
AgentKit
An intuitive LLM prompting framework for multifunctional agents, by explicitly constructing a complex "thought process" from simple natural language prompts.
Stars: 219
AgentKit is a framework for constructing complex human thought processes from simple natural language prompts. It offers a unified way to represent and execute these processes as graphs, making it easy to design and tune agents without any programming experience. AgentKit can be used for a variety of tasks, including generating text, answering questions, and making decisions.
README:
 offers a unified framework for explicitly constructing a complex human "thought process" from simple natural language prompts.
The user puts together chains of nodes, like stacking LEGO pieces. The chains of nodes can be designed to explicitly enforce a naturally structured "thought process".
offers a unified framework for explicitly constructing a complex human "thought process" from simple natural language prompts.
The user puts together chains of nodes, like stacking LEGO pieces. The chains of nodes can be designed to explicitly enforce a naturally structured "thought process".
Different arrangements of nodes could represent different functionalities, allowing the user to integrate various functionalities to build multifunctional agents.
A basic agent could be implemented as simple as a list of prompts for the subtasks and therefore could be designed and tuned by someone without any programming experience.
- Installation
- Getting Started
- Using Built-in LLM_API
- Using AgentKit without Programming Experience
- Node Components
- Commonly Asked Questions
- Citing AgnetKit
Installing the AgentKit stable version is as simple as:
pip install agentkit-llmTo install AgentKit with wandb:
pip install agentkit-llm[logging]To install AgentKit with built-in LLM-API support:
pip install agentkit-llm[all]Otherwise, to install the cutting edge version from the main branch of this repo, run:
git clone https://github.com/holmeswww/AgentKit && cd AgentKit
pip install -e .The basic building block in AgentKit is a node, containing a natural language prompt for a specific subtask. The nodes are linked together by the dependency specifications, which specify the order of evaluation. Different arrangements of nodes can represent different different logic and throught processes.
At inference time, AgentKit evaluates all nodes in specified order as a directed acyclic graph (DAG).
import agentkit
from agentkit import Graph, BaseNode
import agentkit.llm_api
LLM_API_FUNCTION = agentkit.llm_api.get_query("gpt-4-turbo")
LLM_API_FUNCTION.debug = True # Disable this to enable API-level error handling-retry
graph = Graph()
subtask1 = "What are the pros and cons for using LLM Agents for Game AI?"
node1 = BaseNode(subtask1, subtask1, graph, LLM_API_FUNCTION, agentkit.compose_prompt.BaseComposePrompt(), verbose=True)
graph.add_node(node1)
subtask2 = "Give me an outline for an essay titled 'LLM Agents for Games'."
node2 = BaseNode(subtask2, subtask2, graph, LLM_API_FUNCTION, agentkit.compose_prompt.BaseComposePrompt(), verbose=True)
graph.add_node(node2)
subtask3 = "Now, write a full essay on the topic 'LLM Agents for Games'."
node3 = BaseNode(subtask3, subtask3, graph, LLM_API_FUNCTION, agentkit.compose_prompt.BaseComposePrompt(), verbose=True)
graph.add_node(node3)
# add dependencies between nodes
graph.add_edge(subtask1, subtask2)
graph.add_edge(subtask1, subtask3)
graph.add_edge(subtask2, subtask3)
result = graph.evaluate() # outputs a dictionary of prompt, answer pairsLLM_API_FUNCTION can be any LLM API function that takes msg:list and shrink_idx:int, and outputs llm_result:str and usage:dict. Where msg is a prompt (OpenAI format by default), and shrink_idx:int is an index at which the LLM should reduce the length of the prompt in case of overflow.
AgentKit tracks token usage of each node through the LLM_API_FUNCTION with:
usage = {
'prompt': $prompt token counts,
'completion': $completion token counts,
}The built-in agentkit.llm_api functions require installing with [all] setting. See the installation guide for details.
Currently, the built-in API supports OpenAI and Anthropic, see https://pypi.org/project/openai/ and https://pypi.org/project/anthropic/ for details.
To use the OpenAI models, set environment variables OPENAI_KEY and OPENAI_ORG. Alternatively, you can put the openai 'key' and 'organization' in the first 2 lines of ~/.openai/openai.key.
To use the Azure OpenAI models, set environment variables AZURE_OPENAI_API_KEY, AZURE_OPENAI_API_VERSION, AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT, and AZURE_DEPLOYMENT_NAME. Alternatively, you can store the Azure OpenAI API key, API version, Azure endpoint, and deployment name in the first 4 lines of ~/.openai/azure_openai.key.
To use the Anthropic models, set environment variable ANTHROPIC_KEY. Alternatively, you can put the anthropic 'key' in 3rd line of ~/.openai/openai.key.
First, follow the installation guide to install AgentKit with [all] setting.
Then, set environment variables OPENAI_KEY and OPENAI_ORG to be your OpenAI key and org_key.
Finally, run the following to evoke the command line interface (CLI):
git clone https://github.com/holmeswww/AgentKit && cd AgentKit
cd examples/prompt_without_coding
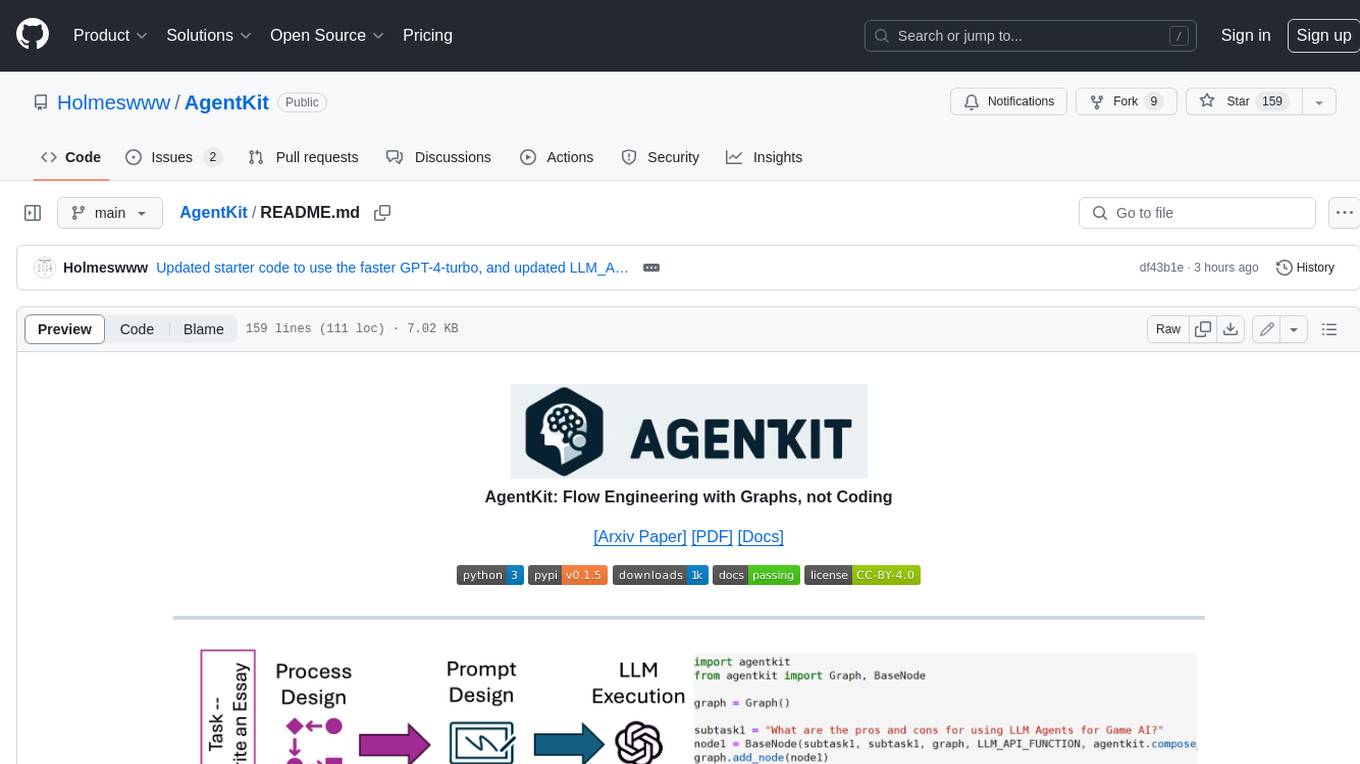
python generate_graph.py Inside each node (as shown to the left of the figure), AgentKit runs a built-in flow that preprocesses the input (Compose), queries the LLM with a preprocessed input and prompt $q_v$, and optionally postprocesses the output of the LLM (After-query).
Inside each node (as shown to the left of the figure), AgentKit runs a built-in flow that preprocesses the input (Compose), queries the LLM with a preprocessed input and prompt $q_v$, and optionally postprocesses the output of the LLM (After-query).
To support advanced capabilities such as branching, AgentKit offers API to dynamically modify the DAG at inference time (as shown to the right of the figure). Nodes/edges could be dynamically added or removed based on the LLM response at some ancestor nodes.
Q: I'm using the default agentkit.llm_api, and graph.evaluate() seems to be stuck.
A: The LLM_API function catches and retries all API errors by default. Set verbose=True for each node to see which node you are stuck on, and LLM_API_FUNCTION.debug=True to see what error is causing the error.
@article{wu2024agentkit,
title={AgentKit: Flow Engineering with Graphs, not Coding},
author={Yue Wu and Yewen Fan and So Yeon Min and Shrimai Prabhumoye and Stephen McAleer and Yonatan Bisk and Ruslan Salakhutdinov and Yuanzhi Li and Tom Mitchell},
year={2024},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2404.11483}
}For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for AgentKit
Similar Open Source Tools

AgentKit
AgentKit is a framework for constructing complex human thought processes from simple natural language prompts. It offers a unified way to represent and execute these processes as graphs, making it easy to design and tune agents without any programming experience. AgentKit can be used for a variety of tasks, including generating text, answering questions, and making decisions.
minja
Minja is a minimalistic C++ Jinja templating engine designed specifically for integration with C++ LLM projects, such as llama.cpp or gemma.cpp. It is not a general-purpose tool but focuses on providing a limited set of filters, tests, and language features tailored for chat templates. The library is header-only, requires C++17, and depends only on nlohmann::json. Minja aims to keep the codebase small, easy to understand, and offers decent performance compared to Python. Users should be cautious when using Minja due to potential security risks, and it is not intended for producing HTML or JavaScript output.
DeepPavlov
DeepPavlov is an open-source conversational AI library built on PyTorch. It is designed for the development of production-ready chatbots and complex conversational systems, as well as for research in the area of NLP and dialog systems. The library offers a wide range of models for tasks such as Named Entity Recognition, Intent/Sentence Classification, Question Answering, Sentence Similarity/Ranking, Syntactic Parsing, and more. DeepPavlov also provides embeddings like BERT, ELMo, and FastText for various languages, along with AutoML capabilities and integrations with REST API, Socket API, and Amazon AWS.
langgraph4j
Langgraph4j is a Java library for language processing tasks such as text classification, sentiment analysis, and named entity recognition. It provides a set of tools and algorithms for analyzing text data and extracting useful information. The library is designed to be efficient and easy to use, making it suitable for both research and production applications.
langroid
Langroid is a Python framework that makes it easy to build LLM-powered applications. It uses a multi-agent paradigm inspired by the Actor Framework, where you set up Agents, equip them with optional components (LLM, vector-store and tools/functions), assign them tasks, and have them collaboratively solve a problem by exchanging messages. Langroid is a fresh take on LLM app-development, where considerable thought has gone into simplifying the developer experience; it does not use Langchain.
stark
STaRK is a large-scale semi-structure retrieval benchmark on Textual and Relational Knowledge Bases. It provides natural-sounding and practical queries crafted to incorporate rich relational information and complex textual properties, closely mirroring real-life scenarios. The benchmark aims to assess how effectively large language models can handle the interplay between textual and relational requirements in queries, using three diverse knowledge bases constructed from public sources.

universal
The Universal Numbers Library is a header-only C++ template library designed for universal number arithmetic, offering alternatives to native integer and floating-point for mixed-precision algorithm development and optimization. It tailors arithmetic types to the application's precision and dynamic range, enabling improved application performance and energy efficiency. The library provides fast implementations of special IEEE-754 formats like quarter precision, half-precision, and quad precision, as well as vendor-specific extensions. It supports static and elastic integers, decimals, fixed-points, rationals, linear floats, tapered floats, logarithmic, interval, and adaptive-precision integers, rationals, and floats. The library is suitable for AI, DSP, HPC, and HFT algorithms.
simpleAI
SimpleAI is a self-hosted alternative to the not-so-open AI API, focused on replicating main endpoints for LLM such as text completion, chat, edits, and embeddings. It allows quick experimentation with different models, creating benchmarks, and handling specific use cases without relying on external services. Users can integrate and declare models through gRPC, query endpoints using Swagger UI or API, and resolve common issues like CORS with FastAPI middleware. The project is open for contributions and welcomes PRs, issues, documentation, and more.
aire
Aire is a modern Laravel form builder with a focus on expressive and beautiful code. It allows easy configuration of form components using fluent method calls or Blade components. Aire supports customization through config files and custom views, data binding with Eloquent models or arrays, method spoofing, CSRF token injection, server-side and client-side validation, and translations. It is designed to run on Laravel 5.8.28 and higher, with support for PHP 7.1 and higher. Aire is actively maintained and under consideration for additional features like read-only plain text, cross-browser support for custom checkboxes and radio buttons, support for Choices.js or similar libraries, improved file input handling, and better support for content prepending or appending to inputs.
AirspeedVelocity.jl
AirspeedVelocity.jl is a tool designed to simplify benchmarking of Julia packages over their lifetime. It provides a CLI to generate benchmarks, compare commits/tags/branches, plot benchmarks, and run benchmark comparisons for every submitted PR as a GitHub action. The tool freezes the benchmark script at a specific revision to prevent old history from affecting benchmarks. Users can configure options using CLI flags and visualize benchmark results. AirspeedVelocity.jl can be used to benchmark any Julia package and offers features like generating tables and plots of benchmark results. It also supports custom benchmarks and can be integrated into GitHub actions for automated benchmarking of PRs.
k8sgpt
K8sGPT is a tool for scanning your Kubernetes clusters, diagnosing, and triaging issues in simple English. It has SRE experience codified into its analyzers and helps to pull out the most relevant information to enrich it with AI.
PDEBench
PDEBench provides a diverse and comprehensive set of benchmarks for scientific machine learning, including challenging and realistic physical problems. The repository consists of code for generating datasets, uploading and downloading datasets, training and evaluating machine learning models as baselines. It features a wide range of PDEs, realistic and difficult problems, ready-to-use datasets with various conditions and parameters. PDEBench aims for extensibility and invites participation from the SciML community to improve and extend the benchmark.
probsem
ProbSem is a repository that provides a framework to leverage large language models (LLMs) for assigning context-conditional probability distributions over queried strings. It supports OpenAI engines and HuggingFace CausalLM models, and is flexible for research applications in linguistics, cognitive science, program synthesis, and NLP. Users can define prompts, contexts, and queries to derive probability distributions over possible completions, enabling tasks like cloze completion, multiple-choice QA, semantic parsing, and code completion. The repository offers CLI and API interfaces for evaluation, with options to customize models, normalize scores, and adjust temperature for probability distributions.

aiomisc
aiomisc is a Python library that provides a collection of utility functions and classes for working with asynchronous I/O in a more intuitive and efficient way. It offers features like worker pools, connection pools, circuit breaker pattern, and retry mechanisms to make asyncio code more robust and easier to maintain. The library simplifies the architecture of software using asynchronous I/O, making it easier for developers to write reliable and scalable asynchronous code.
llama_index
LlamaIndex is a data framework for building LLM applications. It provides tools for ingesting, structuring, and querying data, as well as integrating with LLMs and other tools. LlamaIndex is designed to be easy to use for both beginner and advanced users, and it provides a comprehensive set of features for building LLM applications.
aira-dojo
aira-dojo is a scalable and customizable framework for AI research agents, designed to accelerate hill-climbing on research capabilities toward a fully automated AI research scientist. The framework provides a general abstraction for tasks and agents, implements the MLE-bench task, and includes state-of-the-art agents. It features an isolated code execution environment that integrates smoothly with job schedulers like Slurm, enabling large-scale experiments and rapid iteration across a portfolio of tasks and solvers.
For similar tasks

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

onnxruntime-genai
ONNX Runtime Generative AI is a library that provides the generative AI loop for ONNX models, including inference with ONNX Runtime, logits processing, search and sampling, and KV cache management. Users can call a high level `generate()` method, or run each iteration of the model in a loop. It supports greedy/beam search and TopP, TopK sampling to generate token sequences, has built in logits processing like repetition penalties, and allows for easy custom scoring.

jupyter-ai
Jupyter AI connects generative AI with Jupyter notebooks. It provides a user-friendly and powerful way to explore generative AI models in notebooks and improve your productivity in JupyterLab and the Jupyter Notebook. Specifically, Jupyter AI offers: * An `%%ai` magic that turns the Jupyter notebook into a reproducible generative AI playground. This works anywhere the IPython kernel runs (JupyterLab, Jupyter Notebook, Google Colab, Kaggle, VSCode, etc.). * A native chat UI in JupyterLab that enables you to work with generative AI as a conversational assistant. * Support for a wide range of generative model providers, including AI21, Anthropic, AWS, Cohere, Gemini, Hugging Face, NVIDIA, and OpenAI. * Local model support through GPT4All, enabling use of generative AI models on consumer grade machines with ease and privacy.

khoj
Khoj is an open-source, personal AI assistant that extends your capabilities by creating always-available AI agents. You can share your notes and documents to extend your digital brain, and your AI agents have access to the internet, allowing you to incorporate real-time information. Khoj is accessible on Desktop, Emacs, Obsidian, Web, and Whatsapp, and you can share PDF, markdown, org-mode, notion files, and GitHub repositories. You'll get fast, accurate semantic search on top of your docs, and your agents can create deeply personal images and understand your speech. Khoj is self-hostable and always will be.

langchain_dart
LangChain.dart is a Dart port of the popular LangChain Python framework created by Harrison Chase. LangChain provides a set of ready-to-use components for working with language models and a standard interface for chaining them together to formulate more advanced use cases (e.g. chatbots, Q&A with RAG, agents, summarization, extraction, etc.). The components can be grouped into a few core modules: * **Model I/O:** LangChain offers a unified API for interacting with various LLM providers (e.g. OpenAI, Google, Mistral, Ollama, etc.), allowing developers to switch between them with ease. Additionally, it provides tools for managing model inputs (prompt templates and example selectors) and parsing the resulting model outputs (output parsers). * **Retrieval:** assists in loading user data (via document loaders), transforming it (with text splitters), extracting its meaning (using embedding models), storing (in vector stores) and retrieving it (through retrievers) so that it can be used to ground the model's responses (i.e. Retrieval-Augmented Generation or RAG). * **Agents:** "bots" that leverage LLMs to make informed decisions about which available tools (such as web search, calculators, database lookup, etc.) to use to accomplish the designated task. The different components can be composed together using the LangChain Expression Language (LCEL).

danswer
Danswer is an open-source Gen-AI Chat and Unified Search tool that connects to your company's docs, apps, and people. It provides a Chat interface and plugs into any LLM of your choice. Danswer can be deployed anywhere and for any scale - on a laptop, on-premise, or to cloud. Since you own the deployment, your user data and chats are fully in your own control. Danswer is MIT licensed and designed to be modular and easily extensible. The system also comes fully ready for production usage with user authentication, role management (admin/basic users), chat persistence, and a UI for configuring Personas (AI Assistants) and their Prompts. Danswer also serves as a Unified Search across all common workplace tools such as Slack, Google Drive, Confluence, etc. By combining LLMs and team specific knowledge, Danswer becomes a subject matter expert for the team. Imagine ChatGPT if it had access to your team's unique knowledge! It enables questions such as "A customer wants feature X, is this already supported?" or "Where's the pull request for feature Y?"

infinity
Infinity is an AI-native database designed for LLM applications, providing incredibly fast full-text and vector search capabilities. It supports a wide range of data types, including vectors, full-text, and structured data, and offers a fused search feature that combines multiple embeddings and full text. Infinity is easy to use, with an intuitive Python API and a single-binary architecture that simplifies deployment. It achieves high performance, with 0.1 milliseconds query latency on million-scale vector datasets and up to 15K QPS.
For similar jobs
ChatFAQ
ChatFAQ is an open-source comprehensive platform for creating a wide variety of chatbots: generic ones, business-trained, or even capable of redirecting requests to human operators. It includes a specialized NLP/NLG engine based on a RAG architecture and customized chat widgets, ensuring a tailored experience for users and avoiding vendor lock-in.

agentcloud
AgentCloud is an open-source platform that enables companies to build and deploy private LLM chat apps, empowering teams to securely interact with their data. It comprises three main components: Agent Backend, Webapp, and Vector Proxy. To run this project locally, clone the repository, install Docker, and start the services. The project is licensed under the GNU Affero General Public License, version 3 only. Contributions and feedback are welcome from the community.
anything-llm
AnythingLLM is a full-stack application that enables you to turn any document, resource, or piece of content into context that any LLM can use as references during chatting. This application allows you to pick and choose which LLM or Vector Database you want to use as well as supporting multi-user management and permissions.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.

glide
Glide is a cloud-native LLM gateway that provides a unified REST API for accessing various large language models (LLMs) from different providers. It handles LLMOps tasks such as model failover, caching, key management, and more, making it easy to integrate LLMs into applications. Glide supports popular LLM providers like OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI, AWS Bedrock (Titan), Cohere, Google Gemini, OctoML, and Ollama. It offers high availability, performance, and observability, and provides SDKs for Python and NodeJS to simplify integration.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

onnxruntime-genai
ONNX Runtime Generative AI is a library that provides the generative AI loop for ONNX models, including inference with ONNX Runtime, logits processing, search and sampling, and KV cache management. Users can call a high level `generate()` method, or run each iteration of the model in a loop. It supports greedy/beam search and TopP, TopK sampling to generate token sequences, has built in logits processing like repetition penalties, and allows for easy custom scoring.





