
aiocoap
The Python CoAP library
Stars: 280
aiocoap is a Python library that implements the Constrained Application Protocol (CoAP) using native asyncio methods in Python 3. It supports various CoAP standards such as RFC7252, RFC7641, RFC7959, RFC8323, RFC7967, RFC8132, RFC9176, RFC8613, and draft-ietf-core-oscore-groupcomm-17. The library provides features for clients and servers, including multicast support, blockwise transfer, CoAP over TCP, TLS, and WebSockets, No-Response, PATCH/FETCH, OSCORE, and Group OSCORE. It offers an easy-to-use interface for concurrent operations and is suitable for IoT applications.
README:
.. meta:: :copyright: SPDX-FileCopyrightText: Christian Amsüss and the aiocoap contributors :copyright: SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
The aiocoap package is an implementation of CoAP, the Constrained Application Protocol_. It facilitates writing applications that talk to
network enabled embedded ("IoT" / "Internet of Things") devices.
It is written in Python 3 using its native asyncio_ methods to facilitate
concurrent operations while maintaining an easy to use interface.
.. _Constrained Application Protocol: http://coap.space/
.. _native asyncio: https://docs.python.org/3/library/asyncio
For how to use the aiocoap library, have a look at the guidedtour_, or at the examples_ and tools_ provided.
A full reference is available in the API documentation_.
All examples can be run directly from a source code copy. If you prefer to install it, the usual Python mechanisms apply (see installation_).
.. _API documentation: http://aiocoap.readthedocs.io/en/latest/api.html
This library supports the following standards in full or partially:
- RFC7252_ (CoAP): Supported for clients and servers. Multicast is supported on the server side, and partially for clients. DTLS is supported but experimental, and lacking some security properties. No caching is done inside the library.
- RFC7641_ (Observe): Basic support for clients and servers. Reordering, re-registration, and active cancellation are missing.
- RFC7959_ (Blockwise): Supported both for atomic and random access.
- RFC8323_ (TCP, WebSockets): Supports CoAP over TCP, TLS, and WebSockets (both over HTTP and HTTPS). The TLS parts are server-certificate only; preshared, raw public keys and client certificates are not supported yet.
- RFC7967_ (No-Response): Supported.
- RFC8132_ (PATCH/FETCH): Types and codes known, FETCH observation supported.
- RFC9176_: A standalone resource directory server is provided along with a library function to register at one. They lack support for groups and security considerations, and are generally rather simplistic.
- RFC8613_ (OSCORE): Full support client-side; protected servers can be implemented based on it but are not automatic yet.
- draft-ietf-core-oscore-groupcomm-23_ (Group OSCORE): Supported for both group and pairwise mode in groups that are fully known. (The lack of an implemented joining or persistence mechanism makes this impractical for anything but experimentation.)
- RFC9528_ (EDHOC): Experimental and rudimentary support for configured peers using the lakers_ implementation.
If something described by one of the standards but not implemented, it is
considered a bug; please file at the github issue tracker_. (If it's not on
the list or in the excluded items, file a wishlist item at the same location).
.. _RFC7252: https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7252 .. _RFC7641: https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7641 .. _RFC7959: https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7959 .. _RFC7967: https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7967 .. _RFC8132: https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc8132 .. _RFC8323: https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc8323 .. _RFC8613: https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc8613 .. _RFC9176: https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc9176 .. _RFC9528: https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc9528 .. _draft-ietf-core-oscore-groupcomm-23: https://tools.ietf.org/html/draft-ietf-core-oscore-groupcomm-23 .. _lakers: https://pypi.org/project/lakers-python/
Basic aiocoap works out of the box on Python_ 3.10 or newer (also works on PyPy3_). For full support (DTLS, OSCORE and link-format handling) follow the installation_ instructions as these require additional libraries.
aiocoap provides different network backends for different platforms. The most featureful backend is available for Linux, but most operations work on BSDs, Windows and macOS as well. See the FAQ_ for more details.
If your library depends on aiocoap, it should pick the required extras (as per
installation_) and declare a dependency like aiocoap[linkheader,oscore] >= 0.4b2.
.. _Python: https://www.python.org/ .. _PyPy3: http://pypy.org/ .. _FAQ: http://aiocoap.readthedocs.io/en/latest/faq.html
aiocoap tries to stay close to PEP8_ recommendations and general best practice, and should thus be easy to contribute to.
Bugs (ranging from "design goal" and "wishlist" to typos) are currently tracked
in the github issue tracker_. Pull requests are welcome there; if you start
working on larger changes, please coordinate on the issue tracker.
Security critical bugs may instead be reported in private to [email protected]
(PGP key_) for coordinated disclosure; the maintainer reserves the right to
publish fixes ahead of a planned embargo time at he deems suitable.
Documentation is built using sphinx_ with python3 -m sphinx doc/ ${TARGET};
hacks used there are described in ./doc/README.doc.
Unit tests are implemented in the ./tests/ directory and easiest run using
tox_ (but also available through python3 -m unittest to test the local environment);
complete test coverage is aimed for, but not yet complete (and might never be,
as the error handling for pathological network partners is hard to trigger with
a library designed not to misbehave). The tests are regularly run at the CI suite at codeberg, from where coverage reports are available.
.. _PEP8: http://legacy.python.org/dev/peps/pep-0008/
.. _sphinx: http://sphinx-doc.org/
.. _github issue tracker: https://github.com/chrysn/aiocoap/issues
.. _CI suite at codeberg: https://ci.codeberg.org/repos/12879
.. _coverage reports: https://aiocoap.codeberg.page/aiocoap/coverage/
.. _tox: https://tox.readthedocs.io/
.. _PGP key: https://christian.amsuess.com/pgp
-
https://codeberg.org/aiocoap/aiocoap
This is where the latest source code can be found. Generally, this serves as the project web site.
-
http://aiocoap.readthedocs.org/
Online documentation built from the sources.
-
Further general information on CoAP, the standard documents involved, and other implementations and tools available.
aiocoap is published under the MIT License, and follows the best practice of reuse.software_.
Files in aiocoap/util/vendored/ may have different (but compatible and OSI approved) licenses.
When using aiocoap for a publication, please cite it according to the output of
./setup.py cite [--bibtex].
Copyright Christian Amsüss and the aiocoap contributors.
aiocoap was originally based on txThings_ by Maciej Wasilak. The full list of aiocoap contributors can be obtained from the version control history.
.. Any filtering by a mailmap would apply, but no need to state that unless we do get a mailmap.
.. _guidedtour: http://aiocoap.readthedocs.io/en/latest/guidedtour.html .. _examples: http://aiocoap.readthedocs.io/en/latest/examples.html .. _tools: http://aiocoap.readthedocs.io/en/latest/tools.html .. _installation: http://aiocoap.readthedocs.io/en/latest/installation.html .. _reuse.software: https://reuse.software/ .. _txThings: https://github.com/siskin/txThings
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for aiocoap
Similar Open Source Tools

aiocoap
aiocoap is a Python library that implements the Constrained Application Protocol (CoAP) using native asyncio methods in Python 3. It supports various CoAP standards such as RFC7252, RFC7641, RFC7959, RFC8323, RFC7967, RFC8132, RFC9176, RFC8613, and draft-ietf-core-oscore-groupcomm-17. The library provides features for clients and servers, including multicast support, blockwise transfer, CoAP over TCP, TLS, and WebSockets, No-Response, PATCH/FETCH, OSCORE, and Group OSCORE. It offers an easy-to-use interface for concurrent operations and is suitable for IoT applications.
langchain
LangChain is a framework for developing Elixir applications powered by language models. It enables applications to connect language models to other data sources and interact with the environment. The library provides components for working with language models and off-the-shelf chains for specific tasks. It aims to assist in building applications that combine large language models with other sources of computation or knowledge. LangChain is written in Elixir and is not aimed for parity with the JavaScript and Python versions due to differences in programming paradigms and design choices. The library is designed to make it easy to integrate language models into applications and expose features, data, and functionality to the models.
craftium
Craftium is an open-source platform based on the Minetest voxel game engine and the Gymnasium and PettingZoo APIs, designed for creating fast, rich, and diverse single and multi-agent environments. It allows for connecting to Craftium's Python process, executing actions as keyboard and mouse controls, extending the Lua API for creating RL environments and tasks, and supporting client/server synchronization for slow agents. Craftium is fully extensible, extensively documented, modern RL API compatible, fully open source, and eliminates the need for Java. It offers a variety of environments for research and development in reinforcement learning.

verifAI
VerifAI is a document-based question-answering system that addresses hallucinations in generative large language models and search engines. It retrieves relevant documents, generates answers with references, and verifies answers for accuracy. The engine uses generative search technology and a verification model to ensure no misinformation. VerifAI supports various document formats and offers user registration with a React.js interface. It is open-source and designed to be user-friendly, making it accessible for anyone to use.
aici
The Artificial Intelligence Controller Interface (AICI) lets you build Controllers that constrain and direct output of a Large Language Model (LLM) in real time. Controllers are flexible programs capable of implementing constrained decoding, dynamic editing of prompts and generated text, and coordinating execution across multiple, parallel generations. Controllers incorporate custom logic during the token-by-token decoding and maintain state during an LLM request. This allows diverse Controller strategies, from programmatic or query-based decoding to multi-agent conversations to execute efficiently in tight integration with the LLM itself.

ontogpt
OntoGPT is a Python package for extracting structured information from text using large language models, instruction prompts, and ontology-based grounding. It provides a command line interface and a minimal web app for easy usage. The tool has been evaluated on test data and is used in related projects like TALISMAN for gene set analysis. OntoGPT enables users to extract information from text by specifying relevant terms and provides the extracted objects as output.
multilspy
Multilspy is a Python library developed for research purposes to facilitate the creation of language server clients for querying and obtaining results of static analyses from various language servers. It simplifies the process by handling server setup, communication, and configuration parameters, providing a common interface for different languages. The library supports features like finding function/class definitions, callers, completions, hover information, and document symbols. It is designed to work with AI systems like Large Language Models (LLMs) for tasks such as Monitor-Guided Decoding to ensure code generation correctness and boost compilability.
hi-ml
The Microsoft Health Intelligence Machine Learning Toolbox is a repository that provides low-level and high-level building blocks for Machine Learning / AI researchers and practitioners. It simplifies and streamlines work on deep learning models for healthcare and life sciences by offering tested components such as data loaders, pre-processing tools, deep learning models, and cloud integration utilities. The repository includes two Python packages, 'hi-ml-azure' for helper functions in AzureML, 'hi-ml' for ML components, and 'hi-ml-cpath' for models and workflows related to histopathology images.
mosec
Mosec is a high-performance and flexible model serving framework for building ML model-enabled backend and microservices. It bridges the gap between any machine learning models you just trained and the efficient online service API. * **Highly performant** : web layer and task coordination built with Rust 🦀, which offers blazing speed in addition to efficient CPU utilization powered by async I/O * **Ease of use** : user interface purely in Python 🐍, by which users can serve their models in an ML framework-agnostic manner using the same code as they do for offline testing * **Dynamic batching** : aggregate requests from different users for batched inference and distribute results back * **Pipelined stages** : spawn multiple processes for pipelined stages to handle CPU/GPU/IO mixed workloads * **Cloud friendly** : designed to run in the cloud, with the model warmup, graceful shutdown, and Prometheus monitoring metrics, easily managed by Kubernetes or any container orchestration systems * **Do one thing well** : focus on the online serving part, users can pay attention to the model optimization and business logic
dlio_benchmark
DLIO is an I/O benchmark tool designed for Deep Learning applications. It emulates modern deep learning applications using Benchmark Runner, Data Generator, Format Handler, and I/O Profiler modules. Users can configure various I/O patterns, data loaders, data formats, datasets, and parameters. The tool is aimed at emulating the I/O behavior of deep learning applications and provides a modular design for flexibility and customization.
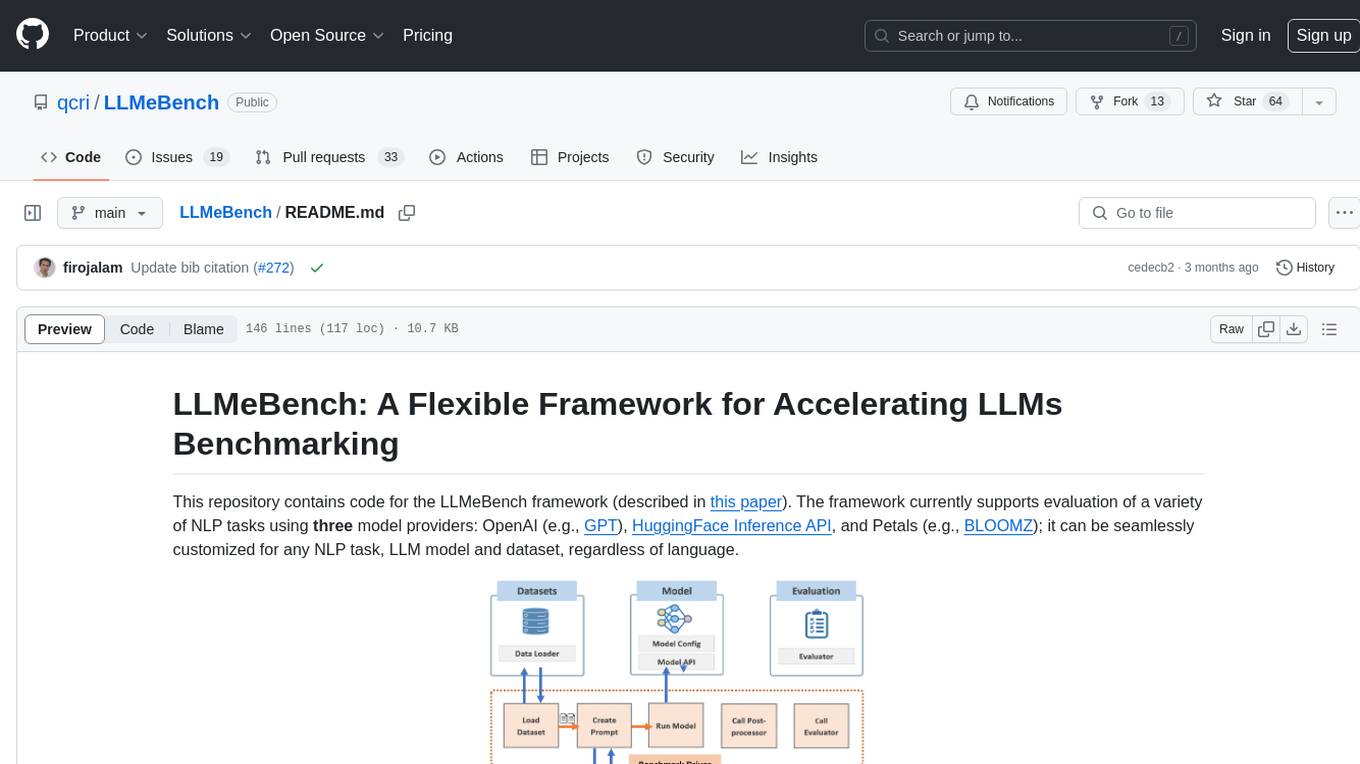
LLMeBench
LLMeBench is a flexible framework designed for accelerating benchmarking of Large Language Models (LLMs) in the field of Natural Language Processing (NLP). It supports evaluation of various NLP tasks using model providers like OpenAI, HuggingFace Inference API, and Petals. The framework is customizable for different NLP tasks, LLM models, and datasets across multiple languages. It features extensive caching capabilities, supports zero- and few-shot learning paradigms, and allows on-the-fly dataset download and caching. LLMeBench is open-source and continuously expanding to support new models accessible through APIs.

project_alice
Alice is an agentic workflow framework that integrates task execution and intelligent chat capabilities. It provides a flexible environment for creating, managing, and deploying AI agents for various purposes, leveraging a microservices architecture with MongoDB for data persistence. The framework consists of components like APIs, agents, tasks, and chats that interact to produce outputs through files, messages, task results, and URL references. Users can create, test, and deploy agentic solutions in a human-language framework, making it easy to engage with by both users and agents. The tool offers an open-source option, user management, flexible model deployment, and programmatic access to tasks and chats.
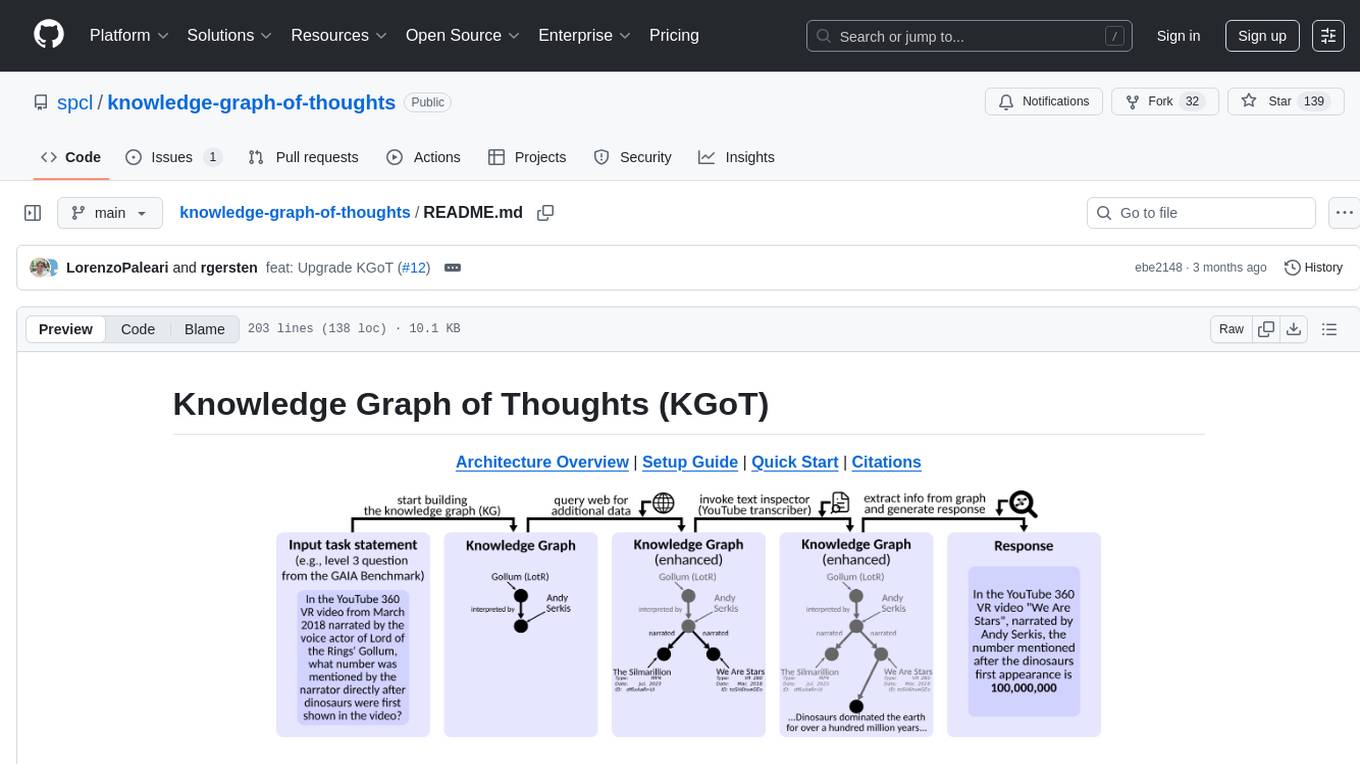
knowledge-graph-of-thoughts
Knowledge Graph of Thoughts (KGoT) is an innovative AI assistant architecture that integrates LLM reasoning with dynamically constructed knowledge graphs (KGs). KGoT extracts and structures task-relevant knowledge into a dynamic KG representation, iteratively enhanced through external tools such as math solvers, web crawlers, and Python scripts. Such structured representation of task-relevant knowledge enables low-cost models to solve complex tasks effectively. The KGoT system consists of three main components: the Controller, the Graph Store, and the Integrated Tools, each playing a critical role in the task-solving process.
agentok
Agentok Studio is a visual tool built for AutoGen, a cutting-edge agent framework from Microsoft and various contributors. It offers intuitive visual tools to simplify the construction and management of complex agent-based workflows. Users can create workflows visually as graphs, chat with agents, and share flow templates. The tool is designed to streamline the development process for creators and developers working on next-generation Multi-Agent Applications.
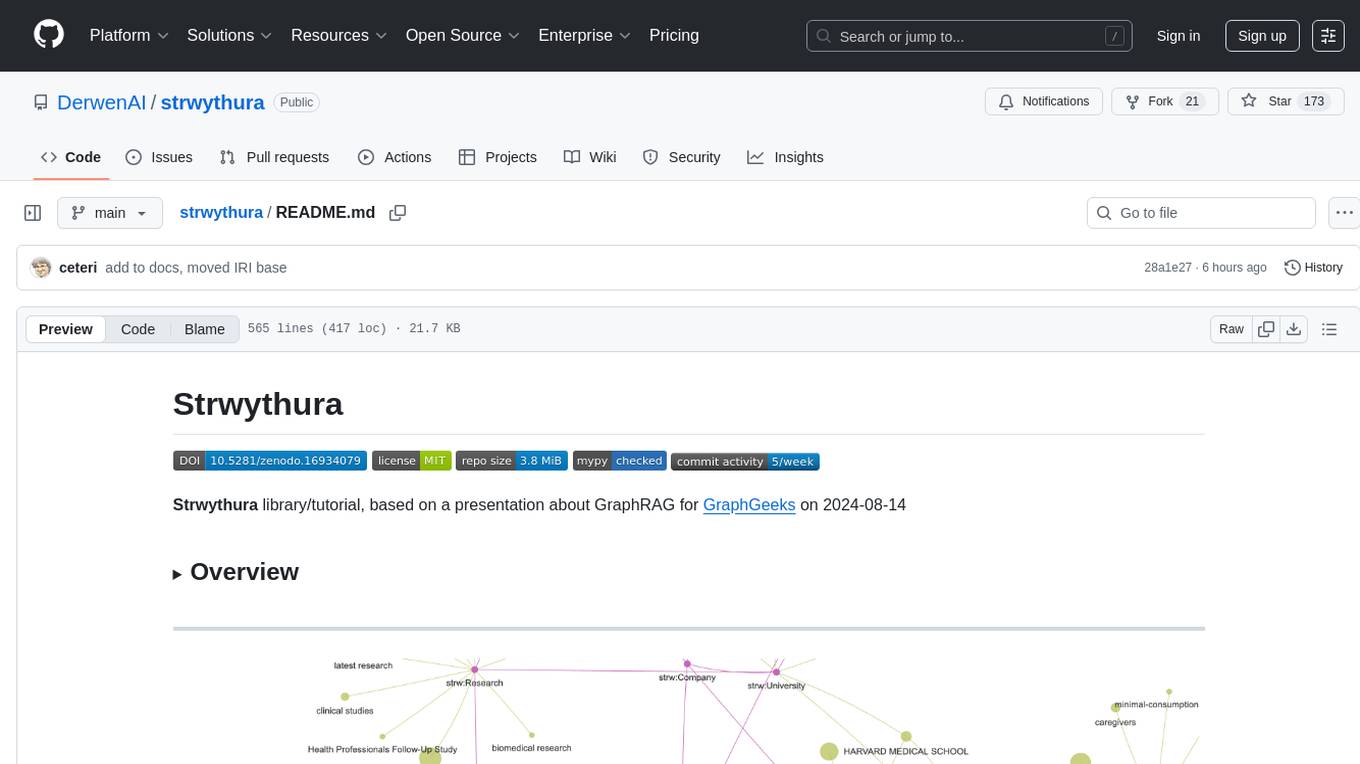
strwythura
Strwythura is a library and tutorial focused on constructing a knowledge graph from unstructured data sources using state-of-the-art models for named entity recognition. It implements an enhanced GraphRAG approach and curates semantics for optimizing AI application outcomes within a specific domain. The tutorial emphasizes the use of sophisticated NLP pipelines based on spaCy, GLiNER, TextRank, and related libraries to provide better/faster/cheaper results with more control over the intentional arrangement of the knowledge graph. It leverages neurosymbolic AI methods and combines practices from natural language processing, graph data science, entity resolution, ontology pipeline, context engineering, and human-in-the-loop processes.
Guardrails
Guardrails is a security tool designed to help developers identify and fix security vulnerabilities in their code. It provides automated scanning and analysis of code repositories to detect potential security issues, such as sensitive data exposure, injection attacks, and insecure configurations. By integrating Guardrails into the development workflow, teams can proactively address security concerns and reduce the risk of security breaches. The tool offers detailed reports and actionable recommendations to guide developers in remediation efforts, ultimately improving the overall security posture of the codebase. Guardrails supports multiple programming languages and frameworks, making it versatile and adaptable to different development environments. With its user-friendly interface and seamless integration with popular version control systems, Guardrails empowers developers to prioritize security without compromising productivity.
For similar tasks

aiocoap
aiocoap is a Python library that implements the Constrained Application Protocol (CoAP) using native asyncio methods in Python 3. It supports various CoAP standards such as RFC7252, RFC7641, RFC7959, RFC8323, RFC7967, RFC8132, RFC9176, RFC8613, and draft-ietf-core-oscore-groupcomm-17. The library provides features for clients and servers, including multicast support, blockwise transfer, CoAP over TCP, TLS, and WebSockets, No-Response, PATCH/FETCH, OSCORE, and Group OSCORE. It offers an easy-to-use interface for concurrent operations and is suitable for IoT applications.
aino
Aino is an experimental HTTP framework for Elixir that uses elli instead of Cowboy like Phoenix and Plug. It focuses on writing handlers to process requests through middleware functions. Aino works on a token instead of a conn, allowing flexibility in adding custom keys. It includes built-in middleware for common tasks and a routing layer for defining routes. Handlers in Aino must return a token with specific keys for response rendering.
ai-gateway
Envoy AI Gateway is an open source project that utilizes Envoy Gateway to manage request traffic from application clients to Generative AI services. The project aims to provide a seamless and efficient solution for handling communication between clients and AI services. It is designed to enhance the performance and scalability of AI applications by leveraging the capabilities of Envoy Gateway. The project welcomes contributions from the community and encourages collaboration to further develop and improve the functionality of the AI Gateway.
tinystruct
Tinystruct is a simple Java framework designed for easy development with better performance. It offers a modern approach with features like CLI and web integration, built-in lightweight HTTP server, minimal configuration philosophy, annotation-based routing, and performance-first architecture. Developers can focus on real business logic without dealing with unnecessary complexities, making it transparent, predictable, and extensible.
hashbrown
Hashbrown is a lightweight and efficient hashing library for Python, designed to provide easy-to-use cryptographic hashing functions for secure data storage and transmission. It supports a variety of hashing algorithms, including MD5, SHA-1, SHA-256, and SHA-512, allowing users to generate hash values for strings, files, and other data types. With Hashbrown, developers can quickly implement data integrity checks, password hashing, digital signatures, and other security features in their Python applications.
flapi
flAPI is a powerful service that automatically generates read-only APIs for datasets by utilizing SQL templates. Built on top of DuckDB, it offers features like automatic API generation, support for Model Context Protocol (MCP), connecting to multiple data sources, caching, security implementation, and easy deployment. The tool allows users to create APIs without coding and enables the creation of AI tools alongside REST endpoints using SQL templates. It supports unified configuration for REST endpoints and MCP tools/resources, concurrent servers for REST API and MCP server, and automatic tool discovery. The tool also provides DuckLake-backed caching for modern, snapshot-based caching with features like full refresh, incremental sync, retention, compaction, and audit logs.
Olares
Olares is an open-source sovereign cloud OS designed for local AI, enabling users to build their own AI assistants, sync data across devices, self-host their workspace, stream media, and more within a sovereign cloud environment. Users can effortlessly run leading AI models, deploy open-source AI apps, access AI apps and models anywhere, and benefit from integrated AI for personalized interactions. Olares offers features like edge AI, personal data repository, self-hosted workspace, private media server, smart home hub, and user-owned decentralized social media. The platform provides enterprise-grade security, secure application ecosystem, unified file system and database, single sign-on, AI capabilities, built-in applications, seamless access, and development tools. Olares is compatible with Linux, Raspberry Pi, Mac, and Windows, and offers a wide range of system-level applications, third-party components and services, and additional libraries and components.
awesome-alt-clouds
Awesome Alt Clouds is a curated list of non-hyperscale cloud providers offering specialized infrastructure and services catering to specific workloads, compliance requirements, and developer needs. The list includes various categories such as Infrastructure Clouds, Sovereign Clouds, Unikernels & WebAssembly, Data Clouds, Workflow and Operations Clouds, Network, Connectivity and Security Clouds, Vibe Clouds, Developer Happiness Clouds, Authorization, Identity, Fraud and Abuse Clouds, Monetization, Finance and Legal Clouds, Customer, Marketing and eCommerce Clouds, IoT, Communications, and Media Clouds, Blockchain Clouds, Source Code Control, Cloud Adjacent, and Future Clouds.
For similar jobs
executorch
ExecuTorch is an end-to-end solution for enabling on-device inference capabilities across mobile and edge devices including wearables, embedded devices and microcontrollers. It is part of the PyTorch Edge ecosystem and enables efficient deployment of PyTorch models to edge devices. Key value propositions of ExecuTorch are: * **Portability:** Compatibility with a wide variety of computing platforms, from high-end mobile phones to highly constrained embedded systems and microcontrollers. * **Productivity:** Enabling developers to use the same toolchains and SDK from PyTorch model authoring and conversion, to debugging and deployment to a wide variety of platforms. * **Performance:** Providing end users with a seamless and high-performance experience due to a lightweight runtime and utilizing full hardware capabilities such as CPUs, NPUs, and DSPs.
holoscan-sdk
The Holoscan SDK is part of NVIDIA Holoscan, the AI sensor processing platform that combines hardware systems for low-latency sensor and network connectivity, optimized libraries for data processing and AI, and core microservices to run streaming, imaging, and other applications, from embedded to edge to cloud. It can be used to build streaming AI pipelines for a variety of domains, including Medical Devices, High Performance Computing at the Edge, Industrial Inspection and more.
panda
Panda is a car interface tool that speaks CAN and CAN FD, running on STM32F413 and STM32H725. It provides safety modes and controls_allowed feature for message handling. The tool ensures code rigor through CI regression tests, including static code analysis, MISRA C:2012 violations check, unit tests, and hardware-in-the-loop tests. The software interface supports Python library, C++ library, and socketcan in kernel. Panda is licensed under the MIT license.

aiocoap
aiocoap is a Python library that implements the Constrained Application Protocol (CoAP) using native asyncio methods in Python 3. It supports various CoAP standards such as RFC7252, RFC7641, RFC7959, RFC8323, RFC7967, RFC8132, RFC9176, RFC8613, and draft-ietf-core-oscore-groupcomm-17. The library provides features for clients and servers, including multicast support, blockwise transfer, CoAP over TCP, TLS, and WebSockets, No-Response, PATCH/FETCH, OSCORE, and Group OSCORE. It offers an easy-to-use interface for concurrent operations and is suitable for IoT applications.

CPP-Notes
CPP-Notes is a comprehensive repository providing detailed insights into the history, evolution, and modern development of the C++ programming language. It covers the foundational concepts of C++ and its transition from C, highlighting key features such as object-oriented programming, generic programming, and modern enhancements introduced in C++11/14/17. The repository delves into the significance of C++ in system programming, library development, and its role as a versatile and efficient language. It explores the historical milestones of C++ development, from its inception in 1979 by Bjarne Stroustrup to the latest C++20 standard, showcasing major advancements like Concepts, Ranges library, Coroutines, Modules, and enhanced concurrency features.
AI-on-the-edge-device
AI-on-the-edge-device is a project that enables users to digitize analog water, gas, power, and other meters using an ESP32 board with a supported camera. It integrates Tensorflow Lite for AI processing, offers a small and affordable device with integrated camera and illumination, provides a web interface for administration and control, supports Homeassistant, Influx DB, MQTT, and REST API. The device captures meter images, extracts Regions of Interest (ROIs), runs them through AI for digitization, and allows users to send data to MQTT, InfluxDb, or access it via REST API. The project also includes 3D-printable housing options and tools for logfile management.
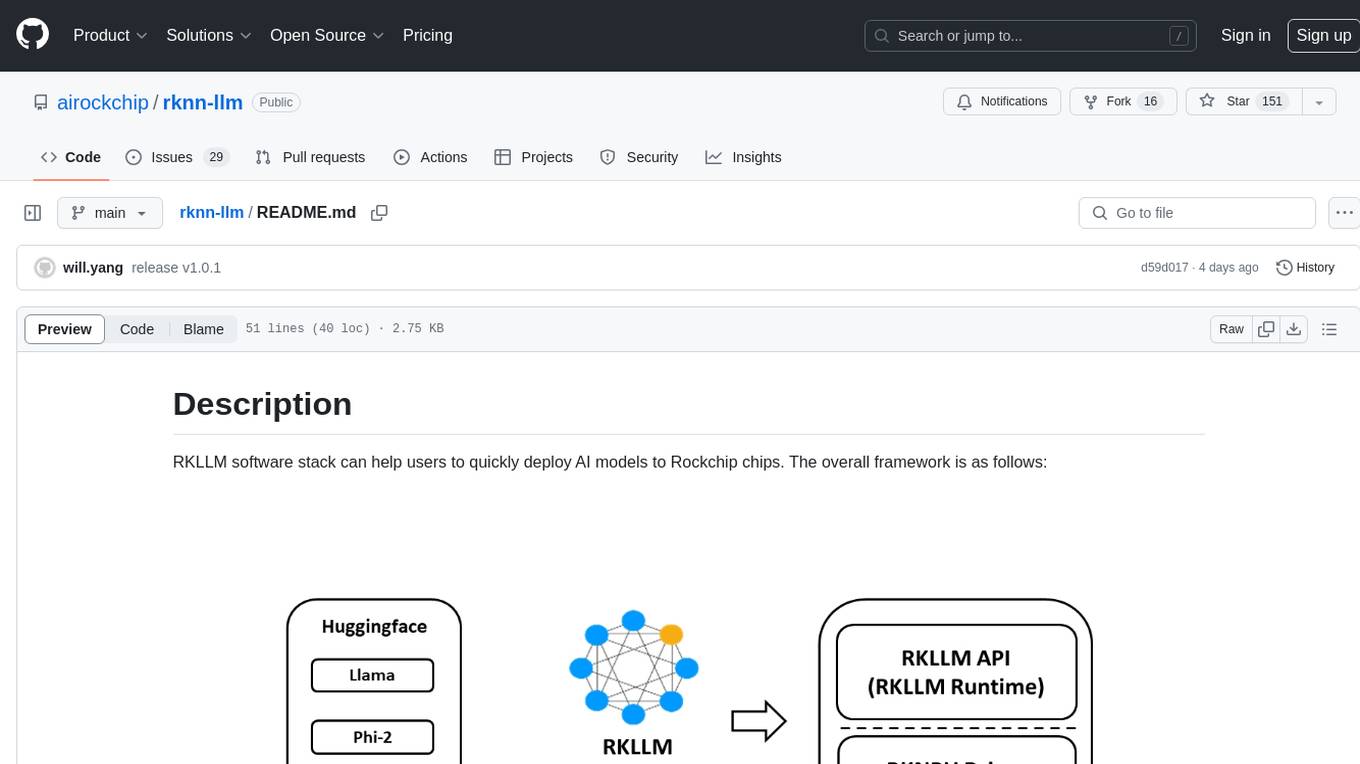
rknn-llm
RKLLM software stack is a toolkit designed to help users quickly deploy AI models to Rockchip chips. It consists of RKLLM-Toolkit for model conversion and quantization, RKLLM Runtime for deploying models on Rockchip NPU platform, and RKNPU kernel driver for hardware interaction. The toolkit supports RK3588 and RK3576 series chips and various models like TinyLLAMA, Qwen, Phi, ChatGLM3, Gemma, InternLM2, and MiniCPM. Users can download packages, docker images, examples, and docs from RKLLM_SDK. Additionally, RKNN-Toolkit2 SDK is available for deploying additional AI models.
awesome-RK3588
RK3588 is a flagship 8K SoC chip by Rockchip, integrating Cortex-A76 and Cortex-A55 cores with NEON coprocessor for 8K video codec. This repository curates resources for developing with RK3588, including official resources, RKNN models, projects, development boards, documentation, tools, and sample code.