
aixt
Microcontrollers programming framework based on Vlang.
Stars: 69
Aixt is a programming framework for microcontrollers using a modern language syntax based on V, with components including the Aixt programming language, Aixt to C Transpiler, and Aixt API. It is designed to be modular, allowing easy incorporation of new devices and boards through a TOML configuration file. The Aixt to C Transpiler translates Aixt source code to C for specific microcontroller compilers. The Aixt language implements a subset of V with differences in variables, strings, arrays, default integers size, structs, functions, and preprocessor commands. The Aixt API provides functions for digital I/O, analog inputs, PWM outputs, and serial ports.
README:
Aixt is a programming framework for microcontrollers which implements a subset of the V programming language, and is able to be used by low-resource devices. Aixt is composed by 3 main components:
- The Aixt's V programming language which is a subset of the original V language.
- The V to C Transpiler, which translate the V source code to C, for the specific C compiler of each microcontroller.
- The Aixt API (almost all written in V), which makes the programming easy by standardizing the setup and I/O functions.
This diagram shows the Aixt blocks and their interactions:
stateDiagram-v2
Aixt: V
state Aixt {
source: Source code
API: Microcontroller API
state API {
PICs: PIC
ATM: AT
STM
ESP
RP2040
PSoC
others2: ...
NXT: NXT brick
}
}
Aixt2C: Transpiler
state Aixt2C {
state V {
Transpiler: Transpiler
}
state json {
setup: Setup files
}
}
C: C
state C {
Tr_Code: Transpiled code
}
state Compiler {
XC8
XC16
arduino_cli
GCC
others: ...
nbc: nbc (NXC)
}
state machine {
BF: Binary file
}
source --> Aixt2C
API --> Aixt2C
Aixt2C --> C
C --> Compiler
Compiler --> machineAixt is designed to be as modular as possible to facilitate the incorporation of new devices and boards. This is mainly possible by using a configuration files (in json format) instead of creating new source code for each new device. That .json file contains the specific parameters of each device, board or compiler such as: variable types, initialization commands, compiler paths, etc.
The transpiler is written in V and uses the V's self native compiler in order to transpile from V to C. This is implemented in the folder src\ and the main source code is the src\aixt.v file. Aixt generates code for 3 different backends:
- c: for the microcontroller native C compiler
- nxc: for the NXC compiler (LEGO Mindstorms NXT)
- arduino: for the Arduino CLI
Aixt's V programing language implements a subset of the V language. The main differences are show as follows:
| feature | V | Aixt's V |
|---|---|---|
| strings | dynamic-sized | fixed-sized and dynamic-sized if supported |
| arrays | dynamic-sized | fixed-sized and dynamic-sized if supported |
| default integers size | 32 bits | depends on the device |
| structs | allow functions (object-oriented) | do not allow functions (only structured programming) |
| functions | multiple return values | only one return value |
| text macros | not allowed | allowed by using @[as_macro] attribute, for functions and constants |
C variables access |
not allowed | allowed by using C.var_name syntax |
| global variables | disabled by default | enabled by default |
/* Turning ON by 5.5 seconds the B7 on a
PIC16F84A microcontroller (XC8 compiler) */
import time
import pin
fn main() {
pin.setup(pin.b7, pin.output)
pin.high(pin.b7) //turn ON the LED on PORTB7
time.sleep_ms(5500)
pin.low(pin.b7)
}// ADC value to serial port on Raspberry Pi Pico (Arduino backend)
import time
import uart
import adc
uart.setup(9600) // baud rate
adc.setup(12) // resolution
for { // infinite loop
analog := adc.read(adc.ch0)
uart.println('ADC channel 0: ${analog}') // use string interpolation
time.sleep_ms(500)
}// "Drawing" an square with a differential platform (motors A and B)
import motor
import time
for {
motor.write(motor.a, 50)
motor.write(motor.b, -50) // reverse
time.sleep_ms(3000)
motor.write(motor.a, -50) // reverse
time.sleep_ms(500)
}The Aixt API is inspired by Micropython, Arduino and Tinygo. The API for all the ports includes at least functions for:
- Digital input/output
- Analog inputs (ADC)
- PWM outputs
- Serial port (UART)
git clone https://github.com/fermarsan/aixt.git
cd aixt
make # make.bat on Windows
run it in a Linux-based system as:
./aixt <command> <device_or_board> <source_file>
or in Windows:
aixt.exe <command> <device_or_board> <source_file>
For running the command aixt from any folder in the file system you can create a symbolic link of it in this way:
run it in a Linux-based system as:
./aixt symlink
or in Windows:
aixt.exe symlink
./aixt -t Emulator test.v
./aixt -b NXT ports/NXT/projects/1_motor.write.v
- The V programming language 0.4.9
- auduino-cli last version (for arduino backend devices only)
- specific C compiler depending on the device
The project's name is inspired in Veasel, the Weasel pet of V Language, and at the same time is a tribute to Ticuna people who live in the Amazon forest between the borders of Colombia, Brasil and Perú. Weasels are mustelids just like otters, so the name Aixt comes from Aixtü, which is a way to say otter in Ticuna language.
Nice, you can contact me via mail.
Email: [email protected]
Cool, go ahead and make the contributions you want, then submit a new pull request
The microcontroller or board that you use is not listed here and you know how to program it in C?... You can easily add it to Aixt, please check CONTRIBUTING.md.
Take a look at TODO.md to find a task for you.
Please check CONTRIBUTING.md to learn how you can contribute.
The Aixt project is licensed under the MIT, which is attached in this repository.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for aixt
Similar Open Source Tools

aixt
Aixt is a programming framework for microcontrollers using a modern language syntax based on V, with components including the Aixt programming language, Aixt to C Transpiler, and Aixt API. It is designed to be modular, allowing easy incorporation of new devices and boards through a TOML configuration file. The Aixt to C Transpiler translates Aixt source code to C for specific microcontroller compilers. The Aixt language implements a subset of V with differences in variables, strings, arrays, default integers size, structs, functions, and preprocessor commands. The Aixt API provides functions for digital I/O, analog inputs, PWM outputs, and serial ports.

xFasterTransformer
xFasterTransformer is an optimized solution for Large Language Models (LLMs) on the X86 platform, providing high performance and scalability for inference on mainstream LLM models. It offers C++ and Python APIs for easy integration, along with example codes and benchmark scripts. Users can prepare models in a different format, convert them, and use the APIs for tasks like encoding input prompts, generating token ids, and serving inference requests. The tool supports various data types and models, and can run in single or multi-rank modes using MPI. A web demo based on Gradio is available for popular LLM models like ChatGLM and Llama2. Benchmark scripts help evaluate model inference performance quickly, and MLServer enables serving with REST and gRPC interfaces.
DeepPavlov
DeepPavlov is an open-source conversational AI library built on PyTorch. It is designed for the development of production-ready chatbots and complex conversational systems, as well as for research in the area of NLP and dialog systems. The library offers a wide range of models for tasks such as Named Entity Recognition, Intent/Sentence Classification, Question Answering, Sentence Similarity/Ranking, Syntactic Parsing, and more. DeepPavlov also provides embeddings like BERT, ELMo, and FastText for various languages, along with AutoML capabilities and integrations with REST API, Socket API, and Amazon AWS.
AgentKit
AgentKit is a framework for constructing complex human thought processes from simple natural language prompts. It offers a unified way to represent and execute these processes as graphs, making it easy to design and tune agents without any programming experience. AgentKit can be used for a variety of tasks, including generating text, answering questions, and making decisions.
speech-to-speech
This repository implements a speech-to-speech cascaded pipeline with consecutive parts including Voice Activity Detection (VAD), Speech to Text (STT), Language Model (LM), and Text to Speech (TTS). It aims to provide a fully open and modular approach by leveraging models available on the Transformers library via the Hugging Face hub. The code is designed for easy modification, with each component implemented as a class. Users can run the pipeline either on a server/client approach or locally, with detailed setup and usage instructions provided in the readme.
PDEBench
PDEBench provides a diverse and comprehensive set of benchmarks for scientific machine learning, including challenging and realistic physical problems. The repository consists of code for generating datasets, uploading and downloading datasets, training and evaluating machine learning models as baselines. It features a wide range of PDEs, realistic and difficult problems, ready-to-use datasets with various conditions and parameters. PDEBench aims for extensibility and invites participation from the SciML community to improve and extend the benchmark.

raglite
RAGLite is a Python toolkit for Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) with PostgreSQL or SQLite. It offers configurable options for choosing LLM providers, database types, and rerankers. The toolkit is fast and permissive, utilizing lightweight dependencies and hardware acceleration. RAGLite provides features like PDF to Markdown conversion, multi-vector chunk embedding, optimal semantic chunking, hybrid search capabilities, adaptive retrieval, and improved output quality. It is extensible with a built-in Model Context Protocol server, customizable ChatGPT-like frontend, document conversion to Markdown, and evaluation tools. Users can configure RAGLite for various tasks like configuring, inserting documents, running RAG pipelines, computing query adapters, evaluating performance, running MCP servers, and serving frontends.
react-native-fast-tflite
A high-performance TensorFlow Lite library for React Native that utilizes JSI for power, zero-copy ArrayBuffers for efficiency, and low-level C/C++ TensorFlow Lite core API for direct memory access. It supports swapping out TensorFlow Models at runtime and GPU-accelerated delegates like CoreML/Metal/OpenGL. Easy VisionCamera integration allows for seamless usage. Users can load TensorFlow Lite models, interpret input and output data, and utilize GPU Delegates for faster computation. The library is suitable for real-time object detection, image classification, and other machine learning tasks in React Native applications.

langserve
LangServe helps developers deploy `LangChain` runnables and chains as a REST API. This library is integrated with FastAPI and uses pydantic for data validation. In addition, it provides a client that can be used to call into runnables deployed on a server. A JavaScript client is available in LangChain.js.
langgraph4j
Langgraph4j is a Java library for language processing tasks such as text classification, sentiment analysis, and named entity recognition. It provides a set of tools and algorithms for analyzing text data and extracting useful information. The library is designed to be efficient and easy to use, making it suitable for both research and production applications.
r2ai
r2ai is a tool designed to run a language model locally without internet access. It can be used to entertain users or assist in answering questions related to radare2 or reverse engineering. The tool allows users to prompt the language model, index large codebases, slurp file contents, embed the output of an r2 command, define different system-level assistant roles, set environment variables, and more. It is accessible as an r2lang-python plugin and can be scripted from various languages. Users can use different models, adjust query templates dynamically, load multiple models, and make them communicate with each other.

wllama
Wllama is a WebAssembly binding for llama.cpp, a high-performance and lightweight language model library. It enables you to run inference directly on the browser without the need for a backend or GPU. Wllama provides both high-level and low-level APIs, allowing you to perform various tasks such as completions, embeddings, tokenization, and more. It also supports model splitting, enabling you to load large models in parallel for faster download. With its Typescript support and pre-built npm package, Wllama is easy to integrate into your React Typescript projects.
llm-vscode
llm-vscode is an extension designed for all things LLM, utilizing llm-ls as its backend. It offers features such as code completion with 'ghost-text' suggestions, the ability to choose models for code generation via HTTP requests, ensuring prompt size fits within the context window, and code attribution checks. Users can configure the backend, suggestion behavior, keybindings, llm-ls settings, and tokenization options. Additionally, the extension supports testing models like Code Llama 13B, Phind/Phind-CodeLlama-34B-v2, and WizardLM/WizardCoder-Python-34B-V1.0. Development involves cloning llm-ls, building it, and setting up the llm-vscode extension for use.
paxml
Pax is a framework to configure and run machine learning experiments on top of Jax.
litserve
LitServe is a high-throughput serving engine for deploying AI models at scale. It generates an API endpoint for a model, handles batching, streaming, autoscaling across CPU/GPUs, and more. Built for enterprise scale, it supports every framework like PyTorch, JAX, Tensorflow, and more. LitServe is designed to let users focus on model performance, not the serving boilerplate. It is like PyTorch Lightning for model serving but with broader framework support and scalability.
swe-rl
SWE-RL is the official codebase for the paper 'SWE-RL: Advancing LLM Reasoning via Reinforcement Learning on Open Software Evolution'. It is the first approach to scale reinforcement learning based LLM reasoning for real-world software engineering, leveraging open-source software evolution data and rule-based rewards. The code provides prompt templates and the implementation of the reward function based on sequence similarity. Agentless Mini, a part of SWE-RL, builds on top of Agentless with improvements like fast async inference, code refactoring for scalability, and support for using multiple reproduction tests for reranking. The tool can be used for localization, repair, and reproduction test generation in software engineering tasks.
For similar tasks

aixt
Aixt is a programming framework for microcontrollers using a modern language syntax based on V, with components including the Aixt programming language, Aixt to C Transpiler, and Aixt API. It is designed to be modular, allowing easy incorporation of new devices and boards through a TOML configuration file. The Aixt to C Transpiler translates Aixt source code to C for specific microcontroller compilers. The Aixt language implements a subset of V with differences in variables, strings, arrays, default integers size, structs, functions, and preprocessor commands. The Aixt API provides functions for digital I/O, analog inputs, PWM outputs, and serial ports.
Awesome-Embedded
Awesome-Embedded is a curated list of resources for embedded systems enthusiasts. It covers a wide range of topics including MCU programming, RTOS, Linux kernel development, assembly programming, machine learning & AI on MCU, utilities, tips & tricks, and more. The repository provides valuable information, tutorials, and tools for individuals interested in embedded systems development.
For similar jobs
executorch
ExecuTorch is an end-to-end solution for enabling on-device inference capabilities across mobile and edge devices including wearables, embedded devices and microcontrollers. It is part of the PyTorch Edge ecosystem and enables efficient deployment of PyTorch models to edge devices. Key value propositions of ExecuTorch are: * **Portability:** Compatibility with a wide variety of computing platforms, from high-end mobile phones to highly constrained embedded systems and microcontrollers. * **Productivity:** Enabling developers to use the same toolchains and SDK from PyTorch model authoring and conversion, to debugging and deployment to a wide variety of platforms. * **Performance:** Providing end users with a seamless and high-performance experience due to a lightweight runtime and utilizing full hardware capabilities such as CPUs, NPUs, and DSPs.
holoscan-sdk
The Holoscan SDK is part of NVIDIA Holoscan, the AI sensor processing platform that combines hardware systems for low-latency sensor and network connectivity, optimized libraries for data processing and AI, and core microservices to run streaming, imaging, and other applications, from embedded to edge to cloud. It can be used to build streaming AI pipelines for a variety of domains, including Medical Devices, High Performance Computing at the Edge, Industrial Inspection and more.
panda
Panda is a car interface tool that speaks CAN and CAN FD, running on STM32F413 and STM32H725. It provides safety modes and controls_allowed feature for message handling. The tool ensures code rigor through CI regression tests, including static code analysis, MISRA C:2012 violations check, unit tests, and hardware-in-the-loop tests. The software interface supports Python library, C++ library, and socketcan in kernel. Panda is licensed under the MIT license.
aiocoap
aiocoap is a Python library that implements the Constrained Application Protocol (CoAP) using native asyncio methods in Python 3. It supports various CoAP standards such as RFC7252, RFC7641, RFC7959, RFC8323, RFC7967, RFC8132, RFC9176, RFC8613, and draft-ietf-core-oscore-groupcomm-17. The library provides features for clients and servers, including multicast support, blockwise transfer, CoAP over TCP, TLS, and WebSockets, No-Response, PATCH/FETCH, OSCORE, and Group OSCORE. It offers an easy-to-use interface for concurrent operations and is suitable for IoT applications.

CPP-Notes
CPP-Notes is a comprehensive repository providing detailed insights into the history, evolution, and modern development of the C++ programming language. It covers the foundational concepts of C++ and its transition from C, highlighting key features such as object-oriented programming, generic programming, and modern enhancements introduced in C++11/14/17. The repository delves into the significance of C++ in system programming, library development, and its role as a versatile and efficient language. It explores the historical milestones of C++ development, from its inception in 1979 by Bjarne Stroustrup to the latest C++20 standard, showcasing major advancements like Concepts, Ranges library, Coroutines, Modules, and enhanced concurrency features.
AI-on-the-edge-device
AI-on-the-edge-device is a project that enables users to digitize analog water, gas, power, and other meters using an ESP32 board with a supported camera. It integrates Tensorflow Lite for AI processing, offers a small and affordable device with integrated camera and illumination, provides a web interface for administration and control, supports Homeassistant, Influx DB, MQTT, and REST API. The device captures meter images, extracts Regions of Interest (ROIs), runs them through AI for digitization, and allows users to send data to MQTT, InfluxDb, or access it via REST API. The project also includes 3D-printable housing options and tools for logfile management.
rknn-llm
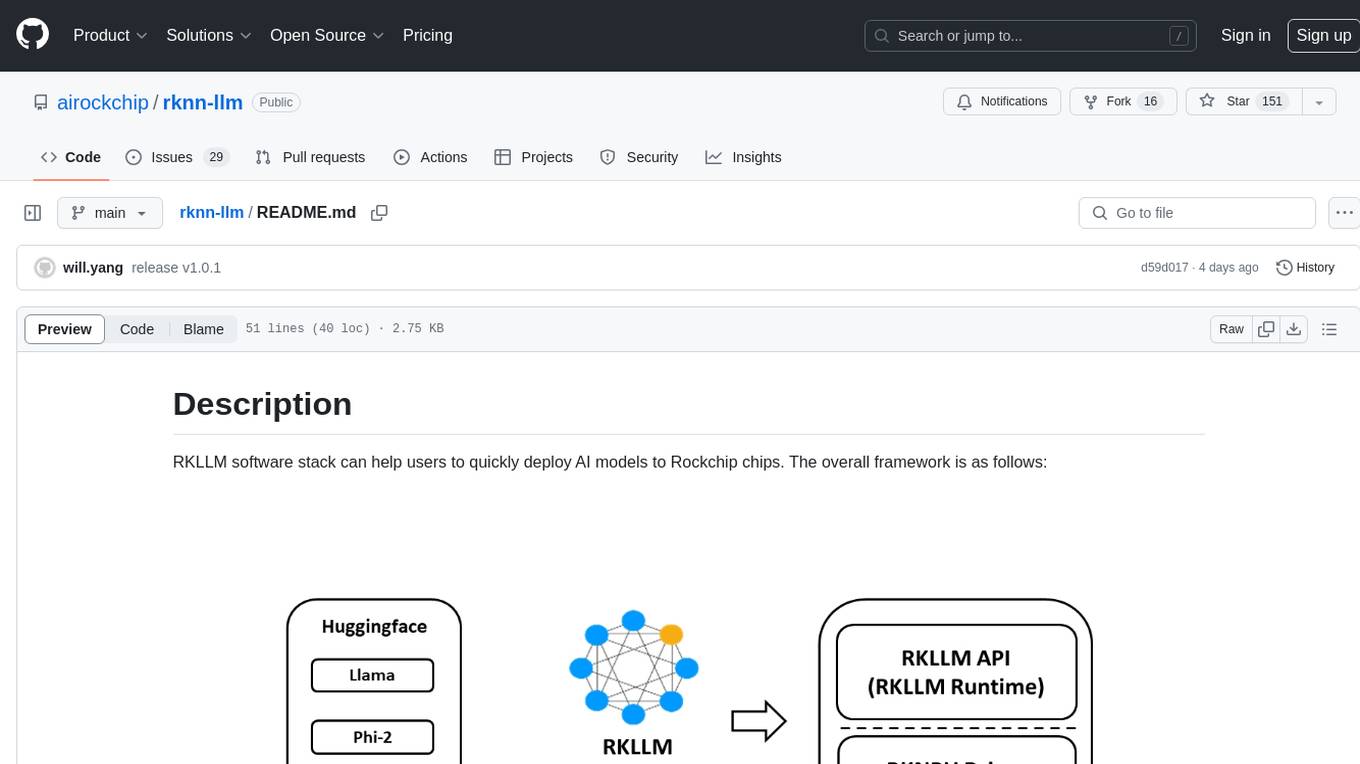
RKLLM software stack is a toolkit designed to help users quickly deploy AI models to Rockchip chips. It consists of RKLLM-Toolkit for model conversion and quantization, RKLLM Runtime for deploying models on Rockchip NPU platform, and RKNPU kernel driver for hardware interaction. The toolkit supports RK3588 and RK3576 series chips and various models like TinyLLAMA, Qwen, Phi, ChatGLM3, Gemma, InternLM2, and MiniCPM. Users can download packages, docker images, examples, and docs from RKLLM_SDK. Additionally, RKNN-Toolkit2 SDK is available for deploying additional AI models.
awesome-RK3588
RK3588 is a flagship 8K SoC chip by Rockchip, integrating Cortex-A76 and Cortex-A55 cores with NEON coprocessor for 8K video codec. This repository curates resources for developing with RK3588, including official resources, RKNN models, projects, development boards, documentation, tools, and sample code.
