zml
Any model. Any hardware. Zero compromise. Built with @ziglang / @openxla / MLIR / @bazelbuild
Stars: 3188
ZML is a high-performance AI inference stack built for production, using Zig language, MLIR, and Bazel. It allows users to create exciting AI projects, run pre-packaged models like MNIST, TinyLlama, OpenLLama, and Meta Llama, and compile models for accelerator runtimes. Users can also run tests, explore examples, and contribute to the project. ZML is licensed under the Apache 2.0 license.
README:
At ZML, we are creating exciting AI products on top of our high-performance AI inference stack. Our stack is built for production, using the amazing Zig language, MLIR, and the power of Bazel.
We're very happy to share our inference stack with the World and hope it allows you, too, to build cool and exciting AI projects.
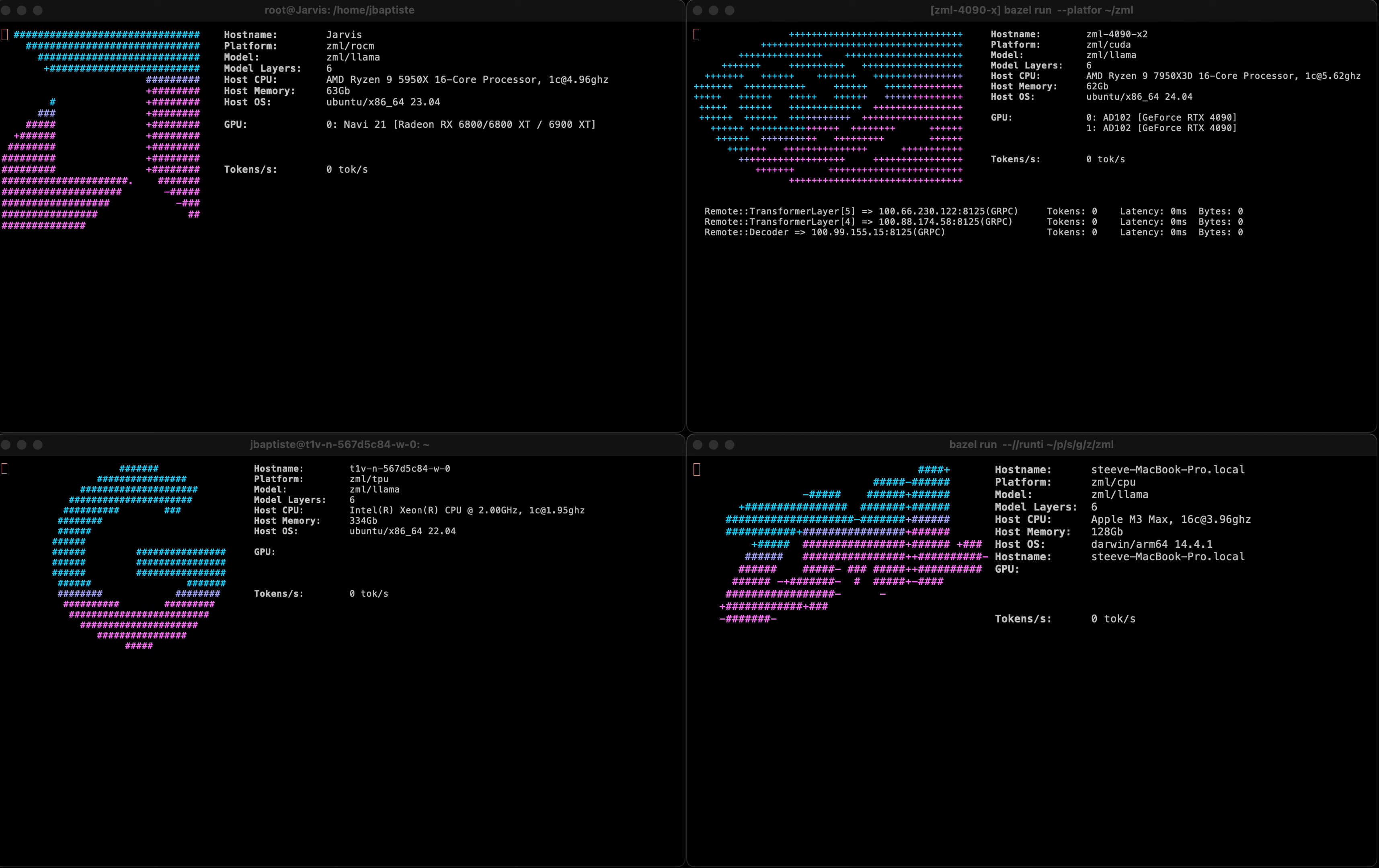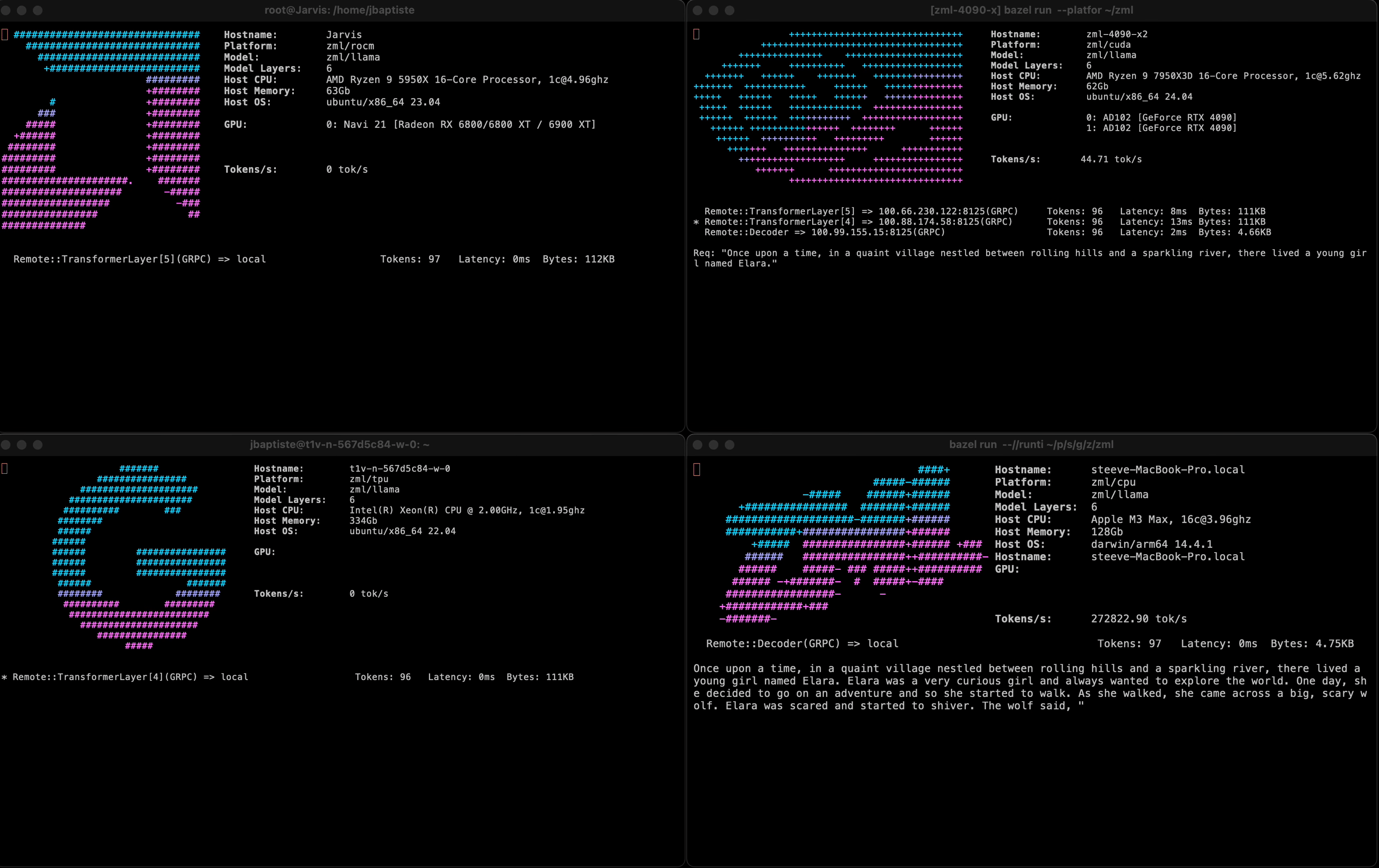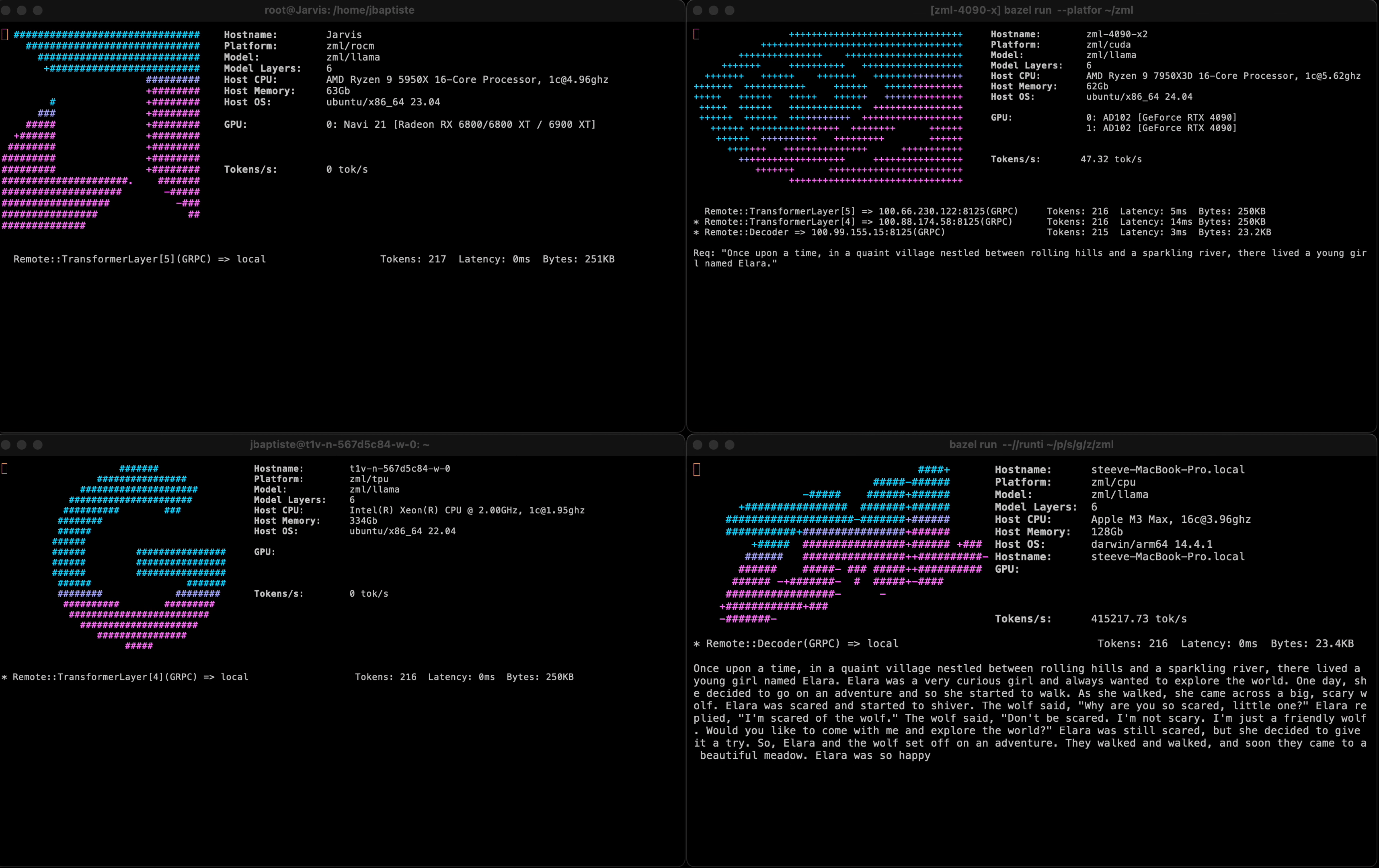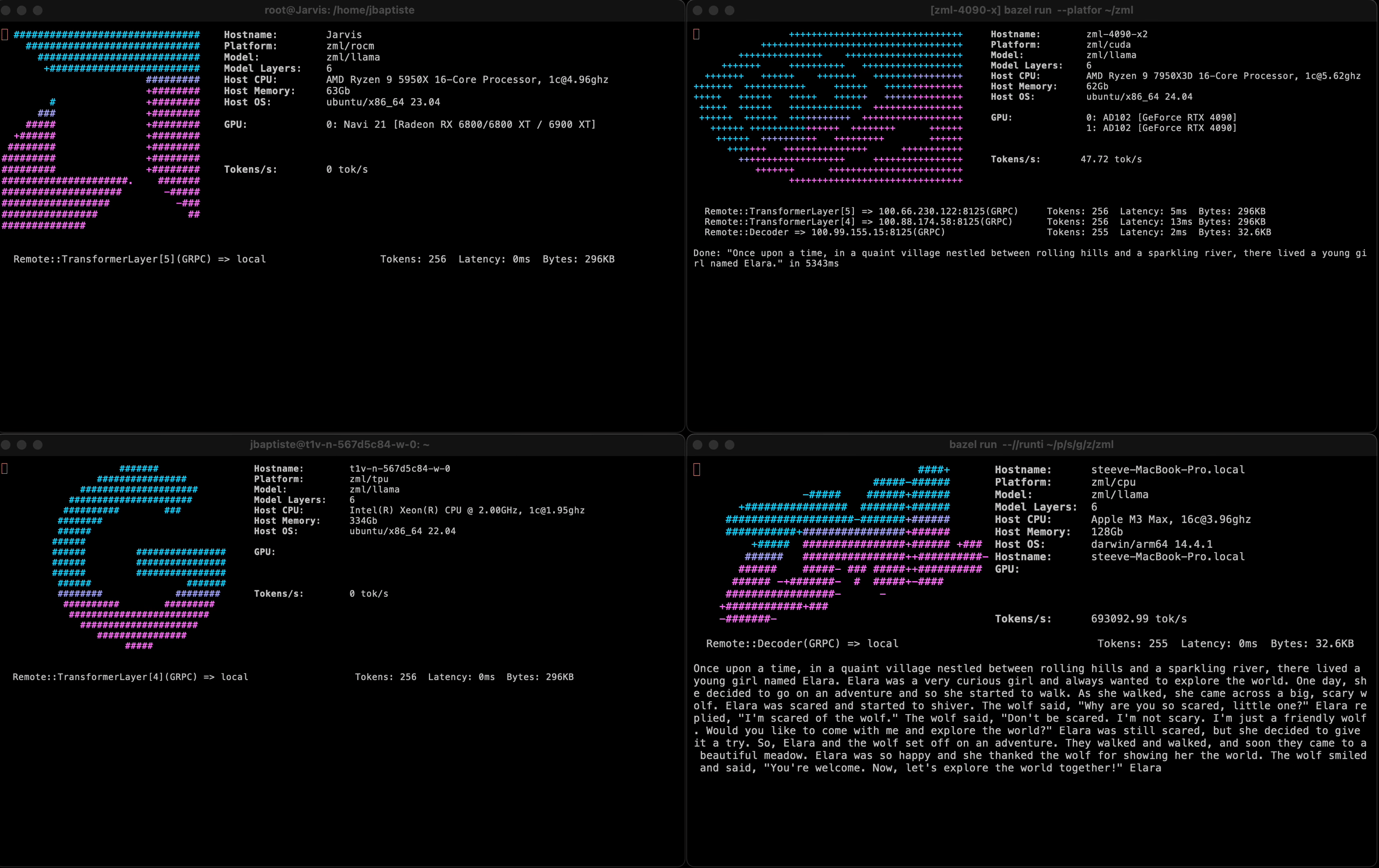
To give you a glimpse of what you can do with ZML, here is an early demo:
It shows a prototype running a LLama3 model sharded on 1 NVIDIA RTX 4090, 1 AMD 6800XT, and 1 Google Cloud TPU v2. All accelerators were hosted in different locations, with activations being passed over a VPN.
All processes used the same model code, cross-compiled on a Mac, and copied onto the servers.
For more inspiration, see also the examples below or check out the examples folder.
We use bazel to build ZML and its dependencies. The only prerequisite is
bazel, which we recommend to download through bazelisk, a version manager
for bazel.
Please note: If you do not wish to install bazel system-wide, we provide
bazel.sh which downloads it to your home folder
and runs it.
Install Bazel (recommended):
curl -L -o /usr/local/bin/bazel 'https://github.com/bazelbuild/bazelisk/releases/download/v1.25.0/bazelisk-linux-amd64'
chmod +x /usr/local/bin/bazel
We have implemented a variety of example models in ZML. See our reference implementations in the examples folder.
The classic handwritten digits
recognition task. The model is tasked to recognize a handwritten digit, which
has been converted to a 28x28 pixel monochrome image. Bazel will download a
pre-trained model, and the test dataset. The program will load the model,
compile it, and classify a randomly picked example from the test dataset.
On the command line:
bazel run --config=release //examples/mnist
# or
./bazel.sh run --config=release //examples/mnist
This model has restrictions, see here. It requires approval from Meta on Huggingface, which can take a few hours to get granted.
Once you've been granted access, you're ready to download a gated model like
Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct!
First, you need to download the model using the huggingface-cli.
Note you don't need to install it yourself,
you can just use the packaged version bazel run //tools/hf --.
bazel run //tools/hf -- download meta-llama/Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct --local-dir $HOME/Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct --exclude='*.pth'
Then, you can run the model.
bazel run --config=release //examples/llama -- --hf-model-path=$HOME/Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct
bazel run --config=release //examples/llama -- --hf-model-path=$HOME/Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct --prompt="What is the capital of France?"
You can also try Llama-3.1-70B-Instruct if you have enough memory.
Like the 8B model above, this model also requires approval. See here for access requirements.
bazel run //tools/hf -- download meta-llama/Llama-3.2-1B-Instruct --local-dir $HOME/Llama-3.2-1B-Instruct --exclude='*.pth'
bazel run --config=release //examples/llama -- --hf-model-path=$HOME/Llama-3.2-1B-Instruct
bazel run --config=release //examples/llama -- --hf-model-path=$HOME/Llama-3.2-1B-Instruct -- --prompt="What is the capital of France?"
For a larger 3.2 model, you can also try Llama-3.2-3B-Instruct.
You can compile models for accelerator runtimes by appending one or more of the following arguments to the command line when compiling / running a model:
- NVIDIA CUDA:
--@zml//runtimes:cuda=true - AMD RoCM:
--@zml//runtimes:rocm=true - Google TPU:
--@zml//runtimes:tpu=true - AWS Trainium/Inferentia 2:
--@zml//runtimes:neuron=true -
AVOID CPU:
--@zml//runtimes:cpu=false
The latter, avoiding compilation for CPU, cuts down compilation time.
So, to run the Llama 3.1 8B model from above on your host sporting an NVIDIA GPU, run the following:
bazel run --config=release //examples/llama \
--@zml//runtimes:cuda=true \
-- --hf-model-path=$HOME/Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct \
--prompt="What is the capital of France?"
bazel test //zml:test
const std = @import("std");
const zml = @import("zml");
/// Model definition
const Mnist = struct {
fc1: Layer,
fc2: Layer,
const Layer = struct {
weight: zml.Tensor,
bias: zml.Tensor,
pub fn forward(self: Layer, input: zml.Tensor) zml.Tensor {
return self.weight.matmul(input).add(self.bias).relu();
}
};
/// just two linear layers + relu activation
pub fn forward(self: Mnist, input: zml.Tensor) zml.Tensor {
std.log.info("Compiling for target: {s}", .{@tagName(input.getContext().target())});
var x = input.flattenAll().convert(.f32);
const layers: []const Layer = &.{ self.fc1, self.fc2 };
for (layers) |layer| {
x = zml.call(layer, .forward, .{x});
}
return x.argMax(0, .u8).indices;
}
};const Sdpa = struct {
pub fn forward(_: Sdpa, ctx: *zml.Context, q_: zml.Tensor, k_: zml.Tensor, v_: zml.Tensor) zml.Tensor {
const q = q_.withTags(.{ .b, .h, .q, .hd });
const k = k_.withTags(.{ .b, .h, .k, .hd });
const v = v_.withTags(.{ .b, .h, .k, .hd });
const attn_mask = zml.nn.causalAttnMask(ctx, .{ .q = q.dim(.q), .k = k.dim(.k) }, q.dtype(), null);
return zml.nn.sdpa(ctx, q, k, v, .{ .attn_mask = attn_mask });
}
};You might want to check out more examples, read through the documentation directly on GitHub, or, for the full rendering experience, browse the online documentation with included API reference.
See here.
ZML is licensed under the Apache 2.0 license.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for zml
Similar Open Source Tools

zml
ZML is a high-performance AI inference stack built for production, using Zig language, MLIR, and Bazel. It allows users to create exciting AI projects, run pre-packaged models like MNIST, TinyLlama, OpenLLama, and Meta Llama, and compile models for accelerator runtimes. Users can also run tests, explore examples, and contribute to the project. ZML is licensed under the Apache 2.0 license.

wllama
Wllama is a WebAssembly binding for llama.cpp, a high-performance and lightweight language model library. It enables you to run inference directly on the browser without the need for a backend or GPU. Wllama provides both high-level and low-level APIs, allowing you to perform various tasks such as completions, embeddings, tokenization, and more. It also supports model splitting, enabling you to load large models in parallel for faster download. With its Typescript support and pre-built npm package, Wllama is easy to integrate into your React Typescript projects.
OpenMusic
OpenMusic is a repository providing an implementation of QA-MDT, a Quality-Aware Masked Diffusion Transformer for music generation. The code integrates state-of-the-art models and offers training strategies for music generation. The repository includes implementations of AudioLDM, PixArt-alpha, MDT, AudioMAE, and Open-Sora. Users can train or fine-tune the model using different strategies and datasets. The model is well-pretrained and can be used for music generation tasks. The repository also includes instructions for preparing datasets, training the model, and performing inference. Contact information is provided for any questions or suggestions regarding the project.
qa-mdt
This repository provides an implementation of QA-MDT, integrating state-of-the-art models for music generation. It offers a Quality-Aware Masked Diffusion Transformer for enhanced music generation. The code is based on various repositories like AudioLDM, PixArt-alpha, MDT, AudioMAE, and Open-Sora. The implementation allows for training and fine-tuning the model with different strategies and datasets. The repository also includes instructions for preparing datasets in LMDB format and provides a script for creating a toy LMDB dataset. The model can be used for music generation tasks, with a focus on quality injection to enhance the musicality of generated music.
react-native-fast-tflite
A high-performance TensorFlow Lite library for React Native that utilizes JSI for power, zero-copy ArrayBuffers for efficiency, and low-level C/C++ TensorFlow Lite core API for direct memory access. It supports swapping out TensorFlow Models at runtime and GPU-accelerated delegates like CoreML/Metal/OpenGL. Easy VisionCamera integration allows for seamless usage. Users can load TensorFlow Lite models, interpret input and output data, and utilize GPU Delegates for faster computation. The library is suitable for real-time object detection, image classification, and other machine learning tasks in React Native applications.
swe-rl
SWE-RL is the official codebase for the paper 'SWE-RL: Advancing LLM Reasoning via Reinforcement Learning on Open Software Evolution'. It is the first approach to scale reinforcement learning based LLM reasoning for real-world software engineering, leveraging open-source software evolution data and rule-based rewards. The code provides prompt templates and the implementation of the reward function based on sequence similarity. Agentless Mini, a part of SWE-RL, builds on top of Agentless with improvements like fast async inference, code refactoring for scalability, and support for using multiple reproduction tests for reranking. The tool can be used for localization, repair, and reproduction test generation in software engineering tasks.
suno-api
Suno AI API is an open-source project that allows developers to integrate the music generation capabilities of Suno.ai into their own applications. The API provides a simple and convenient way to generate music, lyrics, and other audio content using Suno.ai's powerful AI models. With Suno AI API, developers can easily add music generation functionality to their apps, websites, and other projects.
chromem-go
chromem-go is an embeddable vector database for Go with a Chroma-like interface and zero third-party dependencies. It enables retrieval augmented generation (RAG) and similar embeddings-based features in Go apps without the need for a separate database. The focus is on simplicity and performance for common use cases, allowing querying of documents with minimal memory allocations. The project is in beta and may introduce breaking changes before v1.0.0.
hydraai
Generate React components on-the-fly at runtime using AI. Register your components, and let Hydra choose when to show them in your App. Hydra development is still early, and patterns for different types of components and apps are still being developed. Join the discord to chat with the developers. Expects to be used in a NextJS project. Components that have function props do not work.
openai
An open-source client package that allows developers to easily integrate the power of OpenAI's state-of-the-art AI models into their Dart/Flutter applications. The library provides simple and intuitive methods for making requests to OpenAI's various APIs, including the GPT-3 language model, DALL-E image generation, and more. It is designed to be lightweight and easy to use, enabling developers to focus on building their applications without worrying about the complexities of dealing with HTTP requests. Note that this is an unofficial library as OpenAI does not have an official Dart library.
ChatRex
ChatRex is a Multimodal Large Language Model (MLLM) designed to seamlessly integrate fine-grained object perception and robust language understanding. By adopting a decoupled architecture with a retrieval-based approach for object detection and leveraging high-resolution visual inputs, ChatRex addresses key challenges in perception tasks. It is powered by the Rexverse-2M dataset with diverse image-region-text annotations. ChatRex can be applied to various scenarios requiring fine-grained perception, such as object detection, grounded conversation, grounded image captioning, and region understanding.
litserve
LitServe is a high-throughput serving engine for deploying AI models at scale. It generates an API endpoint for a model, handles batching, streaming, autoscaling across CPU/GPUs, and more. Built for enterprise scale, it supports every framework like PyTorch, JAX, Tensorflow, and more. LitServe is designed to let users focus on model performance, not the serving boilerplate. It is like PyTorch Lightning for model serving but with broader framework support and scalability.
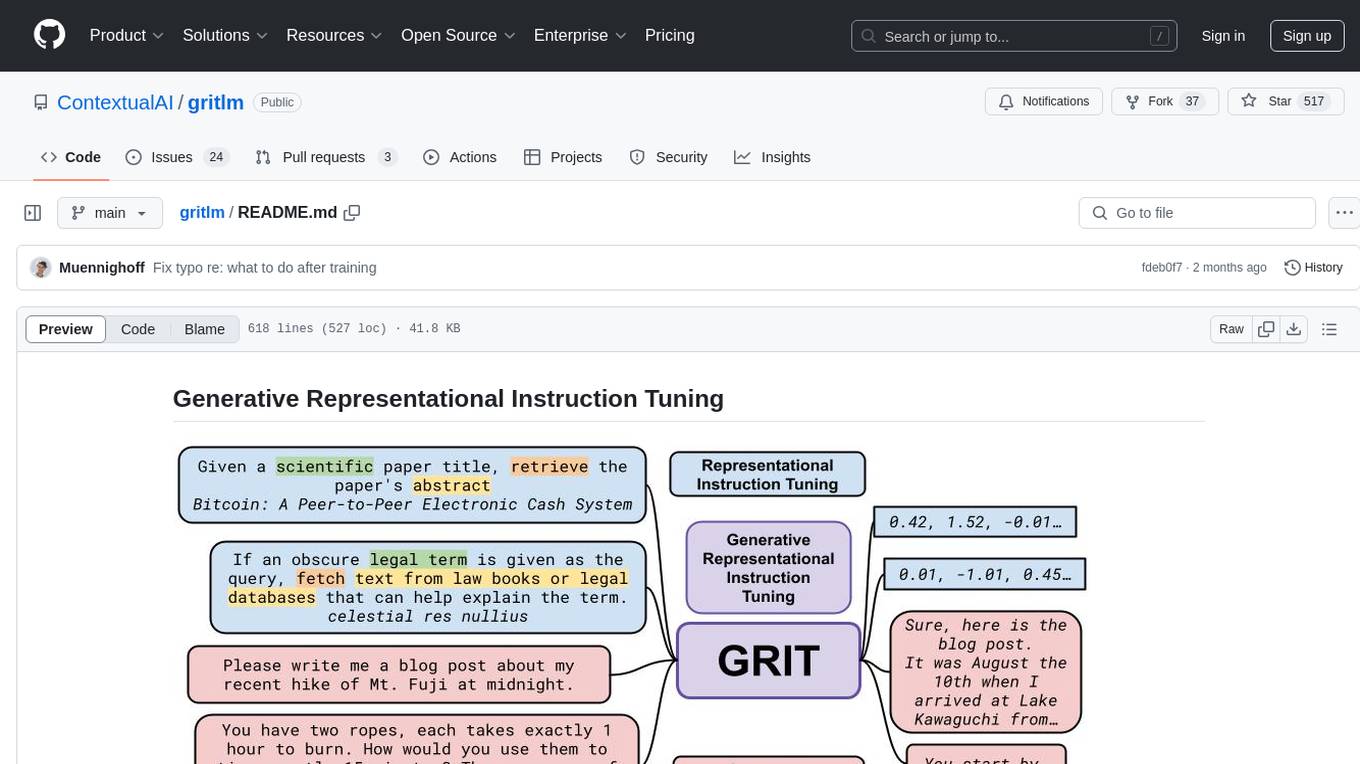
gritlm
The 'gritlm' repository provides all materials for the paper Generative Representational Instruction Tuning. It includes code for inference, training, evaluation, and known issues related to the GritLM model. The repository also offers models for embedding and generation tasks, along with instructions on how to train and evaluate the models. Additionally, it contains visualizations, acknowledgements, and a citation for referencing the work.

zeta
Zeta is a tool designed to build state-of-the-art AI models faster by providing modular, high-performance, and scalable building blocks. It addresses the common issues faced while working with neural nets, such as chaotic codebases, lack of modularity, and low performance modules. Zeta emphasizes usability, modularity, and performance, and is currently used in hundreds of models across various GitHub repositories. It enables users to prototype, train, optimize, and deploy the latest SOTA neural nets into production. The tool offers various modules like FlashAttention, SwiGLUStacked, RelativePositionBias, FeedForward, BitLinear, PalmE, Unet, VisionEmbeddings, niva, FusedDenseGELUDense, FusedDropoutLayerNorm, MambaBlock, Film, hyper_optimize, DPO, and ZetaCloud for different tasks in AI model development.
KVCache-Factory
KVCache-Factory is a unified framework for KV Cache compression of diverse models. It supports multi-GPUs inference with big LLMs and various attention implementations. The tool enables KV cache compression without Flash Attention v2, multi-GPU inference, and specific models like Mistral. It also provides functions for KV cache budget allocation and batch inference. The visualization tools help in understanding the attention patterns of models.
next-token-prediction
Next-Token Prediction is a language model tool that allows users to create high-quality predictions for the next word, phrase, or pixel based on a body of text. It can be used as an alternative to well-known decoder-only models like GPT and Mistral. The tool provides options for simple usage with built-in data bootstrap or advanced customization by providing training data or creating it from .txt files. It aims to simplify methodologies, provide autocomplete, autocorrect, spell checking, search/lookup functionalities, and create pixel and audio transformers for various prediction formats.
For similar tasks
byteir
The ByteIR Project is a ByteDance model compilation solution. ByteIR includes compiler, runtime, and frontends, and provides an end-to-end model compilation solution. Although all ByteIR components (compiler/runtime/frontends) are together to provide an end-to-end solution, and all under the same umbrella of this repository, each component technically can perform independently. The name, ByteIR, comes from a legacy purpose internally. The ByteIR project is NOT an IR spec definition project. Instead, in most scenarios, ByteIR directly uses several upstream MLIR dialects and Google Mhlo. Most of ByteIR compiler passes are compatible with the selected upstream MLIR dialects and Google Mhlo.

zml
ZML is a high-performance AI inference stack built for production, using Zig language, MLIR, and Bazel. It allows users to create exciting AI projects, run pre-packaged models like MNIST, TinyLlama, OpenLLama, and Meta Llama, and compile models for accelerator runtimes. Users can also run tests, explore examples, and contribute to the project. ZML is licensed under the Apache 2.0 license.
edgeai
Embedded inference of Deep Learning models is quite challenging due to high compute requirements. TI’s Edge AI software product helps optimize and accelerate inference on TI’s embedded devices. It supports heterogeneous execution of DNNs across cortex-A based MPUs, TI’s latest generation C7x DSP, and DNN accelerator (MMA). The solution simplifies the product life cycle of DNN development and deployment by providing a rich set of tools and optimized libraries.
sdnext
SD.Next is an Image Diffusion implementation with advanced features. It offers multiple UI options, diffusion models, and built-in controls for text, image, batch, and video processing. The tool is multiplatform, supporting Windows, Linux, MacOS, nVidia, AMD, IntelArc/IPEX, DirectML, OpenVINO, ONNX+Olive, and ZLUDA. It provides optimized processing with the latest torch developments, including model compile, quantize, and compress functionalities. SD.Next also features Interrogate/Captioning with various models, queue management, automatic updates, and mobile compatibility.
mirage
Mirage Persistent Kernel (MPK) is a compiler and runtime system that automatically transforms LLM inference into a single megakernel—a fused GPU kernel that performs all necessary computation and communication within a single kernel launch. This end-to-end GPU fusion approach reduces LLM inference latency by 1.2× to 6.7×, all while requiring minimal developer effort.

tt-xla
TT-XLA is a repository that enables running PyTorch and JAX models on Tenstorrent's AI hardware. It serves as a backend integration between the JAX ecosystem and Tenstorrent's ML accelerators using the PJRT (Portable JAX Runtime) interface. It supports ingestion of PyTorch models through PyTorch/XLA and JAX models via jit compile, providing a StableHLO (SHLO) graph to TT-MLIR compiler.
hass-ollama-conversation
The Ollama Conversation integration adds a conversation agent powered by Ollama in Home Assistant. This agent can be used in automations to query information provided by Home Assistant about your house, including areas, devices, and their states. Users can install the integration via HACS and configure settings such as API timeout, model selection, context size, maximum tokens, and other parameters to fine-tune the responses generated by the AI language model. Contributions to the project are welcome, and discussions can be held on the Home Assistant Community platform.

rclip
rclip is a command-line photo search tool powered by the OpenAI's CLIP neural network. It allows users to search for images using text queries, similar image search, and combining multiple queries. The tool extracts features from photos to enable searching and indexing, with options for previewing results in supported terminals or custom viewers. Users can install rclip on Linux, macOS, and Windows using different installation methods. The repository follows the Conventional Commits standard and welcomes contributions from the community.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.