
PDEBench
PDEBench: An Extensive Benchmark for Scientific Machine Learning
Stars: 793
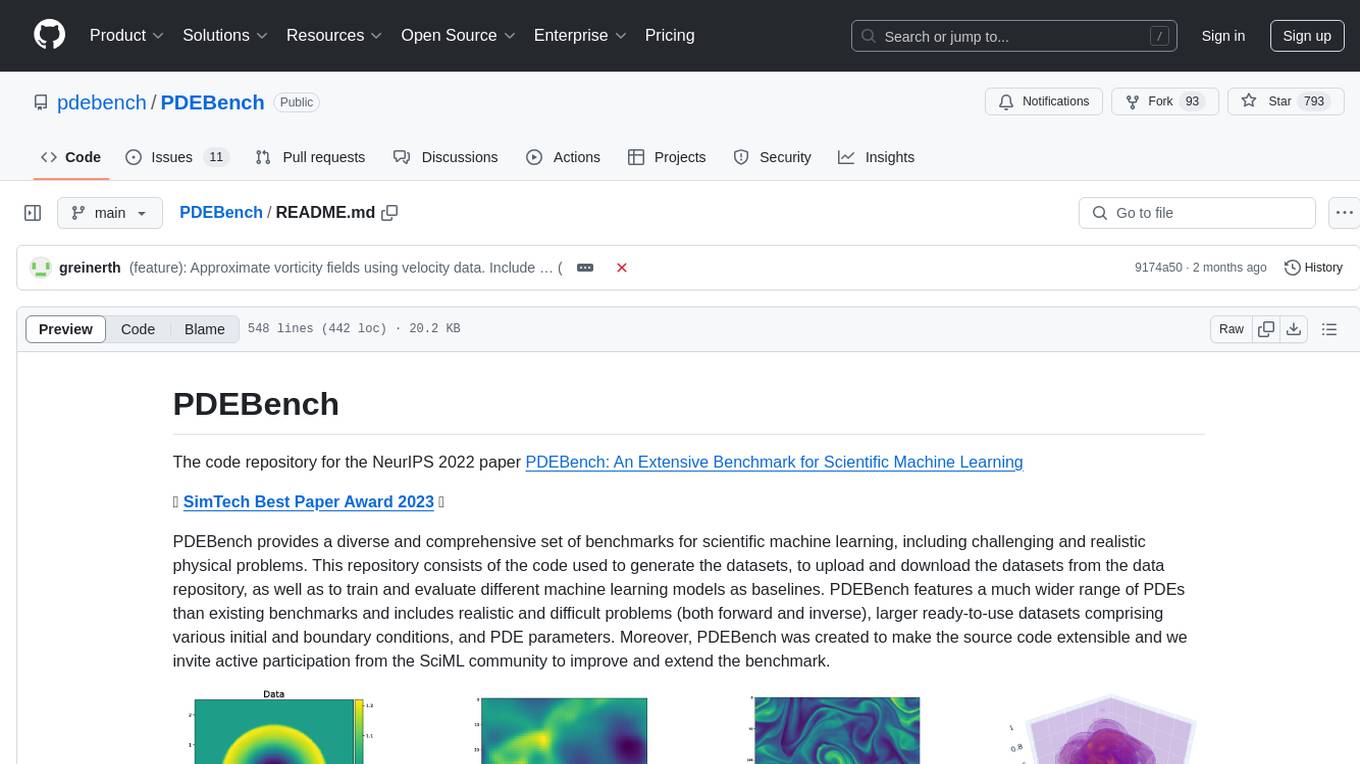
PDEBench provides a diverse and comprehensive set of benchmarks for scientific machine learning, including challenging and realistic physical problems. The repository consists of code for generating datasets, uploading and downloading datasets, training and evaluating machine learning models as baselines. It features a wide range of PDEs, realistic and difficult problems, ready-to-use datasets with various conditions and parameters. PDEBench aims for extensibility and invites participation from the SciML community to improve and extend the benchmark.
README:
The code repository for the NeurIPS 2022 paper PDEBench: An Extensive Benchmark for Scientific Machine Learning
🎉 SimTech Best Paper Award 2023 🎊
PDEBench provides a diverse and comprehensive set of benchmarks for scientific machine learning, including challenging and realistic physical problems. This repository consists of the code used to generate the datasets, to upload and download the datasets from the data repository, as well as to train and evaluate different machine learning models as baselines. PDEBench features a much wider range of PDEs than existing benchmarks and includes realistic and difficult problems (both forward and inverse), larger ready-to-use datasets comprising various initial and boundary conditions, and PDE parameters. Moreover, PDEBench was created to make the source code extensible and we invite active participation from the SciML community to improve and extend the benchmark.
Created and maintained by Makoto Takamoto
<[email protected], [email protected]>, Timothy Praditia
<[email protected]>, Raphael Leiteritz, Dan MacKinlay,
Francesco Alesiani, Dirk Pflüger, and Mathias Niepert.
We also provide datasets and pretrained machine learning models.
PDEBench Datasets: https://darus.uni-stuttgart.de/dataset.xhtml?persistentId=doi:10.18419/darus-2986
PDEBench Pre-Trained Models: https://darus.uni-stuttgart.de/dataset.xhtml?persistentId=doi:10.18419/darus-2987
DOIs
Locally:
pip install --upgrade pip wheel
pip install .From PyPI:
pip install pdebenchTo include dependencies for data generation:
pip install "pdebench[datagen310]"
pip install ".[datagen310]" # locallyor
pip install "pdebench[datagen39]"
pip install ".[datagen39]" # locallyFor GPU support there are additional platform-specific instructions:
For PyTorch, the latest version we support is v1.13.1 see previous-versions/#linux - CUDA 11.7.
For JAX, which is approximately 6 times faster for simulations than PyTorch in our tests, see jax#pip-installation-gpu-cuda-installed-via-pip
If you like you can also install dependencies using anaconda, we suggest to use mambaforge as a distribution. Otherwise you may have to enable the conda-forge channel for the following commands.
Starting from a fresh environment:
conda create -n myenv python=3.9
conda activate myenv
Install dependencies for model training:
conda install deepxde hydra-core h5py -c conda-forge
According to your hardware availability, either install PyTorch with CUDA support:
conda install pytorch==1.13.1 torchvision==0.14.1 torchaudio==0.13.1 pytorch-cuda=11.7 -c pytorch -c nvidia
conda install pytorch==1.13.1 torchvision==0.14.1 torchaudio==0.13.1 cpuonly -c pytorch
Optional dependencies for data generation:
conda install clawpack jax jaxlib python-dotenv
In our tests we used PyTorch as backend for DeepXDE. Please follow the documentation to enable this.
The data generation codes are contained in data_gen:
-
gen_diff_react.pyto generate the 2D diffusion-reaction data. -
gen_diff_sorp.pyto generate the 1D diffusion-sorption data. -
gen_radial_dam_break.pyto generate the 2D shallow-water data. -
gen_ns_incomp.pyto generate the 2D incompressible inhomogeneous Navier-Stokes data. -
plot.pyto plot the generated data. -
uploader.pyto upload the generated data to the data repository. -
.envis the environment data to store Dataverse URL and API token to upload the generated data. Note that the filename should be strictly.env(i.e. remove theexamplefrom the filename) -
configsdirectory contains the yaml files storing the configuration for the simulation. Arguments for the simulation are problem-specific and detailed explanation can be found in the simulation scripts. -
srcdirectory contains the simulation scripts for different problems:sim_diff_react-pyfor 2D diffusion-reaction,sim_diff_sorp.pyfor 1D diffusion-sorption, andswefor the shallow-water equation.
Data Generation for 1D Advection/Burgers/Reaction-Diffusion/2D DarcyFlow/Compressible Navier-Stokes Equations
The data generation codes are contained in data_gen_NLE:
-
utils.pyutil file for data generation, mainly boundary conditions and initial conditions. -
AdvectionEqdirectory with the source codes to generate 1D Advection equation training samples -
BurgersEqdirectory with the source codes to generate 1D Burgers equation training samples -
CompressibleFluiddirectory with the source codes to generate compressible Navier-Stokes equations training samples-
ReactionDiffusionEqdirectory with the source codes to generate 1D Reaction-Diffusion equation training samples (Note: DarcyFlow data can be generated by run_DarcyFlow2D.sh in this folder.)
-
-
savedirectory saving the generated training samples
A typical example to generate training samples (1D Advection Equation): (in
data_gen/data_gen_NLE/AdvectionEq/)
python3 advection_multi_solution_Hydra.py +multi=beta1e0.yamlwhich is assumed to be performed in each directory.
Examples for generating other PDEs are provided in run_trainset.sh in each
PDE's directories. The config files for Hydra are stored in config directory
in each PDE's directory.
1D Advection/Burgers/Reaction-Diffusion/2D DarcyFlow/Compressible Navier-Stokes
Equations save data as a numpy array. So, to read those data via our
dataloaders, the data transformation/merge should be performed. This can be done
using data_gen_NLE/Data_Merge.py whose config file is located at:
data_gen/data_gen_NLE/config/config.yaml. After properly setting the
parameters in the config file (type: name of PDEs, dim: number of
spatial-dimension, bd: boundary condition), the corresponding HDF5 file could be
obtained as:
python3 Data_Merge.pyYou can set the default values for data locations for this project by putting
config vars like this in the .env file:
WORKING_DIR=~/Data/Working
ARCHIVE_DATA_DIR=~/Data/Archive
There is an example in example.env.
The download scripts are provided in data_download. There are two options to download data.
- Using
download_direct.py(recommended)- Retrieves data shards directly using URLs. Sample command for each PDE is given in the README file in the data_download directory.
- Using
download_easydataverse.py(might be slow and you could encounter errors/issues; hence, not recommended!)- Use the config files from the
configdirectory that contains the yaml files storing the configuration. Any files in the dataset matchingargs.filenamewill be downloaded intoargs.data_folder.
- Use the config files from the
In this work, we provide three different ML models to be trained and evaluated against the benchmark datasets, namely FNO, U-Net, and PINN. The codes for the baseline model implementations are contained in models:
-
train_models_forward.pyis the main script to train and evaluate the model. It will call on model-specific script based on the input argument. -
train_models_inverse.pyis the main script to train and evaluate the model for inverse problems. It will call on model-specific script based on the input argument. -
metrics.pyis the script to evaluate the trained models based on various evaluation metrics described in our paper. Additionally, it also plots the prediction and target data. -
analyse_result_forward.pyis the script to convert the saved pickle file from the metrics calculation script into pandas dataframe format and save it as a CSV file. Additionally it also plots a bar chart to compare the results between different models. -
analyse_result_inverse.pyis the script to convert the saved pickle file from the metrics calculation script into pandas dataframe format and save it as a CSV file. This script is used for the inverse problems. Additionally it also plots a bar chart to compare the results between different models. -
fnocontains the scripts of FNO implementation. These are partly adapted from the FNO repository. -
unetcontains the scripts of U-Net implementation. These are partly adapted from the U-Net repository. -
pinncontains the scripts of PINN implementation. These utilize the DeepXDE library. -
inversecontains the model for inverse model based on gradient. -
configcontains the yaml files for the model training input. The default templates for different equations are provided in the args directory. User just needs to copy and paste them to the args keyword in the config.yaml file.
An example to run the forward model training can be found in run_forward_1D.sh, and an example to run the inverse model training can be found in run_inverse.sh.
- model_name: string, containing the baseline model name, either 'FNO', 'Unet', or 'PINN'.
- if_training: bool, set True for training, or False for evaluation.
- continue_training: bool, set True to continue training from a checkpoint.
- num_workers: int, number of workers for the PyTorch dataloader.
- batch_size: int, training batch size.
- initial_step: int, number of time steps used as input for FNO and U-Net.
- t_train: int, number of the last time step used for training (for extrapolation testing, set this to be < Nt).
- model_update: int, number of epochs to save model.
- filename: str, has to match the dataset filename.
- single_file: bool, set False for 2D diffusion-reaction, 1D diffusion-sorption, and the radial dam break scenarios, and set True otherwise.
- reduced_resolution: int, factor to downsample spatial resolution.
- reduced_resolution_t: int, factor to downsample temporal resolution.
- reduced_batch: int, factor to downsample sample size used for training.
- epochs: int, total epochs used for training.
- learning_rate: float, learning rate of the optimizer.
- scheduler_step: int, number of epochs to update the learning rate scheduler.
- scheduler_gamma: float, decay rate of the learning rate.
- in_channels: int, number of input channels
- out_channels: int, number of output channels
- ar_mode: bool, set True for fully autoregressive or pushforward training.
- pushforward: bool, set True for pushforward training, False otherwise (ar_mode also has to be set True).
- unroll_step: int, number of time steps to backpropagate in the pushforward training.
- num_channels: int, number of channels (variables).
- modes: int, number of Fourier modes to multiply.
- width: int, number of channels for the Fourier layer.
- base_path: string, location of the data directory
- training_type: string, type of training, autoregressive, single
- mcmc_num_samples: int, number of generated samples
- mcmc_warmup_steps: 10
- mcmc_num_chains: 1
- num_samples_max: 1000
- in_channels_hid: 64
- inverse_model_type: string, type of inverse inference model, ProbRasterLatent, InitialConditionInterp
- inverse_epochs: int, number of epochs for the gradient based method
- inverse_learning_rate: float, learning rate for the gradient based method
- inverse_verbose_flag: bool, some printing
- plot: bool, set True to activate plotting.
- channel_plot: int, determines which channel/variable to plot.
- x_min: float, left spatial domain.
- x_max: float, right spatial domain.
- y_min: float, lower spatial domain.
- y_max: float, upper spatial domain.
- t_min: float, start of temporal domain.
- t_max: float, end of temporal domain.
We provide the benchmark datasets we used in the paper through our
DaRUS data repository.
The data generation configuration can be found in the paper. Additionally, the
pretrained models are also available to be downloaded from
PDEBench Pretrained Models
DaRus repository. To use the pretrained models, users can specify the argument
continue_training: True in the
config file.
Below is an illustration of the directory structure of PDEBench.
📂 pdebench
|_📁 models
|_📁 pinn # Model: Physics-Informed Neural Network
|_📄 train.py
|_📄 utils.py
|_📄 pde_definitions.py
|_📁 fno # Model: Fourier Neural Operator
|_📄 train.py
|_📄 utils.py
|_📄 fno.py
|_📁 unet # Model: U-Net
|_📄 train.py
|_📄 utils.py
|_📄 unet.py
|_📁 inverse # Model: Gradient-Based Inverse Method
|_📄 train.py
|_📄 utils.py
|_📄 inverse.py
|_📁 config # Config: All config files reside here
|_📄 train_models_inverse.py
|_📄 run_forward_1D.sh
|_📄 analyse_result_inverse.py
|_📄 train_models_forward.py
|_📄 run_inverse.sh
|_📄 metrics.py
|_📄 analyse_result_forward.py
|_📁 data_download # Data: Scripts to download data from DaRUS
|_📁 config
|_📄 download_direct.py
|_📄 download_easydataverse.py
|_📄 visualize_pdes.py
|_📄 README.md
|_📄 download_metadata.csv
|_📁 data_gen # Data: Scripts to generate data
|_📁 configs
|_📁 data_gen_NLE
|_📁 src
|_📁 notebooks
|_📄 gen_diff_sorp.py
|_📄 plot.py
|_📄 example.env
|_📄 gen_ns_incomp.py
|_📄 gen_diff_react.py
|_📄 uploader.py
|_📄 gen_radial_dam_break.py
|_📄 __init__.py
Please cite the following papers if you use PDEBench datasets and/or source code in your research.
PDEBench: An Extensive Benchmark for Scientific Machine Learning - NeurIPS'2022
@inproceedings{PDEBench2022,
author = {Takamoto, Makoto and Praditia, Timothy and Leiteritz, Raphael and MacKinlay, Dan and Alesiani, Francesco and Pflüger, Dirk and Niepert, Mathias},
title = {{PDEBench: An Extensive Benchmark for Scientific Machine Learning}},
year = {2022},
booktitle = {36th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS 2022) Track on Datasets and Benchmarks},
url = {https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.07182}
}
PDEBench Datasets - NeurIPS'2022
@data{darus-2986_2022,
author = {Takamoto, Makoto and Praditia, Timothy and Leiteritz, Raphael and MacKinlay, Dan and Alesiani, Francesco and Pflüger, Dirk and Niepert, Mathias},
publisher = {DaRUS},
title = {{PDEBench Datasets}},
year = {2022},
doi = {10.18419/darus-2986},
url = {https://doi.org/10.18419/darus-2986}
}
Learning Neural PDE Solvers with Parameter-Guided Channel Attention - ICML'2023
@article{cape-takamoto:2023,
author = {Makoto Takamoto and
Francesco Alesiani and
Mathias Niepert},
title = {Learning Neural {PDE} Solvers with Parameter-Guided Channel Attention},
journal = {CoRR},
volume = {abs/2304.14118},
year = {2023},
url = {https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2304.14118},
doi = {10.48550/arXiv.2304.14118},
eprinttype = {arXiv},
eprint = {2304.14118},
}
Vectorized Conditional Neural Fields: A Framework for Solving Time-dependent Parametric Partial Differential Equations - ICLR-W'2024 & ICML'2024
@inproceedings{vcnef-vectorized-conditional-neural-fields-hagnberger:2024,
author = {Hagnberger, Jan and Kalimuthu, Marimuthu and Musekamp, Daniel and Niepert, Mathias},
title = {{Vectorized Conditional Neural Fields: A Framework for Solving Time-dependent Parametric Partial Differential Equations}},
year = {2024},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 41st International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML 2024)}
}
Active Learning for Neural PDE Solvers - NeurIPS-W'2024
@article{active-learn-neuralpde-benchmark-musekamp:2024,
author = {Daniel Musekamp and
Marimuthu Kalimuthu and
David Holzm{\"{u}}ller and
Makoto Takamoto and
Mathias Niepert},
title = {Active Learning for Neural {PDE} Solvers},
journal = {CoRR},
volume = {abs/2408.01536},
year = {2024},
url = {https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2408.01536},
doi = {10.48550/ARXIV.2408.01536},
eprinttype = {arXiv},
eprint = {2408.01536},
}
- Makato Takamoto (NEC laboratories Europe)
- Timothy Praditia (Stuttgart Center for Simulation Science | University of Stuttgart)
- Raphael Leiteritz (Stuttgart Center for Simulation Science | University of Stuttgart)
- Francesco Alesiani (NEC laboratories Europe)
- Dan MacKinlay (CSIRO’s Data61)
- Marimuthu Kalimuthu (Stuttgart Center for Simulation Science | University of Stuttgart)
- John Kim (ANU TechLauncher/CSIRO’s Data61)
- Gefei Shan (ANU TechLauncher/CSIRO’s Data61)
- Yizhou Yang (ANU TechLauncher/CSIRO’s Data61)
- Ran Zhang (ANU TechLauncher/CSIRO’s Data61)
- Simon Brown (ANU TechLauncher/CSIRO’s Data61)
MIT licensed, except where otherwise stated. See LICENSE.txt file.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for PDEBench
Similar Open Source Tools

PDEBench
PDEBench provides a diverse and comprehensive set of benchmarks for scientific machine learning, including challenging and realistic physical problems. The repository consists of code for generating datasets, uploading and downloading datasets, training and evaluating machine learning models as baselines. It features a wide range of PDEs, realistic and difficult problems, ready-to-use datasets with various conditions and parameters. PDEBench aims for extensibility and invites participation from the SciML community to improve and extend the benchmark.
stark
STaRK is a large-scale semi-structure retrieval benchmark on Textual and Relational Knowledge Bases. It provides natural-sounding and practical queries crafted to incorporate rich relational information and complex textual properties, closely mirroring real-life scenarios. The benchmark aims to assess how effectively large language models can handle the interplay between textual and relational requirements in queries, using three diverse knowledge bases constructed from public sources.
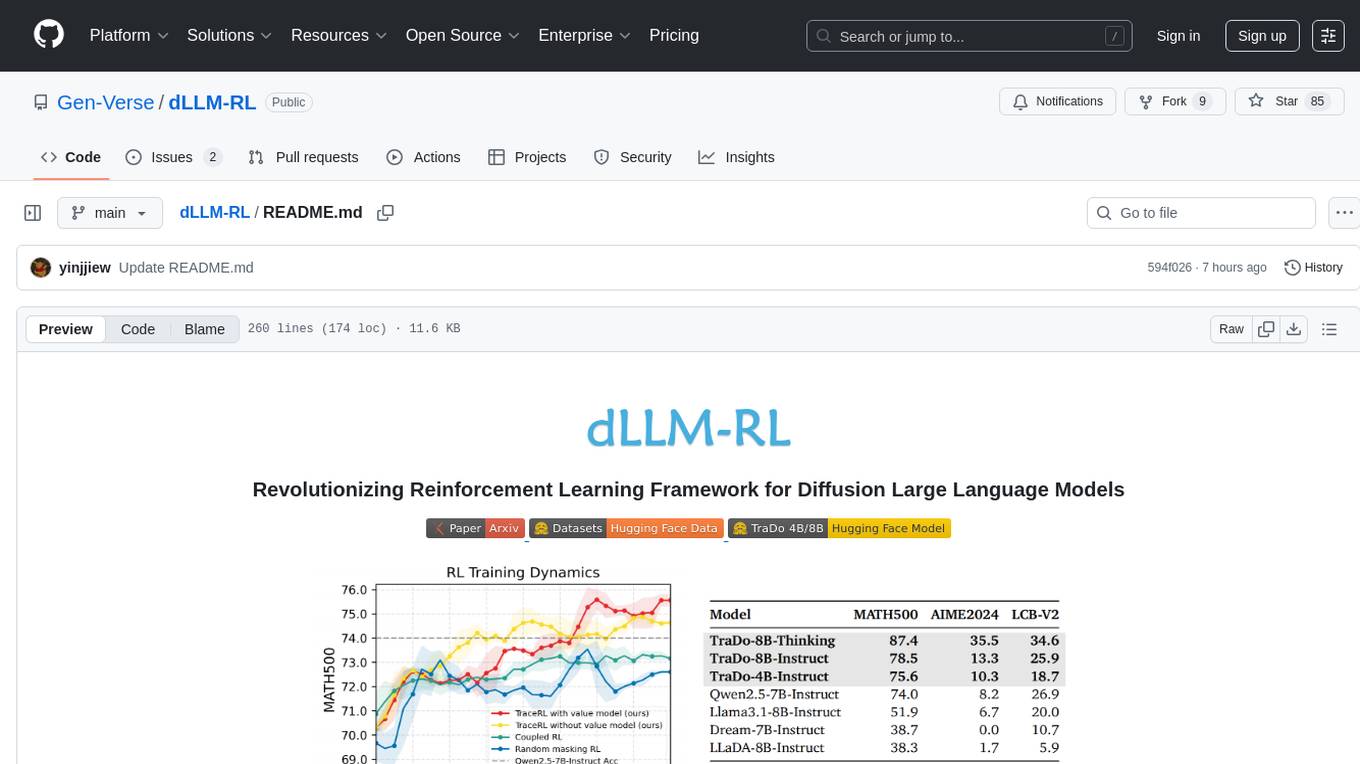
dLLM-RL
dLLM-RL is a revolutionary reinforcement learning framework designed for Diffusion Large Language Models. It supports various models with diverse structures, offers inference acceleration, RL training capabilities, and SFT functionalities. The tool introduces TraceRL for trajectory-aware RL and diffusion-based value models for optimization stability. Users can download and try models like TraDo-4B-Instruct and TraDo-8B-Instruct. The tool also provides support for multi-node setups and easy building of reinforcement learning methods. Additionally, it offers supervised fine-tuning strategies for different models and tasks.
RTL-Coder
RTL-Coder is a tool designed to outperform GPT-3.5 in RTL code generation by providing a fully open-source dataset and a lightweight solution. It targets Verilog code generation and offers an automated flow to generate a large labeled dataset with over 27,000 diverse Verilog design problems and answers. The tool addresses the data availability challenge in IC design-related tasks and can be used for various applications beyond LLMs. The tool includes four RTL code generation models available on the HuggingFace platform, each with specific features and performance characteristics. Additionally, RTL-Coder introduces a new LLM training scheme based on code quality feedback to further enhance model performance and reduce GPU memory consumption.
Pixel-Reasoner
Pixel Reasoner is a framework that introduces reasoning in the pixel-space for Vision-Language Models (VLMs), enabling them to directly inspect, interrogate, and infer from visual evidences. This enhances reasoning fidelity for visual tasks by equipping VLMs with visual reasoning operations like zoom-in and select-frame. The framework addresses challenges like model's imbalanced competence and reluctance to adopt pixel-space operations through a two-phase training approach involving instruction tuning and curiosity-driven reinforcement learning. With these visual operations, VLMs can interact with complex visual inputs such as images or videos to gather necessary information, leading to improved performance across visual reasoning benchmarks.
DeepPavlov
DeepPavlov is an open-source conversational AI library built on PyTorch. It is designed for the development of production-ready chatbots and complex conversational systems, as well as for research in the area of NLP and dialog systems. The library offers a wide range of models for tasks such as Named Entity Recognition, Intent/Sentence Classification, Question Answering, Sentence Similarity/Ranking, Syntactic Parsing, and more. DeepPavlov also provides embeddings like BERT, ELMo, and FastText for various languages, along with AutoML capabilities and integrations with REST API, Socket API, and Amazon AWS.
mlstm_kernels
This repository provides fast and efficient mLSTM training and inference Triton kernels built on Tiled Flash Linear Attention (TFLA). It includes implementations in JAX, PyTorch, and Triton, with chunkwise, parallel, and recurrent kernels for mLSTM. The repository also contains a benchmark library for runtime benchmarks and full mLSTM Huggingface models.
lloco
LLoCO is a technique that learns documents offline through context compression and in-domain parameter-efficient finetuning using LoRA, which enables LLMs to handle long context efficiently.

universal
The Universal Numbers Library is a header-only C++ template library designed for universal number arithmetic, offering alternatives to native integer and floating-point for mixed-precision algorithm development and optimization. It tailors arithmetic types to the application's precision and dynamic range, enabling improved application performance and energy efficiency. The library provides fast implementations of special IEEE-754 formats like quarter precision, half-precision, and quad precision, as well as vendor-specific extensions. It supports static and elastic integers, decimals, fixed-points, rationals, linear floats, tapered floats, logarithmic, interval, and adaptive-precision integers, rationals, and floats. The library is suitable for AI, DSP, HPC, and HFT algorithms.
datadreamer
DataDreamer is an advanced toolkit designed to facilitate the development of edge AI models by enabling synthetic data generation, knowledge extraction from pre-trained models, and creation of efficient and potent models. It eliminates the need for extensive datasets by generating synthetic datasets, leverages latent knowledge from pre-trained models, and focuses on creating compact models suitable for integration into any device and performance for specialized tasks. The toolkit offers features like prompt generation, image generation, dataset annotation, and tools for training small-scale neural networks for edge deployment. It provides hardware requirements, usage instructions, available models, and limitations to consider while using the library.
KVCache-Factory
KVCache-Factory is a unified framework for KV Cache compression of diverse models. It supports multi-GPUs inference with big LLMs and various attention implementations. The tool enables KV cache compression without Flash Attention v2, multi-GPU inference, and specific models like Mistral. It also provides functions for KV cache budget allocation and batch inference. The visualization tools help in understanding the attention patterns of models.

litdata
LitData is a tool designed for blazingly fast, distributed streaming of training data from any cloud storage. It allows users to transform and optimize data in cloud storage environments efficiently and intuitively, supporting various data types like images, text, video, audio, geo-spatial, and multimodal data. LitData integrates smoothly with frameworks such as LitGPT and PyTorch, enabling seamless streaming of data to multiple machines. Key features include multi-GPU/multi-node support, easy data mixing, pause & resume functionality, support for profiling, memory footprint reduction, cache size configuration, and on-prem optimizations. The tool also provides benchmarks for measuring streaming speed and conversion efficiency, along with runnable templates for different data types. LitData enables infinite cloud data processing by utilizing the Lightning.ai platform to scale data processing with optimized machines.
FlexFlow
FlexFlow Serve is an open-source compiler and distributed system for **low latency**, **high performance** LLM serving. FlexFlow Serve outperforms existing systems by 1.3-2.0x for single-node, multi-GPU inference and by 1.4-2.4x for multi-node, multi-GPU inference.
wanda
Official PyTorch implementation of Wanda (Pruning by Weights and Activations), a simple and effective pruning approach for large language models. The pruning approach removes weights on a per-output basis, by the product of weight magnitudes and input activation norms. The repository provides support for various features such as LLaMA-2, ablation study on OBS weight update, zero-shot evaluation, and speedup evaluation. Users can replicate main results from the paper using provided bash commands. The tool aims to enhance the efficiency and performance of language models through structured and unstructured sparsity techniques.
curator
Bespoke Curator is an open-source tool for data curation and structured data extraction. It provides a Python library for generating synthetic data at scale, with features like programmability, performance optimization, caching, and integration with HuggingFace Datasets. The tool includes a Curator Viewer for dataset visualization and offers a rich set of functionalities for creating and refining data generation strategies.
aigverse
aigverse is a Python infrastructure framework that bridges the gap between logic synthesis and AI/ML applications. It allows efficient representation and manipulation of logic circuits, making it easier to integrate logic synthesis and optimization tasks into machine learning pipelines. Built upon EPFL Logic Synthesis Libraries, particularly mockturtle, aigverse provides a high-level Python interface to state-of-the-art algorithms for And-Inverter Graph (AIG) manipulation and logic synthesis, widely used in formal verification, hardware design, and optimization tasks.
For similar tasks
numerapi
Numerapi is a Python client to the Numerai API that allows users to automatically download and upload data for the Numerai machine learning competition. It provides functionalities for downloading training data, uploading predictions, and accessing user, submission, and competitions information for both the main competition and Numerai Signals competition. Users can interact with the API using Python modules or command line interface. Tokens are required for certain actions like uploading predictions or staking, which can be obtained from Numer.ai account settings. The tool also supports features like checking new rounds, getting leaderboards, and managing stakes.

PDEBench
PDEBench provides a diverse and comprehensive set of benchmarks for scientific machine learning, including challenging and realistic physical problems. The repository consists of code for generating datasets, uploading and downloading datasets, training and evaluating machine learning models as baselines. It features a wide range of PDEs, realistic and difficult problems, ready-to-use datasets with various conditions and parameters. PDEBench aims for extensibility and invites participation from the SciML community to improve and extend the benchmark.
cookiecutter-data-science
Cookiecutter Data Science (CCDS) is a tool for setting up a data science project template that incorporates best practices. It provides a logical, reasonably standardized but flexible project structure for doing and sharing data science work. The tool helps users to easily start new data science projects with a well-organized directory structure, including folders for data, models, notebooks, reports, and more. By following the project template created by CCDS, users can streamline their data science workflow and ensure consistency across projects.

LLaSA_training
LLaSA_training is a repository focused on training models for speech synthesis using a large amount of open-source speech data. The repository provides instructions for finetuning models and offers pre-trained models for multilingual speech synthesis. It includes tools for training, data downloading, and data processing using specialized tokenizers for text and speech sequences. The repository also supports direct usage on Hugging Face platform with specific codecs and collections.

labelbox-python
Labelbox is a data-centric AI platform for enterprises to develop, optimize, and use AI to solve problems and power new products and services. Enterprises use Labelbox to curate data, generate high-quality human feedback data for computer vision and LLMs, evaluate model performance, and automate tasks by combining AI and human-centric workflows. The academic & research community uses Labelbox for cutting-edge AI research.
promptfoo
Promptfoo is a tool for testing and evaluating LLM output quality. With promptfoo, you can build reliable prompts, models, and RAGs with benchmarks specific to your use-case, speed up evaluations with caching, concurrency, and live reloading, score outputs automatically by defining metrics, use as a CLI, library, or in CI/CD, and use OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure, Google, HuggingFace, open-source models like Llama, or integrate custom API providers for any LLM API.
vespa
Vespa is a platform that performs operations such as selecting a subset of data in a large corpus, evaluating machine-learned models over the selected data, organizing and aggregating it, and returning it, typically in less than 100 milliseconds, all while the data corpus is continuously changing. It has been in development for many years and is used on a number of large internet services and apps which serve hundreds of thousands of queries from Vespa per second.
python-aiplatform
The Vertex AI SDK for Python is a library that provides a convenient way to use the Vertex AI API. It offers a high-level interface for creating and managing Vertex AI resources, such as datasets, models, and endpoints. The SDK also provides support for training and deploying custom models, as well as using AutoML models. With the Vertex AI SDK for Python, you can quickly and easily build and deploy machine learning models on Vertex AI.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.

