
llmgraph
Create knowledge graphs with LLMs
Stars: 271
llmgraph is a tool that enables users to create knowledge graphs in GraphML, GEXF, and HTML formats by extracting world knowledge from large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT. It supports various entity types and relationships, offers cache support for efficient graph growth, and provides insights into LLM costs. Users can customize the model used and interact with different LLM providers. The tool allows users to generate interactive graphs based on a specified entity type and Wikipedia link, making it a valuable resource for knowledge graph creation and exploration.
README:
Create knowledge graphs with LLMs.
llmgraph enables you to create knowledge graphs in GraphML, GEXF, and HTML formats (generated via pyvis) from a given source entity Wikipedia page. The knowledge graphs are generated by extracting world knowledge from ChatGPT or other large language models (LLMs) as supported by LiteLLM.
For a background on knowledge graphs see a youtube overview by Computerphile
- Create knowledge graphs, given a source entity.
- Uses ChatGPT (or another specified LLM) to extract world knowledge.
- Generate knowledge graphs in HTML, GraphML, and GEXF formats.
- Many entity types and relationships supported by customised prompts.
- Cache support to iteratively grow a knowledge graph, efficiently.
- Outputs
total tokensused to understand LLM costs (even though a default run is only about 1 cent). - Customisable model (default is OpenAI
gpt-4o-minifor speed and cost).
You can install llmgraph using pip, ideally into a Python virtual environment:
pip install llmgraphAlternatively, checkout an example notebook that uses llmgraph and you can run directly in Google Colab.
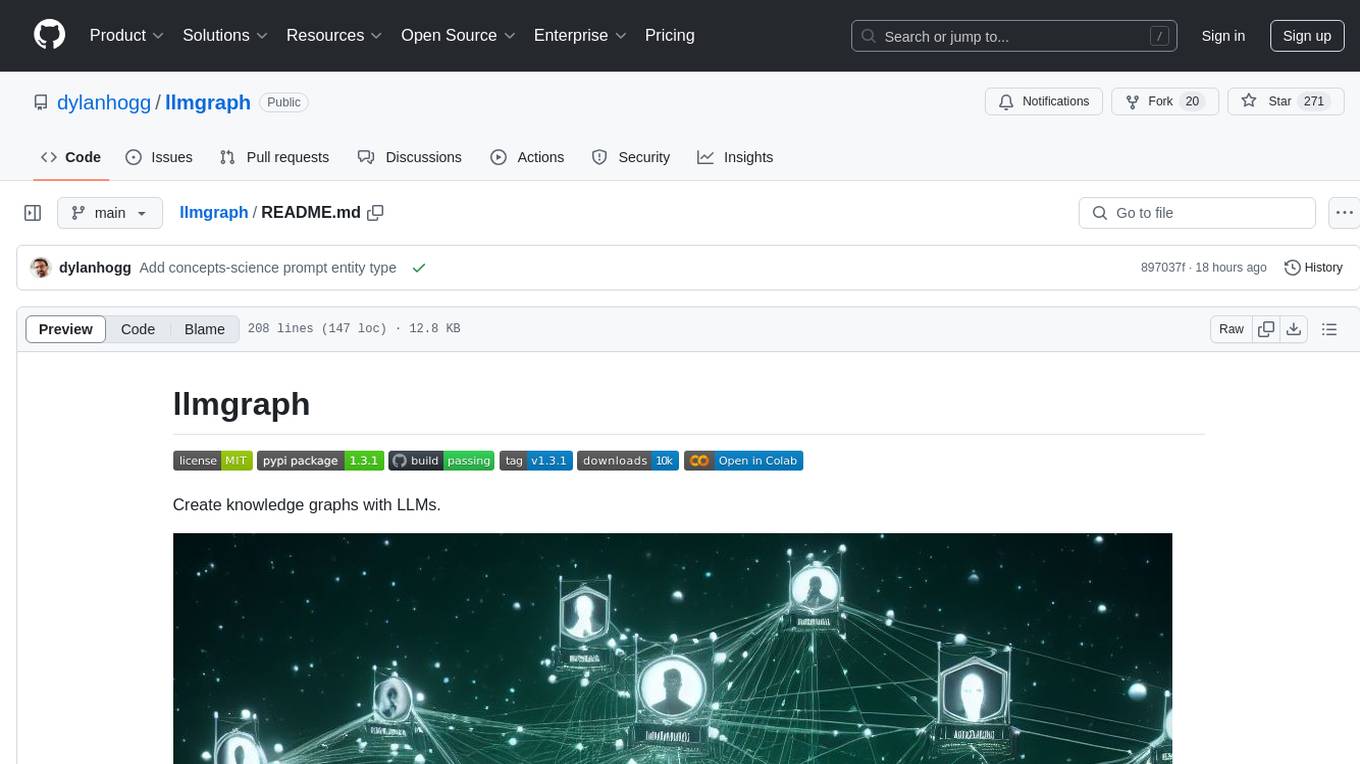
In addition to GraphML and GEXF formats, an HTML pyvis physics enabled graph can be viewed:
 Generate above machine-learning graph:
Generate above machine-learning graph:llmgraph machine-learning "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Artificial_intelligence" --levels 4
View entire graph: machine-learning_artificial-intelligence_v1.0.0_level4_fully_connected.html
The example above was generated with the following command, which requires an entity_type and a quoted entity_wikipedia souce url:
llmgraph machine-learning "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Artificial_intelligence" --levels 3This example creates a 3 level graph, based on the given start node Artificial Intelligence.
By default OpenAI is used and you will need to set an environment variable 'OPENAI_API_KEY' prior to running. See the OpenAI docs for more info. The total tokens used is output as the run progresses. For reference this 3 level example used a total of 7,650 gpt-4o-mini tokens, which is approx 1.5 cents as of Oct 2023.
You can also specify a different LLM provider, including running with a local ollama model. You should be able to specify anything supported by LiteLLM as described here: https://docs.litellm.ai/docs/providers. Note that the prompts to extract related entities were tested with OpenAI and may not work as well with other models.
Local ollama/llama2 model example:
llmgraph machine-learning "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Artificial_intelligence" --levels 3 --llm-model ollama/llama2 --llm-base-url http://localhost:<your_port>The entity_type sets the LLM prompt used to find related entities to include in the graph. The full list can be seen in prompts.yaml and include the following entity types:
automobilebookcomputer-gameconcepts-generalconcepts-sciencecreative-generaldocumentaryfoodmachine-learningmoviemusicpeople-historicalpodcastsoftware-engineeringtv
-
entity_type(TEXT): Entity type (e.g. movie) -
entity_wikipedia(TEXT): Full Wikipedia link to the root entity
-
--entity-root(TEXT): Optional root entity name override if different from the Wikipedia page title [default: None] -
--levels(INTEGER): Number of levels deep to construct from the central root entity [default: 2] -
--max-sum-total-tokens(INTEGER): Maximum sum of tokens for graph generation [default: 200000] -
--output-folder(TEXT): Folder location to write outputs [default: ./_output/] -
--llm-model(TEXT): The model name [default: gpt-4o-mini] -
--llm-temp(FLOAT): LLM temperature value [default: 0.0] -
--llm-base-url(TEXT): LLM will use custom base URL instead of the automatic one [default: None] -
--version: Display llmgraph version and exit. -
--help: Show this message and exit.
Here are some more examples of the HTML graph output for different entity types and root entities (with commands to generate and links to view full interactive graphs).
Install llmgraph to create your own knowledge graphs! Feel free to share interesting results in the issue section above with a documentation label :)
 Command to generate above concepts-general graph:
Command to generate above concepts-general graph:llmgraph concepts-general "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Knowledge_graph" --levels 4
View entire graph: concepts-general_knowledge-graph_v1.0.0_level4_fully_connected.html
 Command to generate above movie graph:
Command to generate above movie graph:llmgraph movie "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Inception" --levels 4
View entire graph: movie_inception_v1.0.0_level4_fully_connected.html
 Command to generate above company graph:
Command to generate above company graph:llmgraph company "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/OpenAI" --levels 4
View entire graph: company_openai_v1.0.0_level4_fully_connected.html
 Command to generate above people-historical graph:
Command to generate above people-historical graph:llmgraph people-historical "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/John_von_Neumann" --levels 4
View entire graph: people-historical_john-von-neumann_v1.0.0_level4_fully_connected.html
Here is an example of the prompt template, with place holders, used to generate related entities from a given source entity. This is applied recursively to create a knowledge graph, merging duplicated nodes as required.
You are knowledgeable about {knowledgeable_about}.
List, in json array format, the top {top_n} {entities} most like '{{entity_root}}'
with Wikipedia link, reasons for similarity, similarity on scale of 0 to 1.
Format your response in json array format as an array with column names: 'name', 'wikipedia_link', 'reason_for_similarity', and 'similarity'.
Example response: {{{{"name": "Example {entity}","wikipedia_link": "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Example_{entity_underscored}","reason_for_similarity": "Reason for similarity","similarity": 0.5}}}}
It works well on the primary tested LLM, being OpenAI gpt-4o-mini. Results are ok, but not as good using Llama2. The prompt source of truth and additional details can be see in prompts.yaml.
Each entity type has custom placeholders, for example concepts-general and documentary:
concepts-general:
system: You are a highly knowledgeable ontologist and creator of knowledge graphs.
knowledgeable_about: many concepts and ontologies.
entities: concepts
entity: concept name
top_n: 5
documentary:
system: You are knowledgeable about documentaries of all types, and genres.
knowledgeable_about: documentaries of all types, and genres
entities: Documentaries
entity: Documentary
top_n: 5
Each call to the LLM API (and Wikipedia) is cached locally in a .joblib_cache folder. This allows an interrupted run to be resumed without duplicating identical calls. It also allows a re-run with a higher --level option to re-use results from the lower level run (assuming the same entity type and source).
- Contrast graph output from different LLM models (e.g. Llama2 vs Mistral vs ChatGPT-4)
- Investigate the hypothosis that this approach provides insight into how an LLM views the world.
- Include more examples in this documentation and make examples available for easy browsing.
- Instructions for running locally and adding a custom
entity_typeprompt. - Better pyviz html output, in particular including reasons for entity relationship in UI and arguments for pixel size etc.
- Parallelise API calls and result processing.
- Remove dependency on Wikipedia entities as a source.
- Contrast results from llmgraphg with other non-LLM graph construction e.g. using wikipedia page links, or direct article embeddings.
Contributions to llmgraph are welcome. Please follow these steps:
- Fork the repository.
- Create a new branch for your feature or bug fix.
- Make your changes and commit them.
- Create a pull request with a description of your changes.
Thanks to @breitburg for implementing the LiteLLM updates.
- https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.10511 - Knowledge Graph Generation From Text
- https://arxiv.org/abs/2310.04562 - Towards Foundation Models for Knowledge Graph Reasoning
- https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.14268 - BertNet: Harvesting Knowledge Graphs with Arbitrary Relations from Pretrained Language Models
- https://arxiv.org/abs/2312.02783 - Large Language Models on Graphs: A Comprehensive Survey
- https://github.com/aws/graph-notebook - Graph Notebook: easily query and visualize graphs
- https://github.com/KiddoZhu/NBFNet-PyG - PyG re-implementation of Neural Bellman-Ford Networks
- https://caminao.blog/knowledge-management-booklet/a-hitchhikers-guide-to-knowledge-galaxies/ - A Hitchhiker’s Guide to Knowledge Galaxies
- https://github.com/PeterGriffinJin/Awesome-Language-Model-on-Graphs - A curated list of papers and resources based on "Large Language Models on Graphs: A Comprehensive Survey".
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for llmgraph
Similar Open Source Tools

llmgraph
llmgraph is a tool that enables users to create knowledge graphs in GraphML, GEXF, and HTML formats by extracting world knowledge from large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT. It supports various entity types and relationships, offers cache support for efficient graph growth, and provides insights into LLM costs. Users can customize the model used and interact with different LLM providers. The tool allows users to generate interactive graphs based on a specified entity type and Wikipedia link, making it a valuable resource for knowledge graph creation and exploration.
VMind
VMind is an open-source solution for intelligent visualization, providing an intelligent chart component based on LLM by VisActor. It allows users to create chart narrative works with natural language interaction, edit charts through dialogue, and export narratives as videos or GIFs. The tool is easy to use, scalable, supports various chart types, and offers one-click export functionality. Users can customize chart styles, specify themes, and aggregate data using LLM models. VMind aims to enhance efficiency in creating data visualization works through dialogue-based editing and natural language interaction.
storm
STORM is a LLM system that writes Wikipedia-like articles from scratch based on Internet search. While the system cannot produce publication-ready articles that often require a significant number of edits, experienced Wikipedia editors have found it helpful in their pre-writing stage. **Try out our [live research preview](https://storm.genie.stanford.edu/) to see how STORM can help your knowledge exploration journey and please provide feedback to help us improve the system 🙏!**
llm-memorization
The 'llm-memorization' project is a tool designed to index, archive, and search conversations with a local LLM using a SQLite database enriched with automatically extracted keywords. It aims to provide personalized context at the start of a conversation by adding memory information to the initial prompt. The tool automates queries from local LLM conversational management libraries, offers a hybrid search function, enhances prompts based on posed questions, and provides an all-in-one graphical user interface for data visualization. It supports both French and English conversations and prompts for bilingual use.
Pixel-Reasoner
Pixel Reasoner is a framework that introduces reasoning in the pixel-space for Vision-Language Models (VLMs), enabling them to directly inspect, interrogate, and infer from visual evidences. This enhances reasoning fidelity for visual tasks by equipping VLMs with visual reasoning operations like zoom-in and select-frame. The framework addresses challenges like model's imbalanced competence and reluctance to adopt pixel-space operations through a two-phase training approach involving instruction tuning and curiosity-driven reinforcement learning. With these visual operations, VLMs can interact with complex visual inputs such as images or videos to gather necessary information, leading to improved performance across visual reasoning benchmarks.
probsem
ProbSem is a repository that provides a framework to leverage large language models (LLMs) for assigning context-conditional probability distributions over queried strings. It supports OpenAI engines and HuggingFace CausalLM models, and is flexible for research applications in linguistics, cognitive science, program synthesis, and NLP. Users can define prompts, contexts, and queries to derive probability distributions over possible completions, enabling tasks like cloze completion, multiple-choice QA, semantic parsing, and code completion. The repository offers CLI and API interfaces for evaluation, with options to customize models, normalize scores, and adjust temperature for probability distributions.
ChatData
ChatData is a robust chat-with-documents application designed to extract information and provide answers by querying the MyScale free knowledge base or uploaded documents. It leverages the Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) framework, millions of Wikipedia pages, and arXiv papers. Features include self-querying retriever, VectorSQL, session management, and building a personalized knowledge base. Users can effortlessly navigate vast data, explore academic papers, and research documents. ChatData empowers researchers, students, and knowledge enthusiasts to unlock the true potential of information retrieval.
generative-models
Generative Models by Stability AI is a repository that provides various generative models for research purposes. It includes models like Stable Video 4D (SV4D) for video synthesis, Stable Video 3D (SV3D) for multi-view synthesis, SDXL-Turbo for text-to-image generation, and more. The repository focuses on modularity and implements a config-driven approach for building and combining submodules. It supports training with PyTorch Lightning and offers inference demos for different models. Users can access pre-trained models like SDXL-base-1.0 and SDXL-refiner-1.0 under a CreativeML Open RAIL++-M license. The codebase also includes tools for invisible watermark detection in generated images.
ai2-scholarqa-lib
Ai2 Scholar QA is a system for answering scientific queries and literature review by gathering evidence from multiple documents across a corpus and synthesizing an organized report with evidence for each claim. It consists of a retrieval component and a three-step generator pipeline. The retrieval component fetches relevant evidence passages using the Semantic Scholar public API and reranks them. The generator pipeline includes quote extraction, planning and clustering, and summary generation. The system is powered by the ScholarQA class, which includes components like PaperFinder and MultiStepQAPipeline. It requires environment variables for Semantic Scholar API and LLMs, and can be run as local docker containers or embedded into another application as a Python package.

sieves
sieves is a library for zero- and few-shot NLP tasks with structured generation, enabling rapid prototyping of NLP applications without the need for training. It simplifies NLP prototyping by bundling capabilities into a single library, providing zero- and few-shot model support, a unified interface for structured generation, built-in tasks for common NLP operations, easy extendability, document-based pipeline architecture, caching to prevent redundant model calls, and more. The tool draws inspiration from spaCy and spacy-llm, offering features like immediate inference, observable pipelines, integrated tools for document parsing and text chunking, ready-to-use tasks such as classification, summarization, translation, and more, persistence for saving and loading pipelines, distillation for specialized model creation, and caching to optimize performance.
rtdl-num-embeddings
This repository provides the official implementation of the paper 'On Embeddings for Numerical Features in Tabular Deep Learning'. It focuses on transforming scalar continuous features into vectors before integrating them into the main backbone of tabular neural networks, showcasing improved performance. The embeddings for continuous features are shown to enhance the performance of tabular DL models and are applicable to various conventional backbones, offering efficiency comparable to Transformer-based models. The repository includes Python packages for practical usage, exploration of metrics and hyperparameters, and reproducing reported results for different algorithms and datasets.

Biomni
Biomni is a general-purpose biomedical AI agent designed to autonomously execute a wide range of research tasks across diverse biomedical subfields. By integrating cutting-edge large language model (LLM) reasoning with retrieval-augmented planning and code-based execution, Biomni helps scientists dramatically enhance research productivity and generate testable hypotheses.
strwythura
Strwythura is a library and tutorial focused on constructing a knowledge graph from unstructured data sources using state-of-the-art models for named entity recognition. It implements an enhanced GraphRAG approach and curates semantics for optimizing AI application outcomes within a specific domain. The tutorial emphasizes the use of sophisticated NLP pipelines based on spaCy, GLiNER, TextRank, and related libraries to provide better/faster/cheaper results with more control over the intentional arrangement of the knowledge graph. It leverages neurosymbolic AI methods and combines practices from natural language processing, graph data science, entity resolution, ontology pipeline, context engineering, and human-in-the-loop processes.
oasis
OASIS is a scalable, open-source social media simulator that integrates large language models with rule-based agents to realistically mimic the behavior of up to one million users on platforms like Twitter and Reddit. It facilitates the study of complex social phenomena such as information spread, group polarization, and herd behavior, offering a versatile tool for exploring diverse social dynamics and user interactions in digital environments. With features like scalability, dynamic environments, diverse action spaces, and integrated recommendation systems, OASIS provides a comprehensive platform for simulating social media interactions at a large scale.

lhotse
Lhotse is a Python library designed to make speech and audio data preparation flexible and accessible. It aims to attract a wider community to speech processing tasks by providing a Python-centric design and an expressive command-line interface. Lhotse offers standard data preparation recipes, PyTorch Dataset classes for speech tasks, and efficient data preparation for model training with audio cuts. It supports data augmentation, feature extraction, and feature-space cut mixing. The tool extends Kaldi's data preparation recipes with seamless PyTorch integration, human-readable text manifests, and convenient Python classes.
AnyGPT
AnyGPT is a unified multimodal language model that utilizes discrete representations for processing various modalities like speech, text, images, and music. It aligns the modalities for intermodal conversions and text processing. AnyInstruct dataset is constructed for generative models. The model proposes a generative training scheme using Next Token Prediction task for training on a Large Language Model (LLM). It aims to compress vast multimodal data on the internet into a single model for emerging capabilities. The tool supports tasks like text-to-image, image captioning, ASR, TTS, text-to-music, and music captioning.
For similar tasks

llmgraph
llmgraph is a tool that enables users to create knowledge graphs in GraphML, GEXF, and HTML formats by extracting world knowledge from large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT. It supports various entity types and relationships, offers cache support for efficient graph growth, and provides insights into LLM costs. Users can customize the model used and interact with different LLM providers. The tool allows users to generate interactive graphs based on a specified entity type and Wikipedia link, making it a valuable resource for knowledge graph creation and exploration.
chatlab
ChatLab is a Python package that simplifies experimenting with OpenAI's chat models. It provides an interactive interface for chatting with the models and registering custom functions. Users can easily create chat experiments, visualize color palettes, work with function registry, create knowledge graphs, and perform direct parallel function calling. The tool enables users to interact with chat models and customize functionalities for various tasks.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.



