
lantern
PostgreSQL vector database extension for building AI applications
Stars: 756
Lantern is an open-source PostgreSQL database extension designed to store vector data, generate embeddings, and handle vector search operations efficiently. It introduces a new index type called 'lantern_hnsw' for vector columns, which speeds up 'ORDER BY ... LIMIT' queries. Lantern utilizes the state-of-the-art HNSW implementation called usearch. Users can easily install Lantern using Docker, Homebrew, or precompiled binaries. The tool supports various distance functions, index construction parameters, and operator classes for efficient querying. Lantern offers features like embedding generation, interoperability with pgvector, parallel index creation, and external index graph generation. It aims to provide superior performance metrics compared to other similar tools and has a roadmap for future enhancements such as cloud-hosted version, hardware-accelerated distance metrics, industry-specific application templates, and support for version control and A/B testing of embeddings.
README:
Lantern is an open-source PostgreSQL database extension to store vector data, generate embeddings, and handle vector search operations.
It provides a new index type for vector columns called lantern_hnsw which speeds up ORDER BY ... LIMIT queries.
Lantern builds and uses usearch, a single-header state-of-the-art HNSW implementation.
If you don’t have PostgreSQL already, use Lantern with Docker to get started quickly:
docker run --pull=always --rm -p 5432:5432 -e "POSTGRES_USER=$USER" -e "POSTGRES_PASSWORD=postgres" -v ./lantern_data:/var/lib/postgresql/data lanterndata/lantern:latest-pg15Then, you can connect to the database via postgresql://$USER:postgres@localhost/postgres.
To install Lantern using homebrew:
brew tap lanterndata/lantern
brew install lantern && lantern_install
You can also install Lantern on top of PostgreSQL from our precompiled binaries via a single make install.
Alternatively, you can use Lantern in one click using Replit.
Prerequisites:
cmake version: >=3.3
gcc && g++ version: >=11 when building portable binaries, >= 12 when building on new hardware or with CPU-specific vectorization
PostgreSQL 11, 12, 13, 14, 15 or 16
Corresponding development package for PostgreSQL (postgresql-server-dev-$version)
To build Lantern on new hardware or with CPU-specific vectorization:
git clone --recursive https://github.com/lanterndata/lantern.git
cd lantern
cmake -DMARCH_NATIVE=ON -S lantern_hnsw -B build
make -C build install -j
To build portable Lantern binaries:
git clone --recursive https://github.com/lanterndata/lantern.git
cd lantern
cmake -DMARCH_NATIVE=OFF -S lantern_hnsw -B build
make -C build install -j
Lantern retains the standard PostgreSQL interface, so it is compatible with all of your favorite tools in the PostgreSQL ecosystem.
First, enable Lantern in SQL (e.g. via psql shell)
CREATE EXTENSION lantern;Note: After running the above, lantern extension is only available on the current postgres DATABASE (single postgres instance may have multiple such DATABASES). When connecting to a different DATABASE, make sure to run the above command for the new one as well. For example:
CREATE DATABASE newdb;
\c newdb
CREATE EXTENSION lantern;Create a table with a vector column and add your data
CREATE TABLE small_world (id integer, vector real[3]);
INSERT INTO small_world (id, vector) VALUES (0, '{0,0,0}'), (1, '{0,0,1}');Create an hnsw index on the table via lantern_hnsw:
CREATE INDEX ON small_world USING lantern_hnsw (vector);Customize lantern_hnsw index parameters depending on your vector data, such as the distance function (e.g., dist_l2sq_ops), index construction parameters, and index search parameters.
CREATE INDEX ON small_world USING lantern_hnsw (vector dist_l2sq_ops)
WITH (M=2, ef_construction=10, ef=4, dim=3);Start querying data
SET enable_seqscan = false;
SELECT id, l2sq_dist(vector, ARRAY[0,0,0]) AS dist
FROM small_world ORDER BY vector <-> ARRAY[0,0,0] LIMIT 1;Lantern supports several distance functions in the index and it has 2 modes for operators:
-
lantern.pgvector_compat=TRUE(default) In this mode there are 3 operators available<->(l2sq),<=>(cosine),<+>(hamming).Note that in this mode, you need to use right operator in order to trigger an index scan.
-
lantern.pgvector_compat=FALSEIn this mode you only need to specify the distance function used for a column at index creation time. Lantern will automatically infer the distance function to use for search so you always use<?>operator in search queries.Note that in this mode, the operator
<?>is intended exclusively for use with index lookups. If you expect to not use the index in a query, use the distance function directly (e.g.l2sq_dist(v1, v2))
To switch between modes set
lantern.pgvector_compatvariable toTRUEorFALSE.
There are four defined operator classes that can be employed during index creation:
-
dist_l2sq_ops: Default for the typereal[] -
dist_vec_l2sq_ops: Default for the typevector -
dist_cos_ops: Applicable to the typereal[] -
dist_vec_cos_ops: Applicable to the typevector -
dist_hamming_ops: Applicable to the typeinteger[]
The M, ef, and ef_construction parameters control the performance of the HNSW algorithm for your use case.
- In general, lower
Mandef_constructionspeed up index creation at the cost of recall. - Lower
Mandefimprove search speed and result in fewer shared buffer hits at the cost of recall. Tuning these parameters will require experimentation for your specific use case.
- If you have previously cloned Lantern and would like to update run
git pull && git submodule update --recursive
- Embedding generation for popular use cases (CLIP model, Hugging Face models, custom model)
- Interoperability with pgvector's data type, so anyone using pgvector can switch to Lantern
- Parallel index creation via an external indexer
- Ability to generate the index graph outside of the database server
- Support for creating the index outside of the database and inside another instance allows you to create an index without interrupting database workflows.
- See all of our helper functions to better enable your workflows
Important takeaways:
- There's three key metrics we track.
CREATE INDEXtime,SELECTthroughput, andSELECTlatency. - We match or outperform pgvector and pg_embedding (Neon) on all of these metrics.
- We plan to continue to make performance improvements to ensure we are the best performing database.
- Cloud-hosted version of Lantern - Sign up here
- Hardware-accelerated distance metrics, tailored for your CPU, enabling faster queries
- Templates and guides for building applications for different industries
- More tools for generating embeddings (support for third party model API’s, more local models)
- Support for version control and A/B test embeddings
- Autotuned index type that will choose appropriate creation parameters
- Support for 1 byte and 2 byte vector elements, and up to 8000 dimensional vectors (PR #19)
- Request a feature at [email protected]
- GitHub issues: report bugs or issues with Lantern
- Need support? Contact [email protected]. We are happy to troubleshoot issues and advise on how to use Lantern for your use case
- We welcome community contributions! Feel free to open an issue or a PR. If you contact [email protected], we can find an open issue or project that fits you
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for lantern
Similar Open Source Tools

lantern
Lantern is an open-source PostgreSQL database extension designed to store vector data, generate embeddings, and handle vector search operations efficiently. It introduces a new index type called 'lantern_hnsw' for vector columns, which speeds up 'ORDER BY ... LIMIT' queries. Lantern utilizes the state-of-the-art HNSW implementation called usearch. Users can easily install Lantern using Docker, Homebrew, or precompiled binaries. The tool supports various distance functions, index construction parameters, and operator classes for efficient querying. Lantern offers features like embedding generation, interoperability with pgvector, parallel index creation, and external index graph generation. It aims to provide superior performance metrics compared to other similar tools and has a roadmap for future enhancements such as cloud-hosted version, hardware-accelerated distance metrics, industry-specific application templates, and support for version control and A/B testing of embeddings.
safety-tooling
This repository, safety-tooling, is designed to be shared across various AI Safety projects. It provides an LLM API with a common interface for OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google models. The aim is to facilitate collaboration among AI Safety researchers, especially those with limited software engineering backgrounds, by offering a platform for contributing to a larger codebase. The repo can be used as a git submodule for easy collaboration and updates. It also supports pip installation for convenience. The repository includes features for installation, secrets management, linting, formatting, Redis configuration, testing, dependency management, inference, finetuning, API usage tracking, and various utilities for data processing and experimentation.

lhotse
Lhotse is a Python library designed to make speech and audio data preparation flexible and accessible. It aims to attract a wider community to speech processing tasks by providing a Python-centric design and an expressive command-line interface. Lhotse offers standard data preparation recipes, PyTorch Dataset classes for speech tasks, and efficient data preparation for model training with audio cuts. It supports data augmentation, feature extraction, and feature-space cut mixing. The tool extends Kaldi's data preparation recipes with seamless PyTorch integration, human-readable text manifests, and convenient Python classes.
mosec
Mosec is a high-performance and flexible model serving framework for building ML model-enabled backend and microservices. It bridges the gap between any machine learning models you just trained and the efficient online service API. * **Highly performant** : web layer and task coordination built with Rust 🦀, which offers blazing speed in addition to efficient CPU utilization powered by async I/O * **Ease of use** : user interface purely in Python 🐍, by which users can serve their models in an ML framework-agnostic manner using the same code as they do for offline testing * **Dynamic batching** : aggregate requests from different users for batched inference and distribute results back * **Pipelined stages** : spawn multiple processes for pipelined stages to handle CPU/GPU/IO mixed workloads * **Cloud friendly** : designed to run in the cloud, with the model warmup, graceful shutdown, and Prometheus monitoring metrics, easily managed by Kubernetes or any container orchestration systems * **Do one thing well** : focus on the online serving part, users can pay attention to the model optimization and business logic
rtdl-num-embeddings
This repository provides the official implementation of the paper 'On Embeddings for Numerical Features in Tabular Deep Learning'. It focuses on transforming scalar continuous features into vectors before integrating them into the main backbone of tabular neural networks, showcasing improved performance. The embeddings for continuous features are shown to enhance the performance of tabular DL models and are applicable to various conventional backbones, offering efficiency comparable to Transformer-based models. The repository includes Python packages for practical usage, exploration of metrics and hyperparameters, and reproducing reported results for different algorithms and datasets.
generative-models
Generative Models by Stability AI is a repository that provides various generative models for research purposes. It includes models like Stable Video 4D (SV4D) for video synthesis, Stable Video 3D (SV3D) for multi-view synthesis, SDXL-Turbo for text-to-image generation, and more. The repository focuses on modularity and implements a config-driven approach for building and combining submodules. It supports training with PyTorch Lightning and offers inference demos for different models. Users can access pre-trained models like SDXL-base-1.0 and SDXL-refiner-1.0 under a CreativeML Open RAIL++-M license. The codebase also includes tools for invisible watermark detection in generated images.
qsv
qsv is a command line program for querying, slicing, indexing, analyzing, filtering, enriching, transforming, sorting, validating, joining, formatting & converting tabular data (CSV, spreadsheets, DBs, parquet, etc). Commands are simple, composable & 'blazing fast'. It is a blazing-fast data-wrangling toolkit with a focus on speed, processing very large files, and being a complete data-wrangling toolkit. It is designed to be portable, easy to use, secure, and easy to contribute to. qsv follows the RFC 4180 CSV standard, requires UTF-8 encoding, and supports various file formats. It has extensive shell completion support, automatic compression/decompression using Snappy, and supports environment variables and dotenv files. qsv has a comprehensive test suite and is dual-licensed under MIT or the UNLICENSE.
llm-memorization
The 'llm-memorization' project is a tool designed to index, archive, and search conversations with a local LLM using a SQLite database enriched with automatically extracted keywords. It aims to provide personalized context at the start of a conversation by adding memory information to the initial prompt. The tool automates queries from local LLM conversational management libraries, offers a hybrid search function, enhances prompts based on posed questions, and provides an all-in-one graphical user interface for data visualization. It supports both French and English conversations and prompts for bilingual use.
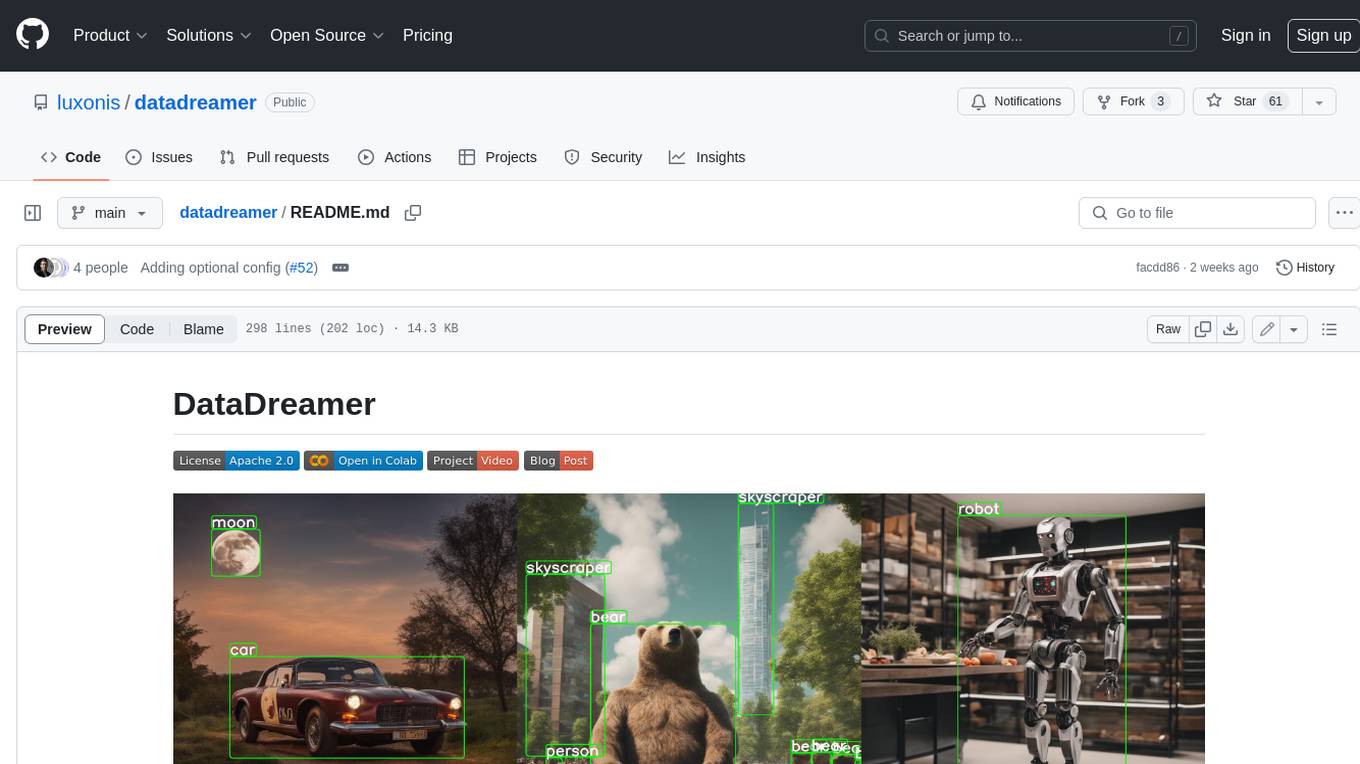
datadreamer
DataDreamer is an advanced toolkit designed to facilitate the development of edge AI models by enabling synthetic data generation, knowledge extraction from pre-trained models, and creation of efficient and potent models. It eliminates the need for extensive datasets by generating synthetic datasets, leverages latent knowledge from pre-trained models, and focuses on creating compact models suitable for integration into any device and performance for specialized tasks. The toolkit offers features like prompt generation, image generation, dataset annotation, and tools for training small-scale neural networks for edge deployment. It provides hardware requirements, usage instructions, available models, and limitations to consider while using the library.

blinkid-android
The BlinkID Android SDK is a comprehensive solution for implementing secure document scanning and extraction. It offers powerful capabilities for extracting data from a wide range of identification documents. The SDK provides features for integrating document scanning into Android apps, including camera requirements, SDK resource pre-bundling, customizing the UX, changing default strings and localization, troubleshooting integration difficulties, and using the SDK through various methods. It also offers options for completely custom UX with low-level API integration. The SDK size is optimized for different processor architectures, and API documentation is available for reference. For any questions or support, users can contact the Microblink team at help.microblink.com.
vector-inference
This repository provides an easy-to-use solution for running inference servers on Slurm-managed computing clusters using vLLM. All scripts in this repository run natively on the Vector Institute cluster environment. Users can deploy models as Slurm jobs, check server status and performance metrics, and shut down models. The repository also supports launching custom models with specific configurations. Additionally, users can send inference requests and set up an SSH tunnel to run inference from a local device.
chatgpt-cli
ChatGPT CLI provides a powerful command-line interface for seamless interaction with ChatGPT models via OpenAI and Azure. It features streaming capabilities, extensive configuration options, and supports various modes like streaming, query, and interactive mode. Users can manage thread-based context, sliding window history, and provide custom context from any source. The CLI also offers model and thread listing, advanced configuration options, and supports GPT-4, GPT-3.5-turbo, and Perplexity's models. Installation is available via Homebrew or direct download, and users can configure settings through default values, a config.yaml file, or environment variables.
neo4j-graphrag-python
The Neo4j GraphRAG package for Python is an official repository that provides features for creating and managing vector indexes in Neo4j databases. It aims to offer developers a reliable package with long-term commitment, maintenance, and fast feature updates. The package supports various Python versions and includes functionalities for creating vector indexes, populating them, and performing similarity searches. It also provides guidelines for installation, examples, and development processes such as installing dependencies, making changes, and running tests.

Trace
Trace is a new AutoDiff-like tool for training AI systems end-to-end with general feedback. It generalizes the back-propagation algorithm by capturing and propagating an AI system's execution trace. Implemented as a PyTorch-like Python library, users can write Python code directly and use Trace primitives to optimize certain parts, similar to training neural networks.
paxml
Pax is a framework to configure and run machine learning experiments on top of Jax.
kvpress
This repository implements multiple key-value cache pruning methods and benchmarks using transformers, aiming to simplify the development of new methods for researchers and developers in the field of long-context language models. It provides a set of 'presses' that compress the cache during the pre-filling phase, with each press having a compression ratio attribute. The repository includes various training-free presses, special presses, and supports KV cache quantization. Users can contribute new presses and evaluate the performance of different presses on long-context datasets.
For similar tasks

lantern
Lantern is an open-source PostgreSQL database extension designed to store vector data, generate embeddings, and handle vector search operations efficiently. It introduces a new index type called 'lantern_hnsw' for vector columns, which speeds up 'ORDER BY ... LIMIT' queries. Lantern utilizes the state-of-the-art HNSW implementation called usearch. Users can easily install Lantern using Docker, Homebrew, or precompiled binaries. The tool supports various distance functions, index construction parameters, and operator classes for efficient querying. Lantern offers features like embedding generation, interoperability with pgvector, parallel index creation, and external index graph generation. It aims to provide superior performance metrics compared to other similar tools and has a roadmap for future enhancements such as cloud-hosted version, hardware-accelerated distance metrics, industry-specific application templates, and support for version control and A/B testing of embeddings.
blockoli
Blockoli is a high-performance tool for code indexing, embedding generation, and semantic search tool for use with LLMs. It is built in Rust and uses the ASTerisk crate for semantic code parsing. Blockoli allows you to efficiently index, store, and search code blocks and their embeddings using vector similarity. Key features include indexing code blocks from a codebase, generating vector embeddings for code blocks using a pre-trained model, storing code blocks and their embeddings in a SQLite database, performing efficient similarity search on code blocks using vector embeddings, providing a REST API for easy integration with other tools and platforms, and being fast and memory-efficient due to its implementation in Rust.
client-js
The Mistral JavaScript client is a library that allows you to interact with the Mistral AI API. With this client, you can perform various tasks such as listing models, chatting with streaming, chatting without streaming, and generating embeddings. To use the client, you can install it in your project using npm and then set up the client with your API key. Once the client is set up, you can use it to perform the desired tasks. For example, you can use the client to chat with a model by providing a list of messages. The client will then return the response from the model. You can also use the client to generate embeddings for a given input. The embeddings can then be used for various downstream tasks such as clustering or classification.
fastllm
A collection of LLM services you can self host via docker or modal labs to support your applications development. The goal is to provide docker containers or modal labs deployments of common patterns when using LLMs and endpoints to integrate easily with existing codebases using the openai api. It supports GPT4all's embedding api, JSONFormer api for chat completion, Cross Encoders based on sentence transformers, and provides documentation using MkDocs.
openai-kotlin
OpenAI Kotlin API client is a Kotlin client for OpenAI's API with multiplatform and coroutines capabilities. It allows users to interact with OpenAI's API using Kotlin programming language. The client supports various features such as models, chat, images, embeddings, files, fine-tuning, moderations, audio, assistants, threads, messages, and runs. It also provides guides on getting started, chat & function call, file source guide, and assistants. Sample apps are available for reference, and troubleshooting guides are provided for common issues. The project is open-source and licensed under the MIT license, allowing contributions from the community.
azure-search-vector-samples
This repository provides code samples in Python, C#, REST, and JavaScript for vector support in Azure AI Search. It includes demos for various languages showcasing vectorization of data, creating indexes, and querying vector data. Additionally, it offers tools like Azure AI Search Lab for experimenting with AI-enabled search scenarios in Azure and templates for deploying custom chat-with-your-data solutions. The repository also features documentation on vector search, hybrid search, creating and querying vector indexes, and REST API references for Azure AI Search and Azure OpenAI Service.
llm
LLM is a CLI utility and Python library for interacting with Large Language Models, both via remote APIs and models that can be installed and run on your own machine. It allows users to run prompts from the command-line, store results in SQLite, generate embeddings, and more. The tool supports self-hosted language models via plugins and provides access to remote and local models. Users can install plugins to access models by different providers, including models that can be installed and run on their own device. LLM offers various options for running Mistral models in the terminal and enables users to start chat sessions with models. Additionally, users can use a system prompt to provide instructions for processing input to the tool.
GenAI-Showcase
The Generative AI Use Cases Repository showcases a wide range of applications in generative AI, including Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), AI Agents, and industry-specific use cases. It provides practical notebooks and guidance on utilizing frameworks such as LlamaIndex and LangChain, and demonstrates how to integrate models from leading AI research companies like Anthropic and OpenAI.
For similar jobs
db2rest
DB2Rest is a modern low-code REST DATA API platform that simplifies the development of intelligent applications. It seamlessly integrates existing and new databases with language models (LMs/LLMs) and vector stores, enabling the rapid delivery of context-aware, reasoning applications without vendor lock-in.

mage-ai
Mage is an open-source data pipeline tool for transforming and integrating data. It offers an easy developer experience, engineering best practices built-in, and data as a first-class citizen. Mage makes it easy to build, preview, and launch data pipelines, and provides observability and scaling capabilities. It supports data integrations, streaming pipelines, and dbt integration.

airbyte
Airbyte is an open-source data integration platform that makes it easy to move data from any source to any destination. With Airbyte, you can build and manage data pipelines without writing any code. Airbyte provides a library of pre-built connectors that make it easy to connect to popular data sources and destinations. You can also create your own connectors using Airbyte's no-code Connector Builder or low-code CDK. Airbyte is used by data engineers and analysts at companies of all sizes to build and manage their data pipelines.

labelbox-python
Labelbox is a data-centric AI platform for enterprises to develop, optimize, and use AI to solve problems and power new products and services. Enterprises use Labelbox to curate data, generate high-quality human feedback data for computer vision and LLMs, evaluate model performance, and automate tasks by combining AI and human-centric workflows. The academic & research community uses Labelbox for cutting-edge AI research.

telemetry-airflow
This repository codifies the Airflow cluster that is deployed at workflow.telemetry.mozilla.org (behind SSO) and commonly referred to as "WTMO" or simply "Airflow". Some links relevant to users and developers of WTMO: * The `dags` directory in this repository contains some custom DAG definitions * Many of the DAGs registered with WTMO don't live in this repository, but are instead generated from ETL task definitions in bigquery-etl * The Data SRE team maintains a WTMO Developer Guide (behind SSO)

airflow
Apache Airflow (or simply Airflow) is a platform to programmatically author, schedule, and monitor workflows. When workflows are defined as code, they become more maintainable, versionable, testable, and collaborative. Use Airflow to author workflows as directed acyclic graphs (DAGs) of tasks. The Airflow scheduler executes your tasks on an array of workers while following the specified dependencies. Rich command line utilities make performing complex surgeries on DAGs a snap. The rich user interface makes it easy to visualize pipelines running in production, monitor progress, and troubleshoot issues when needed.

airbyte-platform
Airbyte is an open-source data integration platform that makes it easy to move data from any source to any destination. With Airbyte, you can build and manage data pipelines without writing any code. Airbyte provides a library of pre-built connectors that make it easy to connect to popular data sources and destinations. You can also create your own connectors using Airbyte's low-code Connector Development Kit (CDK). Airbyte is used by data engineers and analysts at companies of all sizes to move data for a variety of purposes, including data warehousing, data analysis, and machine learning.
chronon
Chronon is a platform that simplifies and improves ML workflows by providing a central place to define features, ensuring point-in-time correctness for backfills, simplifying orchestration for batch and streaming pipelines, offering easy endpoints for feature fetching, and guaranteeing and measuring consistency. It offers benefits over other approaches by enabling the use of a broad set of data for training, handling large aggregations and other computationally intensive transformations, and abstracting away the infrastructure complexity of data plumbing.



