
AgentBench
A Comprehensive Benchmark to Evaluate LLMs as Agents (ICLR'24)
Stars: 2061
AgentBench is a benchmark designed to evaluate Large Language Models (LLMs) as autonomous agents in various environments. It includes 8 distinct environments such as Operating System, Database, Knowledge Graph, Digital Card Game, and Lateral Thinking Puzzles. The tool provides a comprehensive evaluation of LLMs' ability to operate as agents by offering Dev and Test sets for each environment. Users can quickly start using the tool by following the provided steps, configuring the agent, starting task servers, and assigning tasks. AgentBench aims to bridge the gap between LLMs' proficiency as agents and their practical usability.
README:
🌐 Website | 🐦 Twitter | ✉️ Google Group | 📃 Paper
👋 Join our Slack for Q & A or collaboration on next version of AgentBench!
You are now browsing AgentBench v0.2. If you wish to use the older version, you can revert to v0.1.
Based on v0.1, we:
- Updated the framework architecture for easier use and extension
- Adjusted some task settings
- Added test results for more models
- Released the full data for the Dev and Test sets
https://github.com/THUDM/AgentBench/assets/129033897/656eed6e-d9d9-4d07-b568-f43f5a451f04
AgentBench is the first benchmark designed to evaluate LLM-as-Agent across a diverse spectrum of different environments. It encompasses 8 distinct environments to provide a more comprehensive evaluation of the LLMs' ability to operate as autonomous agents in various scenarios. These environments include 5 freshly created domains, namely
- Operating System (OS)
- Database (DB)
- Knowledge Graph (KG)
- Digital Card Game (DCG)
- Lateral Thinking Puzzles (LTP)
as well as 3 recompiled from published datasets:
We offer two splits for each dataset: Dev and Test. The multi-turn interaction requires an LLMs to generate around 4k and 13k times respectively.
Here is the scores on test set (standard) results of AgentBench.
While LLMs begin to manifest their proficiency in LLM-as-Agent, gaps between models and the distance towards practical usability are significant.
This section will guide you on how to quickly use gpt-3.5-turbo-0613 as an agent to launch the dbbench-std and os-std tasks.
For the specific framework structure, please refer to Framework Introduction.
For more detailed configuration and launch methods, please check Configuration Guide
and Program Entrance Guide.
Clone this repo and install the dependencies.
cd AgentBench
conda create -n agent-bench python=3.9
conda activate agent-bench
pip install -r requirements.txtEnsure that Docker is properly installed.
docker psBuild required images for dbbench-std and os-std.
docker pull mysql
docker pull ubuntu
docker build -f data/os_interaction/res/dockerfiles/default data/os_interaction/res/dockerfiles --tag local-os/default
docker build -f data/os_interaction/res/dockerfiles/packages data/os_interaction/res/dockerfiles --tag local-os/packages
docker build -f data/os_interaction/res/dockerfiles/ubuntu data/os_interaction/res/dockerfiles --tag local-os/ubuntuFill in your OpenAI API Key at the correct location in configs/agents/openai-chat.yaml. (e.g. gpt-3.5-turbo-0613)
You can try using python -m src.client.agent_test to check if your agent is configured correctly.
By default, gpt-3.5-turbo-0613 will be started. You can replace it with other agents by modifying the parameters:
python -m src.client.agent_test --config configs/agents/api_agents.yaml --agent gpt-3.5-turbo-0613Starting the task worker involves specific tasks. Manual starting might be cumbersome; hence, we provide an automated script.
The assumption for this step is that ports from 5000 to 5015 are available. For Mac OS system, you may want to follow here to free port 5000 to use.
python -m src.start_task -aThis will launch five task_workers each for dbbench-std and os-std tasks and automatically connect them
to the controller on port 5000. After executing this command, please allow approximately 1 minute for the task setup to complete. If the terminal shows ".... 200 OK", you can open another terminal and follow step 4.
This step is to actually start the tasks.
If everything is correctly configured so far, you can now initiate the task tests.
python -m src.assignerIf you wish to launch more tasks or use other models, you can refer to the content in Configuration Guide and Program Entrance Guide.
For the environment of the remaining five tasks, you will need to download the Docker images we provide.
longinyu/agentbench-ltp
longinyu/agentbench-webshop
longinyu/agentbench-mind2web
longinyu/agentbench-card_game
longinyu/agentbench-alfworld
The resource consumption of a single task_worker for the eight tasks is roughly as follows; consider this when launching:
| Task Name | Start-up Speed | Memory Consumption |
|---|---|---|
| webshop | ~3min | ~15G |
| mind2web | ~5min | ~1G |
| db | ~20s | < 500M |
| alfworld | ~10s | < 500M |
| card_game | ~5s | < 500M |
| ltp | ~5s | < 500M |
| os | ~5s | < 500M |
| kg | ~5s | < 500M |
the KnowledgeGraph task depends on an online service which now is not stable, if you want to deploy the service locally, you can follow steps below:
step1.
download the database and setup the service freebase-setup.
step2.
change this line sparql_url: "http://164.107.116.56:3093/sparql" to sparql_url: "<your service api of sparql>" in /configs/tasks/kg.yaml.
P.S. you should start your KG service before you start the agent tasks services.
If you wish to add new tasks to AgentBench, you may refer to Extension Guide.
Avalon task is merged from AvalonBench, which implements a multi-agent framework.
@article{liu2023agentbench,
title = {AgentBench: Evaluating LLMs as Agents},
author = {Xiao Liu and Hao Yu and Hanchen Zhang and Yifan Xu and Xuanyu Lei and Hanyu Lai and Yu Gu and Hangliang Ding and Kaiwen Men and Kejuan Yang and Shudan Zhang and Xiang Deng and Aohan Zeng and Zhengxiao Du and Chenhui Zhang and Sheng Shen and Tianjun Zhang and Yu Su and Huan Sun and Minlie Huang and Yuxiao Dong and Jie Tang},
year = {2023},
journal = {arXiv preprint arXiv: 2308.03688}
}
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for AgentBench
Similar Open Source Tools

AgentBench
AgentBench is a benchmark designed to evaluate Large Language Models (LLMs) as autonomous agents in various environments. It includes 8 distinct environments such as Operating System, Database, Knowledge Graph, Digital Card Game, and Lateral Thinking Puzzles. The tool provides a comprehensive evaluation of LLMs' ability to operate as agents by offering Dev and Test sets for each environment. Users can quickly start using the tool by following the provided steps, configuring the agent, starting task servers, and assigning tasks. AgentBench aims to bridge the gap between LLMs' proficiency as agents and their practical usability.
RD-Agent
RD-Agent is a tool designed to automate critical aspects of industrial R&D processes, focusing on data-driven scenarios to streamline model and data development. It aims to propose new ideas ('R') and implement them ('D') automatically, leading to solutions of significant industrial value. The tool supports scenarios like Automated Quantitative Trading, Data Mining Agent, Research Copilot, and more, with a framework to push the boundaries of research in data science. Users can create a Conda environment, install the RDAgent package from PyPI, configure GPT model, and run various applications for tasks like quantitative trading, model evolution, medical prediction, and more. The tool is intended to enhance R&D processes and boost productivity in industrial settings.
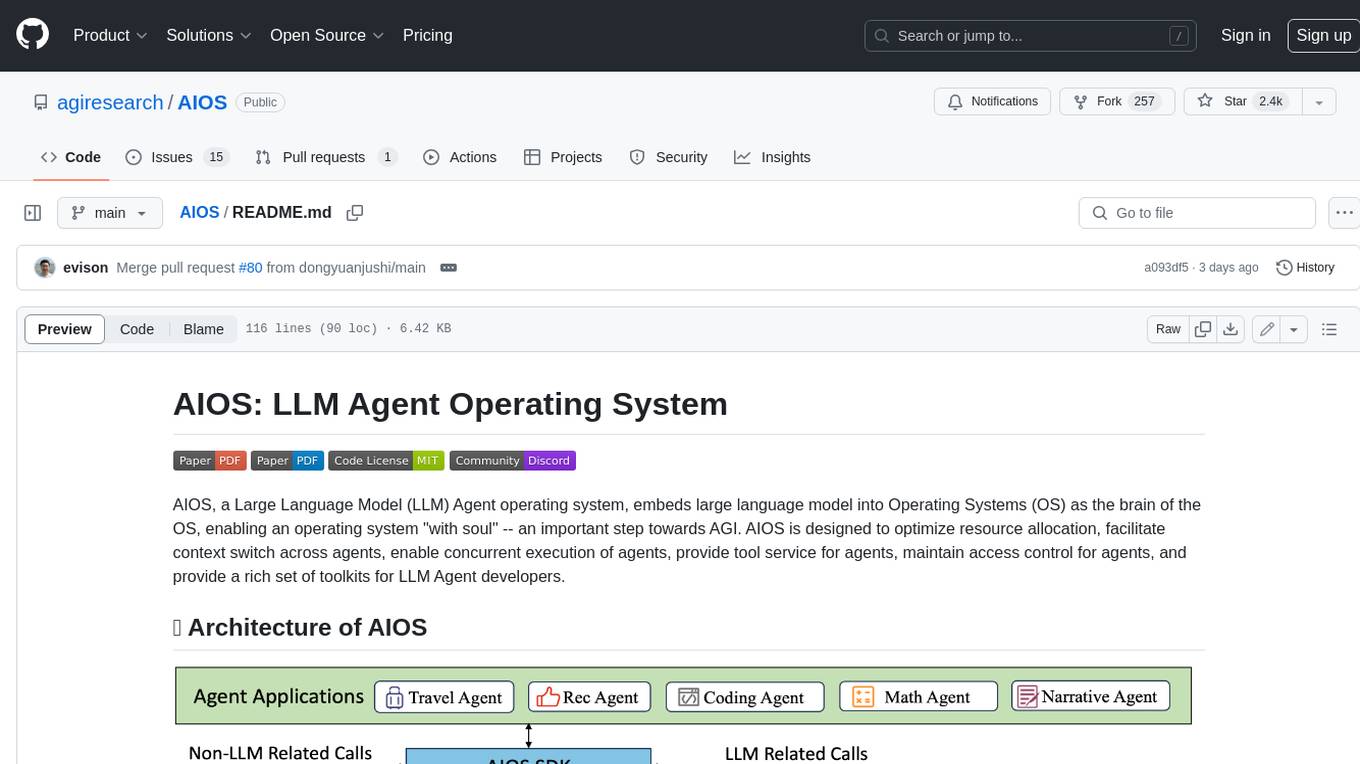
AIOS
AIOS, a Large Language Model (LLM) Agent operating system, embeds large language model into Operating Systems (OS) as the brain of the OS, enabling an operating system "with soul" -- an important step towards AGI. AIOS is designed to optimize resource allocation, facilitate context switch across agents, enable concurrent execution of agents, provide tool service for agents, maintain access control for agents, and provide a rich set of toolkits for LLM Agent developers.
TaskWeaver
TaskWeaver is a code-first agent framework designed for planning and executing data analytics tasks. It interprets user requests through code snippets, coordinates various plugins to execute tasks in a stateful manner, and preserves both chat history and code execution history. It supports rich data structures, customized algorithms, domain-specific knowledge incorporation, stateful execution, code verification, easy debugging, security considerations, and easy extension. TaskWeaver is easy to use with CLI and WebUI support, and it can be integrated as a library. It offers detailed documentation, demo examples, and citation guidelines.

helix-db
HelixDB is a database designed specifically for AI applications, providing a single platform to manage all components needed for AI applications. It supports graph + vector data model and also KV, documents, and relational data. Key features include built-in tools for MCP, embeddings, knowledge graphs, RAG, security, logical isolation, and ultra-low latency. Users can interact with HelixDB using the Helix CLI tool and SDKs in TypeScript and Python. The roadmap includes features like organizational auth, server code improvements, 3rd party integrations, educational content, and binary quantisation for better performance. Long term projects involve developing in-house tools for knowledge graph ingestion, graph-vector storage engine, and network protocol & serdes libraries.
evalverse
Evalverse is an open-source project designed to support Large Language Model (LLM) evaluation needs. It provides a standardized and user-friendly solution for processing and managing LLM evaluations, catering to AI research engineers and scientists. Evalverse supports various evaluation methods, insightful reports, and no-code evaluation processes. Users can access unified evaluation with submodules, request evaluations without code via Slack bot, and obtain comprehensive reports with scores, rankings, and visuals. The tool allows for easy comparison of scores across different models and swift addition of new evaluation tools.
TokenFormer
TokenFormer is a fully attention-based neural network architecture that leverages tokenized model parameters to enhance architectural flexibility. It aims to maximize the flexibility of neural networks by unifying token-token and token-parameter interactions through the attention mechanism. The architecture allows for incremental model scaling and has shown promising results in language modeling and visual modeling tasks. The codebase is clean, concise, easily readable, state-of-the-art, and relies on minimal dependencies.
RainbowGPT
RainbowGPT is a versatile tool that offers a range of functionalities, including Stock Analysis for financial decision-making, MySQL Management for database navigation, and integration of AI technologies like GPT-4 and ChatGlm3. It provides a user-friendly interface suitable for all skill levels, ensuring seamless information flow and continuous expansion of emerging technologies. The tool enhances adaptability, creativity, and insight, making it a valuable asset for various projects and tasks.
MetaGPT
MetaGPT is a multi-agent framework that enables GPT to work in a software company, collaborating to tackle more complex tasks. It assigns different roles to GPTs to form a collaborative entity for complex tasks. MetaGPT takes a one-line requirement as input and outputs user stories, competitive analysis, requirements, data structures, APIs, documents, etc. Internally, MetaGPT includes product managers, architects, project managers, and engineers. It provides the entire process of a software company along with carefully orchestrated SOPs. MetaGPT's core philosophy is "Code = SOP(Team)", materializing SOP and applying it to teams composed of LLMs.
arbigent
Arbigent (Arbiter-Agent) is an AI agent testing framework designed to make AI agent testing practical for modern applications. It addresses challenges faced by traditional UI testing frameworks and AI agents by breaking down complex tasks into smaller, dependent scenarios. The framework is customizable for various AI providers, operating systems, and form factors, empowering users with extensive customization capabilities. Arbigent offers an intuitive UI for scenario creation and a powerful code interface for seamless test execution. It supports multiple form factors, optimizes UI for AI interaction, and is cost-effective by utilizing models like GPT-4o mini. With a flexible code interface and open-source nature, Arbigent aims to revolutionize AI agent testing in modern applications.
FlexFlow
FlexFlow Serve is an open-source compiler and distributed system for **low latency**, **high performance** LLM serving. FlexFlow Serve outperforms existing systems by 1.3-2.0x for single-node, multi-GPU inference and by 1.4-2.4x for multi-node, multi-GPU inference.

axoned
Axone is a public dPoS layer 1 designed for connecting, sharing, and monetizing resources in the AI stack. It is an open network for collaborative AI workflow management compatible with any data, model, or infrastructure, allowing sharing of data, algorithms, storage, compute, APIs, both on-chain and off-chain. The 'axoned' node of the AXONE network is built on Cosmos SDK & Tendermint consensus, enabling companies & individuals to define on-chain rules, share off-chain resources, and create new applications. Validators secure the network by maintaining uptime and staking $AXONE for rewards. The blockchain supports various platforms and follows Semantic Versioning 2.0.0. A docker image is available for quick start, with documentation on querying networks, creating wallets, starting nodes, and joining networks. Development involves Go and Cosmos SDK, with smart contracts deployed on the AXONE blockchain. The project provides a Makefile for building, installing, linting, and testing. Community involvement is encouraged through Discord, open issues, and pull requests.
LLM-Pruner
LLM-Pruner is a tool for structural pruning of large language models, allowing task-agnostic compression while retaining multi-task solving ability. It supports automatic structural pruning of various LLMs with minimal human effort. The tool is efficient, requiring only 3 minutes for pruning and 3 hours for post-training. Supported LLMs include Llama-3.1, Llama-3, Llama-2, LLaMA, BLOOM, Vicuna, and Baichuan. Updates include support for new LLMs like GQA and BLOOM, as well as fine-tuning results achieving high accuracy. The tool provides step-by-step instructions for pruning, post-training, and evaluation, along with a Gradio interface for text generation. Limitations include issues with generating repetitive or nonsensical tokens in compressed models and manual operations for certain models.
LLamaSharp
LLamaSharp is a cross-platform library to run 🦙LLaMA/LLaVA model (and others) on your local device. Based on llama.cpp, inference with LLamaSharp is efficient on both CPU and GPU. With the higher-level APIs and RAG support, it's convenient to deploy LLM (Large Language Model) in your application with LLamaSharp.
basiclingua-LLM-Based-NLP
BasicLingua is a Python library that provides functionalities for linguistic tasks such as tokenization, stemming, lemmatization, and many others. It is based on the Gemini Language Model, which has demonstrated promising results in dealing with text data. BasicLingua can be used as an API or through a web demo. It is available under the MIT license and can be used in various projects.
deep-research
Deep Research is a lightning-fast tool that uses powerful AI models to generate comprehensive research reports in just a few minutes. It leverages advanced 'Thinking' and 'Task' models, combined with an internet connection, to provide fast and insightful analysis on various topics. The tool ensures privacy by processing and storing all data locally. It supports multi-platform deployment, offers support for various large language models, web search functionality, knowledge graph generation, research history preservation, local and server API support, PWA technology, multi-key payload support, multi-language support, and is built with modern technologies like Next.js and Shadcn UI. Deep Research is open-source under the MIT License.
For similar tasks

AgentBench
AgentBench is a benchmark designed to evaluate Large Language Models (LLMs) as autonomous agents in various environments. It includes 8 distinct environments such as Operating System, Database, Knowledge Graph, Digital Card Game, and Lateral Thinking Puzzles. The tool provides a comprehensive evaluation of LLMs' ability to operate as agents by offering Dev and Test sets for each environment. Users can quickly start using the tool by following the provided steps, configuring the agent, starting task servers, and assigning tasks. AgentBench aims to bridge the gap between LLMs' proficiency as agents and their practical usability.
fabrice-ai
A lightweight, functional, and composable framework for building AI agents that work together to solve complex tasks. Built with TypeScript and designed to be serverless-ready. Fabrice embraces functional programming principles, remains stateless, and stays focused on composability. It provides core concepts like easy teamwork creation, infrastructure-agnosticism, statelessness, and includes all tools and features needed to build AI teams. Agents are specialized workers with specific roles and capabilities, able to call tools and complete tasks. Workflows define how agents collaborate to achieve a goal, with workflow states representing the current state of the workflow. Providers handle requests to the LLM and responses. Tools extend agent capabilities by providing concrete actions they can perform. Execution involves running the workflow to completion, with options for custom execution and BDD testing.
flowdeer-dist
FlowDeer Tree is an AI tool designed for managing complex workflows and facilitating deep thoughts. It provides features such as displaying thinking chains, assigning tasks to AI members, utilizing task conclusions as context, copying and importing AI members in JSON format, adjusting node sequences, calling external APIs as plugins, and customizing default task splitting, execution, summarization, and output rewriting prompts. The tool aims to streamline workflow processes and enhance productivity by leveraging artificial intelligence capabilities.

EpicStaff
EpicStaff is a powerful project management tool designed to streamline team collaboration and task management. It provides a user-friendly interface for creating and assigning tasks, tracking progress, and communicating with team members in real-time. With features such as task prioritization, deadline reminders, and file sharing capabilities, EpicStaff helps teams stay organized and productive. Whether you're working on a small project or managing a large team, EpicStaff is the perfect solution to keep everyone on the same page and ensure project success.
AgentGPT
AgentGPT is a platform that allows users to configure and deploy autonomous AI agents. Users can name their own custom AI and set it on any goal. The AI will think of tasks, execute them, and learn from the results to reach the goal. The platform provides a demo experience, automatic setup CLI, and a tech stack including Next.js, FastAPI, Prisma, TailwindCSS, Zod, and more. AgentGPT is designed to help users easily create and deploy AI agents for various tasks.
vibe-kanban
Vibe Kanban is a tool designed to streamline the process of planning, reviewing, and orchestrating tasks for human engineers working with AI coding agents. It allows users to easily switch between different coding agents, orchestrate their execution, review work, start dev servers, and track task statuses. The tool centralizes the configuration of coding agent MCP configs, providing a comprehensive solution for managing coding tasks efficiently.
AgentUp
AgentUp is an active development tool that provides a developer-first agent framework for creating AI agents with enterprise-grade infrastructure. It allows developers to define agents with configuration, ensuring consistent behavior across environments. The tool offers secure design, configuration-driven architecture, extensible ecosystem for customizations, agent-to-agent discovery, asynchronous task architecture, deterministic routing, and MCP support. It supports multiple agent types like reactive agents and iterative agents, making it suitable for chatbots, interactive applications, research tasks, and more. AgentUp is built by experienced engineers from top tech companies and is designed to make AI agents production-ready, secure, and reliable.
agentpool
AgentPool is a unified agent orchestration hub that allows users to configure and manage heterogeneous AI agents via YAML and expose them through standardized protocols. It acts as a protocol bridge, enabling users to define all agents in one YAML file and expose them through ACP or AG-UI protocols. Users can coordinate, delegate, and communicate with different agents through a unified interface. The tool supports multi-agent coordination, rich YAML configuration, server protocols like ACP and OpenCode, and additional capabilities such as structured output, storage & analytics, file abstraction, triggers, and streaming TTS. It offers CLI and programmatic usage patterns for running agents and interacting with the tool.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.




