
cladder
We develop benchmarks and analysis tools to evaluate the causal reasoning abilities of LLMs.
Stars: 82
CLadder is a repository containing the CLadder dataset for evaluating causal reasoning in language models. The dataset consists of yes/no questions in natural language that require statistical and causal inference to answer. It includes fields such as question_id, given_info, question, answer, reasoning, and metadata like query_type and rung. The dataset also provides prompts for evaluating language models and example questions with associated reasoning steps. Additionally, it offers dataset statistics, data variants, and code setup instructions for using the repository.
README:
🚀 Get the dataset now! cladder-v1.zip
- zip file size: 6.5MB
- Version: v1
- Date: 2023-05-25
- Huggingface dataset: https://huggingface.co/datasets/causalnlp/CLadder
This repo contains the full CLadder dataset (and code) for evaluating (formal) causal reasoning in language models. The dataset asks yes/no questions in natural language that generally require statistical and causal inference to answer.
Although there are several different variants, the main dataset (including questions from all variants) is cladder-v1-balanced.json, so that is the recommended file to use for most purposes.
"CLadder: Assessing Causal Reasoning in Language Models" by Zhijing Jin*, Yuen Chen*, Felix Leeb*, Luigi Gresele*, Ojasv Kamal, Zhiheng Lyu, Kevin Blin, Fernando Gonzalez, Max Kleiman-Weiner, Mrinmaya Sachan, Bernhard Schölkopf.
Citation:
@inproceedings{jin2023cladder,
author = {Zhijing Jin and Yuen Chen and Felix Leeb and Luigi Gresele and Ojasv Kamal and Zhiheng Lyu and Kevin Blin and Fernando Gonzalez and Max Kleiman-Weiner and Mrinmaya Sachan and Bernhard Sch{\"{o}}lkopf},
title = "{CL}adder: {A}ssessing Causal Reasoning in Language Models",
year = "2023",
booktitle = "NeurIPS",
url = "https://openreview.net/forum?id=e2wtjx0Yqu",
}You can download our data either from huggingface (https://huggingface.co/datasets/causalnlp/CLadder), or cladder-v1.zip in our repo.
In our data, each sample represents a single question. Each question has the following fields:
-
question_id: a unique (for the file) identifier for the question -
desc_id: a more descriptive identifier for the question (generally not needed) -
given_info: natural language supplementary information that should be given to the model to answer the question. -
question: the question itself, in natural language -
answer: the answer to the question {yes, no} -
reasoning: a step-by-step explanation of the causal reasoning used to answer the question -
meta: metadata about the question, including the following fields:-
query_type: the type of question, one of {ATE, marginal, correlation, ETT, NDE, NIE, etc.} -
rung: the rung of the ladder of causation that the question corresponds to -
story_id: the id of the story used to verbalize the question -
graph_id: the id of the causal graph structure used to verbalize the question -
model_id: the id of the underlying model used to generate the question (corresponding to a model incladder-v1-meta-models.json) -
groundtruth: the groundtruth value of what the question is asking about
-
When evaluating a language model, it is recommended that the prompt includes 3 components:
- The
backgroundfield of the model corresponding to the question (found incladder-v1-meta-models.jsonusing themodel_idfield of the question's metadata). - The
given_infofield of the question. - The
questionfield of the question.
For example, the prompt corresponding to question 16825 (which asks about the average treatment effect for a simple instrumental variable setting) in cladder-v1-balanced.json could be:
Imagine a self-contained, hypothetical world with only the following conditions, and without any unmentioned factors or causal relationships: Unobserved confounders has a direct effect on education level and salary. Proximity to a college has a direct effect on education level. Education level has a direct effect on salary. Unobserved confounders is unobserved.
For people living far from a college, the probability of high salary is 35%. For people living close to a college, the probability of high salary is 53%. For people living far from a college, the probability of college degree or higher is 40%. For people living close to a college, the probability of college degree or higher is 73%.
Will college degree or higher decrease the chance of high salary?
Here the correct answer is no. The associated reasoning steps found in the reasoning field are:
Step 0: Let V2 = proximity to a college; V1 = unobserved confounders; X = education level; Y = salary.
Step 1: V1->X,V2->X,V1->Y,X->Y
Step 2: E[Y | do(X = 1)] - E[Y | do(X = 0)]
Step 3: [P(Y=1|V2=1)-P(Y=1|V2=0)]/[P(X=1|V2=1)-P(X=1|V2=0)]
Step 4: P(Y=1 | V2=0) = 0.35; P(Y=1 | V2=1) = 0.53; P(X=1 | V2=0) = 0.40; P(X=1 | V2=1) = 0.73
Step 5: (0.53 - 0.35) / (0.73 - 0.40) = 0.55
Solution: 0.55 > 0
Note that in addition to the background field, the model information found in cladder-v1-meta-models.json contains sufficient information to fully reconstruct the underlying causal model used to generate this question (and 59 others).
Here are some basic statistics for the main dataset (cladder-v1-balanced.json).
Number of questions: 10,112 Answers: {"yes": 5,056, "no": 5,056}
Query Types:
| Query Type | Rung | Code | Number | Percent |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Correlation | 1 | correlation | 1422 | 14.1% |
| Marginal Distribution | 1 | marginal | 1580 | 15.6% |
| Expaining Away Effect | 1 | exp_away | 158 | 1.6% |
| Average Treatment Effect | 2 | ate | 1422 | 14.1% |
| Backdoor Adjustment Set | 2 | backadj | 1580 | 15.6% |
| Collider Bias | 2 | collider_bias | 158 | 1.6% |
| Effect of the Treatment on the Treated | 3 | ett | 1264 | 12.5% |
| Natural Direct Effect | 3 | nde | 316 | 3.1% |
| Natural Indirect Effect | 3 | nie | 790 | 7.8% |
| Counterfactual (deterministic) | 3 | det-counterfactual | 1422 | 14.1% |
Graph Types:
| Graph Type | Number | Percent |
|---|---|---|
| IV | 790 | 7.8% |
| arrowhead | 1264 | 12.5% |
| chain | 1106 | 10.9% |
| collision | 632 | 6.2% |
| confounding | 948 | 9.4% |
| diamond | 1106 | 10.9% |
| diamondcut | 948 | 9.4% |
| fork | 948 | 9.4% |
| frontdoor | 1106 | 10.9% |
| mediation | 1264 | 12.5% |
If you want to dig a little deeper into understanding how well language models perform causal reasoning, we also include a few variants of the dataset (each of which contains about 10k questions, and the balanced dataset is made up of an even mix of these variants):
-
cladder-v1-aggregate.json: a combination of all the variants below but where each story has approximately the same number of questions (100-200). -
cladder-v1-q-easy.json: questions that are easy to answer (i.e. the causal mechanisms generally conform to what you would expect) -
cladder-v1-q-hard.json: the structure of the causal graph remains unchanged, but the strengths of causal mechanisms are generally counterintuitive -
cladder-v1-q-commonsense.json: an even mix of easy and hard questions -
cladder-v1-q-anticommonsense.json: for each causal graph we replace one of the variables (either treatment or outcome) with a randomly selected one that common sense would tell you is not related to the other variable at all. -
cladder-v1-q-nonsense.json: here the graph structure remains unchanged, but all variables are replaced from semantically meaningful concepts to randomly generated 4-letter words.
To use the codes in this repo, first clone this repo:
git clone https://github.com/causalNLP/causalbenchmark
cd causalbenchmark
Then, install the dependencies:
pip install -r requirements.txt
Finally, install the package:
pip install -e .
Check to make sure everything is setup correctly by running the unit tests:
pytest
Generate demo data using
fig generate demo
Checkout the corresponding config file here.
And the script which is implemented in generator.py - the function generate_and_store.
Also, you can run the unit tests with
pytest
Check the eval/ folder for all the run_*.py code files in to see how to run different LLMs in inference mode on our data.
We saved a copy of all model output files, which you can access here.
Thanks again for your interest in our work! Feel free to post a github issue if you have any questions.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for cladder
Similar Open Source Tools

cladder
CLadder is a repository containing the CLadder dataset for evaluating causal reasoning in language models. The dataset consists of yes/no questions in natural language that require statistical and causal inference to answer. It includes fields such as question_id, given_info, question, answer, reasoning, and metadata like query_type and rung. The dataset also provides prompts for evaluating language models and example questions with associated reasoning steps. Additionally, it offers dataset statistics, data variants, and code setup instructions for using the repository.
cambrian
Cambrian-1 is a fully open project focused on exploring multimodal Large Language Models (LLMs) with a vision-centric approach. It offers competitive performance across various benchmarks with models at different parameter levels. The project includes training configurations, model weights, instruction tuning data, and evaluation details. Users can interact with Cambrian-1 through a Gradio web interface for inference. The project is inspired by LLaVA and incorporates contributions from Vicuna, LLaMA, and Yi. Cambrian-1 is licensed under Apache 2.0 and utilizes datasets and checkpoints subject to their respective original licenses.
moatless-tools
Moatless Tools is a hobby project focused on experimenting with using Large Language Models (LLMs) to edit code in large existing codebases. The project aims to build tools that insert the right context into prompts and handle responses effectively. It utilizes an agentic loop functioning as a finite state machine to transition between states like Search, Identify, PlanToCode, ClarifyChange, and EditCode for code editing tasks.
AI-Toolbox
AI-Toolbox is a C++ library aimed at representing and solving common AI problems, with a focus on MDPs, POMDPs, and related algorithms. It provides an easy-to-use interface that is extensible to many problems while maintaining readable code. The toolbox includes tutorials for beginners in reinforcement learning and offers Python bindings for seamless integration. It features utilities for combinatorics, polytopes, linear programming, sampling, distributions, statistics, belief updating, data structures, logging, seeding, and more. Additionally, it supports bandit/normal games, single agent MDP/stochastic games, single agent POMDP, and factored/joint multi-agent scenarios.
TableLLM
TableLLM is a large language model designed for efficient tabular data manipulation tasks in real office scenarios. It can generate code solutions or direct text answers for tasks like insert, delete, update, query, merge, and chart operations on tables embedded in spreadsheets or documents. The model has been fine-tuned based on CodeLlama-7B and 13B, offering two scales: TableLLM-7B and TableLLM-13B. Evaluation results show its performance on benchmarks like WikiSQL, Spider, and self-created table operation benchmark. Users can use TableLLM for code and text generation tasks on tabular data.
DB-GPT-Hub
DB-GPT-Hub is an experimental project leveraging Large Language Models (LLMs) for Text-to-SQL parsing. It includes stages like data collection, preprocessing, model selection, construction, and fine-tuning of model weights. The project aims to enhance Text-to-SQL capabilities, reduce model training costs, and enable developers to contribute to improving Text-to-SQL accuracy. The ultimate goal is to achieve automated question-answering based on databases, allowing users to execute complex database queries using natural language descriptions. The project has successfully integrated multiple large models and established a comprehensive workflow for data processing, SFT model training, prediction output, and evaluation.
Cherry_LLM
Cherry Data Selection project introduces a self-guided methodology for LLMs to autonomously discern and select cherry samples from open-source datasets, minimizing manual curation and cost for instruction tuning. The project focuses on selecting impactful training samples ('cherry data') to enhance LLM instruction tuning by estimating instruction-following difficulty. The method involves phases like 'Learning from Brief Experience', 'Evaluating Based on Experience', and 'Retraining from Self-Guided Experience' to improve LLM performance.
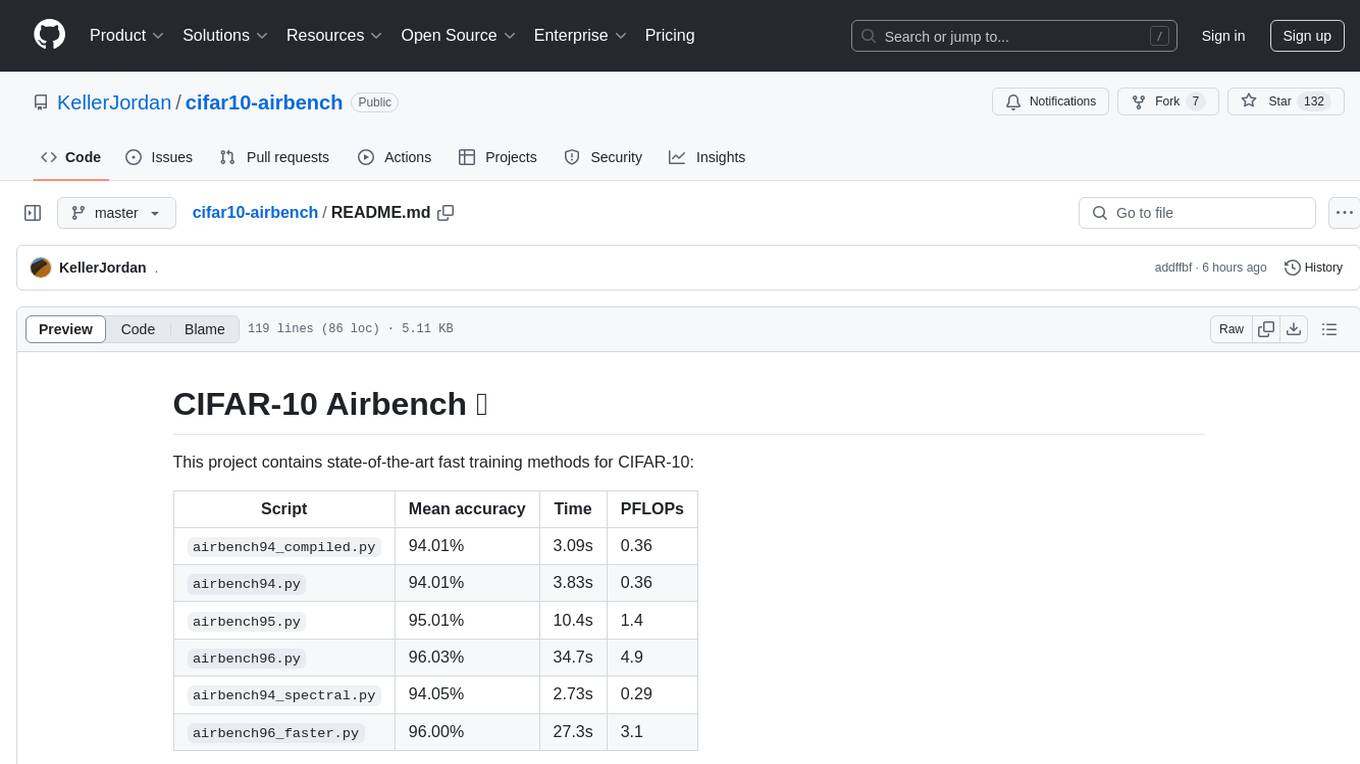
cifar10-airbench
CIFAR-10 Airbench is a project offering fast and stable training baselines for CIFAR-10 dataset, facilitating machine learning research. It provides easily runnable PyTorch scripts for training neural networks with high accuracy levels. The methods used in this project aim to accelerate research on fundamental properties of deep learning. The project includes GPU-accelerated dataloader for custom experiments and trainings, and can be used for data selection and active learning experiments. The training methods provided are faster than standard ResNet training, offering improved performance for research projects.
call-center-ai
Call Center AI is an AI-powered call center solution leveraging Azure and OpenAI GPT. It allows for AI agent-initiated phone calls or direct calls to the bot from a configured phone number. The bot is customizable for various industries like insurance, IT support, and customer service, with features such as accessing claim information, conversation history, language change, SMS sending, and more. The project is a proof of concept showcasing the integration of Azure Communication Services, Azure Cognitive Services, and Azure OpenAI for an automated call center solution.
AQLM
AQLM is the official PyTorch implementation for Extreme Compression of Large Language Models via Additive Quantization. It includes prequantized AQLM models without PV-Tuning and PV-Tuned models for LLaMA, Mistral, and Mixtral families. The repository provides inference examples, model details, and quantization setups. Users can run prequantized models using Google Colab examples, work with different model families, and install the necessary inference library. The repository also offers detailed instructions for quantization, fine-tuning, and model evaluation. AQLM quantization involves calibrating models for compression, and users can improve model accuracy through finetuning. Additionally, the repository includes information on preparing models for inference and contributing guidelines.
pytorch-grad-cam
This repository provides advanced AI explainability for PyTorch, offering state-of-the-art methods for Explainable AI in computer vision. It includes a comprehensive collection of Pixel Attribution methods for various tasks like Classification, Object Detection, Semantic Segmentation, and more. The package supports high performance with full batch image support and includes metrics for evaluating and tuning explanations. Users can visualize and interpret model predictions, making it suitable for both production and model development scenarios.
basiclingua-LLM-Based-NLP
BasicLingua is a Python library that provides functionalities for linguistic tasks such as tokenization, stemming, lemmatization, and many others. It is based on the Gemini Language Model, which has demonstrated promising results in dealing with text data. BasicLingua can be used as an API or through a web demo. It is available under the MIT license and can be used in various projects.

Qwen
Qwen is a series of large language models developed by Alibaba DAMO Academy. It outperforms the baseline models of similar model sizes on a series of benchmark datasets, e.g., MMLU, C-Eval, GSM8K, MATH, HumanEval, MBPP, BBH, etc., which evaluate the models’ capabilities on natural language understanding, mathematic problem solving, coding, etc. Qwen models outperform the baseline models of similar model sizes on a series of benchmark datasets, e.g., MMLU, C-Eval, GSM8K, MATH, HumanEval, MBPP, BBH, etc., which evaluate the models’ capabilities on natural language understanding, mathematic problem solving, coding, etc. Qwen-72B achieves better performance than LLaMA2-70B on all tasks and outperforms GPT-3.5 on 7 out of 10 tasks.
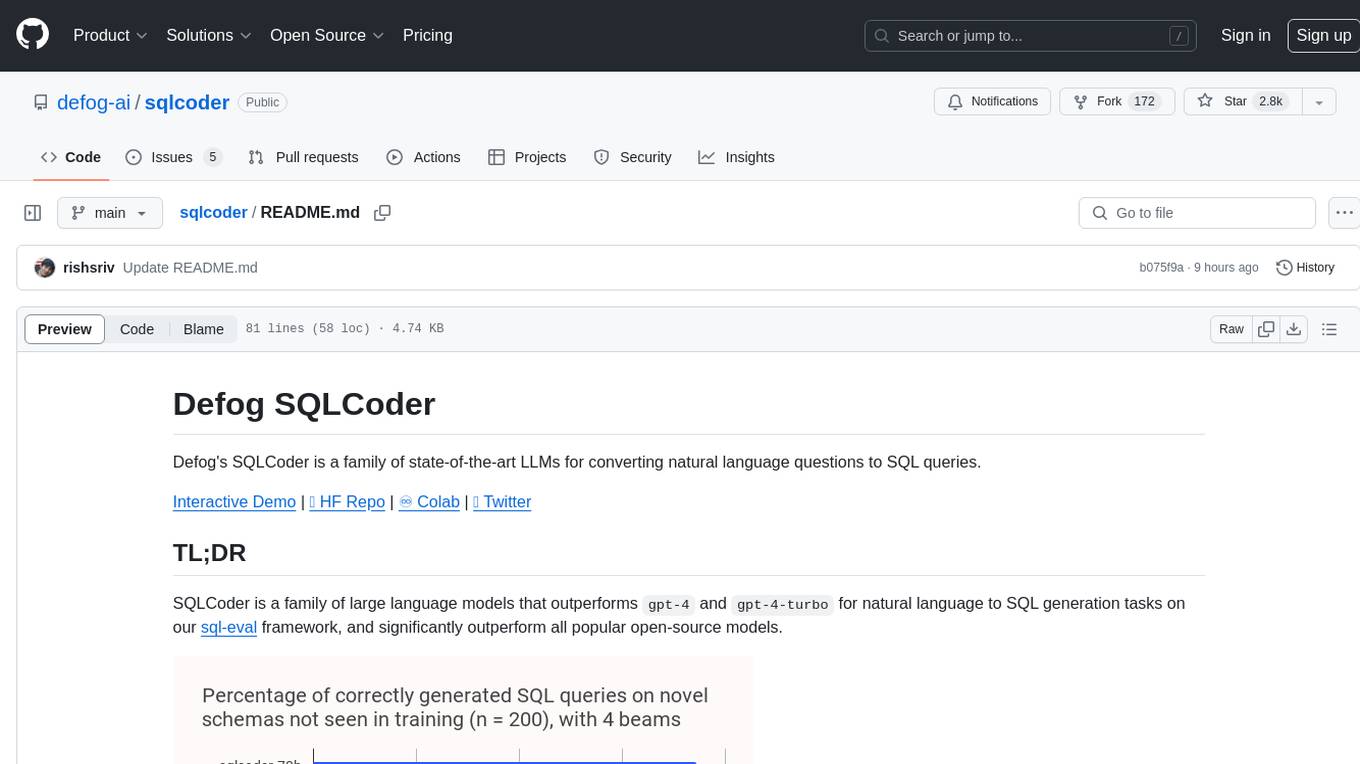
sqlcoder
Defog's SQLCoder is a family of state-of-the-art large language models (LLMs) designed for converting natural language questions into SQL queries. It outperforms popular open-source models like gpt-4 and gpt-4-turbo on SQL generation tasks. SQLCoder has been trained on more than 20,000 human-curated questions based on 10 different schemas, and the model weights are licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0. Users can interact with SQLCoder through the 'transformers' library and run queries using the 'sqlcoder launch' command in the terminal. The tool has been tested on NVIDIA GPUs with more than 16GB VRAM and Apple Silicon devices with some limitations. SQLCoder offers a demo on their website and supports quantized versions of the model for consumer GPUs with sufficient memory.
LLM-Pruner
LLM-Pruner is a tool for structural pruning of large language models, allowing task-agnostic compression while retaining multi-task solving ability. It supports automatic structural pruning of various LLMs with minimal human effort. The tool is efficient, requiring only 3 minutes for pruning and 3 hours for post-training. Supported LLMs include Llama-3.1, Llama-3, Llama-2, LLaMA, BLOOM, Vicuna, and Baichuan. Updates include support for new LLMs like GQA and BLOOM, as well as fine-tuning results achieving high accuracy. The tool provides step-by-step instructions for pruning, post-training, and evaluation, along with a Gradio interface for text generation. Limitations include issues with generating repetitive or nonsensical tokens in compressed models and manual operations for certain models.

llm_processes
This repository contains code for LLM Processes, which focuses on generating numerical predictive distributions conditioned on natural language. It supports various LLMs through Hugging Face transformer APIs and includes experiments on prompt engineering, 1D synthetic data, comparison to LLMTime, Fashion MNIST, black-box optimization, weather regression, in-context learning, and text conditioning. The code requires Python 3.9+, PyTorch 2.3.0+, and other dependencies for running experiments and reproducing results.
For similar tasks

cladder
CLadder is a repository containing the CLadder dataset for evaluating causal reasoning in language models. The dataset consists of yes/no questions in natural language that require statistical and causal inference to answer. It includes fields such as question_id, given_info, question, answer, reasoning, and metadata like query_type and rung. The dataset also provides prompts for evaluating language models and example questions with associated reasoning steps. Additionally, it offers dataset statistics, data variants, and code setup instructions for using the repository.
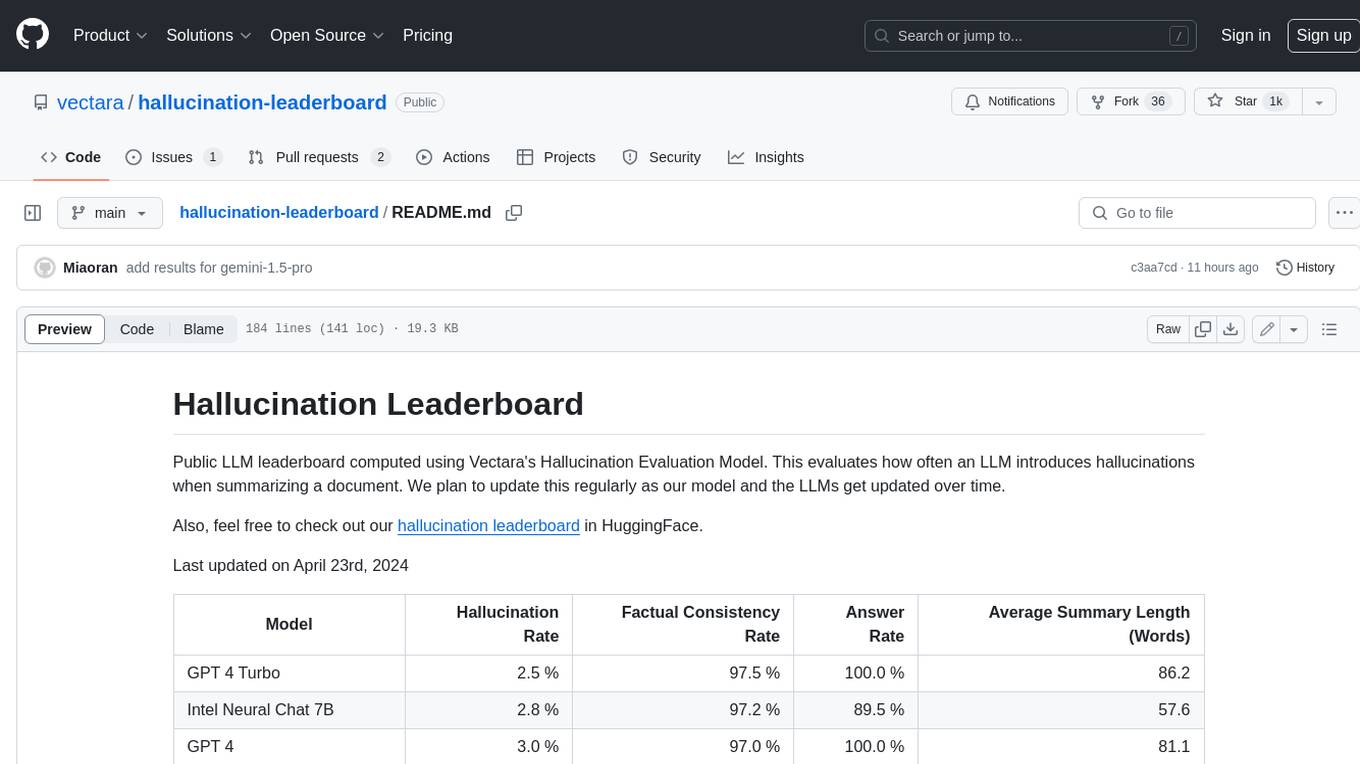
hallucination-leaderboard
This leaderboard evaluates the hallucination rate of various Large Language Models (LLMs) when summarizing documents. It uses a model trained by Vectara to detect hallucinations in LLM outputs. The leaderboard includes models from OpenAI, Anthropic, Google, Microsoft, Amazon, and others. The evaluation is based on 831 documents that were summarized by all the models. The leaderboard shows the hallucination rate, factual consistency rate, answer rate, and average summary length for each model.

h2o-llmstudio
H2O LLM Studio is a framework and no-code GUI designed for fine-tuning state-of-the-art large language models (LLMs). With H2O LLM Studio, you can easily and effectively fine-tune LLMs without the need for any coding experience. The GUI is specially designed for large language models, and you can finetune any LLM using a large variety of hyperparameters. You can also use recent finetuning techniques such as Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) and 8-bit model training with a low memory footprint. Additionally, you can use Reinforcement Learning (RL) to finetune your model (experimental), use advanced evaluation metrics to judge generated answers by the model, track and compare your model performance visually, and easily export your model to the Hugging Face Hub and share it with the community.
llm-jp-eval
LLM-jp-eval is a tool designed to automatically evaluate Japanese large language models across multiple datasets. It provides functionalities such as converting existing Japanese evaluation data to text generation task evaluation datasets, executing evaluations of large language models across multiple datasets, and generating instruction data (jaster) in the format of evaluation data prompts. Users can manage the evaluation settings through a config file and use Hydra to load them. The tool supports saving evaluation results and logs using wandb. Users can add new evaluation datasets by following specific steps and guidelines provided in the tool's documentation. It is important to note that using jaster for instruction tuning can lead to artificially high evaluation scores, so caution is advised when interpreting the results.
Awesome-LLM
Awesome-LLM is a curated list of resources related to large language models, focusing on papers, projects, frameworks, tools, tutorials, courses, opinions, and other useful resources in the field. It covers trending LLM projects, milestone papers, other papers, open LLM projects, LLM training frameworks, LLM evaluation frameworks, tools for deploying LLM, prompting libraries & tools, tutorials, courses, books, and opinions. The repository provides a comprehensive overview of the latest advancements and resources in the field of large language models.
bocoel
BoCoEL is a tool that leverages Bayesian Optimization to efficiently evaluate large language models by selecting a subset of the corpus for evaluation. It encodes individual entries into embeddings, uses Bayesian optimization to select queries, retrieves from the corpus, and provides easily managed evaluations. The tool aims to reduce computation costs during evaluation with a dynamic budget, supporting models like GPT2, Pythia, and LLAMA through integration with Hugging Face transformers and datasets. BoCoEL offers a modular design and efficient representation of the corpus to enhance evaluation quality.
uncheatable_eval
Uncheatable Eval is a tool designed to assess the language modeling capabilities of LLMs on real-time, newly generated data from the internet. It aims to provide a reliable evaluation method that is immune to data leaks and cannot be gamed. The tool supports the evaluation of Hugging Face AutoModelForCausalLM models and RWKV models by calculating the sum of negative log probabilities on new texts from various sources such as recent papers on arXiv, new projects on GitHub, news articles, and more. Uncheatable Eval ensures that the evaluation data is not included in the training sets of publicly released models, thus offering a fair assessment of the models' performance.
llms
The 'llms' repository is a comprehensive guide on Large Language Models (LLMs), covering topics such as language modeling, applications of LLMs, statistical language modeling, neural language models, conditional language models, evaluation methods, transformer-based language models, practical LLMs like GPT and BERT, prompt engineering, fine-tuning LLMs, retrieval augmented generation, AI agents, and LLMs for computer vision. The repository provides detailed explanations, examples, and tools for working with LLMs.
For similar jobs
prometheus-eval
Prometheus-Eval is a repository dedicated to evaluating large language models (LLMs) in generation tasks. It provides state-of-the-art language models like Prometheus 2 (7B & 8x7B) for assessing in pairwise ranking formats and achieving high correlation scores with benchmarks. The repository includes tools for training, evaluating, and using these models, along with scripts for fine-tuning on custom datasets. Prometheus aims to address issues like fairness, controllability, and affordability in evaluations by simulating human judgments and proprietary LM-based assessments.

cladder
CLadder is a repository containing the CLadder dataset for evaluating causal reasoning in language models. The dataset consists of yes/no questions in natural language that require statistical and causal inference to answer. It includes fields such as question_id, given_info, question, answer, reasoning, and metadata like query_type and rung. The dataset also provides prompts for evaluating language models and example questions with associated reasoning steps. Additionally, it offers dataset statistics, data variants, and code setup instructions for using the repository.
awesome-llm-unlearning
This repository tracks the latest research on machine unlearning in large language models (LLMs). It offers a comprehensive list of papers, datasets, and resources relevant to the topic.
COLD-Attack
COLD-Attack is a framework designed for controllable jailbreaks on large language models (LLMs). It formulates the controllable attack generation problem and utilizes the Energy-based Constrained Decoding with Langevin Dynamics (COLD) algorithm to automate the search of adversarial LLM attacks with control over fluency, stealthiness, sentiment, and left-right-coherence. The framework includes steps for energy function formulation, Langevin dynamics sampling, and decoding process to generate discrete text attacks. It offers diverse jailbreak scenarios such as fluent suffix attacks, paraphrase attacks, and attacks with left-right-coherence.
Awesome-LLM-in-Social-Science
Awesome-LLM-in-Social-Science is a repository that compiles papers evaluating Large Language Models (LLMs) from a social science perspective. It includes papers on evaluating, aligning, and simulating LLMs, as well as enhancing tools in social science research. The repository categorizes papers based on their focus on attitudes, opinions, values, personality, morality, and more. It aims to contribute to discussions on the potential and challenges of using LLMs in social science research.
awesome-llm-attributions
This repository focuses on unraveling the sources that large language models tap into for attribution or citation. It delves into the origins of facts, their utilization by the models, the efficacy of attribution methodologies, and challenges tied to ambiguous knowledge reservoirs, biases, and pitfalls of excessive attribution.
context-cite
ContextCite is a tool for attributing statements generated by LLMs back to specific parts of the context. It allows users to analyze and understand the sources of information used by language models in generating responses. By providing attributions, users can gain insights into how the model makes decisions and where the information comes from.
confabulations
LLM Confabulation Leaderboard evaluates large language models based on confabulations and non-response rates to challenging questions. It includes carefully curated questions with no answers in provided texts, aiming to differentiate between various models. The benchmark combines confabulation and non-response rates for comprehensive ranking, offering insights into model performance and tendencies. Additional notes highlight the meticulous human verification process, challenges faced by LLMs in generating valid responses, and the use of temperature settings. Updates and other benchmarks are also mentioned, providing a holistic view of the evaluation landscape.