rag
🚀 Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) with txtai. Combine search and LLMs to find insights with your own data.
Stars: 349
RAG with txtai is a Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) Streamlit application that helps generate factually correct content by limiting the context in which a Large Language Model (LLM) can generate answers. It supports two categories of RAG: Vector RAG, where context is supplied via a vector search query, and Graph RAG, where context is supplied via a graph path traversal query. The application allows users to run queries, add data to the index, and configure various parameters to control its behavior.
README:
This project is a Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) Streamlit application backed by txtai.
Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) helps generate factually correct content by limiting the context in which a LLM can generate answers. This is typically done with a search query that hydrates a prompt with a relevant context.
This application supports two categories of RAG.
- Vector RAG: Context supplied via a vector search query
- Graph RAG: Context supplied via a graph path traversal query
The two primary ways to run this application are as a Docker container and with a Python virtual environment. Running through Docker is recommended, at least to get an idea of the application's capabilities.
neuml/rag is available on Docker Hub:
This can be run with the default settings as follows.
docker run -d --gpus=all -it -p 8501:8501 neuml/rag
The application can also be directly installed and run. It's recommended that this be run within a Python virtual environment.
pip install -r requirements.txt
Start the application.
streamlit run rag.py
The short video clip above gives a brief overview on this RAG system. It shows a basic vector RAG query. It also shows a Graph RAG query with uploaded data. The following sections cover more on these concepts.
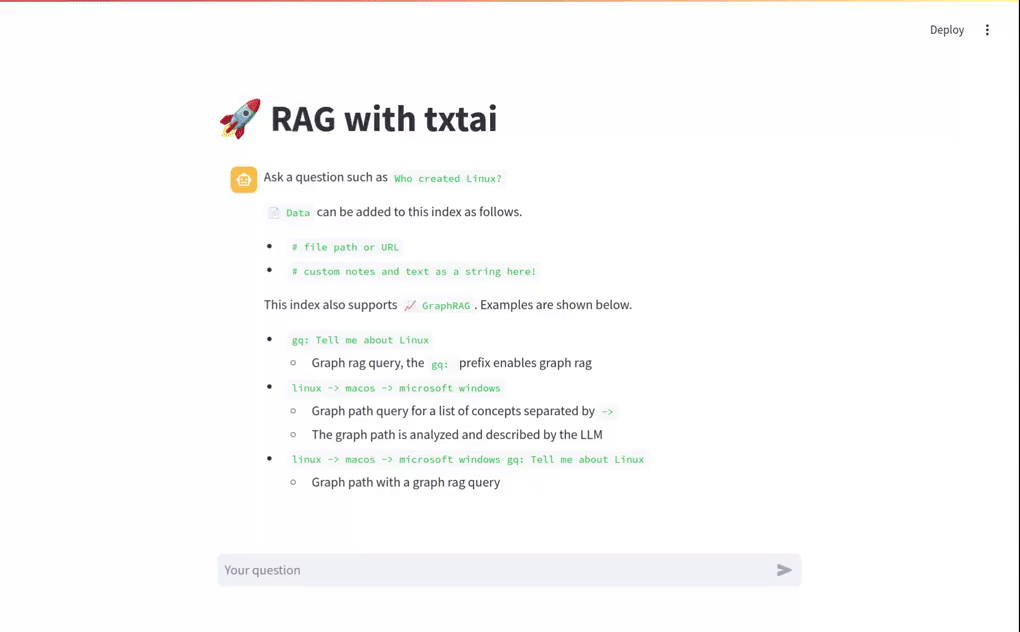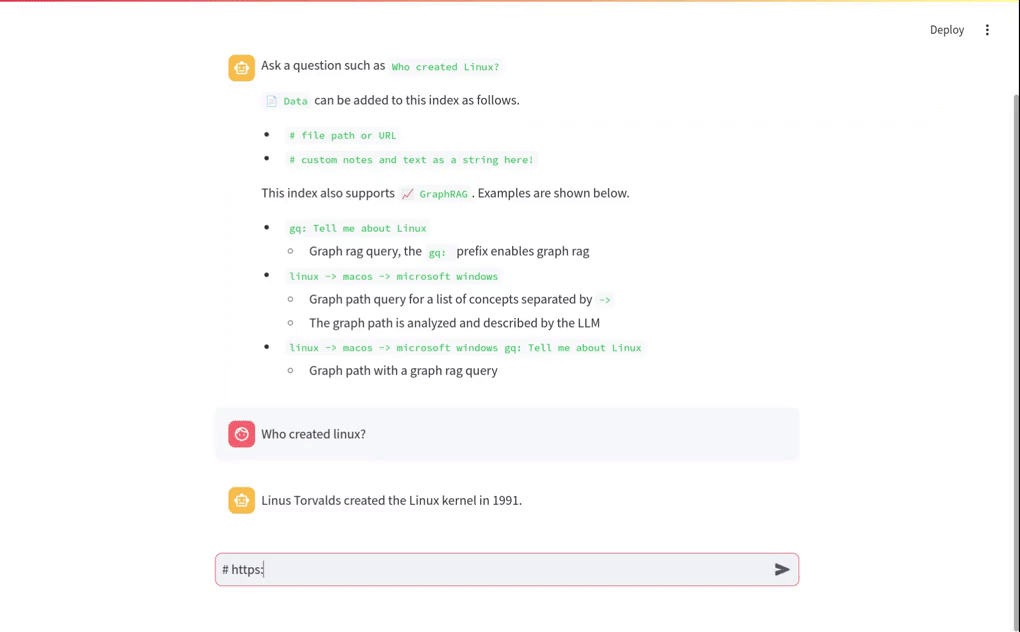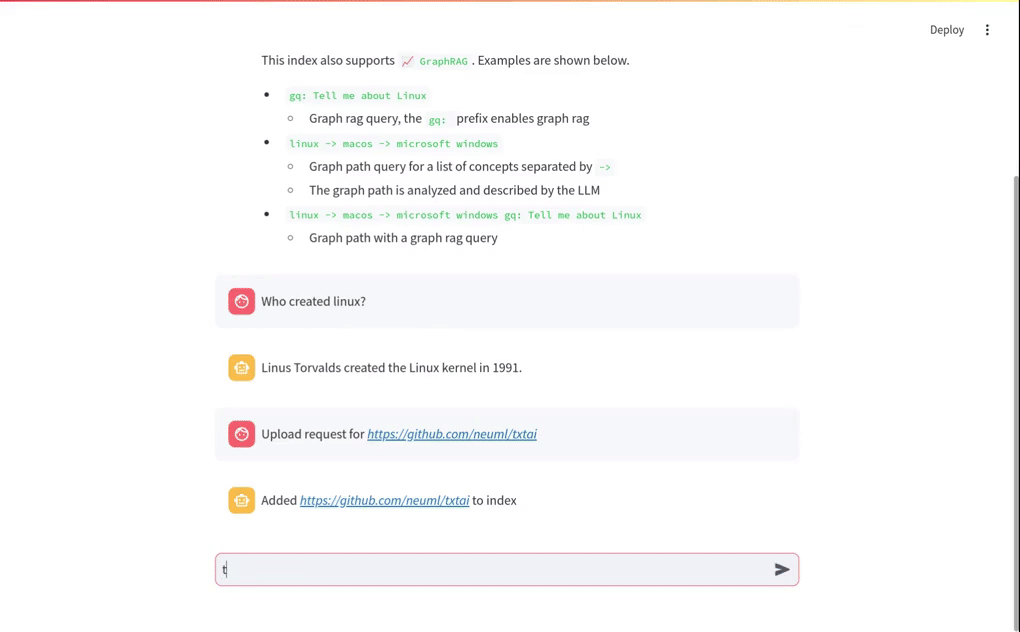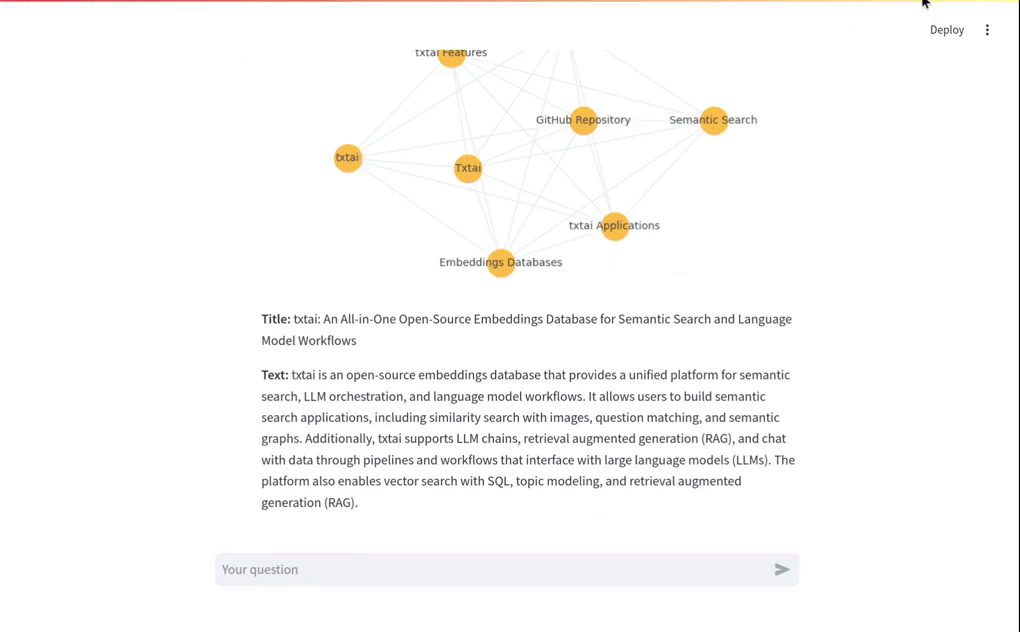
Traditional RAG or vector RAG runs a vector search to find the top N most relevant matches to a user's input. Those matches are passed to an LLM and the answer is returned.
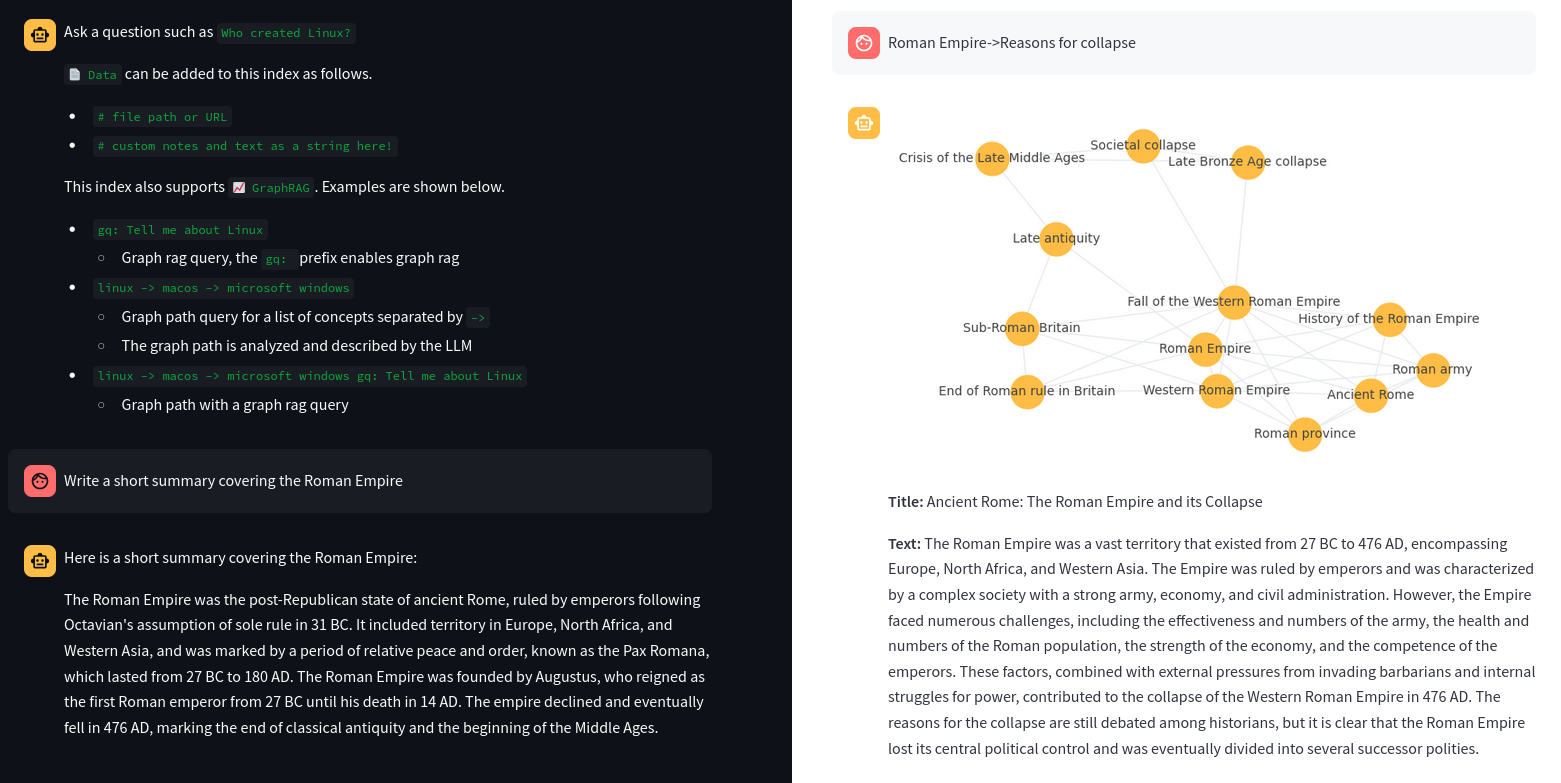
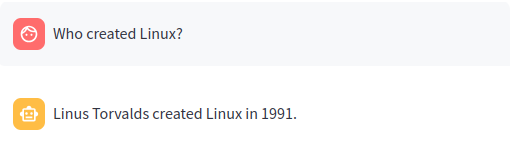
The query Who created Linux? runs a vector search for the best matching documents in the Embeddings index. Those matches are then placed into a LLM prompt. The LLM prompt is executed and the answer is returned.
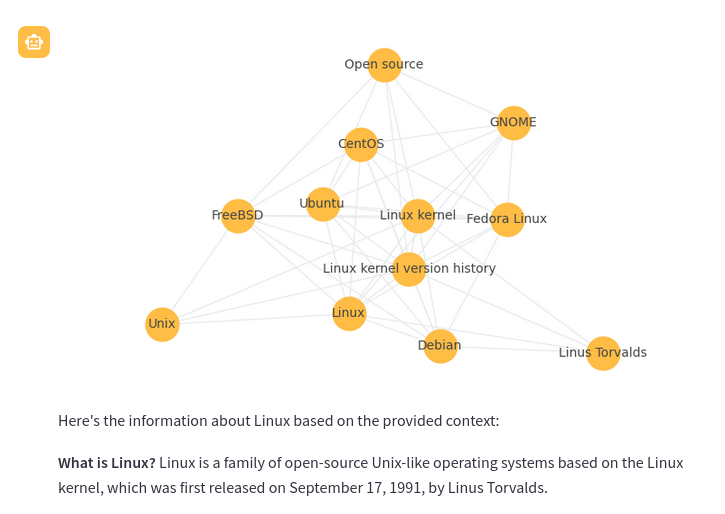
Graph RAG is a new method that uses knowledge or semantic graphs to generate a context. Instead of a vector search, graph path queries are run. Graph RAG in the context of this application supports the following methods to generate context.
-
Graph query with the
gq:prefix. This is a form of graph query expansion. It starts with a vector search to find the top n results. Those results are then expanded using a graph network stored alongside the vector database.gq: Tell me about Linux
-
Graph path query. This query takes a list of concepts and finds the nodes that match closest to those concepts. A graph path traversal then runs to build a context of nodes related to those concepts. The result of this traversal is passed to the LLM as the context.
linux -> macos -> microsoft windows
-
Combination of both. This first runs a graph path query then runs a graph query only within the context of that path traversal.
linux -> macos -> microsoft windows gq: Tell me about Linux
Every Graph RAG query response will also show a corresponding graph to help understand how the query works. Each node in the graph is a section (paragraph). The node nodes are generated with a LLM prompt that applies a topic label at upload time.
Regardless of whether the RAG application was a new Embeddings index or an existing one, additional data can be added.
Data can be added as follows.
| Method | |
|---|---|
# file path or URL |
 |
# custom notes and text as a string here! |
 |
When a query begins with a # the URL or file is read by the RAG application and loaded into the index. This method also supports loading text directly into the index. For example # txtai is an all-in-one embeddings database would create a new entry in the Embeddings database.
The RAG application has a number of environment variables that can be set to control how the application behaves.
| Variable | Description | Default Value |
|---|---|---|
| TITLE | Main title of the application | 🚀 RAG with txtai |
| EXAMPLES | List of queries separated by ;
|
Who created Linux? |
gq: Tell me about Linux |
||
linux -> macos -> microsoft windows |
||
linux -> macos -> microsoft windows gq: Tell me about Linux |
||
| LLM | Path to LLM | x86-64: Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct-AWQ-INT4 |
| arm64 : Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct-GGUF | ||
| EMBEDDINGS | Embeddings database path | neuml/txtai-wikipedia-slim |
| MAXLENGTH | Maximum generation length | 2048 for topics, 4096 for RAG |
| CONTEXT | RAG context size | 10 |
| TEXTBACKEND | Text extraction backend | available |
| DATA | Optional directory to index data from | None |
| PERSIST | Optional directory to save index updates to | None |
| TOPICSBATCH | Optional batch size for LLM topic queries | None |
Note: AWQ models are only supported on x86-64 machines
In the application, these settings can be shown by typing :settings.
See the following examples for setting this configuration with the Docker container. When running within a Python virtual environment, simply set these as environment variables.
docker run -d --gpus=all -it -p 8501:8501 -e LLM=hugging-quants/Meta-Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct-AWQ-INT4 neuml/rag
docker run -d --gpus=all -it -p 8501:8501 --add-host=host.docker.internal:host-gateway \
-e LLM=ollama/llama3.1:8b-instruct-q4_K_M -e OLLAMA_API_BASE=http://host.docker.internal:11434 \
neuml/rag
docker run -d --gpus=all -it -p 8501:8501 -e LLM=gpt-4o -e OPENAI_API_KEY=your-api-key neuml/rag
docker run -d --gpus=all -it -p 8501:8501 -e EMBEDDINGS=neuml/arxiv neuml/rag
docker run -d --gpus=all -it -p 8501:8501 -e EMBEDDINGS= neuml/rag
docker run -d --gpus=all -it -p 8501:8501 -e DATA=/data/path -v local/path:/data/path neuml/rag
docker run -d --gpus=all -it -p 8501:8501 -e TEXTBACKEND=docling neuml/rag
docker run -d --gpus=all -it -p 8501:8501 -e DATA=/data/path -e EMBEDDINGS=/data/embeddings \
-e PERSIST=/data/embeddings -e HF_HOME=/data/modelcache -v localdata:/data neuml/rag
See the documentation for the LLM pipeline and Embeddings for more information.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for rag
Similar Open Source Tools

rag
RAG with txtai is a Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) Streamlit application that helps generate factually correct content by limiting the context in which a Large Language Model (LLM) can generate answers. It supports two categories of RAG: Vector RAG, where context is supplied via a vector search query, and Graph RAG, where context is supplied via a graph path traversal query. The application allows users to run queries, add data to the index, and configure various parameters to control its behavior.
chatgpt-cli
ChatGPT CLI provides a powerful command-line interface for seamless interaction with ChatGPT models via OpenAI and Azure. It features streaming capabilities, extensive configuration options, and supports various modes like streaming, query, and interactive mode. Users can manage thread-based context, sliding window history, and provide custom context from any source. The CLI also offers model and thread listing, advanced configuration options, and supports GPT-4, GPT-3.5-turbo, and Perplexity's models. Installation is available via Homebrew or direct download, and users can configure settings through default values, a config.yaml file, or environment variables.
text-embeddings-inference
Text Embeddings Inference (TEI) is a toolkit for deploying and serving open source text embeddings and sequence classification models. TEI enables high-performance extraction for popular models like FlagEmbedding, Ember, GTE, and E5. It implements features such as no model graph compilation step, Metal support for local execution on Macs, small docker images with fast boot times, token-based dynamic batching, optimized transformers code for inference using Flash Attention, Candle, and cuBLASLt, Safetensors weight loading, and production-ready features like distributed tracing with Open Telemetry and Prometheus metrics.
mLoRA
mLoRA (Multi-LoRA Fine-Tune) is an open-source framework for efficient fine-tuning of multiple Large Language Models (LLMs) using LoRA and its variants. It allows concurrent fine-tuning of multiple LoRA adapters with a shared base model, efficient pipeline parallelism algorithm, support for various LoRA variant algorithms, and reinforcement learning preference alignment algorithms. mLoRA helps save computational and memory resources when training multiple adapters simultaneously, achieving high performance on consumer hardware.
maxtext
MaxText is a high-performance, highly scalable, open-source LLM written in pure Python/Jax and targeting Google Cloud TPUs and GPUs for training and inference. MaxText achieves high MFUs and scales from single host to very large clusters while staying simple and "optimization-free" thanks to the power of Jax and the XLA compiler. MaxText aims to be a launching off point for ambitious LLM projects both in research and production. We encourage users to start by experimenting with MaxText out of the box and then fork and modify MaxText to meet their needs.
moatless-tools
Moatless Tools is a hobby project focused on experimenting with using Large Language Models (LLMs) to edit code in large existing codebases. The project aims to build tools that insert the right context into prompts and handle responses effectively. It utilizes an agentic loop functioning as a finite state machine to transition between states like Search, Identify, PlanToCode, ClarifyChange, and EditCode for code editing tasks.
exllamav2
ExLlamaV2 is an inference library designed for running local LLMs on modern consumer GPUs. The library supports paged attention via Flash Attention 2.5.7+, offers a new dynamic generator with features like dynamic batching, smart prompt caching, and K/V cache deduplication. It also provides an API for local or remote inference using TabbyAPI, with extended features like HF model downloading and support for HF Jinja2 chat templates. ExLlamaV2 aims to optimize performance and speed across different GPU models, with potential future optimizations and variations in speeds. The tool can be integrated with TabbyAPI for OpenAI-style web API compatibility and supports a standalone web UI called ExUI for single-user interaction with chat and notebook modes. ExLlamaV2 also offers support for text-generation-webui and lollms-webui through specific loaders and bindings.
runpod-worker-comfy
runpod-worker-comfy is a serverless API tool that allows users to run any ComfyUI workflow to generate an image. Users can provide input images as base64-encoded strings, and the generated image can be returned as a base64-encoded string or uploaded to AWS S3. The tool is built on Ubuntu + NVIDIA CUDA and provides features like built-in checkpoints and VAE models. Users can configure environment variables to upload images to AWS S3 and interact with the RunPod API to generate images. The tool also supports local testing and deployment to Docker hub using Github Actions.
llm2sh
llm2sh is a command-line utility that leverages Large Language Models (LLMs) to translate plain-language requests into shell commands. It provides a convenient way to interact with your system using natural language. The tool supports multiple LLMs for command generation, offers a customizable configuration file, YOLO mode for running commands without confirmation, and is easily extensible with new LLMs and system prompts. Users can set up API keys for OpenAI, Claude, Groq, and Cerebras to use the tool effectively. llm2sh does not store user data or command history, and it does not record or send telemetry by itself, but the LLM APIs may collect and store requests and responses for their purposes.
co-llm
Co-LLM (Collaborative Language Models) is a tool for learning to decode collaboratively with multiple language models. It provides a method for data processing, training, and inference using a collaborative approach. The tool involves steps such as formatting/tokenization, scoring logits, initializing Z vector, deferral training, and generating results using multiple models. Co-LLM supports training with different collaboration pairs and provides baseline training scripts for various models. In inference, it uses 'vllm' services to orchestrate models and generate results through API-like services. The tool is inspired by allenai/open-instruct and aims to improve decoding performance through collaborative learning.
sql-eval
This repository contains the code that Defog uses for the evaluation of generated SQL. It's based off the schema from the Spider, but with a new set of hand-selected questions and queries grouped by query category. The testing procedure involves generating a SQL query, running both the 'gold' query and the generated query on their respective database to obtain dataframes with the results, comparing the dataframes using an 'exact' and a 'subset' match, logging these alongside other metrics of interest, and aggregating the results for reporting. The repository provides comprehensive instructions for installing dependencies, starting a Postgres instance, importing data into Postgres, importing data into Snowflake, using private data, implementing a query generator, and running the test with different runners.

skyvern
Skyvern automates browser-based workflows using LLMs and computer vision. It provides a simple API endpoint to fully automate manual workflows, replacing brittle or unreliable automation solutions. Traditional approaches to browser automations required writing custom scripts for websites, often relying on DOM parsing and XPath-based interactions which would break whenever the website layouts changed. Instead of only relying on code-defined XPath interactions, Skyvern adds computer vision and LLMs to the mix to parse items in the viewport in real-time, create a plan for interaction and interact with them. This approach gives us a few advantages: 1. Skyvern can operate on websites it’s never seen before, as it’s able to map visual elements to actions necessary to complete a workflow, without any customized code 2. Skyvern is resistant to website layout changes, as there are no pre-determined XPaths or other selectors our system is looking for while trying to navigate 3. Skyvern leverages LLMs to reason through interactions to ensure we can cover complex situations. Examples include: 1. If you wanted to get an auto insurance quote from Geico, the answer to a common question “Were you eligible to drive at 18?” could be inferred from the driver receiving their license at age 16 2. If you were doing competitor analysis, it’s understanding that an Arnold Palmer 22 oz can at 7/11 is almost definitely the same product as a 23 oz can at Gopuff (even though the sizes are slightly different, which could be a rounding error!) Want to see examples of Skyvern in action? Jump to #real-world-examples-of- skyvern
LEADS
LEADS is a lightweight embedded assisted driving system designed to simplify the development of instrumentation, control, and analysis systems for racing cars. It is written in Python and C/C++ with impressive performance. The system is customizable and provides abstract layers for component rearrangement. It supports hardware components like Raspberry Pi and Arduino, and can adapt to various hardware types. LEADS offers a modular structure with a focus on flexibility and lightweight design. It includes robust safety features, modern GUI design with dark mode support, high performance on different platforms, and powerful ESC systems for traction control and braking. The system also supports real-time data sharing, live video streaming, and AI-enhanced data analysis for driver training. LEADS VeC Remote Analyst enables transparency between the driver and pit crew, allowing real-time data sharing and analysis. The system is designed to be user-friendly, adaptable, and efficient for racing car development.
exllamav2
ExLlamaV2 is an inference library for running local LLMs on modern consumer GPUs. It is a faster, better, and more versatile codebase than its predecessor, ExLlamaV1, with support for a new quant format called EXL2. EXL2 is based on the same optimization method as GPTQ and supports 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and 8-bit quantization. It allows for mixing quantization levels within a model to achieve any average bitrate between 2 and 8 bits per weight. ExLlamaV2 can be installed from source, from a release with prebuilt extension, or from PyPI. It supports integration with TabbyAPI, ExUI, text-generation-webui, and lollms-webui. Key features of ExLlamaV2 include: - Faster and better kernels - Cleaner and more versatile codebase - Support for EXL2 quantization format - Integration with various web UIs and APIs - Community support on Discord

Trace
Trace is a new AutoDiff-like tool for training AI systems end-to-end with general feedback. It generalizes the back-propagation algorithm by capturing and propagating an AI system's execution trace. Implemented as a PyTorch-like Python library, users can write Python code directly and use Trace primitives to optimize certain parts, similar to training neural networks.
weblinx
WebLINX is a Python library and dataset for real-world website navigation with multi-turn dialogue. The repository provides code for training models reported in the WebLINX paper, along with a comprehensive API to work with the dataset. It includes modules for data processing, model evaluation, and utility functions. The modeling directory contains code for processing, training, and evaluating models such as DMR, LLaMA, MindAct, Pix2Act, and Flan-T5. Users can install specific dependencies for HTML processing, video processing, model evaluation, and library development. The evaluation module provides metrics and functions for evaluating models, with ongoing work to improve documentation and functionality.
For similar tasks
awadb
AwaDB is an AI native database designed for embedding vectors. It simplifies database usage by eliminating the need for schema definition and manual indexing. The system ensures real-time search capabilities with millisecond-level latency. Built on 5 years of production experience with Vearch, AwaDB incorporates best practices from the community to offer stability and efficiency. Users can easily add and search for embedded sentences using the provided client libraries or RESTful API.

rag
RAG with txtai is a Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) Streamlit application that helps generate factually correct content by limiting the context in which a Large Language Model (LLM) can generate answers. It supports two categories of RAG: Vector RAG, where context is supplied via a vector search query, and Graph RAG, where context is supplied via a graph path traversal query. The application allows users to run queries, add data to the index, and configure various parameters to control its behavior.
llm-compression-intelligence
This repository presents the findings of the paper "Compression Represents Intelligence Linearly". The study reveals a strong linear correlation between the intelligence of LLMs, as measured by benchmark scores, and their ability to compress external text corpora. Compression efficiency, derived from raw text corpora, serves as a reliable evaluation metric that is linearly associated with model capabilities. The repository includes the compression corpora used in the paper, code for computing compression efficiency, and data collection and processing pipelines.
edsl
The Expected Parrot Domain-Specific Language (EDSL) package enables users to conduct computational social science and market research with AI. It facilitates designing surveys and experiments, simulating responses using large language models, and performing data labeling and other research tasks. EDSL includes built-in methods for analyzing, visualizing, and sharing research results. It is compatible with Python 3.9 - 3.11 and requires API keys for LLMs stored in a `.env` file.
fast-stable-diffusion
Fast-stable-diffusion is a project that offers notebooks for RunPod, Paperspace, and Colab Pro adaptations with AUTOMATIC1111 Webui and Dreambooth. It provides tools for running and implementing Dreambooth, a stable diffusion project. The project includes implementations by XavierXiao and is sponsored by Runpod, Paperspace, and Colab Pro.

RobustVLM
This repository contains code for the paper 'Robust CLIP: Unsupervised Adversarial Fine-Tuning of Vision Embeddings for Robust Large Vision-Language Models'. It focuses on fine-tuning CLIP in an unsupervised manner to enhance its robustness against visual adversarial attacks. By replacing the vision encoder of large vision-language models with the fine-tuned CLIP models, it achieves state-of-the-art adversarial robustness on various vision-language tasks. The repository provides adversarially fine-tuned ViT-L/14 CLIP models and offers insights into zero-shot classification settings and clean accuracy improvements.
TempCompass
TempCompass is a benchmark designed to evaluate the temporal perception ability of Video LLMs. It encompasses a diverse set of temporal aspects and task formats to comprehensively assess the capability of Video LLMs in understanding videos. The benchmark includes conflicting videos to prevent models from relying on single-frame bias and language priors. Users can clone the repository, install required packages, prepare data, run inference using examples like Video-LLaVA and Gemini, and evaluate the performance of their models across different tasks such as Multi-Choice QA, Yes/No QA, Caption Matching, and Caption Generation.
LLM-LieDetector
This repository contains code for reproducing experiments on lie detection in black-box LLMs by asking unrelated questions. It includes Q/A datasets, prompts, and fine-tuning datasets for generating lies with language models. The lie detectors rely on asking binary 'elicitation questions' to diagnose whether the model has lied. The code covers generating lies from language models, training and testing lie detectors, and generalization experiments. It requires access to GPUs and OpenAI API calls for running experiments with open-source models. Results are stored in the repository for reproducibility.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.