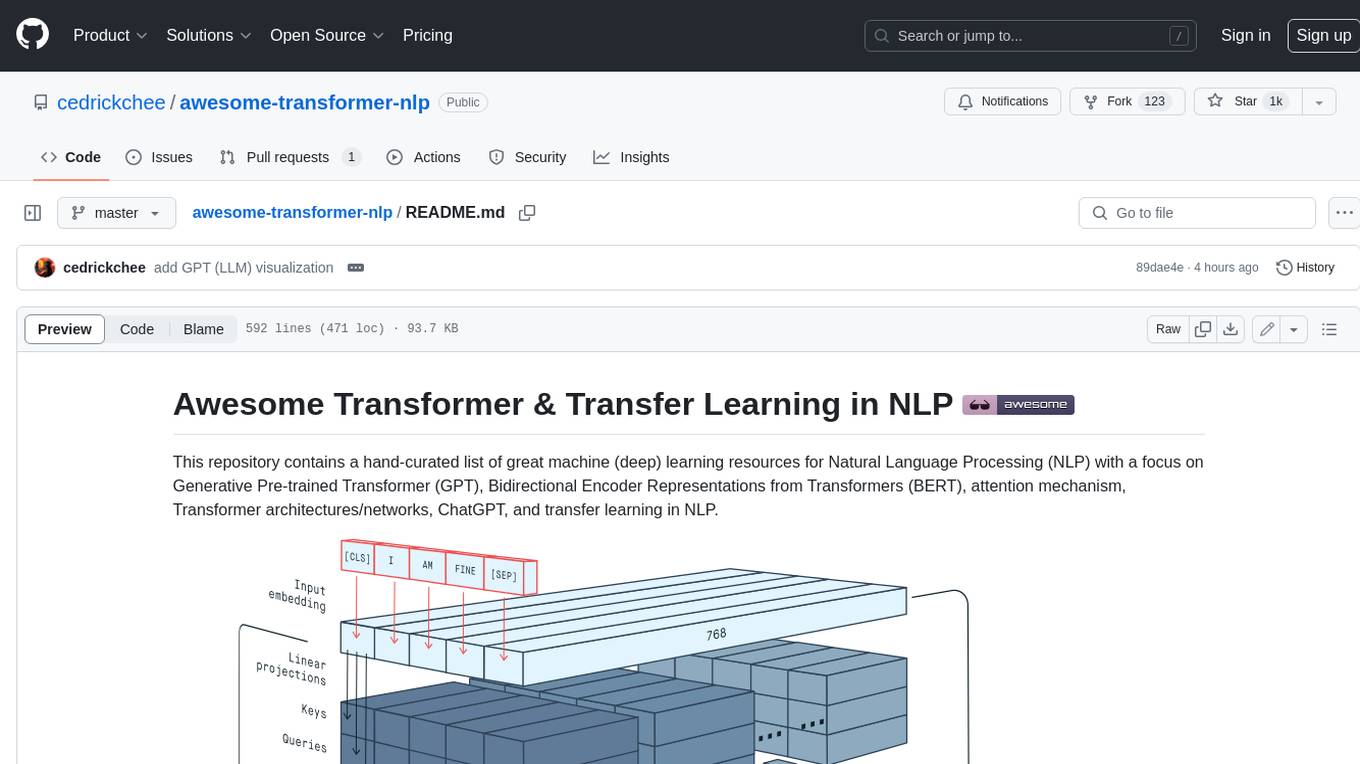
awesome-transformer-nlp
This repository contains a hand-curated list of great machine (deep) learning resources for Natural Language Processing (NLP) with a focus on Generative Pre-trained Transformer (GPT), Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT), attention mechanism, Transformer architectures/networks, Chatbot, and transfer learning in NLP.
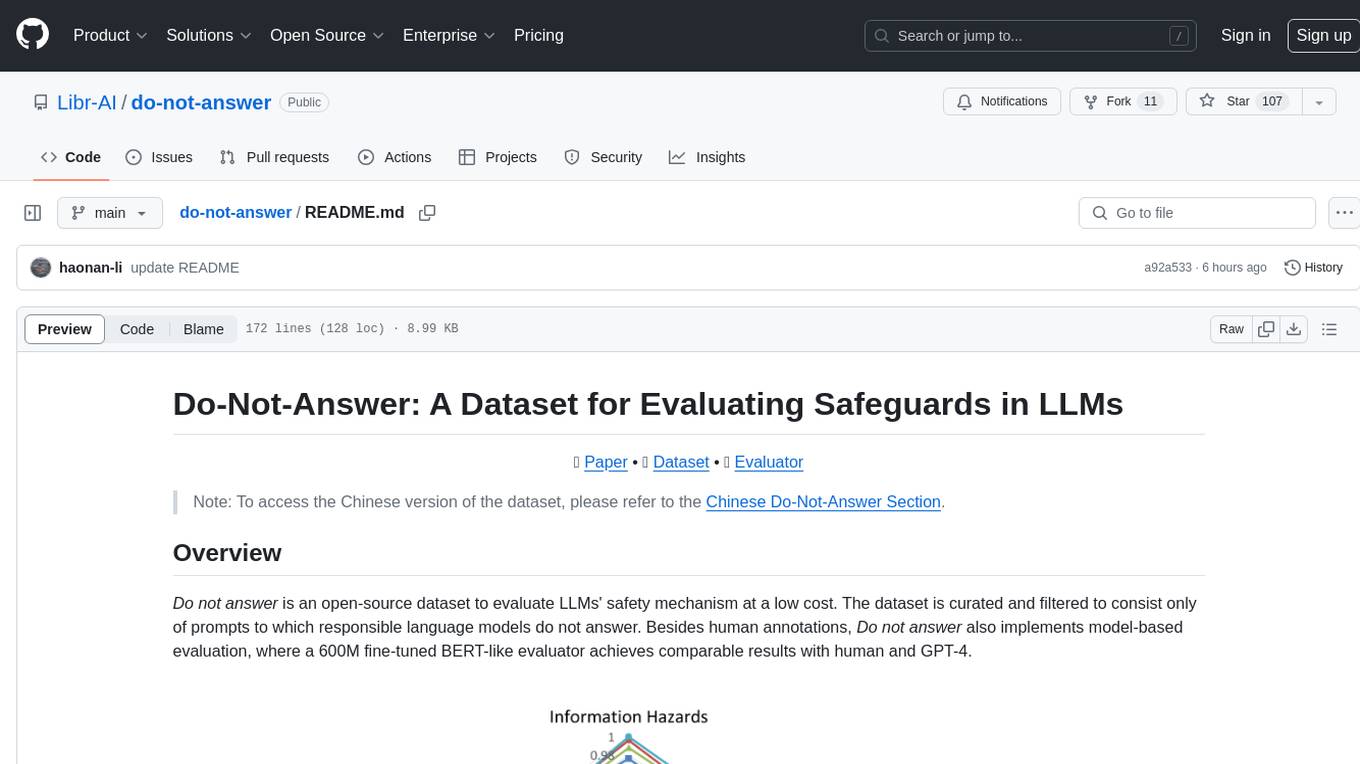
do-not-answer
Do-Not-Answer is an open-source dataset curated to evaluate Large Language Models' safety mechanisms at a low cost. It consists of prompts to which responsible language models do not answer. The dataset includes human annotations and model-based evaluation using a fine-tuned BERT-like evaluator. The dataset covers 61 specific harms and collects 939 instructions across five risk areas and 12 harm types. Response assessment is done for six models, categorizing responses into harmfulness and action categories. Both human and automatic evaluations show the safety of models across different risk areas. The dataset also includes a Chinese version with 1,014 questions for evaluating Chinese LLMs' risk perception and sensitivity to specific words and phrases.
TurtleBenchmark
Turtle Benchmark is a novel and cheat-proof benchmark test used to evaluate large language models (LLMs). It is based on the Turtle Soup game, focusing on logical reasoning and context understanding abilities. The benchmark does not require background knowledge or model memory, providing all necessary information for judgment from stories under 200 words. The results are objective and unbiased, quantifiable as correct/incorrect/unknown, and impossible to cheat due to using real user-generated questions and dynamic data generation during online gameplay.
babilong
BABILong is a generative benchmark designed to evaluate the performance of NLP models in processing long documents with distributed facts. It consists of 20 tasks that simulate interactions between characters and objects in various locations, requiring models to distinguish important information from irrelevant details. The tasks vary in complexity and reasoning aspects, with test samples potentially containing millions of tokens. The benchmark aims to challenge and assess the capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) in handling complex, long-context information.
R1-Searcher
R1-searcher is a tool designed to incentivize the search capability in large reasoning models (LRMs) via reinforcement learning. It enables LRMs to invoke web search and obtain external information during the reasoning process by utilizing a two-stage outcome-supervision reinforcement learning approach. The tool does not require instruction fine-tuning for cold start and is compatible with existing Base LLMs or Chat LLMs. It includes training code, inference code, model checkpoints, and a detailed technical report.
LLMsForTimeSeries
LLMsForTimeSeries is a repository that questions the usefulness of language models in time series forecasting. The work shows that simple baselines outperform most language model-based time series forecasting models. It includes ablation studies on LLM-based TSF methods and introduces the PAttn method, showcasing the performance of patching and attention structures in forecasting. The repository provides datasets, setup instructions, and scripts for running ablations on different datasets.
data-to-paper
Data-to-paper is an AI-driven framework designed to guide users through the process of conducting end-to-end scientific research, starting from raw data to the creation of comprehensive and human-verifiable research papers. The framework leverages a combination of LLM and rule-based agents to assist in tasks such as hypothesis generation, literature search, data analysis, result interpretation, and paper writing. It aims to accelerate research while maintaining key scientific values like transparency, traceability, and verifiability. The framework is field-agnostic, supports both open-goal and fixed-goal research, creates data-chained manuscripts, involves human-in-the-loop interaction, and allows for transparent replay of the research process.
SeaLLMs
SeaLLMs are a family of language models optimized for Southeast Asian (SEA) languages. They were pre-trained from Llama-2, on a tailored publicly-available dataset, which comprises texts in Vietnamese 🇻🇳, Indonesian 🇮🇩, Thai 🇹🇭, Malay 🇲🇾, Khmer🇰🇭, Lao🇱🇦, Tagalog🇵🇭 and Burmese🇲🇲. The SeaLLM-chat underwent supervised finetuning (SFT) and specialized self-preferencing DPO using a mix of public instruction data and a small number of queries used by SEA language native speakers in natural settings, which **adapt to the local cultural norms, customs, styles and laws in these areas**. SeaLLM-13b models exhibit superior performance across a wide spectrum of linguistic tasks and assistant-style instruction-following capabilities relative to comparable open-source models. Moreover, they outperform **ChatGPT-3.5** in non-Latin languages, such as Thai, Khmer, Lao, and Burmese.
Sarvadnya
Sarvadnya is a repository focused on interfacing custom data using Large Language Models (LLMs) through Proof-of-Concepts (PoCs) like Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) and Fine-Tuning. It aims to enable domain adaptation for LLMs to answer on user-specific corpora. The repository also covers topics such as Indic-languages models, 3D World Simulations, Knowledge Graphs Generation, Signal Processing, Drones, UAV Image Processing, and Floor Plan Segmentation. It provides insights into building chatbots of various modalities, preparing videos, and creating content for different platforms like Medium, LinkedIn, and YouTube. The tech stacks involved range from enterprise solutions like Google Doc AI and Microsoft Azure Language AI Services to open-source tools like Langchain and HuggingFace.
uptrain
UpTrain is an open-source unified platform to evaluate and improve Generative AI applications. We provide grades for 20+ preconfigured evaluations (covering language, code, embedding use cases), perform root cause analysis on failure cases and give insights on how to resolve them.
Slow_Thinking_with_LLMs
STILL is an open-source project exploring slow-thinking reasoning systems, focusing on o1-like reasoning systems. The project has released technical reports on enhancing LLM reasoning with reward-guided tree search algorithms and implementing slow-thinking reasoning systems using an imitate, explore, and self-improve framework. The project aims to replicate the capabilities of industry-level reasoning systems by fine-tuning reasoning models with long-form thought data and iteratively refining training datasets.
miyagi
Project Miyagi showcases Microsoft's Copilot Stack in an envisioning workshop aimed at designing, developing, and deploying enterprise-grade intelligent apps. By exploring both generative and traditional ML use cases, Miyagi offers an experiential approach to developing AI-infused product experiences that enhance productivity and enable hyper-personalization. Additionally, the workshop introduces traditional software engineers to emerging design patterns in prompt engineering, such as chain-of-thought and retrieval-augmentation, as well as to techniques like vectorization for long-term memory, fine-tuning of OSS models, agent-like orchestration, and plugins or tools for augmenting and grounding LLMs.
Controllable-RAG-Agent
This repository contains a sophisticated deterministic graph-based solution for answering complex questions using a controllable autonomous agent. The solution is designed to ensure that answers are solely based on the provided data, avoiding hallucinations. It involves various steps such as PDF loading, text preprocessing, summarization, database creation, encoding, and utilizing large language models. The algorithm follows a detailed workflow involving planning, retrieval, answering, replanning, content distillation, and performance evaluation. Heuristics and techniques implemented focus on content encoding, anonymizing questions, task breakdown, content distillation, chain of thought answering, verification, and model performance evaluation.
learn-agentic-ai
Learn Agentic AI is a repository that is part of the Panaversity Certified Agentic and Robotic AI Engineer program. It covers AI-201 and AI-202 courses, providing fundamentals and advanced knowledge in Agentic AI. The repository includes video playlists, projects, and project submission guidelines for students to enhance their understanding and skills in the field of AI engineering.
PocketFlow
Pocket Flow is a 100-line minimalist LLM framework designed for (Multi-)Agents, Task Decomposition, RAG, etc. It aims to be the framework used by LLMs, focusing on stripping away low-level implementation details and emphasizing high-level programming paradigms. Pocket Flow serves as a learning resource and provides a core abstraction of a nested directed graph for breaking down tasks into multiple steps.
For similar tasks

confabulations
LLM Confabulation Leaderboard evaluates large language models based on confabulations and non-response rates to challenging questions. It includes carefully curated questions with no answers in provided texts, aiming to differentiate between various models. The benchmark combines confabulation and non-response rates for comprehensive ranking, offering insights into model performance and tendencies. Additional notes highlight the meticulous human verification process, challenges faced by LLMs in generating valid responses, and the use of temperature settings. Updates and other benchmarks are also mentioned, providing a holistic view of the evaluation landscape.
LLM-Agent-Survey
LLM-Agent-Survey is a comprehensive repository that provides a curated list of papers related to Large Language Model (LLM) agents. The repository categorizes papers based on LLM-Profiled Roles and includes high-quality publications from prestigious conferences and journals. It aims to offer a systematic understanding of LLM-based agents, covering topics such as tool use, planning, and feedback learning. The repository also includes unpublished papers with insightful analysis and novelty, marked for future updates. Users can explore a wide range of surveys, tool use cases, planning workflows, and benchmarks related to LLM agents.
lighteval
LightEval is a lightweight LLM evaluation suite that Hugging Face has been using internally with the recently released LLM data processing library datatrove and LLM training library nanotron. We're releasing it with the community in the spirit of building in the open. Note that it is still very much early so don't expect 100% stability ^^' In case of problems or question, feel free to open an issue!
Firefly
Firefly is an open-source large model training project that supports pre-training, fine-tuning, and DPO of mainstream large models. It includes models like Llama3, Gemma, Qwen1.5, MiniCPM, Llama, InternLM, Baichuan, ChatGLM, Yi, Deepseek, Qwen, Orion, Ziya, Xverse, Mistral, Mixtral-8x7B, Zephyr, Vicuna, Bloom, etc. The project supports full-parameter training, LoRA, QLoRA efficient training, and various tasks such as pre-training, SFT, and DPO. Suitable for users with limited training resources, QLoRA is recommended for fine-tuning instructions. The project has achieved good results on the Open LLM Leaderboard with QLoRA training process validation. The latest version has significant updates and adaptations for different chat model templates.
Awesome-Text2SQL
Awesome Text2SQL is a curated repository containing tutorials and resources for Large Language Models, Text2SQL, Text2DSL, Text2API, Text2Vis, and more. It provides guidelines on converting natural language questions into structured SQL queries, with a focus on NL2SQL. The repository includes information on various models, datasets, evaluation metrics, fine-tuning methods, libraries, and practice projects related to Text2SQL. It serves as a comprehensive resource for individuals interested in working with Text2SQL and related technologies.
create-million-parameter-llm-from-scratch
The 'create-million-parameter-llm-from-scratch' repository provides a detailed guide on creating a Large Language Model (LLM) with 2.3 million parameters from scratch. The blog replicates the LLaMA approach, incorporating concepts like RMSNorm for pre-normalization, SwiGLU activation function, and Rotary Embeddings. The model is trained on a basic dataset to demonstrate the ease of creating a million-parameter LLM without the need for a high-end GPU.
StableToolBench
StableToolBench is a new benchmark developed to address the instability of Tool Learning benchmarks. It aims to balance stability and reality by introducing features such as a Virtual API System with caching and API simulators, a new set of solvable queries determined by LLMs, and a Stable Evaluation System using GPT-4. The Virtual API Server can be set up either by building from source or using a prebuilt Docker image. Users can test the server using provided scripts and evaluate models with Solvable Pass Rate and Solvable Win Rate metrics. The tool also includes model experiments results comparing different models' performance.
BetaML.jl
The Beta Machine Learning Toolkit is a package containing various algorithms and utilities for implementing machine learning workflows in multiple languages, including Julia, Python, and R. It offers a range of supervised and unsupervised models, data transformers, and assessment tools. The models are implemented entirely in Julia and are not wrappers for third-party models. Users can easily contribute new models or request implementations. The focus is on user-friendliness rather than computational efficiency, making it suitable for educational and research purposes.
For similar jobs
prometheus-eval
Prometheus-Eval is a repository dedicated to evaluating large language models (LLMs) in generation tasks. It provides state-of-the-art language models like Prometheus 2 (7B & 8x7B) for assessing in pairwise ranking formats and achieving high correlation scores with benchmarks. The repository includes tools for training, evaluating, and using these models, along with scripts for fine-tuning on custom datasets. Prometheus aims to address issues like fairness, controllability, and affordability in evaluations by simulating human judgments and proprietary LM-based assessments.
cladder
CLadder is a repository containing the CLadder dataset for evaluating causal reasoning in language models. The dataset consists of yes/no questions in natural language that require statistical and causal inference to answer. It includes fields such as question_id, given_info, question, answer, reasoning, and metadata like query_type and rung. The dataset also provides prompts for evaluating language models and example questions with associated reasoning steps. Additionally, it offers dataset statistics, data variants, and code setup instructions for using the repository.
awesome-llm-unlearning
This repository tracks the latest research on machine unlearning in large language models (LLMs). It offers a comprehensive list of papers, datasets, and resources relevant to the topic.
COLD-Attack
COLD-Attack is a framework designed for controllable jailbreaks on large language models (LLMs). It formulates the controllable attack generation problem and utilizes the Energy-based Constrained Decoding with Langevin Dynamics (COLD) algorithm to automate the search of adversarial LLM attacks with control over fluency, stealthiness, sentiment, and left-right-coherence. The framework includes steps for energy function formulation, Langevin dynamics sampling, and decoding process to generate discrete text attacks. It offers diverse jailbreak scenarios such as fluent suffix attacks, paraphrase attacks, and attacks with left-right-coherence.
Awesome-LLM-in-Social-Science
Awesome-LLM-in-Social-Science is a repository that compiles papers evaluating Large Language Models (LLMs) from a social science perspective. It includes papers on evaluating, aligning, and simulating LLMs, as well as enhancing tools in social science research. The repository categorizes papers based on their focus on attitudes, opinions, values, personality, morality, and more. It aims to contribute to discussions on the potential and challenges of using LLMs in social science research.
awesome-llm-attributions
This repository focuses on unraveling the sources that large language models tap into for attribution or citation. It delves into the origins of facts, their utilization by the models, the efficacy of attribution methodologies, and challenges tied to ambiguous knowledge reservoirs, biases, and pitfalls of excessive attribution.
context-cite
ContextCite is a tool for attributing statements generated by LLMs back to specific parts of the context. It allows users to analyze and understand the sources of information used by language models in generating responses. By providing attributions, users can gain insights into how the model makes decisions and where the information comes from.

confabulations
LLM Confabulation Leaderboard evaluates large language models based on confabulations and non-response rates to challenging questions. It includes carefully curated questions with no answers in provided texts, aiming to differentiate between various models. The benchmark combines confabulation and non-response rates for comprehensive ranking, offering insights into model performance and tendencies. Additional notes highlight the meticulous human verification process, challenges faced by LLMs in generating valid responses, and the use of temperature settings. Updates and other benchmarks are also mentioned, providing a holistic view of the evaluation landscape.