
llama-zip
LLM-powered lossless compression tool
Stars: 158
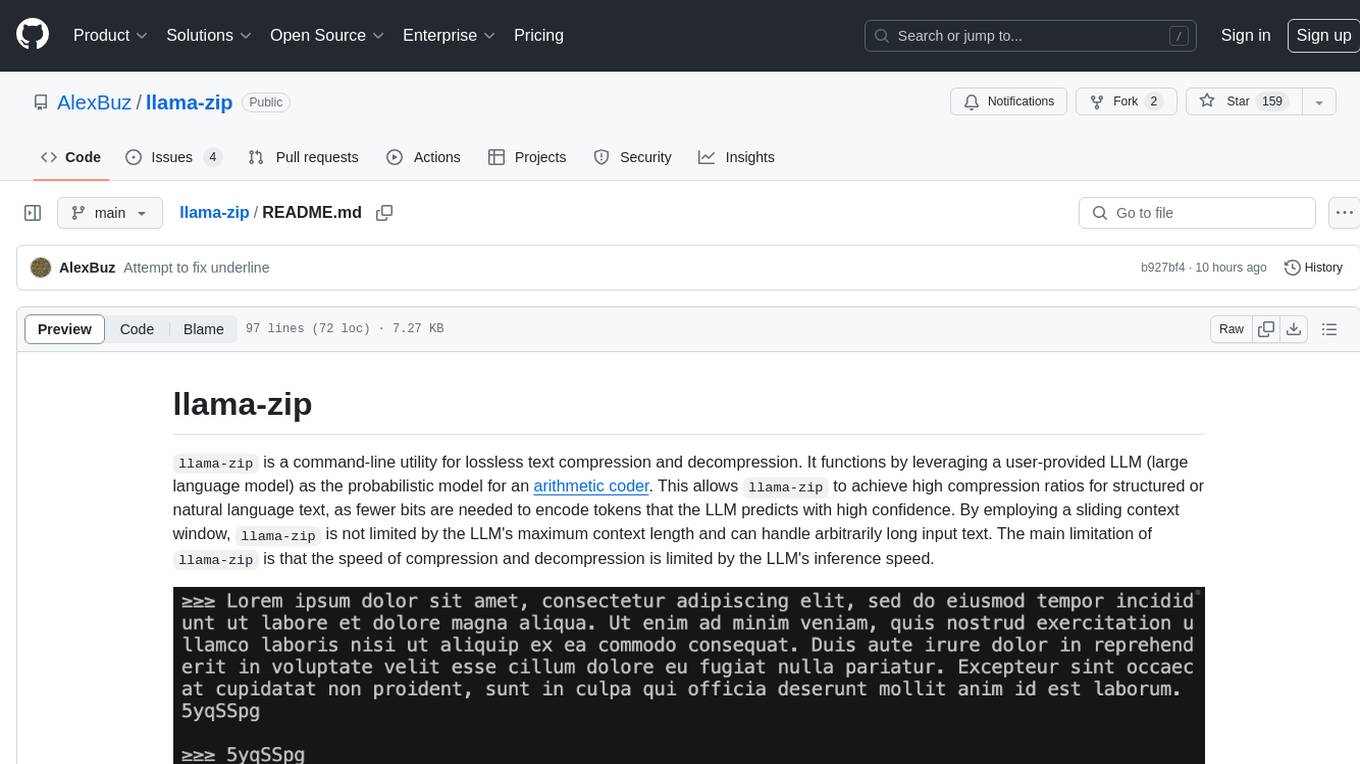
llama-zip is a command-line utility for lossless text compression and decompression. It leverages a user-provided large language model (LLM) as the probabilistic model for an arithmetic coder, achieving high compression ratios for structured or natural language text. The tool is not limited by the LLM's maximum context length and can handle arbitrarily long input text. However, the speed of compression and decompression is limited by the LLM's inference speed.
README:
llama-zip is a command-line utility for lossless text compression and decompression. It functions by leveraging a user-provided LLM (large language model) as the probabilistic model for an arithmetic coder. This allows llama-zip to achieve high compression ratios for structured or natural language text, as fewer bits are needed to encode tokens that the LLM predicts with high confidence. By employing a sliding context window, llama-zip is not limited by the LLM's maximum context length and can handle arbitrarily long input text. The main limitation of llama-zip is that the speed of compression and decompression is limited by the LLM's inference speed.
In the table below, the compression ratios achieved by llama-zip on the text files of the Calgary Corpus (as well as on llama-zip's own source code) are compared to other popular or high-performance compression utilities. Compression ratios are calculated by dividing the number of bytes in the input by the number of bytes in the output, so higher values indicate better compression. For llama-zip, the LLM used was Llama 3 8B (Q4_K_M) with a window overlap of 25%. For the other utilities, the maximum compression level was used.
| File | llama-zip | bzip2 | paq8pxd | xz | zpaq | zstd |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| bib | 8.523 | 4.051 | 5.590 | 3.636 | 4.611 | 3.485 |
| book1 | 6.943 | 3.305 | 4.204 | 2.941 | 3.823 | 2.904 |
| book2 | 8.127 | 3.880 | 5.325 | 3.596 | 4.649 | 3.514 |
| news | 5.590 | 3.180 | 4.494 | 3.171 | 3.817 | 3.073 |
| paper1 | 7.637 | 3.211 | 4.212 | 3.074 | 3.572 | 3.017 |
| paper2 | 8.375 | 3.283 | 4.135 | 3.015 | 3.679 | 2.982 |
| progc | 4.425 | 3.158 | 4.352 | 3.151 | 3.495 | 3.096 |
| progl | 5.194 | 4.599 | 7.347 | 4.787 | 5.554 | 4.728 |
| progp | 6.309 | 4.611 | 7.508 | 4.772 | 5.348 | 4.724 |
| trans | 9.810 | 5.235 | 8.409 | 5.613 | 6.597 | 5.417 |
| llama_zip.py | 5.859 | 3.508 | 4.689 | 3.552 | 3.018 | 3.633 |
The best-performing compressor for each file is listed in bold, and the second-best is underlined.
git clone https://github.com/alexbuz/llama-zip.git
cd llama-zip
pip3 install .To use llama-zip, you must first download an LLM that is compatible with llama.cpp, such as Llama 3 8B. Make sure to download a quantized version (one of the .gguf files listed on the "Files and versions" tab on Hugging Face) that is small enough to fit in your system's memory.
llama-zip <llm_path> [options] <mode> [input]
llama-zip supports three modes of operation:
-
Compress mode (specified by the
-cor--compressflag): The string to be compressed can be provided as an argument or piped to stdin. The compressed output will be encoded in base64 and printed to stdout. -
Decompress mode (specified by the
-dor--decompressflag): The compressed string can be provided as an argument or piped to stdin. The decompressed output will be printed to stdout. -
Interactive mode (specified by the
-ior--interactiveflag): A prompt is displayed where the user can enter strings to be compressed or decompressed. When a base64-encoded string is entered, it will be decompressed; otherwise, the entered string will be compressed. After each compression or decompression operation, the user is prompted to enter another string. To exit interactive mode, pressCtrl+C.-
Note: If you would like to compress a string that consists entirely of base64 characters (i.e., letters, numbers,
+, and/, without any other symbols or spaces), you must use compression mode directly, as interactive mode assumes that base64-encoded strings are meant to be decompressed and will result in nonsensical output if the input did not come from a compression operation. Alternatively, you can add a non-base64 character to your string (such as a space at the end) if you don't mind your string being compressed with that extra character.
-
Note: If you would like to compress a string that consists entirely of base64 characters (i.e., letters, numbers,
-
-w,--window-overlap: The number of tokens to overlap between the end of the previous context window and the start of the next window, when compressing a string whose length exceeds the LLM's maximum context length. This can be specified as a percentage of the LLM's context length or as a fixed number of tokens. The default is0%, meaning that the context window is cleared entirely when it is filled. Higher values can improve compression ratios but will slow down compression and decompression, since parts of the text will need to be re-evaluated when the context window slides. Note that when decompressing, the window overlap must be set to the same value that was used during compression in order to recover the original text. -
--n_gpu_layers: The--n_gpu_layersargument in the code specifies the number of layers in the model that should be offloaded to the GPU for computation. This can significantly speed up the processing time, especially for larger models, as the GPU is typically much faster at performing matrix operations than a CPU. If--n_gpu_layersis set to -1 or None, all layers of the model will be offloaded to the GPU. Check llama.cpp's readme for better understanding of this parameter.
-
Compressing a string:
llama-zip /path/to/Meta-Llama-3-8B.Q8_0.gguf -c "The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog." # Output: SxapgbY
-
Compressing text from a file:
llama-zip /path/to/Meta-Llama-3-8B.Q8_0.gguf -c < /path/to/gettysburg_address.txt # Output: 4vTMmKKTXWAcNZwPwkqN84
-
Compressing text from a file and saving the output to another file:
llama-zip /path/to/Meta-Llama-3-8B.Q8_0.gguf -c < /path/to/input.txt > /path/to/output.compressed
-
Decompressing a compressed string:
llama-zip /path/to/Meta-Llama-3-8B.Q8_0.gguf -d SxapgbY # Output: The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog. -
Decompressing text from a file:
llama-zip /path/to/Meta-Llama-3-8B.Q8_0.gguf -d < /path/to/input.compressed # Output: [decompressed text]
-
Decompressing text from a file and saving the output to another file:
llama-zip /path/to/Meta-Llama-3-8B.Q8_0.gguf -d < /path/to/input.compressed > /path/to/output.txt
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for llama-zip
Similar Open Source Tools

llama-zip
llama-zip is a command-line utility for lossless text compression and decompression. It leverages a user-provided large language model (LLM) as the probabilistic model for an arithmetic coder, achieving high compression ratios for structured or natural language text. The tool is not limited by the LLM's maximum context length and can handle arbitrarily long input text. However, the speed of compression and decompression is limited by the LLM's inference speed.
exllamav2
ExLlamaV2 is an inference library for running local LLMs on modern consumer GPUs. It is a faster, better, and more versatile codebase than its predecessor, ExLlamaV1, with support for a new quant format called EXL2. EXL2 is based on the same optimization method as GPTQ and supports 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and 8-bit quantization. It allows for mixing quantization levels within a model to achieve any average bitrate between 2 and 8 bits per weight. ExLlamaV2 can be installed from source, from a release with prebuilt extension, or from PyPI. It supports integration with TabbyAPI, ExUI, text-generation-webui, and lollms-webui. Key features of ExLlamaV2 include: - Faster and better kernels - Cleaner and more versatile codebase - Support for EXL2 quantization format - Integration with various web UIs and APIs - Community support on Discord
exllamav2
ExLlamaV2 is an inference library designed for running local LLMs on modern consumer GPUs. The library supports paged attention via Flash Attention 2.5.7+, offers a new dynamic generator with features like dynamic batching, smart prompt caching, and K/V cache deduplication. It also provides an API for local or remote inference using TabbyAPI, with extended features like HF model downloading and support for HF Jinja2 chat templates. ExLlamaV2 aims to optimize performance and speed across different GPU models, with potential future optimizations and variations in speeds. The tool can be integrated with TabbyAPI for OpenAI-style web API compatibility and supports a standalone web UI called ExUI for single-user interaction with chat and notebook modes. ExLlamaV2 also offers support for text-generation-webui and lollms-webui through specific loaders and bindings.
AQLM
AQLM is the official PyTorch implementation for Extreme Compression of Large Language Models via Additive Quantization. It includes prequantized AQLM models without PV-Tuning and PV-Tuned models for LLaMA, Mistral, and Mixtral families. The repository provides inference examples, model details, and quantization setups. Users can run prequantized models using Google Colab examples, work with different model families, and install the necessary inference library. The repository also offers detailed instructions for quantization, fine-tuning, and model evaluation. AQLM quantization involves calibrating models for compression, and users can improve model accuracy through finetuning. Additionally, the repository includes information on preparing models for inference and contributing guidelines.

Qwen
Qwen is a series of large language models developed by Alibaba DAMO Academy. It outperforms the baseline models of similar model sizes on a series of benchmark datasets, e.g., MMLU, C-Eval, GSM8K, MATH, HumanEval, MBPP, BBH, etc., which evaluate the models’ capabilities on natural language understanding, mathematic problem solving, coding, etc. Qwen models outperform the baseline models of similar model sizes on a series of benchmark datasets, e.g., MMLU, C-Eval, GSM8K, MATH, HumanEval, MBPP, BBH, etc., which evaluate the models’ capabilities on natural language understanding, mathematic problem solving, coding, etc. Qwen-72B achieves better performance than LLaMA2-70B on all tasks and outperforms GPT-3.5 on 7 out of 10 tasks.
cambrian
Cambrian-1 is a fully open project focused on exploring multimodal Large Language Models (LLMs) with a vision-centric approach. It offers competitive performance across various benchmarks with models at different parameter levels. The project includes training configurations, model weights, instruction tuning data, and evaluation details. Users can interact with Cambrian-1 through a Gradio web interface for inference. The project is inspired by LLaVA and incorporates contributions from Vicuna, LLaMA, and Yi. Cambrian-1 is licensed under Apache 2.0 and utilizes datasets and checkpoints subject to their respective original licenses.
thepipe
The Pipe is a multimodal-first tool for feeding files and web pages into vision-language models such as GPT-4V. It is best for LLM and RAG applications that require a deep understanding of tricky data sources. The Pipe is available as a hosted API at thepi.pe, or it can be set up locally.
text-embeddings-inference
Text Embeddings Inference (TEI) is a toolkit for deploying and serving open source text embeddings and sequence classification models. TEI enables high-performance extraction for popular models like FlagEmbedding, Ember, GTE, and E5. It implements features such as no model graph compilation step, Metal support for local execution on Macs, small docker images with fast boot times, token-based dynamic batching, optimized transformers code for inference using Flash Attention, Candle, and cuBLASLt, Safetensors weight loading, and production-ready features like distributed tracing with Open Telemetry and Prometheus metrics.
TPI-LLM
TPI-LLM (Tensor Parallelism Inference for Large Language Models) is a system designed to bring LLM functions to low-resource edge devices, addressing privacy concerns by enabling LLM inference on edge devices with limited resources. It leverages multiple edge devices for inference through tensor parallelism and a sliding window memory scheduler to minimize memory usage. TPI-LLM demonstrates significant improvements in TTFT and token latency compared to other models, and plans to support infinitely large models with low token latency in the future.
moatless-tools
Moatless Tools is a hobby project focused on experimenting with using Large Language Models (LLMs) to edit code in large existing codebases. The project aims to build tools that insert the right context into prompts and handle responses effectively. It utilizes an agentic loop functioning as a finite state machine to transition between states like Search, Identify, PlanToCode, ClarifyChange, and EditCode for code editing tasks.
wanda
Official PyTorch implementation of Wanda (Pruning by Weights and Activations), a simple and effective pruning approach for large language models. The pruning approach removes weights on a per-output basis, by the product of weight magnitudes and input activation norms. The repository provides support for various features such as LLaMA-2, ablation study on OBS weight update, zero-shot evaluation, and speedup evaluation. Users can replicate main results from the paper using provided bash commands. The tool aims to enhance the efficiency and performance of language models through structured and unstructured sparsity techniques.

skyvern
Skyvern automates browser-based workflows using LLMs and computer vision. It provides a simple API endpoint to fully automate manual workflows, replacing brittle or unreliable automation solutions. Traditional approaches to browser automations required writing custom scripts for websites, often relying on DOM parsing and XPath-based interactions which would break whenever the website layouts changed. Instead of only relying on code-defined XPath interactions, Skyvern adds computer vision and LLMs to the mix to parse items in the viewport in real-time, create a plan for interaction and interact with them. This approach gives us a few advantages: 1. Skyvern can operate on websites it’s never seen before, as it’s able to map visual elements to actions necessary to complete a workflow, without any customized code 2. Skyvern is resistant to website layout changes, as there are no pre-determined XPaths or other selectors our system is looking for while trying to navigate 3. Skyvern leverages LLMs to reason through interactions to ensure we can cover complex situations. Examples include: 1. If you wanted to get an auto insurance quote from Geico, the answer to a common question “Were you eligible to drive at 18?” could be inferred from the driver receiving their license at age 16 2. If you were doing competitor analysis, it’s understanding that an Arnold Palmer 22 oz can at 7/11 is almost definitely the same product as a 23 oz can at Gopuff (even though the sizes are slightly different, which could be a rounding error!) Want to see examples of Skyvern in action? Jump to #real-world-examples-of- skyvern
pgvecto.rs
pgvecto.rs is a Postgres extension written in Rust that provides vector similarity search functions. It offers ultra-low-latency, high-precision vector search capabilities, including sparse vector search and full-text search. With complete SQL support, async indexing, and easy data management, it simplifies data handling. The extension supports various data types like FP16/INT8, binary vectors, and Matryoshka embeddings. It ensures system performance with production-ready features, high availability, and resource efficiency. Security and permissions are managed through easy access control. The tool allows users to create tables with vector columns, insert vector data, and calculate distances between vectors using different operators. It also supports half-precision floating-point numbers for better performance and memory usage optimization.
Cherry_LLM
Cherry Data Selection project introduces a self-guided methodology for LLMs to autonomously discern and select cherry samples from open-source datasets, minimizing manual curation and cost for instruction tuning. The project focuses on selecting impactful training samples ('cherry data') to enhance LLM instruction tuning by estimating instruction-following difficulty. The method involves phases like 'Learning from Brief Experience', 'Evaluating Based on Experience', and 'Retraining from Self-Guided Experience' to improve LLM performance.
ai-dial-core
AI DIAL Core is an HTTP Proxy that provides a unified API to different chat completion and embedding models, assistants, and applications. It is written in Java 17 and built on Eclipse Vert.x. The core functionality includes handling static and dynamic settings, deployment on Kubernetes using Helm charts, and storing user data in Blob Storage and Redis. It supports various identity providers, storage providers like AWS S3, Google Cloud Storage, and Azure Blob Store, and features like AI DIAL Addons, Interceptors, Assistants, Applications, and Models with customizable parameters and configurations.
basiclingua-LLM-Based-NLP
BasicLingua is a Python library that provides functionalities for linguistic tasks such as tokenization, stemming, lemmatization, and many others. It is based on the Gemini Language Model, which has demonstrated promising results in dealing with text data. BasicLingua can be used as an API or through a web demo. It is available under the MIT license and can be used in various projects.
For similar tasks

llama-zip
llama-zip is a command-line utility for lossless text compression and decompression. It leverages a user-provided large language model (LLM) as the probabilistic model for an arithmetic coder, achieving high compression ratios for structured or natural language text. The tool is not limited by the LLM's maximum context length and can handle arbitrarily long input text. However, the speed of compression and decompression is limited by the LLM's inference speed.
zippy
ZipPy is a research repository focused on fast AI detection using compression techniques. It aims to provide a faster approximation for AI detection that is embeddable and scalable. The tool uses LZMA and zlib compression ratios to indirectly measure the perplexity of a text, allowing for the detection of low-perplexity text. By seeding a compression stream with AI-generated text and comparing the compression ratio of the seed data with the sample appended, ZipPy can identify similarities in word choice and structure to classify text as AI or human-generated.
For similar jobs

lollms-webui
LoLLMs WebUI (Lord of Large Language Multimodal Systems: One tool to rule them all) is a user-friendly interface to access and utilize various LLM (Large Language Models) and other AI models for a wide range of tasks. With over 500 AI expert conditionings across diverse domains and more than 2500 fine tuned models over multiple domains, LoLLMs WebUI provides an immediate resource for any problem, from car repair to coding assistance, legal matters, medical diagnosis, entertainment, and more. The easy-to-use UI with light and dark mode options, integration with GitHub repository, support for different personalities, and features like thumb up/down rating, copy, edit, and remove messages, local database storage, search, export, and delete multiple discussions, make LoLLMs WebUI a powerful and versatile tool.

Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement
The Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement repository provides packaged Industry Scenario DREAM Demos with ARM templates (Containing a demo web application, Power BI reports, Synapse resources, AML Notebooks etc.) that can be deployed in a customer’s subscription using the CAPE tool within a matter of few hours. Partners can also deploy DREAM Demos in their own subscriptions using DPoC.

minio
MinIO is a High Performance Object Storage released under GNU Affero General Public License v3.0. It is API compatible with Amazon S3 cloud storage service. Use MinIO to build high performance infrastructure for machine learning, analytics and application data workloads.

mage-ai
Mage is an open-source data pipeline tool for transforming and integrating data. It offers an easy developer experience, engineering best practices built-in, and data as a first-class citizen. Mage makes it easy to build, preview, and launch data pipelines, and provides observability and scaling capabilities. It supports data integrations, streaming pipelines, and dbt integration.

AiTreasureBox
AiTreasureBox is a versatile AI tool that provides a collection of pre-trained models and algorithms for various machine learning tasks. It simplifies the process of implementing AI solutions by offering ready-to-use components that can be easily integrated into projects. With AiTreasureBox, users can quickly prototype and deploy AI applications without the need for extensive knowledge in machine learning or deep learning. The tool covers a wide range of tasks such as image classification, text generation, sentiment analysis, object detection, and more. It is designed to be user-friendly and accessible to both beginners and experienced developers, making AI development more efficient and accessible to a wider audience.

tidb
TiDB is an open-source distributed SQL database that supports Hybrid Transactional and Analytical Processing (HTAP) workloads. It is MySQL compatible and features horizontal scalability, strong consistency, and high availability.

airbyte
Airbyte is an open-source data integration platform that makes it easy to move data from any source to any destination. With Airbyte, you can build and manage data pipelines without writing any code. Airbyte provides a library of pre-built connectors that make it easy to connect to popular data sources and destinations. You can also create your own connectors using Airbyte's no-code Connector Builder or low-code CDK. Airbyte is used by data engineers and analysts at companies of all sizes to build and manage their data pipelines.

labelbox-python
Labelbox is a data-centric AI platform for enterprises to develop, optimize, and use AI to solve problems and power new products and services. Enterprises use Labelbox to curate data, generate high-quality human feedback data for computer vision and LLMs, evaluate model performance, and automate tasks by combining AI and human-centric workflows. The academic & research community uses Labelbox for cutting-edge AI research.
