
open-unlearning
A unified, easily extensible repository for LLM unlearning benchmarks (TOFU, MUSE) - enabling new evaluations, methods, and tasks.
Stars: 130
OpenUnlearning is an easily extensible framework that unifies LLM unlearning evaluation benchmarks. It provides efficient implementations of TOFU and MUSE unlearning benchmarks, supporting 5 unlearning methods, 3+ datasets, 6+ evaluation metrics, and 7+ LLMs. Users can easily extend the framework to incorporate more variants, collaborate by adding new benchmarks, unlearning methods, datasets, and evaluation metrics, and drive progress in the field.
README:
We provide efficient and streamlined implementations of the TOFU, MUSE unlearning benchmarks while supporting 5 unlearning methods, 3+ datasets, 6+ evaluation metrics, and 7+ LLMs. Each of these can be easily extended to incorporate more variants.
We invite the LLM unlearning community to collaborate by adding new benchmarks, unlearning methods, datasets and evaluation metrics here to expand OpenUnlearning's features, gain feedback from wider usage and drive progress in the field.
⚠️ Notice (Updated: February 27, 2025)
This repository replaces the original TOFU codebase, which can be found atgithub.com/locuslab/tofuand isn't maintained anymore.
We provide several variants for each of the components in the unlearning pipeline.
| Component | Available Options |
|---|---|
| Benchmarks | TOFU, MUSE |
| Unlearning Methods | GradAscent, GradDiff, NPO, SimNPO, DPO |
| Evaluation Metrics | Verbatim Probability, Verbatim ROUGE, QA-ROUGE, MIA Attacks, TruthRatio, Model Utility |
| Datasets | MUSE-News (BBC), MUSE-Books (Harry Potter), TOFU (different splits) |
| Model Families | TOFU: LLaMA-3.2, LLaMA-3.1, LLaMA-2; MUSE: LLaMA-2, ICLM; Additional: Phi-3.5, Phi-1.5, Gemma |
- 📖 Overview
- 🗃️ Available Components
- ⚡ Quickstart
- 🔄 Updated TOFU benchmark
- 🧪 Running Experiments
- ➕ How to Add New Components
- 📚 Further Documentation
- 🔗 Support & Contributors
- 📝 Citing this work
- 🤝 Acknowledgements
- 📄 License
conda create -n unlearning python=3.11
conda activate unlearning
pip install .
pip install --no-build-isolation flash-attn==2.6.3Download the log files containing metric results from the models used in the supported benchmarks (including the retain model logs used to compare the unlearned models against).
python setup_data.py # populates saves/eval with evaluation results of the uploaded modelsWe've updated Open-Unlearning's TOFU benchmark target models to use a wider variety of newer architectures with sizes varying from 1B to 8B. These include LLaMA 3.2 1B, LLaMA 3.2 3B, LLaMA 3.1 8B, and the original LLaMA-2 7B from the old version of TOFU.
For each architecture, we have finetuned with four different splits of the TOFU datasets: full, retain90, retain95, retain99, for a total of 16 finetuned models. The first serves as the target (base model for unlearning) and the rest are retain models used to measure performance against for each forget split. These models are on HuggingFace and the paths to these models can be set in the experimental configs or in command-line overrides.
We provide an easily configurable interface for running evaluations by leveraging Hydra configs. For a more detailed documentation of aspects like running experiments, commonly overriden arguments, interfacing with configurations, distributed training and simple finetuning of models, refer docs/experiments.md.
An example command for launching an unlearning process with GradAscent on the TOFU forget10 split:
python src/train.py --config-name=unlearn.yaml experiment=unlearn/tofu/default \
forget_split=forget10 retain_split=retain90 trainer=GradAscent task_name=SAMPLE_UNLEARN-
experiment- Path to the Hydra config fileconfigs/experiment/unlearn/muse/default.yamlwith default experimental settings for TOFU unlearning, e.g. train dataset, eval benchmark details, model paths etc.. -
forget_split/retain_split- Sets the forget and retain dataset splits. -
trainer- Loadconfigs/trainer/GradAscent.yamland override the unlearning method with the handler (see config) implemented insrc/trainer/unlearn/grad_ascent.py.
An example command for launching a TOFU evaluation process on forget10 split:
python src/eval.py --config-name=eval.yaml experiment=eval/tofu/default \
model=Llama-3.2-1B-Instruct \
model.model_args.pretrained_model_name_or_path=open-unlearning/tofu_Llama-3.2-1B-Instruct_full \
task_name=SAMPLE_EVAL-
experiment- Path to the evaluation configurationconfigs/experiment/eval/tofu/default.yaml. -
model- Sets up the model and tokenizer configs for theLlama-3.2-1B-Instructmodel. -
model.model_args.pretrained_model_name_or_path- Overrides the default experiment config to evaluate a model from a HuggingFace ID (can use a local model checkpoint path as well).
For more details about creating and running evaluations, refer docs/evaluation.md.
The scripts below execute standard baseline unlearning experiments on the TOFU and MUSE datasets, evaluated using their corresponding benchmarks. The expected results for these are in docs/results.md.
bash scripts/tofu_unlearn.sh
bash scripts/muse_unlearn.shAdding a new component (trainer, evaluation metric, benchmark, model, or dataset) requires defining a new class, registering it, and creating a configuration file. Learn more about adding new components in docs/components.md.
Please feel free to raise a pull request for any new features after setting up the environment in development mode.
pip install .[dev]For more in-depth information on specific aspects of the framework, refer to the following documents:
| Documentation | Contains |
|---|---|
docs/components.md |
Instructions on how to add new components such as trainers, benchmarks, metrics, models, datasets, etc. |
docs/evaluation.md |
Detailed instructions on creating and running evaluation metrics and benchmarks. |
docs/experiments.md |
Guide on running experiments in various configurations and settings, including distributed training, fine-tuning, and overriding arguments. |
docs/hydra.md |
Explanation of the Hydra features used in configuration management for experiments. |
docs/results.md |
Reference results from various unlearning methods run using this framework on TOFU and MUSE benchmarks. |
Developed and maintained by Vineeth Dorna (@Dornavineeth) and Anmol Mekala (@molereddy).
If you encounter any issues or have questions, feel free to raise an issue in the repository 🛠️.
If you use OpenUnlearning in your research, please cite:
@misc{openunlearning2025,
title={OpenUnlearning: A Unified Framework for LLM Unlearning Benchmarks},
author={Dorna, Vineeth and Mekala, Anmol and Zhao, Wenlong and McCallum, Andrew and Kolter, J Zico and Maini, Pratyush},
year={2025},
howpublished={\url{https://github.com/locuslab/open-unlearning}},
note={Accessed: February 27, 2025}
}
@inproceedings{maini2024tofu,
title={TOFU: A Task of Fictitious Unlearning for LLMs},
author={Maini, Pratyush and Feng, Zhili and Schwarzschild, Avi and Lipton, Zachary Chase and Kolter, J Zico},
booktitle={First Conference on Language Modeling},
year={2024}
}Expand for bibtex to cite other benchmarks used from OpenUnlearning
@article{shi2024muse,
title={Muse: Machine unlearning six-way evaluation for language models},
author={Shi, Weijia and Lee, Jaechan and Huang, Yangsibo and Malladi, Sadhika and Zhao, Jieyu and Holtzman, Ari and Liu, Daogao and Zettlemoyer, Luke and Smith, Noah A and Zhang, Chiyuan},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2407.06460},
year={2024}
}- This repo is inspired from LLaMA-Factory.
- The TOFU and MUSE benchmarks served as the foundation for our re-implementation.
This project is licensed under the MIT License. See the LICENSE file for details.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for open-unlearning
Similar Open Source Tools

open-unlearning
OpenUnlearning is an easily extensible framework that unifies LLM unlearning evaluation benchmarks. It provides efficient implementations of TOFU and MUSE unlearning benchmarks, supporting 5 unlearning methods, 3+ datasets, 6+ evaluation metrics, and 7+ LLMs. Users can easily extend the framework to incorporate more variants, collaborate by adding new benchmarks, unlearning methods, datasets, and evaluation metrics, and drive progress in the field.
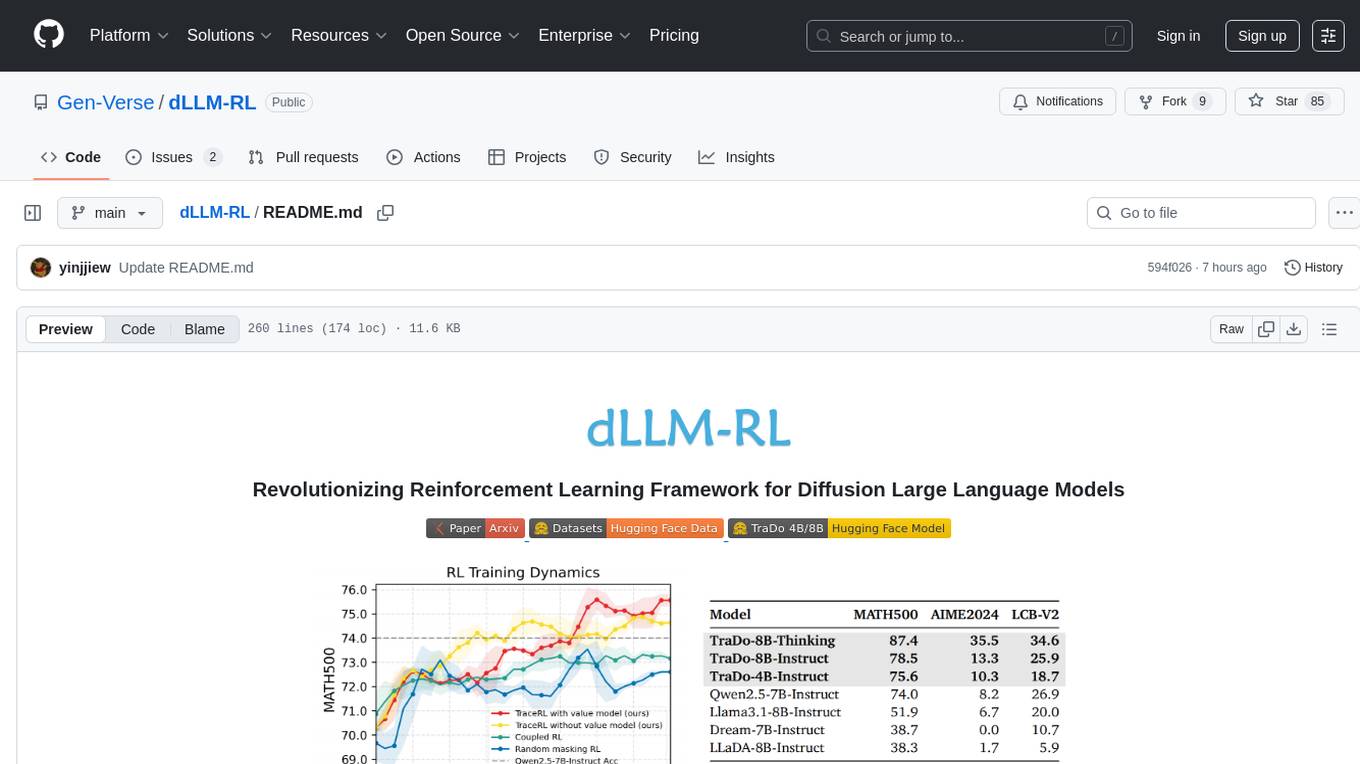
dLLM-RL
dLLM-RL is a revolutionary reinforcement learning framework designed for Diffusion Large Language Models. It supports various models with diverse structures, offers inference acceleration, RL training capabilities, and SFT functionalities. The tool introduces TraceRL for trajectory-aware RL and diffusion-based value models for optimization stability. Users can download and try models like TraDo-4B-Instruct and TraDo-8B-Instruct. The tool also provides support for multi-node setups and easy building of reinforcement learning methods. Additionally, it offers supervised fine-tuning strategies for different models and tasks.
LLMBox
LLMBox is a comprehensive library designed for implementing Large Language Models (LLMs) with a focus on a unified training pipeline and comprehensive model evaluation. It serves as a one-stop solution for training and utilizing LLMs, offering flexibility and efficiency in both training and utilization stages. The library supports diverse training strategies, comprehensive datasets, tokenizer vocabulary merging, data construction strategies, parameter efficient fine-tuning, and efficient training methods. For utilization, LLMBox provides comprehensive evaluation on various datasets, in-context learning strategies, chain-of-thought evaluation, evaluation methods, prefix caching for faster inference, support for specific LLM models like vLLM and Flash Attention, and quantization options. The tool is suitable for researchers and developers working with LLMs for natural language processing tasks.
atropos
Atropos is a robust and scalable framework for Reinforcement Learning Environments with Large Language Models (LLMs). It provides a flexible platform to accelerate LLM-based RL research across diverse interactive settings. Atropos supports multi-turn and asynchronous RL interactions, integrates with various inference APIs, offers a standardized training interface for experimenting with different RL algorithms, and allows for easy scalability by launching more environment instances. The framework manages diverse environment types concurrently for heterogeneous, multi-modal training.

Biomni
Biomni is a general-purpose biomedical AI agent designed to autonomously execute a wide range of research tasks across diverse biomedical subfields. By integrating cutting-edge large language model (LLM) reasoning with retrieval-augmented planning and code-based execution, Biomni helps scientists dramatically enhance research productivity and generate testable hypotheses.
evidently
Evidently is an open-source Python library designed for evaluating, testing, and monitoring machine learning (ML) and large language model (LLM) powered systems. It offers a wide range of functionalities, including working with tabular, text data, and embeddings, supporting predictive and generative systems, providing over 100 built-in metrics for data drift detection and LLM evaluation, allowing for custom metrics and tests, enabling both offline evaluations and live monitoring, and offering an open architecture for easy data export and integration with existing tools. Users can utilize Evidently for one-off evaluations using Reports or Test Suites in Python, or opt for real-time monitoring through the Dashboard service.

guidellm
GuideLLM is a platform for evaluating and optimizing the deployment of large language models (LLMs). By simulating real-world inference workloads, GuideLLM enables users to assess the performance, resource requirements, and cost implications of deploying LLMs on various hardware configurations. This approach ensures efficient, scalable, and cost-effective LLM inference serving while maintaining high service quality. The tool provides features for performance evaluation, resource optimization, cost estimation, and scalability testing.
labo
LABO is a time series forecasting and analysis framework that integrates pre-trained and fine-tuned LLMs with multi-domain agent-based systems. It allows users to create and tune agents easily for various scenarios, such as stock market trend prediction and web public opinion analysis. LABO requires a specific runtime environment setup, including system requirements, Python environment, dependency installations, and configurations. Users can fine-tune their own models using LABO's Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) for computational efficiency and continuous model updates. Additionally, LABO provides a Python library for building model training pipelines and customizing agents for specific tasks.
deep-research
Deep Research is a lightning-fast tool that uses powerful AI models to generate comprehensive research reports in just a few minutes. It leverages advanced 'Thinking' and 'Task' models, combined with an internet connection, to provide fast and insightful analysis on various topics. The tool ensures privacy by processing and storing all data locally. It supports multi-platform deployment, offers support for various large language models, web search functionality, knowledge graph generation, research history preservation, local and server API support, PWA technology, multi-key payload support, multi-language support, and is built with modern technologies like Next.js and Shadcn UI. Deep Research is open-source under the MIT License.

MInference
MInference is a tool designed to accelerate pre-filling for long-context Language Models (LLMs) by leveraging dynamic sparse attention. It achieves up to a 10x speedup for pre-filling on an A100 while maintaining accuracy. The tool supports various decoding LLMs, including LLaMA-style models and Phi models, and provides custom kernels for attention computation. MInference is useful for researchers and developers working with large-scale language models who aim to improve efficiency without compromising accuracy.
codellm-devkit
Codellm-devkit (CLDK) is a Python library that serves as a multilingual program analysis framework bridging traditional static analysis tools and Large Language Models (LLMs) specialized for code (CodeLLMs). It simplifies the process of analyzing codebases across multiple programming languages, enabling the extraction of meaningful insights and facilitating LLM-based code analysis. The library provides a unified interface for integrating outputs from various analysis tools and preparing them for effective use by CodeLLMs. Codellm-devkit aims to enable the development and experimentation of robust analysis pipelines that combine traditional program analysis tools and CodeLLMs, reducing friction in multi-language code analysis and ensuring compatibility across different tools and LLM platforms. It is designed to seamlessly integrate with popular analysis tools like WALA, Tree-sitter, LLVM, and CodeQL, acting as a crucial intermediary layer for efficient communication between these tools and CodeLLMs. The project is continuously evolving to include new tools and frameworks, maintaining its versatility for code analysis and LLM integration.

mlflow
MLflow is a platform to streamline machine learning development, including tracking experiments, packaging code into reproducible runs, and sharing and deploying models. MLflow offers a set of lightweight APIs that can be used with any existing machine learning application or library (TensorFlow, PyTorch, XGBoost, etc), wherever you currently run ML code (e.g. in notebooks, standalone applications or the cloud). MLflow's current components are:
* `MLflow Tracking
ProX
ProX is a lm-based data refinement framework that automates the process of cleaning and improving data used in pre-training large language models. It offers better performance, domain flexibility, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness compared to traditional methods. The framework has been shown to improve model performance by over 2% and boost accuracy by up to 20% in tasks like math. ProX is designed to refine data at scale without the need for manual adjustments, making it a valuable tool for data preprocessing in natural language processing tasks.
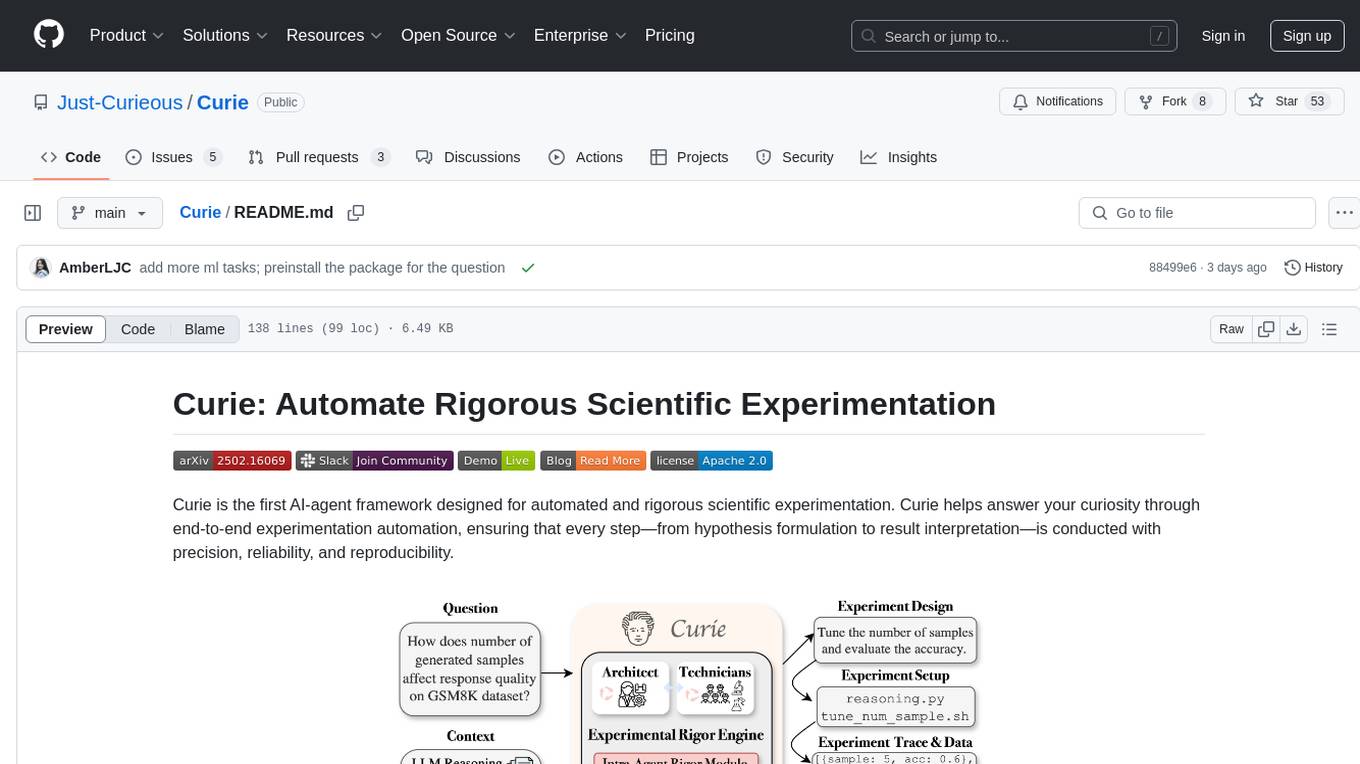
Curie
Curie is an AI-agent framework designed for automated and rigorous scientific experimentation. It automates end-to-end workflow management, ensures methodical procedure, reliability, and interpretability, and supports ML research, system analysis, and scientific discovery. It provides a benchmark with questions from 4 Computer Science domains. Users can customize experiment agents and adapt to their own tasks by configuring base_config.json. Curie is suitable for hyperparameter tuning, algorithm behavior analysis, system performance benchmarking, and automating computational simulations.
tinyllm
tinyllm is a lightweight framework designed for developing, debugging, and monitoring LLM and Agent powered applications at scale. It aims to simplify code while enabling users to create complex agents or LLM workflows in production. The core classes, Function and FunctionStream, standardize and control LLM, ToolStore, and relevant calls for scalable production use. It offers structured handling of function execution, including input/output validation, error handling, evaluation, and more, all while maintaining code readability. Users can create chains with prompts, LLM models, and evaluators in a single file without the need for extensive class definitions or spaghetti code. Additionally, tinyllm integrates with various libraries like Langfuse and provides tools for prompt engineering, observability, logging, and finite state machine design.

fuse-med-ml
FuseMedML is a Python framework designed to accelerate machine learning-based discovery in the medical field by promoting code reuse. It provides a flexible design concept where data is stored in a nested dictionary, allowing easy handling of multi-modality information. The framework includes components for creating custom models, loss functions, metrics, and data processing operators. Additionally, FuseMedML offers 'batteries included' key components such as fuse.data for data processing, fuse.eval for model evaluation, and fuse.dl for reusable deep learning components. It supports PyTorch and PyTorch Lightning libraries and encourages the creation of domain extensions for specific medical domains.
For similar tasks

open-unlearning
OpenUnlearning is an easily extensible framework that unifies LLM unlearning evaluation benchmarks. It provides efficient implementations of TOFU and MUSE unlearning benchmarks, supporting 5 unlearning methods, 3+ datasets, 6+ evaluation metrics, and 7+ LLMs. Users can easily extend the framework to incorporate more variants, collaborate by adding new benchmarks, unlearning methods, datasets, and evaluation metrics, and drive progress in the field.

labelbox-python
Labelbox is a data-centric AI platform for enterprises to develop, optimize, and use AI to solve problems and power new products and services. Enterprises use Labelbox to curate data, generate high-quality human feedback data for computer vision and LLMs, evaluate model performance, and automate tasks by combining AI and human-centric workflows. The academic & research community uses Labelbox for cutting-edge AI research.
promptfoo
Promptfoo is a tool for testing and evaluating LLM output quality. With promptfoo, you can build reliable prompts, models, and RAGs with benchmarks specific to your use-case, speed up evaluations with caching, concurrency, and live reloading, score outputs automatically by defining metrics, use as a CLI, library, or in CI/CD, and use OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure, Google, HuggingFace, open-source models like Llama, or integrate custom API providers for any LLM API.
vespa
Vespa is a platform that performs operations such as selecting a subset of data in a large corpus, evaluating machine-learned models over the selected data, organizing and aggregating it, and returning it, typically in less than 100 milliseconds, all while the data corpus is continuously changing. It has been in development for many years and is used on a number of large internet services and apps which serve hundreds of thousands of queries from Vespa per second.
python-aiplatform
The Vertex AI SDK for Python is a library that provides a convenient way to use the Vertex AI API. It offers a high-level interface for creating and managing Vertex AI resources, such as datasets, models, and endpoints. The SDK also provides support for training and deploying custom models, as well as using AutoML models. With the Vertex AI SDK for Python, you can quickly and easily build and deploy machine learning models on Vertex AI.
ScandEval
ScandEval is a framework for evaluating pretrained language models on mono- or multilingual language tasks. It provides a unified interface for benchmarking models on a variety of tasks, including sentiment analysis, question answering, and machine translation. ScandEval is designed to be easy to use and extensible, making it a valuable tool for researchers and practitioners alike.
opencompass
OpenCompass is a one-stop platform for large model evaluation, aiming to provide a fair, open, and reproducible benchmark for large model evaluation. Its main features include: * Comprehensive support for models and datasets: Pre-support for 20+ HuggingFace and API models, a model evaluation scheme of 70+ datasets with about 400,000 questions, comprehensively evaluating the capabilities of the models in five dimensions. * Efficient distributed evaluation: One line command to implement task division and distributed evaluation, completing the full evaluation of billion-scale models in just a few hours. * Diversified evaluation paradigms: Support for zero-shot, few-shot, and chain-of-thought evaluations, combined with standard or dialogue-type prompt templates, to easily stimulate the maximum performance of various models. * Modular design with high extensibility: Want to add new models or datasets, customize an advanced task division strategy, or even support a new cluster management system? Everything about OpenCompass can be easily expanded! * Experiment management and reporting mechanism: Use config files to fully record each experiment, and support real-time reporting of results.
flower
Flower is a framework for building federated learning systems. It is designed to be customizable, extensible, framework-agnostic, and understandable. Flower can be used with any machine learning framework, for example, PyTorch, TensorFlow, Hugging Face Transformers, PyTorch Lightning, scikit-learn, JAX, TFLite, MONAI, fastai, MLX, XGBoost, Pandas for federated analytics, or even raw NumPy for users who enjoy computing gradients by hand.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.


