
fastllm
A collection of LLM services you can self host via docker or modal labs to support your applications development
Stars: 154
A collection of LLM services you can self host via docker or modal labs to support your applications development. The goal is to provide docker containers or modal labs deployments of common patterns when using LLMs and endpoints to integrate easily with existing codebases using the openai api. It supports GPT4all's embedding api, JSONFormer api for chat completion, Cross Encoders based on sentence transformers, and provides documentation using MkDocs.
README:
A collection of LLM services you can self host via docker or modal labs to support your applications development
The goal of this repo is to provide a series of docker containers, or modal labs deployments of common patterns when using LLMs and provide endpoints that allows you to intergrate easily with existing codebases that use the popular openai api.
- Support GPT4all's embedding api and match it to
openai.com/v1/embedding - Support JSONFormer api to match it to chatcompletion with function_calls
- Support Cross Encoders based on sentence transformers for any huggingface model
- Provide great documentation and runbooks using MkDocs
Before you begin, ensure that you have the following installed on your system:
- Git: Visit the Git website to download and install Git on your operating system.
- Docker: Visit the Docker website to download and install Docker on your operating system.
To clone the repository to your local machine, follow these steps:
-
Open a terminal or command prompt.
-
Change the current directory to where you want to store the repository.
-
Run the following command to clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/jxnl/fastllm.gitThis will create a local copy of the repository on your machine.
Once you have cloned the repository, navigate to the root directory of the application where the Dockerfile is located.
To build the Docker image, use the docker build command. The syntax is as follows:
docker build -t <image_name>:<tag> .-
<image_name>: Choose a meaningful name for your Docker image, e.g.,my-app. -
<tag>: Specify a version or tag for your image, e.g.,v1.0.
Replace <image_name> and <tag> with your desired values. The . at the end of the command refers to the current directory, which is where the Dockerfile resides.
Example:
docker build -t my-app:v1.0 .The Docker build process will read the Dockerfile instructions and create an image containing your application and its dependencies.
Once the Docker image is built, you can run a container based on that image:
docker run -d -p <host_port>:8000 <image_name>:<tag>-
<host_port>: The port number on your host machine where you want to access the application. -
8000: The port number exposed by the application inside the Docker container.
Example:
docker run -d -p 8000:8000 my-app:v1.0After running the container, you can access the application running inside the container through your web browser or any HTTP client by visiting http://localhost:8000.
To start using a Docker image from Docker Hub, follow these steps:
-
Open a terminal or command prompt.
-
Run the following command to pull the desired Docker image from Docker Hub:
docker pull jxnl/embed-gpt4all
docker run -d -p 8000:8000 jxnl/embed-gpt4all:latestimport openai
openai.api_base = "http://localhost:8000"This will download the xnl/embed-gpt4all image from Docker Hub with the "latest" tag.
Once the Docker image is pulled, you can run a container based on that image:
This command will run the jxnl/embed-gpt4all container in detached mode (-d) and forward port 8000 on the host to port 8000 inside the container.
After running the container, you can access the application running inside the container through your web browser or any HTTP client by visiting http://localhost:8000.
To stop a running container, use the docker stop command followed by the container ID or name:
docker stop <container_id_or_name>To remove a stopped container, use the docker rm command followed by the container ID or name:
docker rm <container_id_or_name>To stop a running container, use the docker stop command followed by the container ID or name:
docker stop <container_id_or_name>To remove a stopped container, use the docker rm command followed by the container ID or name:
docker rm <container_id_or_name>To remove the Docker image, use the docker rmi command followed by the image ID or name:
docker rmi <image_id_or_name>Remember that removing an image is irreversible and cannot be undone.
Contributions are welcome! If you have any suggestions, improvements, or bug fixes, please open an issue or submit a pull request.
This project is licensed under the MIT License
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for fastllm
Similar Open Source Tools

fastllm
A collection of LLM services you can self host via docker or modal labs to support your applications development. The goal is to provide docker containers or modal labs deployments of common patterns when using LLMs and endpoints to integrate easily with existing codebases using the openai api. It supports GPT4all's embedding api, JSONFormer api for chat completion, Cross Encoders based on sentence transformers, and provides documentation using MkDocs.
aisheets
Hugging Face AI Sheets is an open-source tool for building, enriching, and transforming datasets using AI models with no code. It can be deployed locally or on the Hub, providing access to thousands of open models. Users can easily generate datasets, run data generation scripts, and customize inference endpoints for text generation. The tool supports custom LLMs and offers advanced configuration options for authentication, inference, and miscellaneous settings. With AI Sheets, users can leverage the power of AI models without writing any code, making dataset management and transformation efficient and accessible.
CLI
Bito CLI provides a command line interface to the Bito AI chat functionality, allowing users to interact with the AI through commands. It supports complex automation and workflows, with features like long prompts and slash commands. Users can install Bito CLI on Mac, Linux, and Windows systems using various methods. The tool also offers configuration options for AI model type, access key management, and output language customization. Bito CLI is designed to enhance user experience in querying AI models and automating tasks through the command line interface.
openui
OpenUI is a tool designed to simplify the process of building UI components by allowing users to describe UI using their imagination and see it rendered live. It supports converting HTML to React, Svelte, Web Components, etc. The tool is open source and aims to make UI development fun, fast, and flexible. It integrates with various AI services like OpenAI, Groq, Gemini, Anthropic, Cohere, and Mistral, providing users with the flexibility to use different models. OpenUI also supports LiteLLM for connecting to various LLM services and allows users to create custom proxy configs. The tool can be run locally using Docker or Python, and it offers a development environment for quick setup and testing.
bolt-python-ai-chatbot
The 'bolt-python-ai-chatbot' is a Slack chatbot app template that allows users to integrate AI-powered conversations into their Slack workspace. Users can interact with the bot in conversations and threads, send direct messages for private interactions, use commands to communicate with the bot, customize bot responses, and store user preferences. The app supports integration with Workflow Builder, custom language models, and different AI providers like OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google Cloud Vertex AI. Users can create user objects, manage user states, and select from various AI models for communication.

fasttrackml
FastTrackML is an experiment tracking server focused on speed and scalability, fully compatible with MLFlow. It provides a user-friendly interface to track and visualize your machine learning experiments, making it easy to compare different models and identify the best performing ones. FastTrackML is open source and can be easily installed and run with pip or Docker. It is also compatible with the MLFlow Python package, making it easy to integrate with your existing MLFlow workflows.
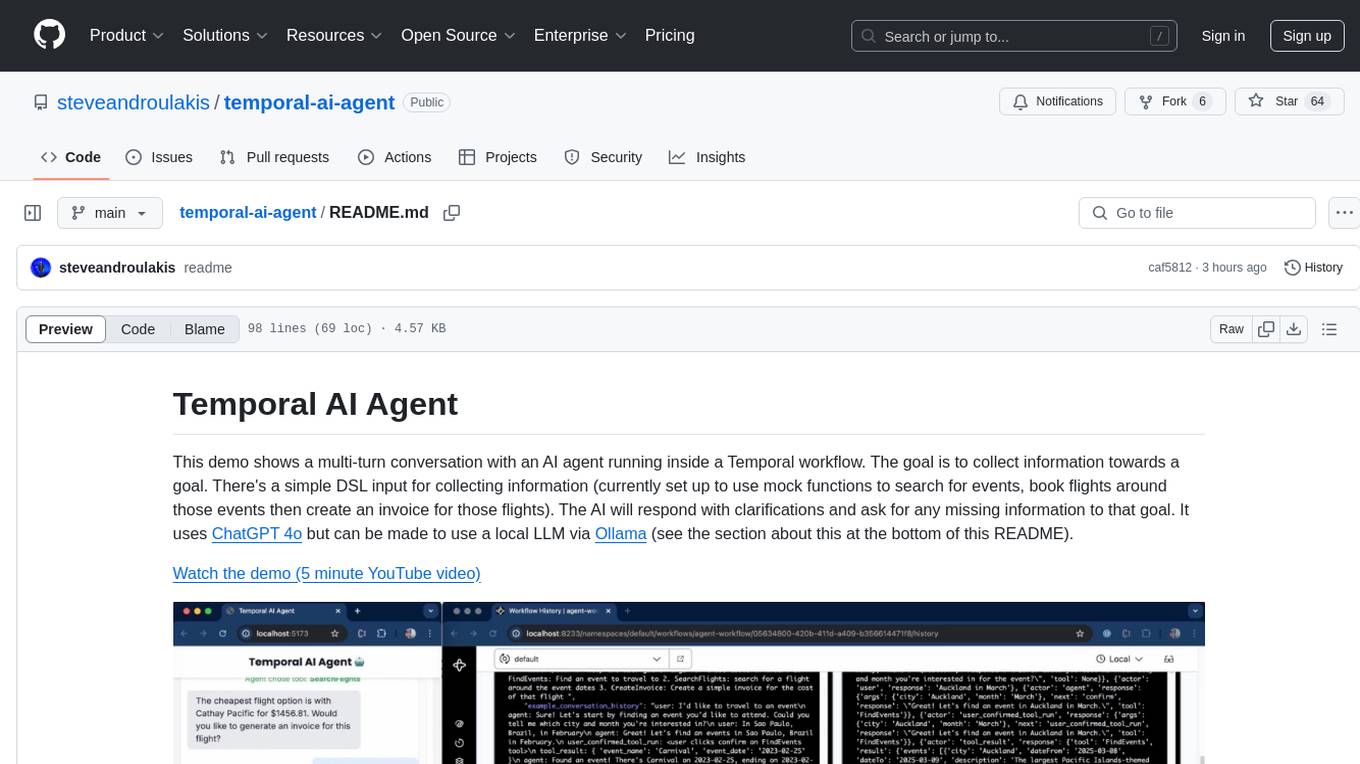
temporal-ai-agent
Temporal AI Agent is a demo showcasing a multi-turn conversation with an AI agent running inside a Temporal workflow. The agent collects information towards a goal using a simple DSL input. It is currently set up to search for events, book flights around those events, and create an invoice for those flights. The AI agent responds with clarifications and prompts for missing information. Users can configure the agent to use ChatGPT 4o or a local LLM via Ollama. The tool requires Rapidapi key for sky-scrapper to find flights and a Stripe key for creating invoices. Users can customize the agent by modifying tool and goal definitions in the codebase.
AilyticMinds
AilyticMinds Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app designed for easy deployment and improved backend compatibility. It provides a user-friendly interface for creating and hosting chatbots, with features like mobile layout optimization and support for various providers. The tool utilizes Supabase for data storage and management, offering a secure and scalable solution for chatbot development. Users can quickly set up their own instances locally or in the cloud, with detailed instructions provided for installation and configuration.
aiarena-web
aiarena-web is a website designed for running the aiarena.net infrastructure. It consists of different modules such as core functionality, web API endpoints, frontend templates, and a module for linking users to their Patreon accounts. The website serves as a platform for obtaining new matches, reporting results, featuring match replays, and connecting with Patreon supporters. The project is licensed under GPLv3 in 2019.
0chain
Züs is a high-performance cloud on a fast blockchain offering privacy and configurable uptime. It uses erasure code to distribute data between data and parity servers, allowing flexibility for IT managers to design for security and uptime. Users can easily share encrypted data with business partners through a proxy key sharing protocol. The ecosystem includes apps like Blimp for cloud migration, Vult for personal cloud storage, and Chalk for NFT artists. Other apps include Bolt for secure wallet and staking, Atlus for blockchain explorer, and Chimney for network participation. The QoS protocol challenges providers based on response time, while the privacy protocol enables secure data sharing. Züs supports hybrid and multi-cloud architectures, allowing users to improve regulatory compliance and security requirements.
metaflow-service
Metaflow Service is a metadata service implementation for Metaflow, providing a thin wrapper around a database to keep track of metadata associated with Flows, Runs, Steps, Tasks, and Artifacts. It includes features for managing DB migrations, launching compatible versions of the metadata service, and executing flows locally. The service can be run using Docker or as a standalone service, with options for testing and running unit/integration tests. Users can interact with the service via API endpoints or utility CLI tools.
polis
Polis is an AI powered sentiment gathering platform that offers a more organic approach than surveys and requires less effort than focus groups. It provides a comprehensive wiki, main deployment at https://pol.is, discussions, issue tracking, and project board for users. Polis can be set up using Docker infrastructure and offers various commands for building and running containers. Users can test their instance, update the system, and deploy Polis for production. The tool also provides developer conveniences for code reloading, type checking, and database connections. Additionally, Polis supports end-to-end browser testing using Cypress and offers troubleshooting tips for common Docker and npm issues.
ai-town
AI Town is a virtual town where AI characters live, chat, and socialize. This project provides a deployable starter kit for building and customizing your own version of AI Town. It features a game engine, database, vector search, auth, text model, deployment, pixel art generation, background music generation, and local inference. You can customize your own simulation by creating characters and stories, updating spritesheets, changing the background, and modifying the background music.
seer
Seer is a service that provides AI capabilities to Sentry by running inference on Sentry issues and providing user insights. It is currently in early development and not yet compatible with self-hosted Sentry instances. The tool requires access to internal Sentry resources and is intended for internal Sentry employees. Users can set up the environment, download model artifacts, integrate with local Sentry, run evaluations for Autofix AI agent, and deploy to a sandbox staging environment. Development commands include applying database migrations, creating new migrations, running tests, and more. The tool also supports VCRs for recording and replaying HTTP requests.
tutor-gpt
Tutor-GPT is an LLM powered learning companion developed by Plastic Labs. It dynamically reasons about your learning needs and updates its own prompts to best serve you. It is an expansive learning companion that uses theory of mind experiments to provide personalized learning experiences. The project is split into different modules for backend logic, including core logic, discord bot implementation, FastAPI API interface, NextJS web front end, common utilities, and SQL scripts for setting up local supabase. Tutor-GPT is powered by Honcho to build robust user representations and create personalized experiences for each user. Users can run their own instance of the bot by following the provided instructions.
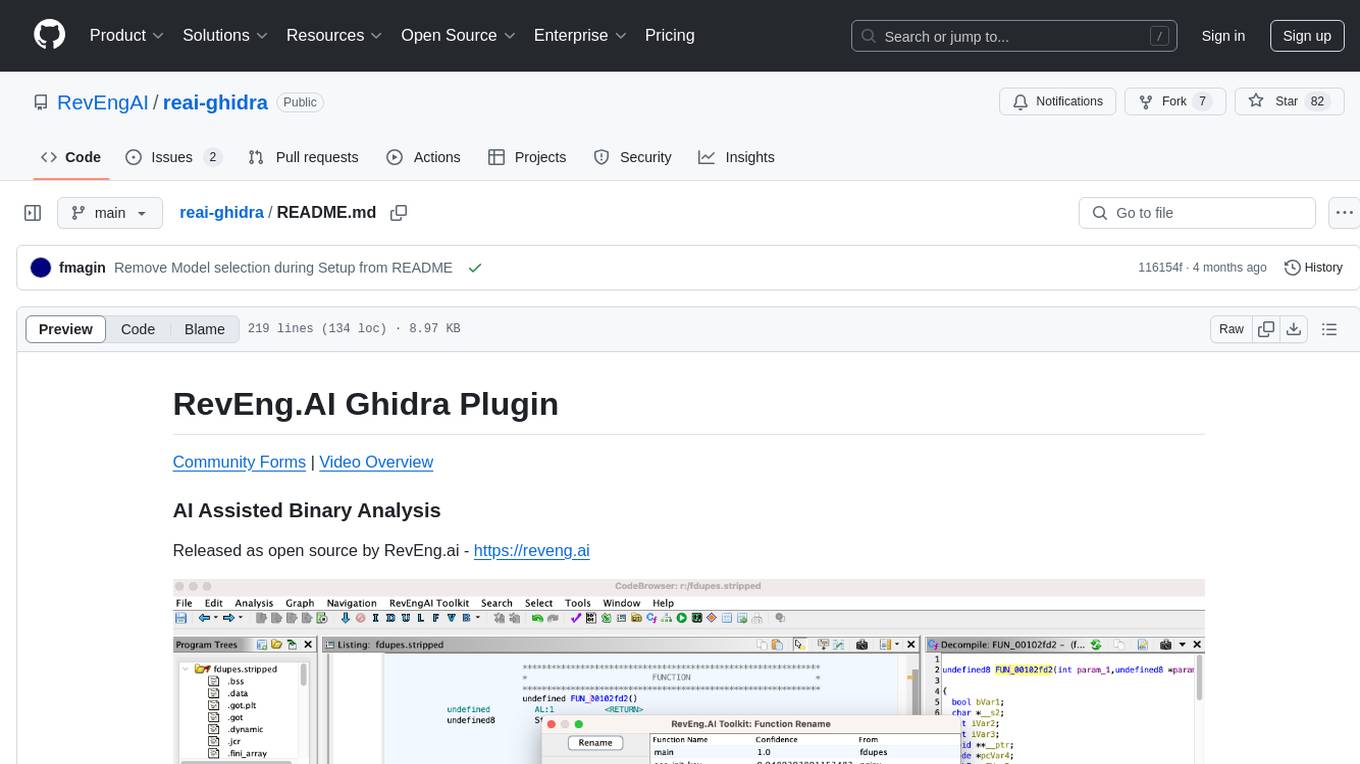
reai-ghidra
The RevEng.AI Ghidra Plugin by RevEng.ai allows users to interact with their API within Ghidra for Binary Code Similarity analysis to aid in Reverse Engineering stripped binaries. Users can upload binaries, rename functions above a confidence threshold, and view similar functions for a selected function.
For similar tasks

fastllm
A collection of LLM services you can self host via docker or modal labs to support your applications development. The goal is to provide docker containers or modal labs deployments of common patterns when using LLMs and endpoints to integrate easily with existing codebases using the openai api. It supports GPT4all's embedding api, JSONFormer api for chat completion, Cross Encoders based on sentence transformers, and provides documentation using MkDocs.
llm-apps-java-spring-ai
The 'LLM Applications with Java and Spring AI' repository provides samples demonstrating how to build Java applications powered by Generative AI and Large Language Models (LLMs) using Spring AI. It includes projects for question answering, chat completion models, prompts, templates, multimodality, output converters, embedding models, document ETL pipeline, function calling, image models, and audio models. The repository also lists prerequisites such as Java 21, Docker/Podman, Mistral AI API Key, OpenAI API Key, and Ollama. Users can explore various use cases and projects to leverage LLMs for text generation, vector transformation, document processing, and more.

simple-openai
Simple-OpenAI is a Java library that provides a simple way to interact with the OpenAI API. It offers consistent interfaces for various OpenAI services like Audio, Chat Completion, Image Generation, and more. The library uses CleverClient for HTTP communication, Jackson for JSON parsing, and Lombok to reduce boilerplate code. It supports asynchronous requests and provides methods for synchronous calls as well. Users can easily create objects to communicate with the OpenAI API and perform tasks like text-to-speech, transcription, image generation, and chat completions.
gateway
Adaline Gateway is a fully local production-grade Super SDK that offers a unified interface for calling over 200+ LLMs. It is production-ready, supports batching, retries, caching, callbacks, and OpenTelemetry. Users can create custom plugins and providers for seamless integration with their infrastructure.
sandbox
Sandbox is an open-source cloud-based code editing environment with custom AI code autocompletion and real-time collaboration. It consists of a frontend built with Next.js, TailwindCSS, Shadcn UI, Clerk, Monaco, and Liveblocks, and a backend with Express, Socket.io, Cloudflare Workers, D1 database, R2 storage, Workers AI, and Drizzle ORM. The backend includes microservices for database, storage, and AI functionalities. Users can run the project locally by setting up environment variables and deploying the containers. Contributions are welcome following the commit convention and structure provided in the repository.
openorch
OpenOrch is a daemon that transforms servers into a powerful development environment, running AI models, containers, and microservices. It serves as a blend of Kubernetes and a language-agnostic backend framework for building applications on fixed-resource setups. Users can deploy AI models and build microservices, managing applications while retaining control over infrastructure and data.
airo
Airo is a tool designed to simplify the process of deploying containers to self-hosted servers. It allows users to focus on building their products without the complexity of Kubernetes or CI/CD pipelines. With Airo, users can easily build and push Docker images, deploy instantly with a single command, update configurations securely using SSH, and set up HTTPS and reverse proxy automatically using Caddy.
ai-containers
This repository contains Dockerfiles, scripts, yaml files, Helm charts, etc. used to scale out AI containers with versions of TensorFlow and PyTorch optimized for Intel platforms. Scaling is done with python, Docker, kubernetes, kubeflow, cnvrg.io, Helm, and other container orchestration frameworks for use in the cloud and on-premise.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.